IB ESS: Final Exam
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Ecocentric
pure ecology & nature is central to humanity and emphasizes a less materialist approach to life with greater self-sufficiency of societies
Technocentric
believes that technological development can provide solutions to environmental problems
Anthropocentric
believes humans must sustainably manage the global system
Environmental Manager
believe governments need to legislate to protect environment and resources from overexploitation and make sustainable economics - humans have ethical duty to protect & nurture Earth
Cornucopian
through technology & inventiveness, humans can solve any environmental problem & improve living standards - little government intervention
Biocentric
all life has inherent value - no harm to individual species
Deep Ecologist
put more value on nature than humanity - believe in biorights; no human intervention in nature
System / Systems Diagram
set of components that function together & form integrated units
Open System
exchanges matter & energy with its surroundings
Closed System
exchanges energy with its surroundings
Isolated System
exchanges no energy or matter with its surroundings
Transfer
a change in location
Transformation
a change in chemical nature, state, or energy
Matter
gas, liquid, solid
Atoms
makes up matter
1st Law of Thermodynamics / Principle of Conservation of Energy
energy is neither created nor destroyed
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
the entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will increase over time
Entropy
the measure of the disorder of a system - refers to spreading out or dispersal of energy
Enthalpy
equivalent to total heat content of a system
Equilibrium: Steady State, Static, Unstable/stable
the tendency to return to its original state
-the system is constant with continuous inputs & outputs
-no change over time
-unstable: returns to new equilibrium; stable: returns to same
Efficiency (Energy)
useful energy, work or output produced by a process divided by the amount of energy consumed, bring the input to the process
Negative Feedback
damp down, neutralize, or counteract any deviation from an equilibrium; stablizies systems in steady-state
Positive Feedback
further increases or decreases in output that enhances the change in the system
System Resilience
how a system responds to a disturbance
-more resilient: more distrubance dealt with
Tipping Point
reached when ecosystem experiences a shift to a new state in which there are significant changes to its biodiversity & services it provides
Ecological Overshoot
surpassing the sustainable level of resources exploitation
Sustainable Development
development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Natural Capita
goods & services the environment provides humans with in order to provide natural income
Natural Income
natural resources that can be sold for profit
Abiotic vs. Biotic
Abiotic: non-living physical factors influencing organisms & the ecosystem
Biotic: living organisms
Species
a group of organisms sharing common characteristics that interbreed & produced fertile offspring
Population
a group of organisms of same specifies living in the same area at the same time
Community
a group of populations living & influencing with each other in a common habitat
Habitat
environment in which a species normally lives
Ecosystem
community & the physical environment it interacts with
Biome
collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
Biosphere
collection of biomes; Earth
Fundamental Niche vs. Realized Niche
Fundamental: full range of conditions & resources in which a species could survive & reproduce
Realized: actual conditions & resources in which a species exists due to biome interactions
Limiting Factor (Density Independent vs. Dependent)
factors which slow down growth of popuation
Carrying Capacity
maximum number of a species that can be sustanbly supported by a given area
Intra vs. Interspecific Competition
Intra: between members of same species
Inter: between members of different species
Population Dynamics
study of factors that cause changes in population sizes
Competitive Exclusion
one species totally out competes another species
Predation
predator (hunter) feeds on prey (attacked)
Tragedy of the Commons
individuals act in own self-interest to harvest a resource but destroy long-term future of that resource to there is none for anyone
Environmental Impact Assessment
report prepared before a development project to change the use of land
Ecological Footprint
a model used to estimate the demands that the human population places in the environment
Pollution/Types
the addition of a substance or agent to an environment at a rate greater than that at which it can be rendured harmless by the environment
Primary/Secondary Pollutants
Primary: active in emission
Secondary: formed by primary pollutants undergoing physical or chemical changes
Point source/Non-Point Source Pollutants
Point: release of polltants from single, clearly indentifiable site
Non-point: release of pollutants from numerous, widely dispersed origins
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
resistant to breaking down & remain active in the environment for a long time
Biodegradable Pollutants
do not persist in the environment & break down quickly
Pollution Management
-change human activites
-regulate/prevent release of pollutant
-work to clean up/restore damaged ecosystems
Herbivory
animal eating a plant
Parastism
a relationship between two species in which one species lives in or on another, gaining its food from it
Mutualism
relation between two or more species in which all benefit & none suffer
Bioaccumulation/Magnification
Accumulation: build-up of persistent/non-biodegradable pollutants within an organism or trophic level
Magnification: increase in concentration of presistent/non-biodegradable pollutants along a food chain
Commensalism
relationship between two species where on benefits from the other without attacking it
S-curves vs. J-curves (Reasons behind increase/decrease)
S: exponential growth, but growth rate slows to population with constant size
J: exponential growth, then collapse
Birth vs. Death Rate
Birth: number of live deaths per 1000 of a population each year
Death: number of deaths per 1000 of a population each yeah
Environmental Resistance
area between exponential growth curve & the S-curve
Exponential vs. Logistic Growth
Exponential: no limiting factors slowing growth
Logistic: limited resources slow down growth
Photosynthesis (Process)
plants convert light energy into chemical energy
6CO2 + 12H2O --light--> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Cellular Respiration (Process)
conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide & water in all living organisms, releasing energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ----> 12H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
Primary Productivity (Gross and Net)
Gross: total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by plants
Net: GPP - respiration
Food Chain/Web (Trophic Levels) and Trophic Efficiency
Chain: flow of energy between organisms
Web: series of food chains
Trophic efficiency: amount of energy transferred to the next trophic level (10%)
Ecological Pyramids (Numbers, Biomass, Productivity)
Numbers: number of organism at each trophic level
Biomass: biomass at each trophic level
Productivity: rate of flow of energy of biomass through each trophic level
Secondary Productivity (Gross and Net)
Gross: total energy/biomass assimilated by consumers
GPP: food eaten - fecal loss
Net: total gain in energy/biomass after respiration
Assimilaton
process of food cross wall of alimentary canal (gut wall) to be absorbed & used to power life processes
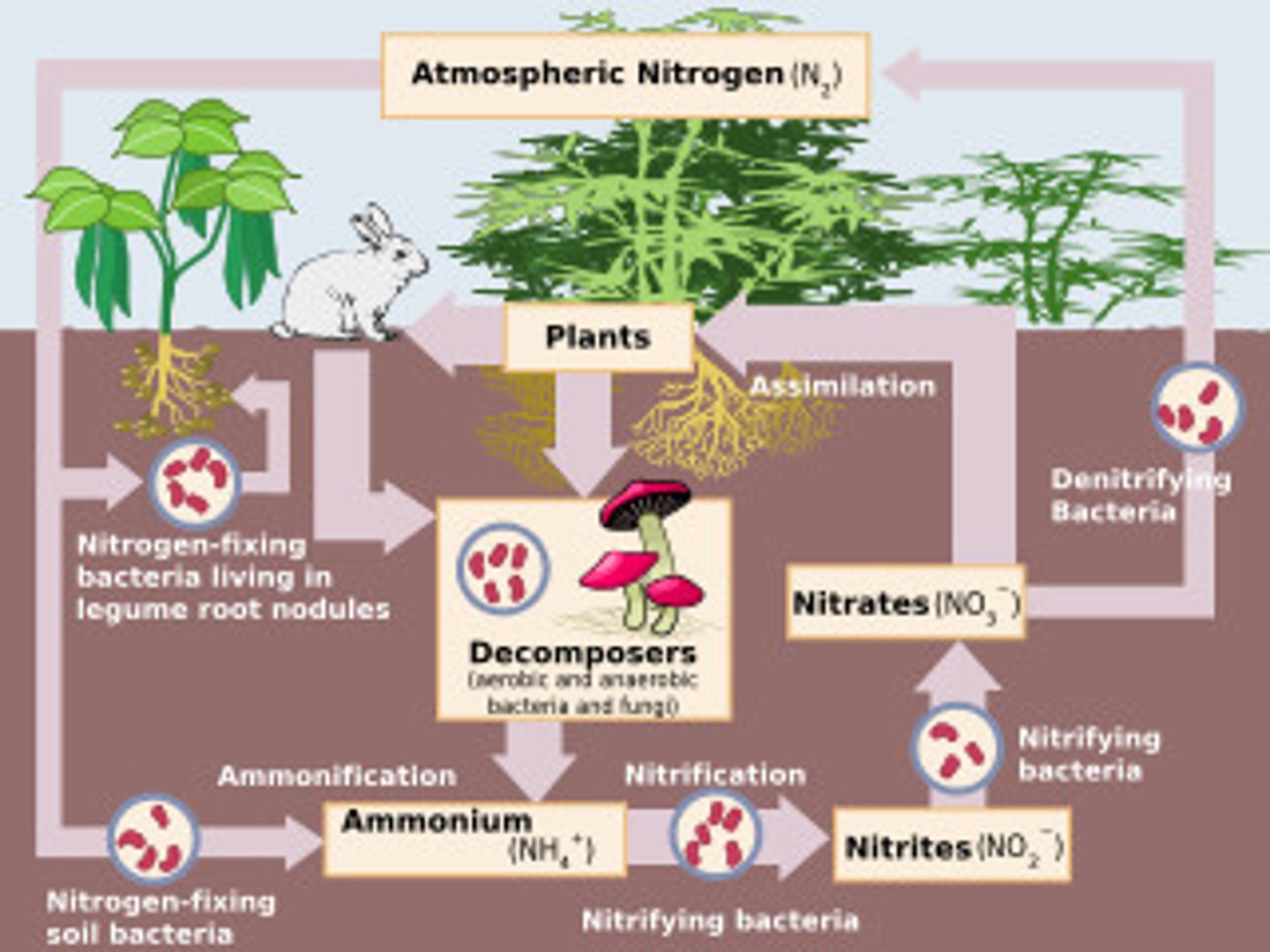
Nitrogen cycle
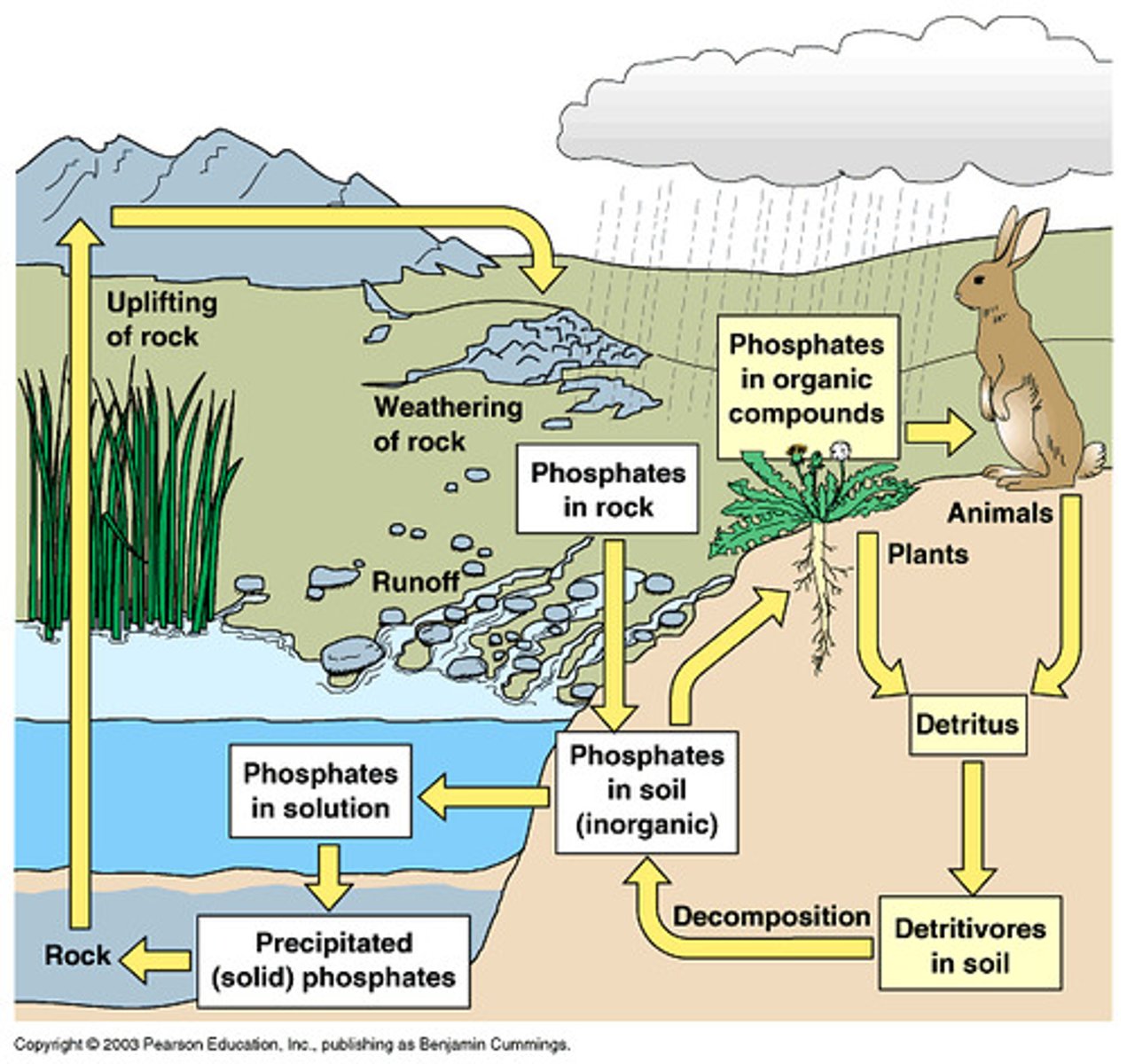
Phosphorus cycle
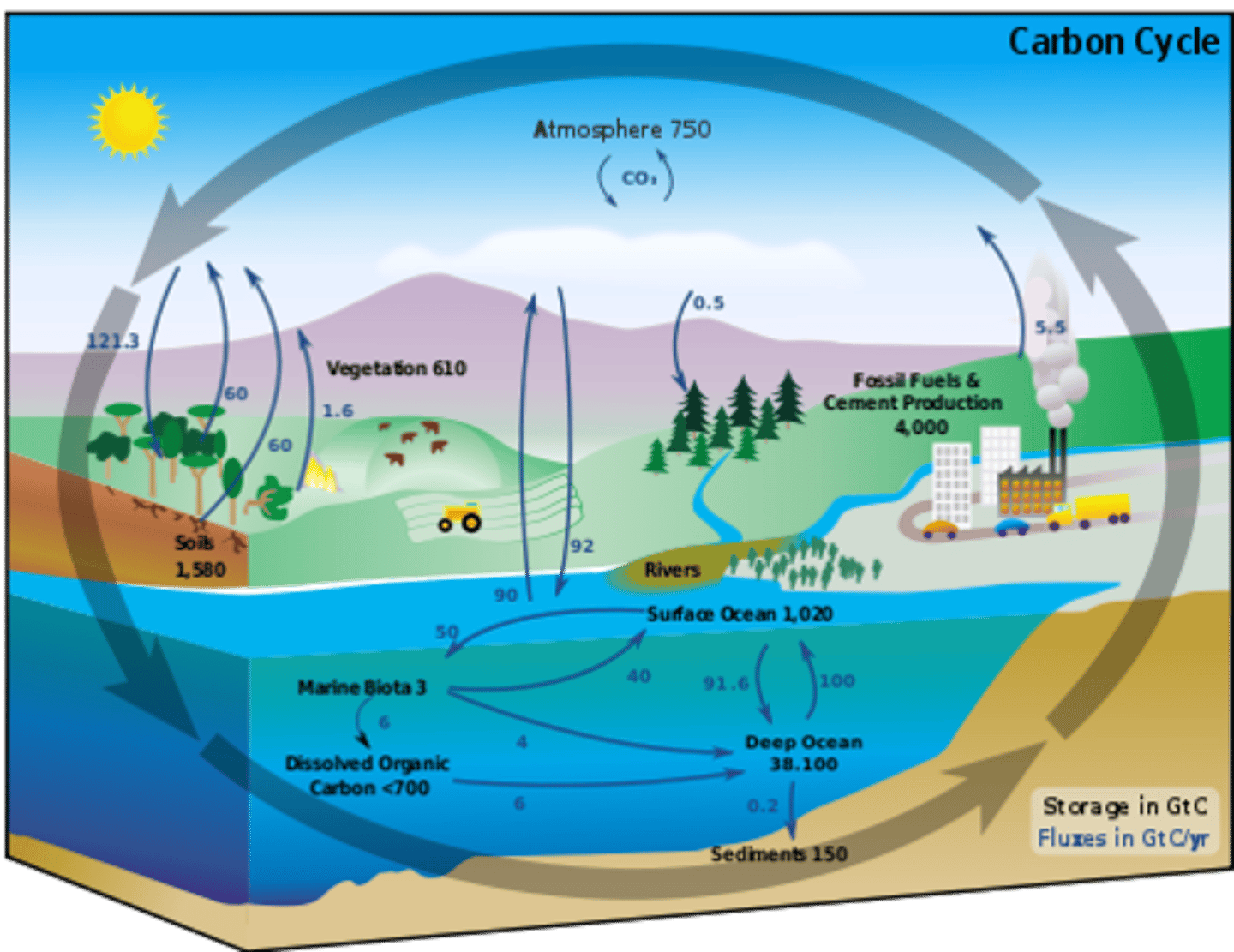
Carbon cycle
Energy Budget vs. Energy Subsidy
Budget: quantity of energy entering, staying within & leaving the animal/population
Subsidy: additional energy that needs to be put in a system above that which limits from the sum's energy
Climate Change and Biome Shift (Cause/Effects)
altering the distribution of biomes
Biome shift: biomees moving to a different climate
Zonation
change in community along environmental gradient due to factors such as altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore
Succession (Primary vs. Secondary, Seral Stages)
process of change over time in an ecosystem
Primary: bare ground
Secondary: soil has already formed
R and K Selected Species
R: species with small size, short life cycle, rapid growth & high production
K: species with large size, longer life cycles, slower growth, & delayed reproduction
Climax Community (Sub-Climax vs. Plagioclimax)
stable & self-perpetuating; maximum possible development
Sub-climax: only continue development if limiting factor removed
Plagioclimax: continue development if human activity ceases
Pioneer Species
feral species to colonize an area
Kite Diagram
graph showing the density or distributon of a species that has been found along a transect
Sampling Methods (Quadrats, Transects-Belt, Line, continuous and interrupted, Lincoln Index/Simpson Diversity Index, Catching Organisms: Large/Small, Motile, Non-motile)
Quadrat: frame of specific size which may be divided into sub-sections
Transect-belt: strip of chosen width through ecosystem (parallel lines)
Transect-line: measuring tape laid out in direction of environmental gradient
Continuous: whole line/belt sampled
Interrupted: samples taken at points along line/belt
Lincoln: capture, mark, release, recapture
Simpson number of different species & relative number of individuals of each species
Small/motile: pitfall traps, nets, etc.
Turbidity
cloudiness of body of fresh water
Dissolved Oxygen vs. Biochemical Oxygen Demand
DO: measures oxygen concentration of water
BOD: DO needed to break down organic material in given volume of water
Dichotomous Keys
tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world
Biodiversity (genetic, species, habitat)
Genetic: range of genetic material present in population of species
Species: number of species & their relative proportions
Habitat: range of different habitats in ecosystem/biome
Biodiversity Hotspot
region with a high level of biodiversity that is under threat from human activites
Theory of Evolution (Origin of Species)
each individual is different/differently adapted to its environment
-whole population gradually changes over time
Speciation (Allopatric vs. Sympatric)
formation of a new species when populations of a species become isolated or evolve differently
Allopatric: biological species become isolated
Sympatric: non-species evolves within same area as ancestor
Isolation (Geographic, Temporal, Reproductive)
Geographic population separated by a physical barrier
Temporal: prevents mating because species breed at different times
Reproductive: the different species cannot reproduce with one another
Continental Drift/Plate Tectonics
Continental drift: movement of plates on crust
Plate tectonics: study of movement of plates
Mass Extinction (Extinction Rates)
species become extinct at a rate far greater than the background rate (one species per million species per year)
Weed Species
species with potential for overpopulating an area & upsetting the normal biological balance
Natural Hazards vs. Disasters
Natural hazards: naturally occuring events that may have a negative impact on the environment
Disasters: caused by human activites
Inertia (in reference to disasters)
property of an ecosystem to resist change when subjected to a disruptive force
Invasive (non-active) species
exotic species drastically upset a natural ecosystem
Over exploitation
human population expand & technology allows better catching, hunting, harvesting
11 characteristics that make a species prone to extinction
narrow geographical range, small population size/declining numbers, low population density/large territories, low populations, large body, low reproductive potential, seasonal migrants, poor dispersal, specialized feeders/niches, edible to humans, island organisms
IUCN Red List Criteria
extinct, extinct in wild, critically endangered, endangered, vulnerable, near threatened, least concerned, data deficient, not evaluated
Direct values vs. Indirect values of biodiversity
Direct: food sources, natural product
Indirect: environmental services, science/education, biological control agents, gene pools, future potential, human health, human rights, recreational, ecotourism, ethical/intrinsic value, biorights
Approaches to Conservation/Preservation of Biodiversity
Conservation: sustainable use/management of natural resources
Preservation: attempts to exclude human acitvity in area where humans have not yet encroached