gas exchange
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
how would you calculate the atmospheric partial pressure of oxygen?
atmospheric pressure (760mmHg) x 21% oxygen in air = 159mmHg is the partial pressure of oxygen
what happens to oxygen partial pressure as it moves from the trachea to the alveoli?
decreases
why does the partial pressure of oxygen decrease as it travels from trachea to alveoli?
air is humidified so there is a higher percentage of water
how many haem groups does a haemogloblin contain?
4
how many oxygen molecules can one haemoglobin carry?
4
what is the alveolocapillary membrane also called?
blood-air barrier
what does the blood-air barrier consist of? (3)
- capillary endothelium
- fused basement membrane
- alveolar epithelium
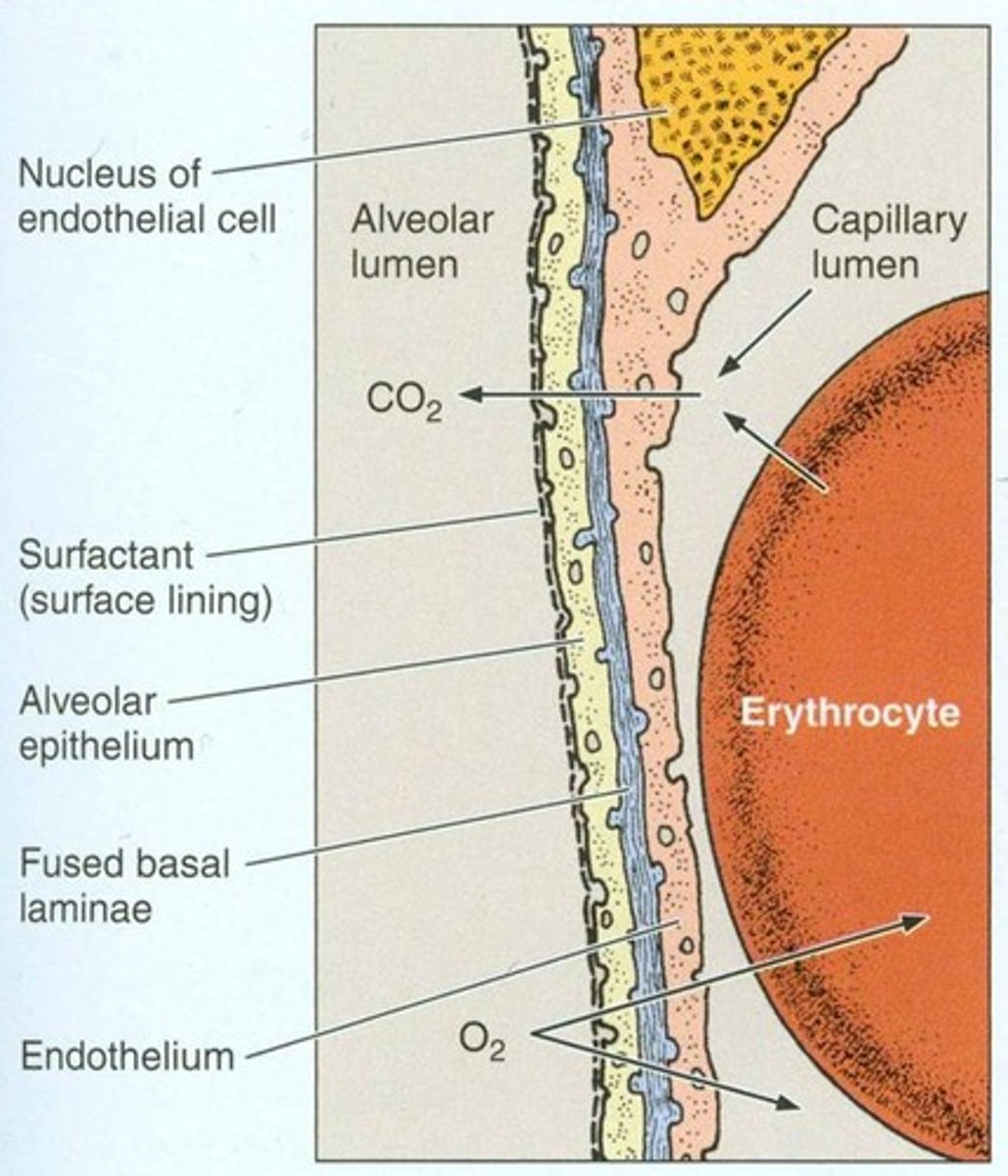
what is fick's law of diffusion?
the diffusion rate of gas is proportional to:
- partial pressure difference across barrier
- solubility of gas
- tissue surface area
and inversely proportional to tissue thickness
what are the 2 ways oxygen can be transported?
- dissolved O2
- bound to haemoglobin
how much of total oxygen is carried by dissolved O2?
0.3% - not very efficient
how would you work out the total concentration of oxygen in blood?
O2 bound to Hb + dissolved O2
what is the equation for oxygen delivery (DO2)?
DO2 per minute = cardiac output x O2 content
what are the 2 conformational states fo haemoglobin?
- relaxed (oxygenated)
- tense (fully deoxygenated)
what happens when the last O2 is released? (2)
- beta chains move apart
- DPG enters and binds to decreases the affinity for oxygen
what happens as more O2 bind? (2)
- Hb has higher affinity to O2 (cooperativity)
- Hb moves from tense to relaxed state
what are the factors affecting affinity of Hb for oxygen?
- pH/CO2
- DPG
- temperature
what causes a shift to right of Oxy Hb dissociation curve?
increase in:
- CO2
- temperature
- DPG
- metabolism
- H+ conc - acidic
what does a right shift of dissociation curve cause?
- lower affinity for oxygen
- oxyhaemoglobin dissociates more readily
what causes a shift to the left of oxy hb dissociation curve?
decrease in:
- CO2
- temperature
- DPG
- metabolism
- H+ conc - alkali
or:
- alkalosis
- CO poisoning
- foetal hb
what does a left shift of dissociation curve cause?
- higher affinity for oxygen
- oxyhaemoglobin does not readily dissociate
what are the 3 ways CO2 can be transported in the blood?
- dissolved CO₂
- as bicarbonate
- as carbamino compounds
how much CO2 is dissolved in plasma?
10%
how much CO2 is transported as bicarbonate?
60%
how is bicarbonate formed?
- CO₂ diffuses into rbc
- CO₂ + H₂O ⇌ H₂CO₃ ⇌ H+ + HCO₃-
- by carbonic anhydrase
what happens after bicarbonate is formed in RBCs
- bicarbonate is transported back into blood plasma via a chloride-bicarbonate exchanger
- bicarbonate can now act as a buffer to H+
how does bicarbonate contribute to bohr effect?
- the H+ leftover in RBCs binds to hb to produce deoxyhaemoglobin
- hence more O₂ released from haemoglobin in active tissues where H+ concentration (because of increased CO2) is higher
how are bicarbonate ions removed from plasma?
- in lungs oxygen binds to hb and promotes R state which releases H+ ions
- H+ ions are free to react with bicarbonate to produce CO₂ and H₂O
- CO₂ is exhaled
due to Haldane effect
how much CO₂ is transported as carbamino compounds?
30%
how are carbamino compounds formed?
at high concs of CO₂ it binds to amino acids and amine groups of Hb to create carbaminohaemoglobin
what is the haldane effect?
- when O₂ conc is lower (active tissues)
- O₂ is released from Hb
- deoxy Hb reacts readily with CO₂
- this increases CO₂-carrying
how is CO₂ released from carbamino compounds?
- at high concs of O₂ (lungs) Hb preferentially binds to O₂ again
- this promotes the release of CO₂