IMC Unit 2: Micro Economics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the Production Possibility Frontier
Describes the maximum quantities of goods produced using all available resources in an economy
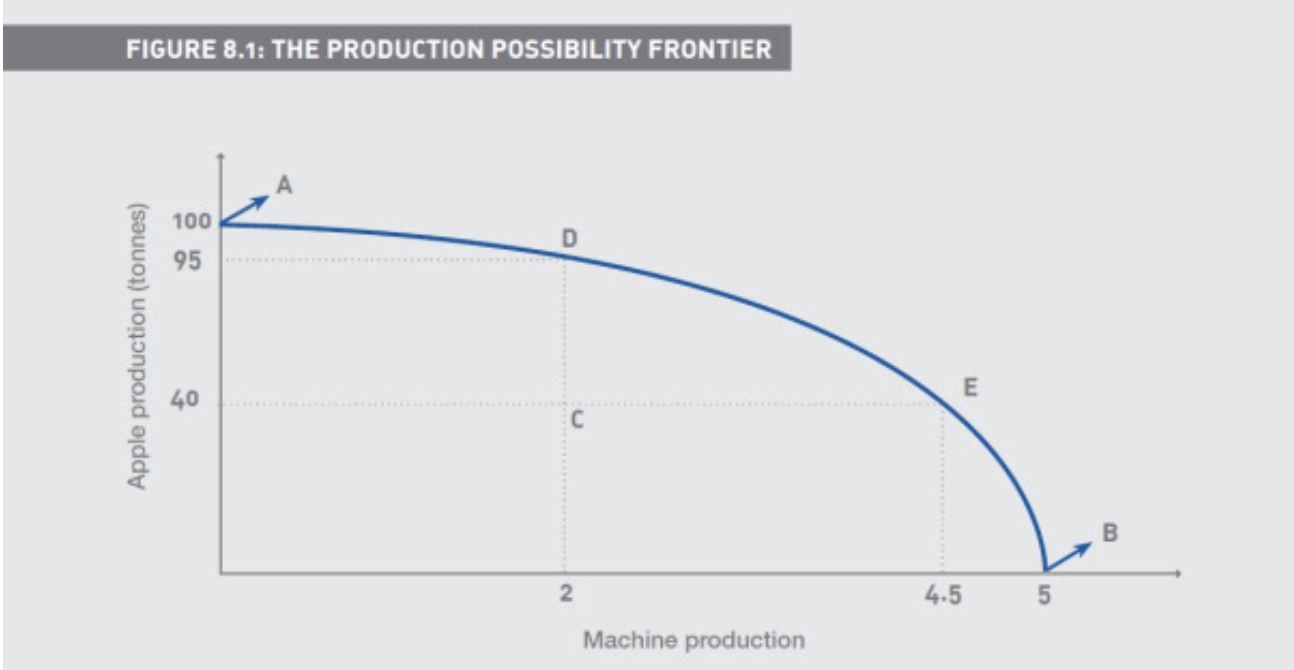
What are the inputs in the Production Possibility Frontier
Labour
Land
Capital
What are factors effecting demand
• Complementary goods
• Substitute goods
• Consumer income
• Tastes
• Advertising
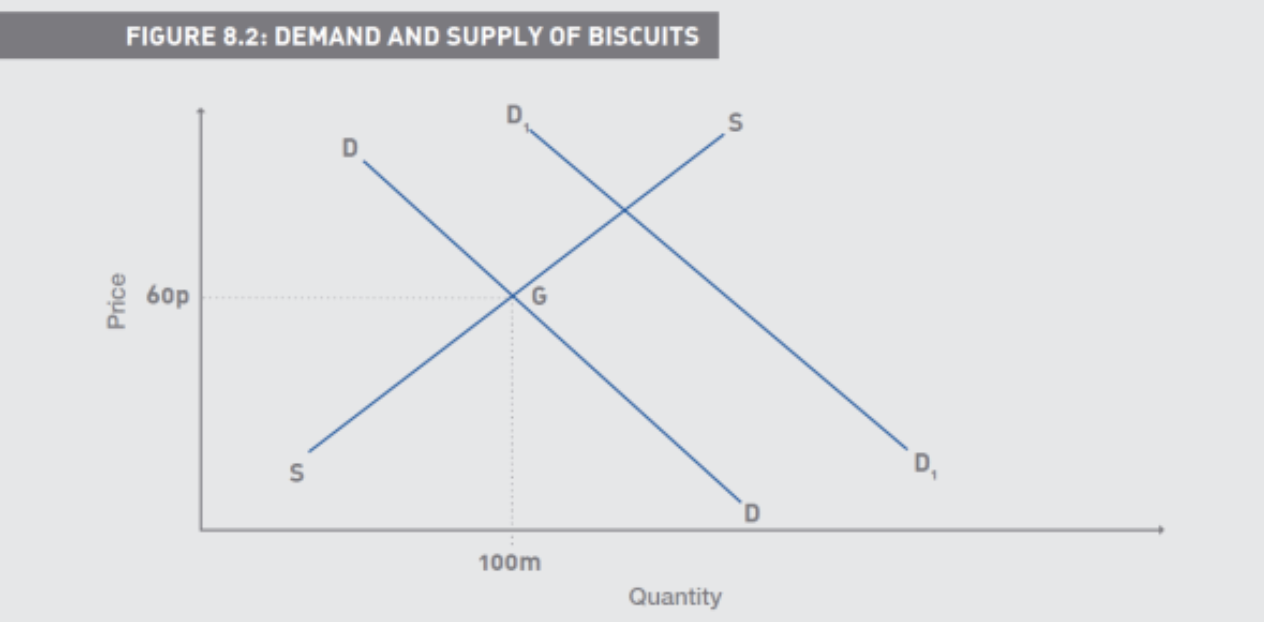
What is Price elasticity of Demand
Elastic demand: greater than one
Inelastic demand: less than one
Shift ALONG the curve
What is Cross elasticity of Demand
Positive result implies substitute goods
Negative result implies complimentary goods
Shift IN the curve
What is Income elasticity of Demand
Positive result implies normal goods
• Greater than 1 implies luxury goods
• Negative result implies inferior goods (necessities)
• Giffen goods
• Shift IN the curve
What is Supernormal profit (Economic Profit)
Profit in excess of
• Measured (accounting) costs
• Opportunity (economic) costs
• Costs associated with the next best use of the unborrowed
capital tied up in the business and the use of the owner’s tim
How do companies profit maximise
Firms will produce output until the level is reached where marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal
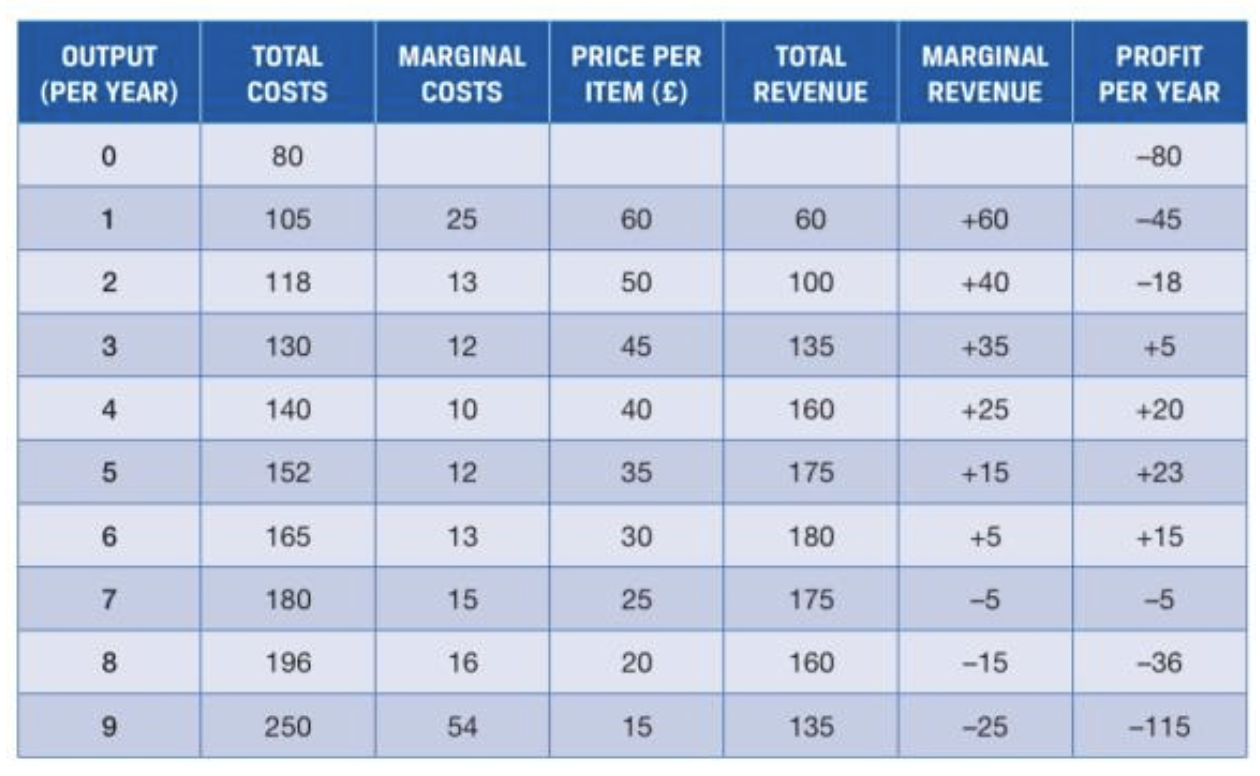
What is Economies of Scale
An lncrease inputs leads to a more than proportionate
increase in output
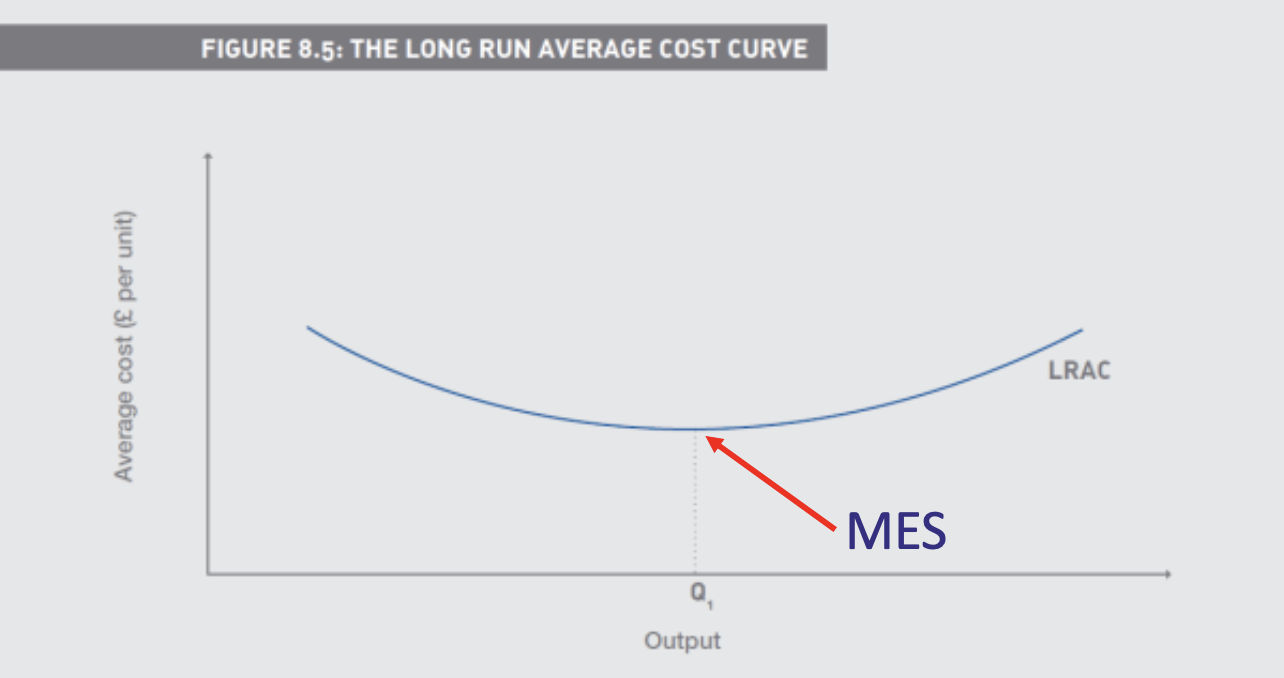
What is the bottom of the Long Run average cost curve
The minimum efficient scale
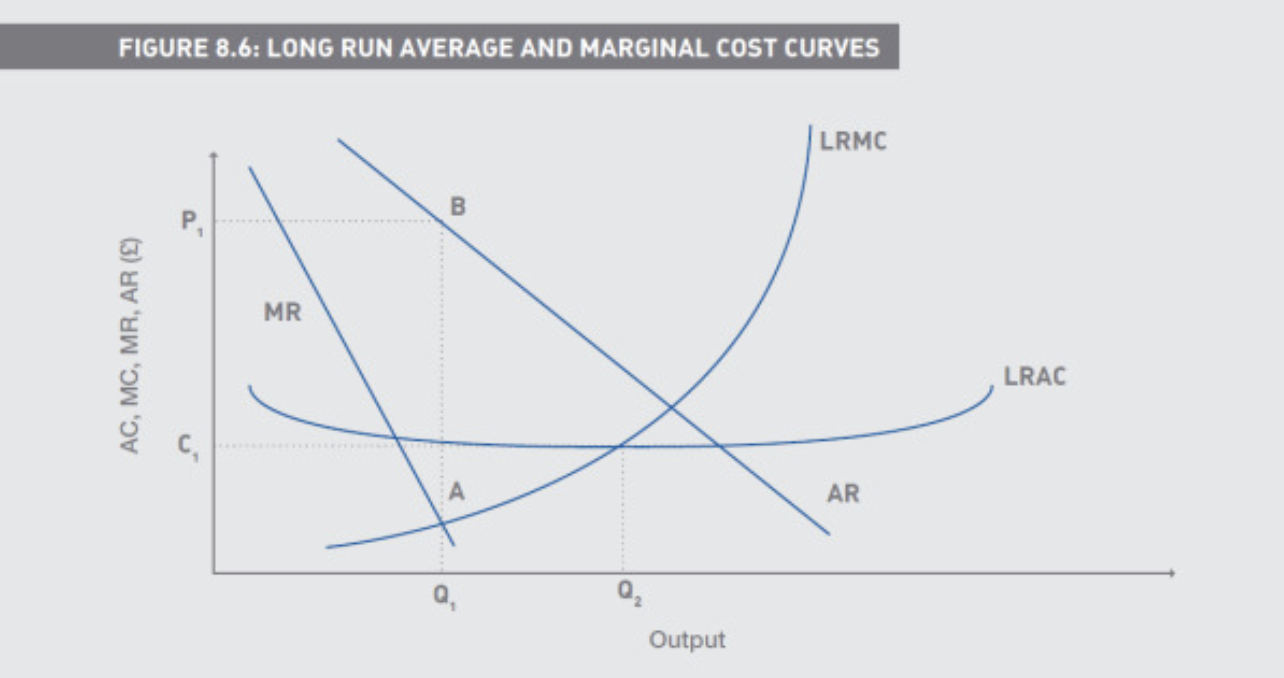
How are Firm’s output determined in Short and Long Run
A is where MR = MC, Q1 is optimal output
Q2 is where diseconomies of scale start to kick in
What is perfect competition
A market structure in which neither buyers nor sellers believe that they can influence the market price by any actions of their own
Horizontal demand line (AR)
How do Buyers and Sellers view themselves in Perfect Competition
as Pricetakers
What are the characteristics of Perfect Competition
Homogeneous product
Large number of independent firms, each small relative to
industry size
No barriers to entry or exit
Perfect information
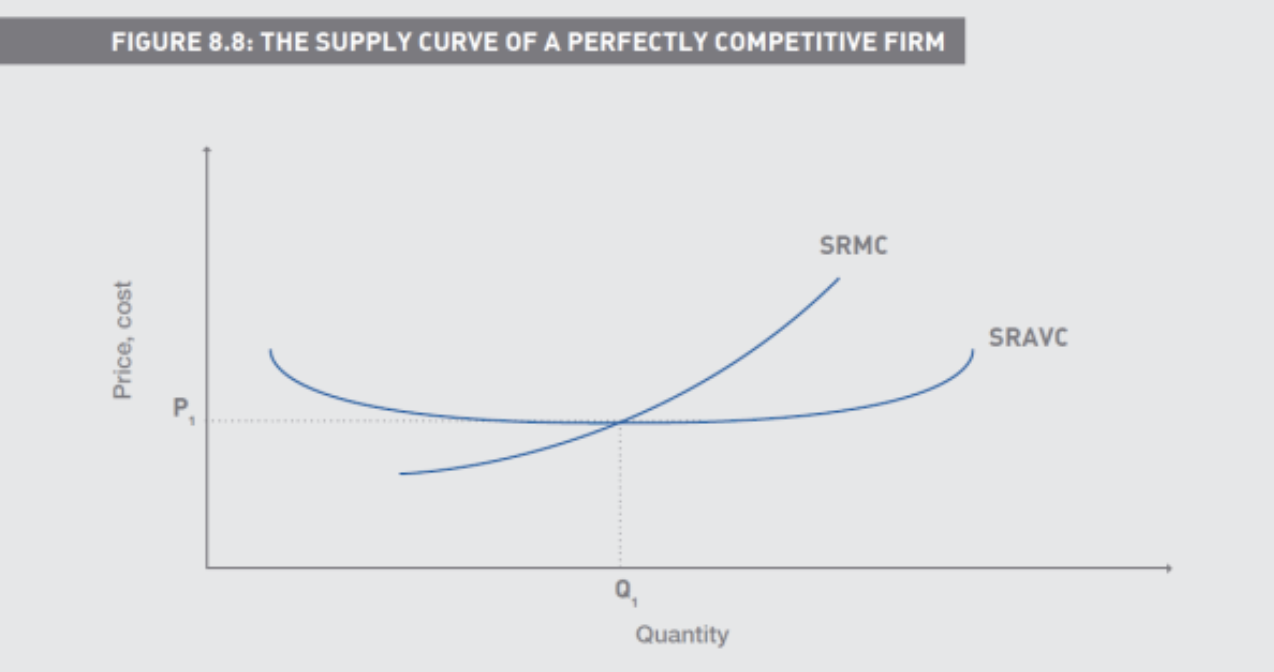
How is the supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm
In the short run, we equate MR with SRMC, and check to see if this
intersection is above the SRAVC curve
If not, then the firm will not produce
Variable costs must be covered in the short run
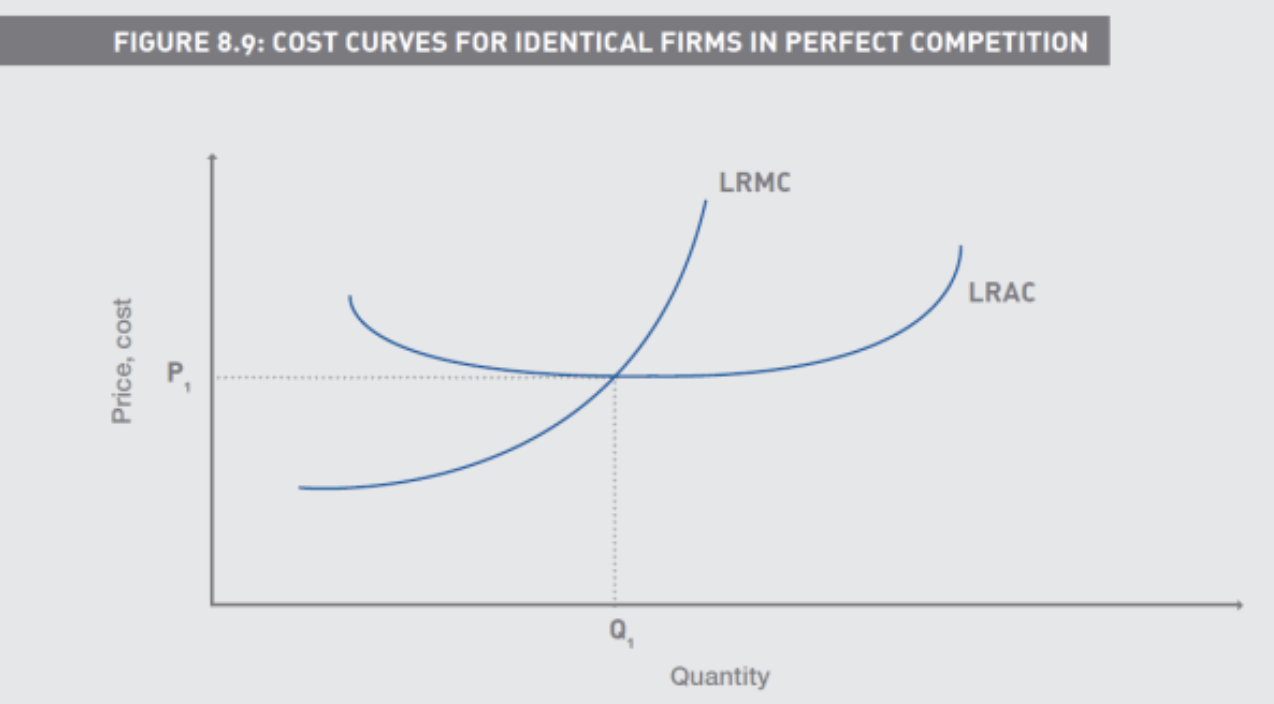
How are the cost curves of Identical Firms in Perfect Competition
In the short run the decision to shut down was taken based on the SRAVC, whereas in the long run we use the LRATC
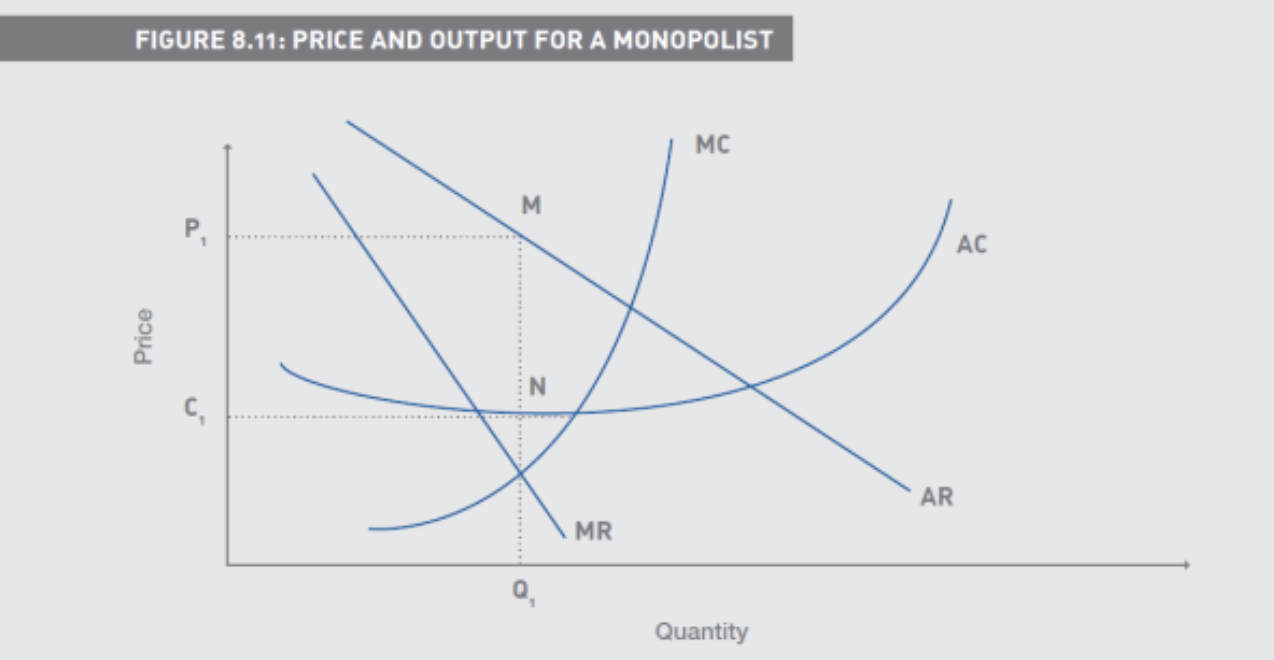
What are features of a Pure Monopoly
A single supplier
Patents/Licenses
• Supernormal (or monopolistic) profits are sustainable in the long
run
Price discrimination
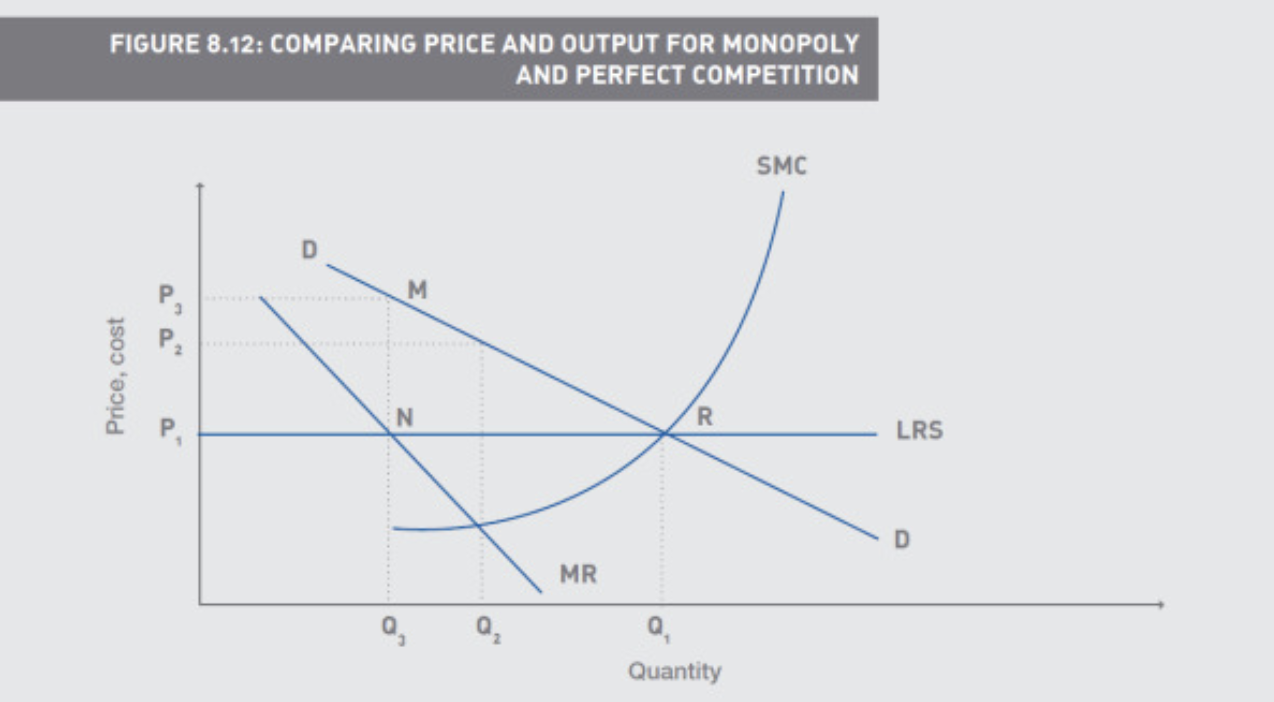
Comparing Pure Monopoly and Perfect Competition
SMC is short run supply
LRS is long run supply
Shows a monopolist may produce less at a higher price
What are the features of Monopolisitc Competition and Oligopolies
Relative few firms
Significant barriers to entry
Homogeneous products
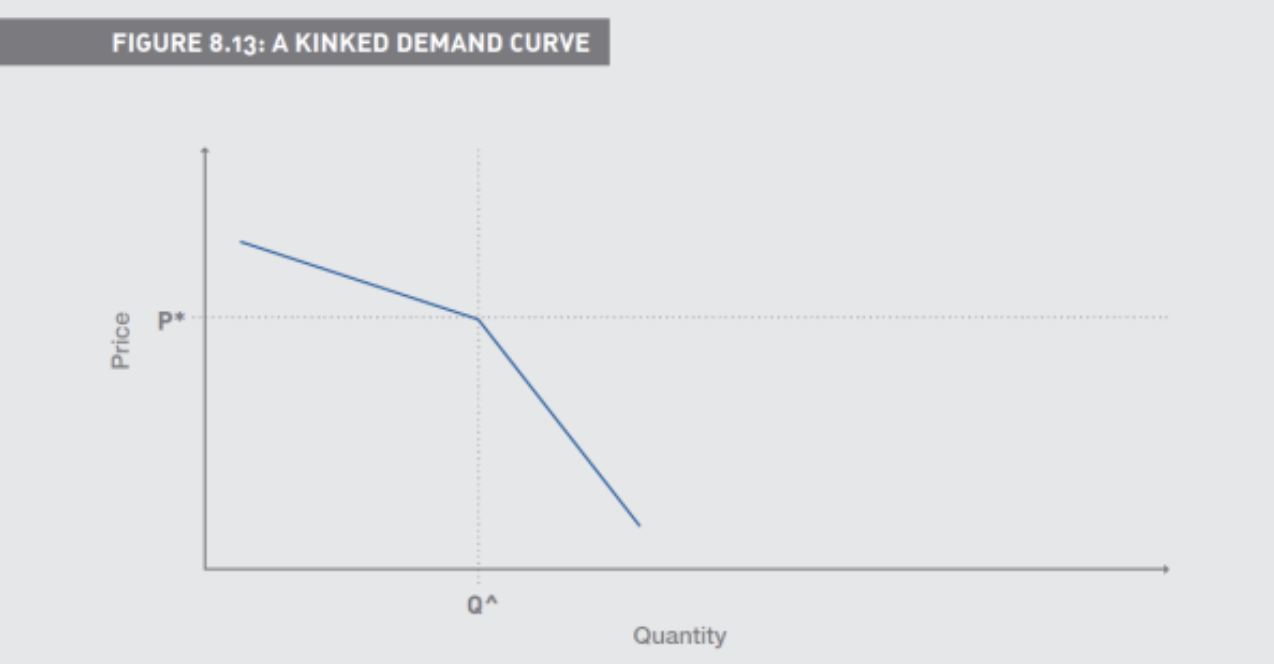
Why is the demand curve kinked
Because if one firm changes their price others are assumed to follow suit
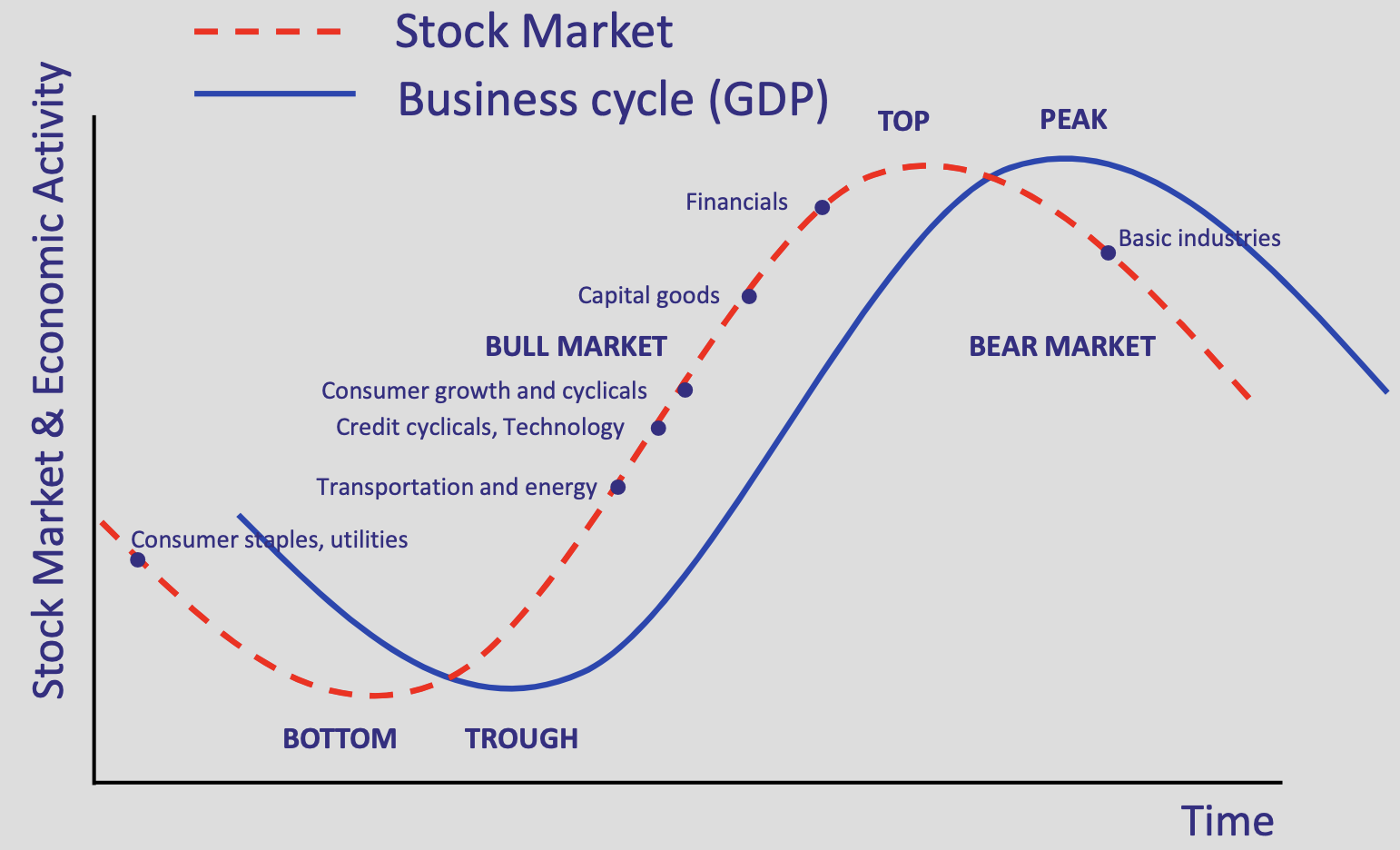
How do business cycles and Industry performance trend over time
What are Porter’s Five Competitive Forces
Bargaining power of the suppliers
Bargaining power of the buyers/customers
Threat of new entrants
Threat of substitutes
Rivalry between current competitors
What are the 5 phases of the product life cycle
Introduction
Growth
Mature
Decline
Obsolescence
What happens in the Introduction Phase
Product sales growing slowly, heavy promotion cost
leading to low or negative profits
What happens in the Growth Phase
Involves a rapid increase in sales as the product becomes
more known; profits rise, competitors attracted
What happens in the Mature Phase
Product is established and well known, promotional
spending falls and economies of scale are present, while competitors have entered the market and hence product innovation is required
What happens in the Decline Phase
Sees a loss of market share and profitability, and a
decision as to whether to continue marketing expenditure to sustain
sales. During this phase a product re-launch may be considered
What happens in the Obsolescence Phase
The product has reached the end of its natural life. Profits
disappear. The timescale will vary between products
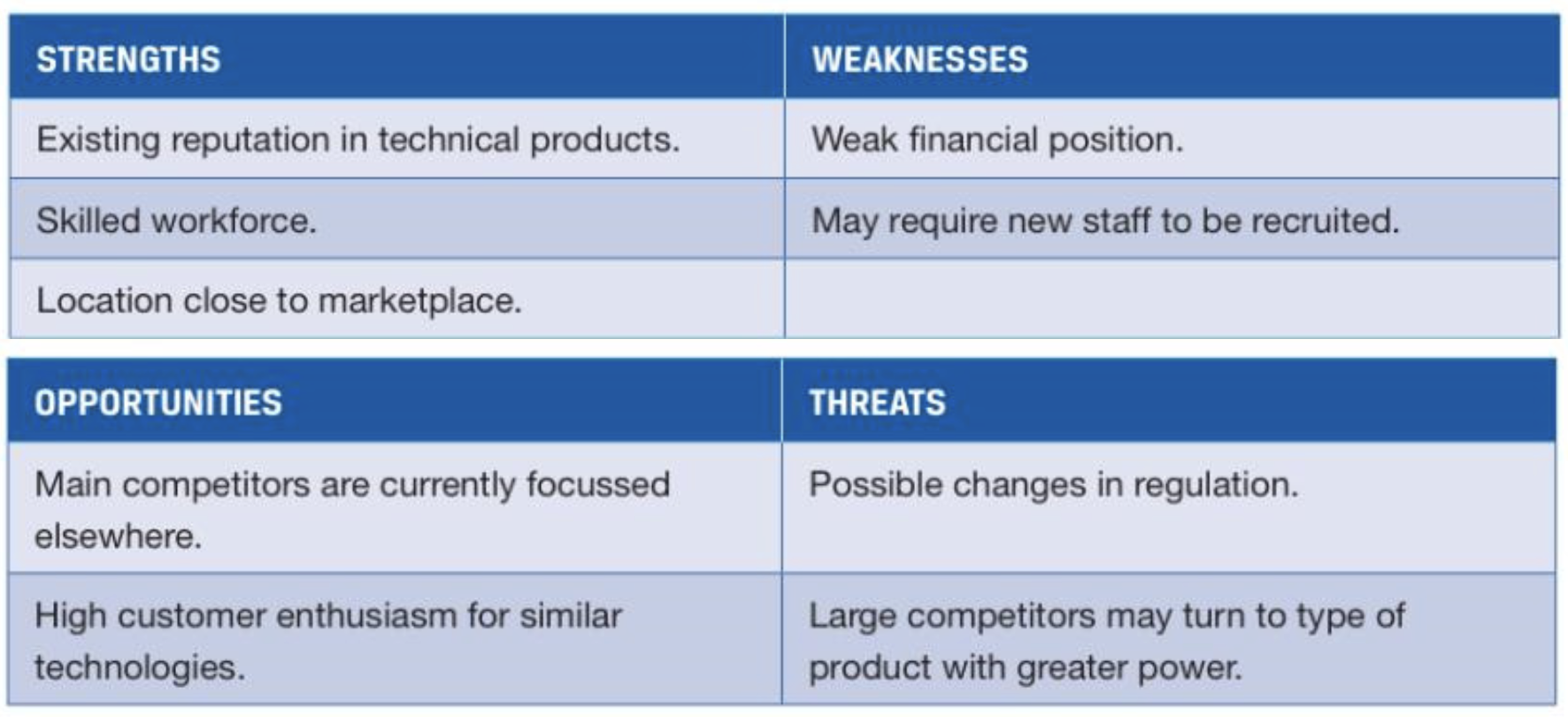
What is Swot Analysis
Strengths and weaknesses are internal (firm)
Opportunities and threats are external (market space)
What are the 4Ps of Product Research/ Marketing
Product
• Is it as described
Placement
• Is it available where target market shops
Promotion
• Is it appropriate to target customers
Price
• Does it represents good value
• Image