Meteorology Unit 1 - Atmospheric Properties
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Weather
describes conditions in the atmosphere that are happening right now, short term or daily measurement, daily decisions to make
Meterology
the study of things high up
Weather Measurements
wind speed, types of clouds, temperature, average rainfall
Climate
long term weather patterns over a specified time frame or specific area, it takes 30 years before the climate is solidified in a place
Climate Measurements
measure the weather for an extended period of time
Cause of weather
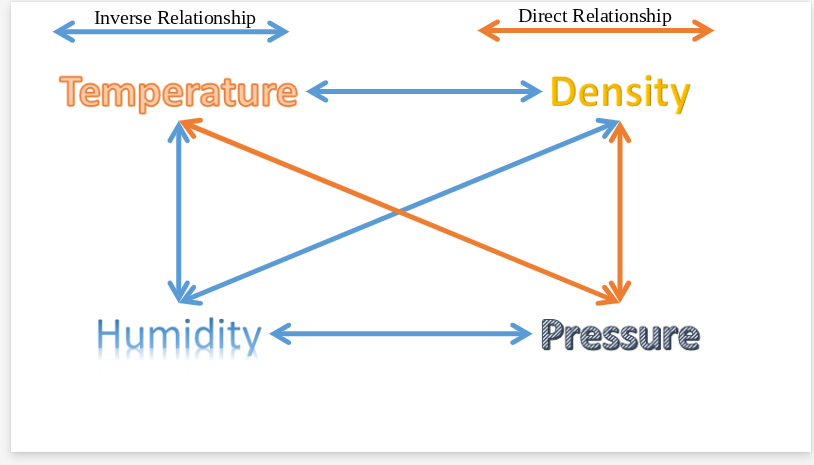
temperature, humidity, density, and pressure
Temperature
measure of thermal energy (heat), includes Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin
Humidity
measure of the amount of moisture in the air, measured in the amount of water vapor (in grams) present in each kilogram of air (humidity ratio)
Relative Humidity
take humidity ratio and include the air temperature and the maximum amount of water the air can hold- displayed as a percentage, if the temperature goes up, relative humidity goes down and vice versa, weather station
Absolute Humidity
the actual amount of water vapor present in the air, moisture per cubic meter of air, totally independent of temperature
Density
related to both the type of material that an object is made of and how closely packed the material (kg/l) or (k/m³)
Pressure
the force exerted over a given area or object, either because of gravity pulling on it or other motion the object has
Pascal
force per unit of surface area
Atmosphere (ATM)
equal to the average air pressure at sea level at a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius
Height
as pressure decreases, what else decreases?
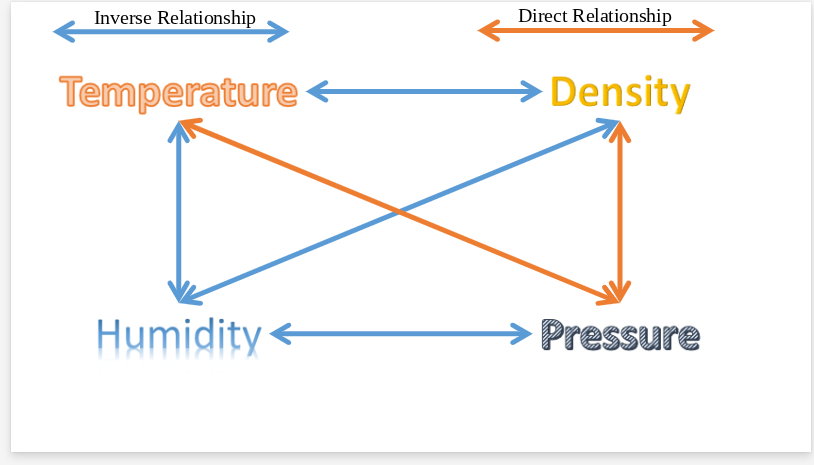
Temperature and density
as pressure increases, what also increases?
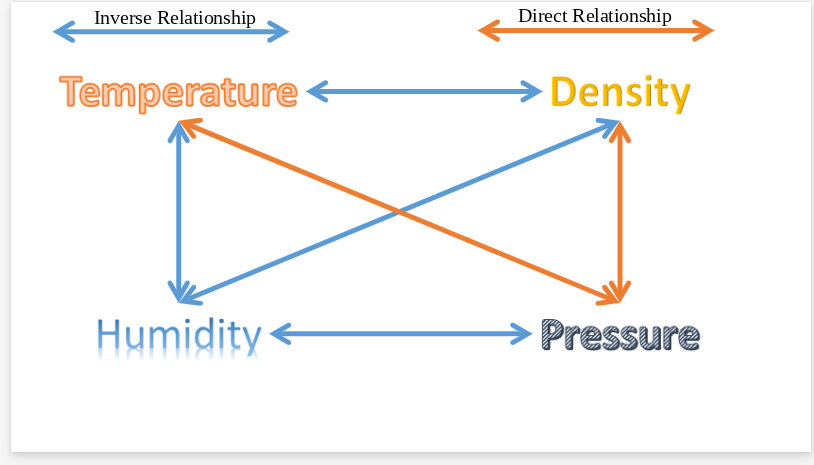
density
As temperature increases, what decreases?
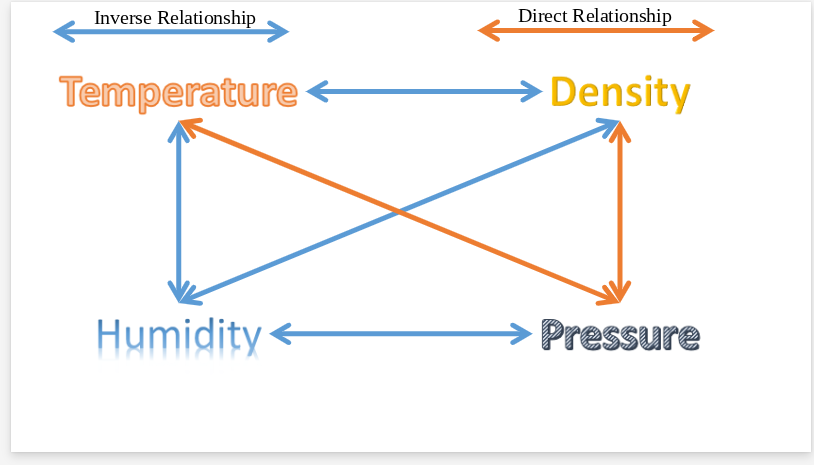
lower
When air is at at higher temperatures, relative humidity is
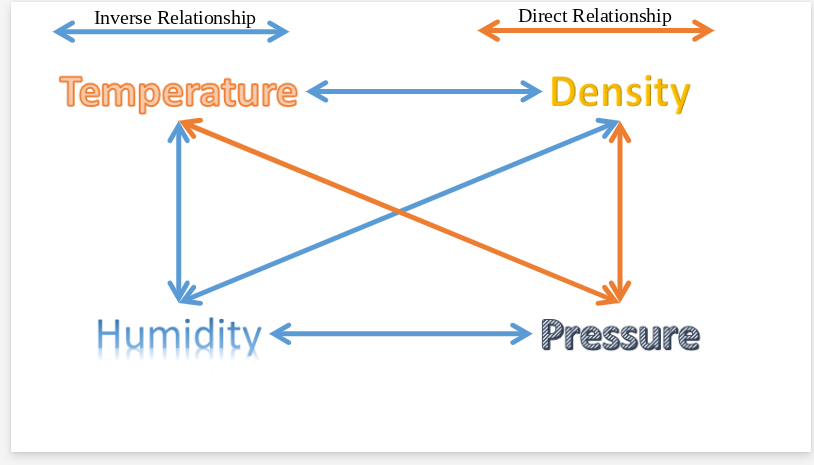
higher
when air temperature is lower, relative humidity is
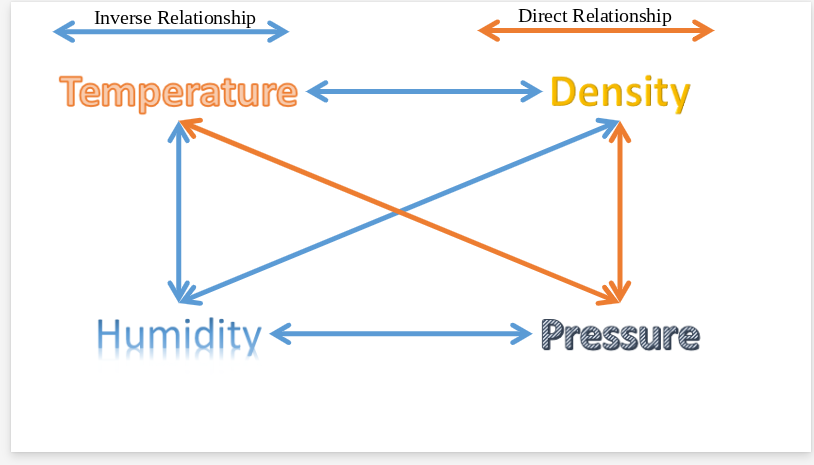
pressure and density
As humidity increases, what factors decrease?
Insolation
the exposure to the sun’s rays, the smaller the amount of area it strikes, the more energy is given
Effects of Insolation
distribution of sun’s energy leads to seasons and the creation of biome’s, the equator always has the average amount of insolation
Atmosphere
The envelope of gases surrounding the Earth or another planet
Atmosphere’s 5 layers
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Exposhere
Troposphere
the closest layer to the ground, this is where weather happens, temperature generally decreases with height, the upper boundary is called the tropopause, includes the jet stream
Stratosphere
houses the ozone layer at the bottom part, the temperature increases with height, relatively calm
Mesosphere
colder and lower density layer with about 0.1% of total atmosphere, temperature decreases with height, contains ratios of Nitrogen and Oxygen similar to the troposphere, except the concentrations are 1000 times less, little water vapor and the air is too thin for weather to occur, meteors break and burn up here
Ozone Layers
blocks UV-A (lowest layer), UV-B, UV-C
Thermosphere
the largest and uppermost layer, the air is hot but very thin, temperature increases with height due to direct heating from the Sun, most of the Ionosphere (northern lights) regions are located here, the ISS is located within the upper range along with other satellites, region containing Aurora Borealis and Australis
Exosphere
atmosphere vs. space, there are gases gravitationally bound in this region, but the area is so thin that they are considered collisionless.
78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 0.9% Argon
Composition of the Atmosphere