5. Light Microscopy (LM) Types
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TAMU BMEN 311 - Imaging Living Systems [Light Microscopy Types]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Contrast enhancement
distinguish fine structural details and visualize transparent or low-contrast specimens more clearly.
improves visibility of transparent features
specimans examined in LM
biological tissues and cells
transparent microorganisms (bacteria and protozoa)
cellular components like organelles
Types of Light Microscopy
Brightfield*
Darkfield
Phase Contrast
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)
Polarized Light
BRIGHTFIELD
standard lab microscope
produces image on a bright background
Cells and tissues have intrinsically low contrast when imaged in brightfield mode
using histology stains to improve contrast = toxic → KILLS CELLS
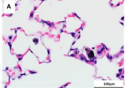
Brightfield applications
routine examination of blood smears, histology, and cytology studies
DARKFIELD
stars become visible at night
Increases contrast without staining
producing a bright image on a darker background
useful for viewing THIN, LIVE specimens
sensitive to debris
Darkfield applications
image syphilis
studying external details
tiny diffracting objects like bacteria and isolated organelles
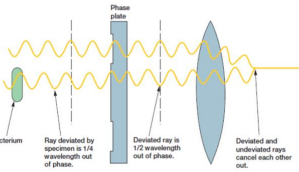
PHASE CONTRAST
uses refraction and interference caused by speciman’s structures create high-contrast, high-resolution images
no staining, useful for viewing live specimens.
utilizes phase shifts caused by differences in refractive indices to enhance contrast in transparent, thin specimens.
subject to “halo” artifacts
phase contrast applications
nuclei, neurons membranes, cell division, tissue engineering applications
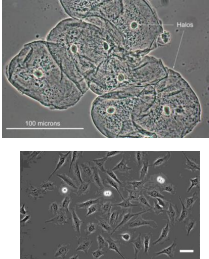

Label the image
brightfield
dark field
phase contrast
DIFFERENTIAL INTERFERENCE CONTRAST (DIC)
interference patterns → enhance contrast = high-contrast images of living organisms with (pseudo) 3D appearance
useful in distinguishing structures
enhances contrast in specimens with slight variations in thickness and refractive index
USEFUL FOR THINK SPECIMANS
NO “halo” artifacts
expensive
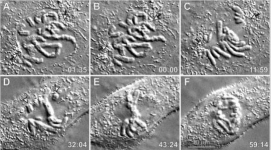
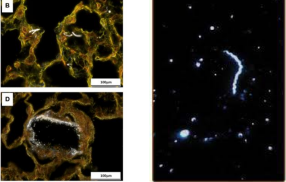
DIC Applications
cell motility, cellular structure, cell division (pic), tissue engineering applications
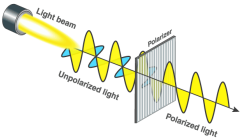
POLARIZING LIGHT
polarized light and filter to study birefringent specimens
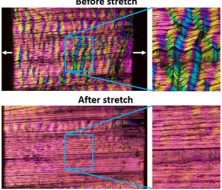
Birefringence
optical property of a material
refractive index depends on polarization and propagation direction of light. (aka double refraction)
Polarizing Light Applications
spindle and collagen fibers (pic), gout crystals, (normal and malaria-infected) red blood cells; optically anisotropic specimens (birefringent)
light polarization