Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
what is traumatic ulcerative granuloma w stromal eosinophilia (tugse)
deep chronic ulceration due to damaged muscle- from repetitive trauma
what is the common age group w traumatic ulcerative granuloma w stromal eosinophilia (tugse)
usually adults
common location of traumatic ulcerative granuloma w stromal eosinophilia (tugse)
tongue > buccal and lip
tx for traumatic ulcerative granuloma w stromal eosinophilia (tugse)
incisional biopsy and remove cause of trauma
how long would you wait to biopsy an ulcer, why would you do this
MUST DO A BIOPSY on ulcers that are present for more than 2 weeks; can look clinically similar to squamous cell carcinoma
what are the 5 non-endocrine systemic diseases we go through
jaundice
amyloidosis
crohn disease
hypophosphatasia
Vit D resistant rickets
what are the 5 endocrine systemic diseases we go through
pituitary (gigantism/ acromegaly/ dwarfism)
thyroid (hypo/hyperthyroidism)
parathyroid (hyperparathyroidism)
pancreas (T1/2DM)
adrenal (addisons, cushings synd/disease)
jaundice is also known as
icterus
what is jaundice
excess bilirubin in the bloodstream accumulates in yellowish discoloration of the skin and mucosa
what is the bilirubin level in someone w jaundice
exceeds 2 mg/dl
what are the 5 common causes of jaundice
physiologic or pathologic:
hemolytic anemia/sickle cell anemia
liver disease
bile duct obstruction
cancer
gilbert syndrome (glucuronosyltransferase)
are there oral manifestations w jaundice
no- just the yellow skin color usually

what are you suspicious of
jaundice
what is amyloidosis
group of conditions characterized by the deposition of an extracellular, proteinaceous substance termed amyloid
most of the time amyloidosis is systemic, why is this concerning
can lead to death most of the time within a few years due to cardiac or renal failure
there are 5 classifications of amyloidosis but we only need to know 2! what are they
organ limited
primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis
features of organ limited amyloidosis (2)
limited to one organ
infrequent oral features
what age group and gender type is more affected by primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis
older males
in primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis, 15-20% are due to…
multiple myeloma
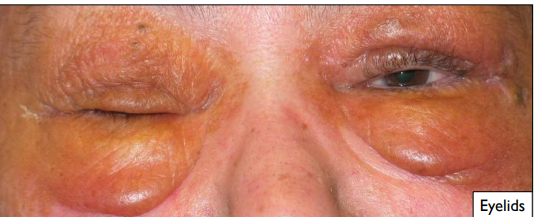
extra-oral locations affected by primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis
extra-oral: eyelid, neck, lips
intra-oral manifestations of primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis
thick lips (rock-solid), macroglossia
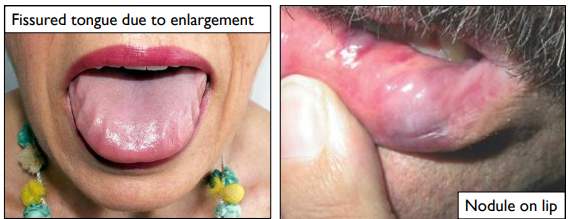
how can skin appears in primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis
smooth-surfaced, firm, waxy papules and plaques
what is Chrohn’s disease
inflammatory and immunologically mediated condition of unknown cause
common age affected by Crohn’s disease
teenagers
location affected by Crohn’s disease
anywhere along the GI tract
common symptoms of Crohn’s disease
abdominal cramping, diarrhea, pain, nausea, and fever; weight loss and malnutrition may develop
in Crohn’s disease, oral lesions are significant bc they precede…
the GI lesions 30% of the time
what are some oral manifestations of Crohn’s disease
diffuse, nodular swelling
cobblestone appearance of oral mucosa
linear ulcerations of the buccal vestibule
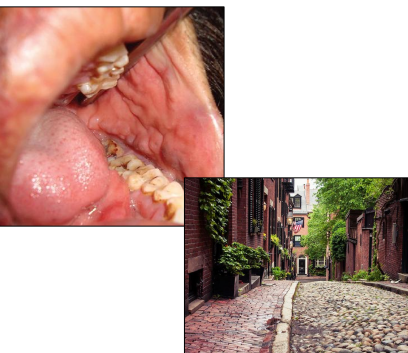
tx for oral lesions in Crohn’s disease
sulfa drug/prednisone; oral lesions will clear w tx of GI disease
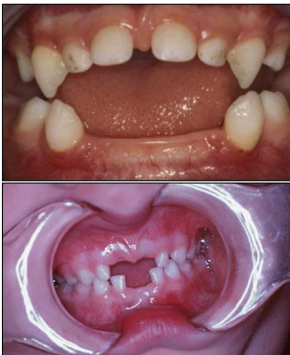
what is hypophosphatasia
rare metabolic disease where there is a decrease in alkaline phosphatase enzyme
mode of inheritance in hypophosphatasia
AD
oral manifestations pf hypophosphatasia
lack of cementum
premature loss of teeth: esp lower incisors
bone abnormalities
what is vitamin d-resistant rickets also known as
hereditary hypophosphatemia
what is the mode of inheritance of vitamin d-resistant rickets/ hereditary hypophosphatemia
X-linked
does vitamin d-resistant rickets/ hereditary hypophosphatemia affected M or F more
M
common age affected by vitamin d-resistant rickets/ hereditary hypophosphatemia
early age: infancy/childhood
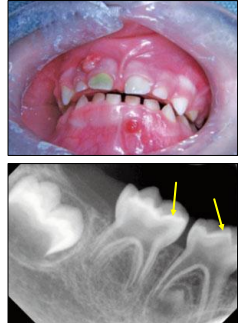
what is vitamin d-resistant rickets/ hereditary hypophosphatemia
low serum phosphate (no problem w the enzyme)
low calcium
normal vitamin D
oral manifestations of vitamin d-resistant rickets/ hereditary hypophosphatemia
large pulp horns extending to DEJ
multiple non-vital teeth
absence of caries or trauma
what is the most common cause of anemia
iron deficiency
clinical (non-oral) manifestations of iron deficiency anemia
fatigue, tired, lightheaded, lack of energy
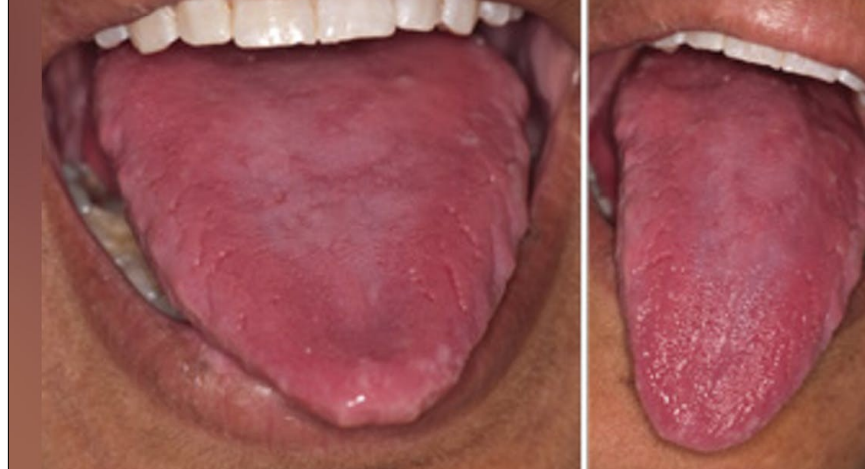
oral manifestations of iron deficiency anemia
angular cheilitis, atrophic tongue, glossitis, burning sensation maybe due to candidiasis
what is plummer-vinson syndrome also known as
paterson-kelly syndrome
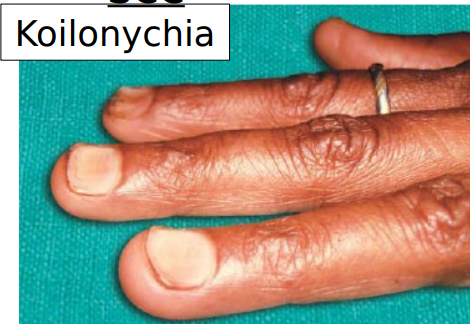
what is plummer vinson syndrome/paterson-kelly syndrome
rare condition in women of scandinavian or north european background
clinical (non-oral) manifestations of plummer vinson syndrome/paterson-kelly syndrome
iron deficiency anemia
dysphagia
koilonychia
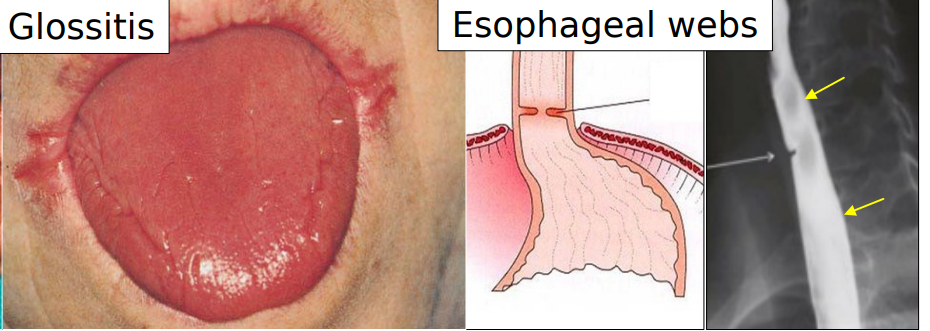
oral manifestations of plummer vinson syndrome/paterson-kelly syndrome
atrophic glossitis
esophageal webs
premalignant and associated w oral and esophageal SCC
etiology of gigantism
inc in growth hormone from pituitary gland before closure of the epiphyseal plates
is gigantism pre or post puberty
pre-pubertal
is acromegaly pre or post puberty
post-pubertal
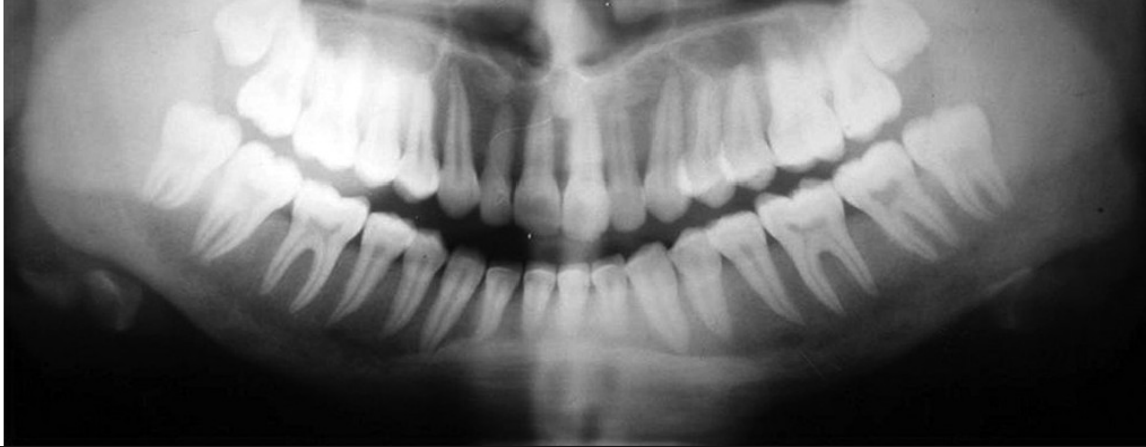
oral manifestations of gigantism
enlarged mandible + prognathism
generalized macrodontia
etiology of acromegaly
inc in growth hormone from pituitary gland after closure of epiphyseal plate
what is dwarfism
dec secretion of growth hormone from the pituitary gland
oral manifestations of dwarfism
maxilla/mandible smaller
midface underdeveloped
microdontia
malocclusion
delayed eruption and prolonged retention of teeth
development of roots is delayed
failure of development of 3rd molars
what gland plays a primary role in regulation of cellular metabolism
thyroid gland
what is hyperthyroidism
hyperfunction of thyroid gland, mass in the anterior midline of the neck
what are the most common causes of hyperthyroidism
Grave’s disease, toxic multinodular goiter
clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism
weight loss
tachycardia
excessive perspiration
tremor
warm smooth skin
exophthalmos
glossopyrosis (burning of the tongue)
thyroid storm
what is thyroid storm
complication in dental tx due to other manifestations being heightened at the clinic (like tachycardia)
what are the two types of hypothyroidism
cretinism (congenital hypothyroidism)- kids
myxedema (acquired hypothyroidism)- adults
what are common manifestations of hypothyroidism
enlarged tongue, cold intolerance, thinning of hair
funx of parathyroid gland
regulation of Ca levels via phosphate diuresis and intestinal reabsorption of Ca
intraoral manifestations of hyperparathyroidism
sometimes radiolucent lesions in the jaws, often multiple
loss of normal trabecular bone pattern
ground glass or frosted glass appearance
loss of lamina dura around the teeth
what is addison’s disease also know as
hypoadrenocorticism- insufficient production of corticosteroid
a pt w addison’s disease can go through what is called Addison crisis, what is this
when there are low levels of corticosteroids in your body, these patients, especially under stressful situation, can go into kind of a hypovolemic shock bc they don't have the hormones to help them cope with the stress
addison’s disease is mostly systemic, but sometimes you can see one intraoral manifestation
a brown pigmentation that can can be on the lips intra orally and on the skin; more of that bronze color
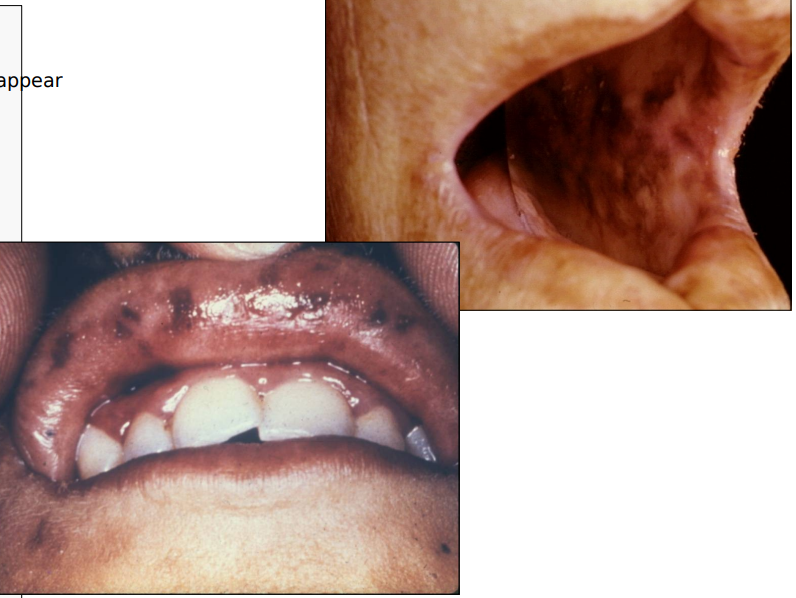
addison’s disease most common age group affected
adults
cushing disease vs cushing syndrome
disease: endogenous cause, overproduction of cortisol caused by pituitary tumor, adrenal tumor, or unknown
syndrome: exogenous cause, taking medicines containing glucocorticosteroids
what are some common clinical manifestations that can be used to describe cushing’s syndrome
moon face, buffalo hump, purple striae
what is T1 diabetes
complete lack of insulin; young age onset
what is T2 diabetes
inadequate insulin production or resistant of target tissue
is T1 or T2 diabetes more common
T2
clinical manifestations of T1 D
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, ketoacidosis
intra-oral manifestations of T2 D
periodontal disease
delayed healing
infection
oral candidiasis (30%)
xerostomia (30%)
what is the normal blood glucose range
70-120 mg/dL