6th Grade - Rocks
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Rock
A solid mixture of minerals and other materials. Earth's crust is made of rocks.
Grains
The particles of minerals or other rocks that give a rock its texture.
Texture
The look and feel of a rock's surface, determined by the size, shape, and pattern of a rock's grains.
Igneous rock
A type of rock that forms from the freezing of molten rock at or below the surface.

Sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together.

Metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. The heat and pressure can result from collisions between continental plates.
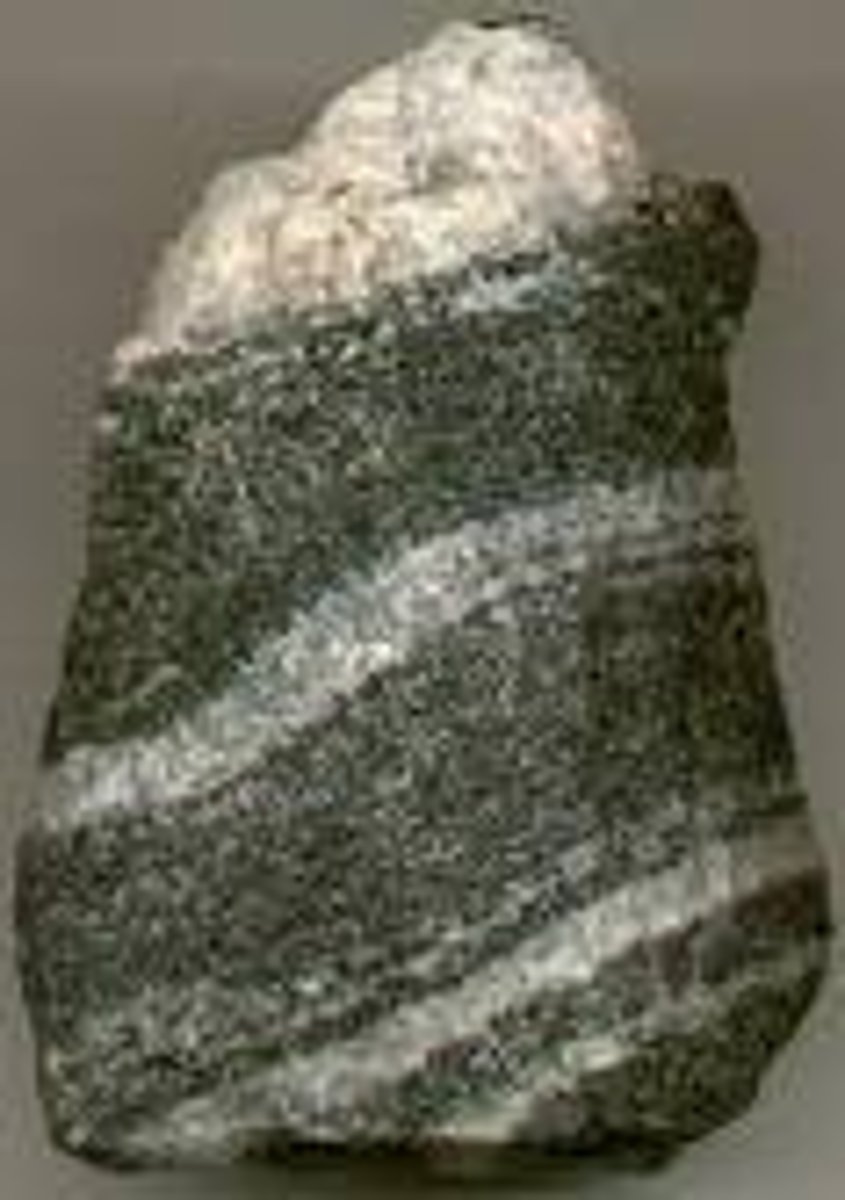

Extrusive Igneous rock
Igneous rock that forms when lava freezes on Earth's surface.
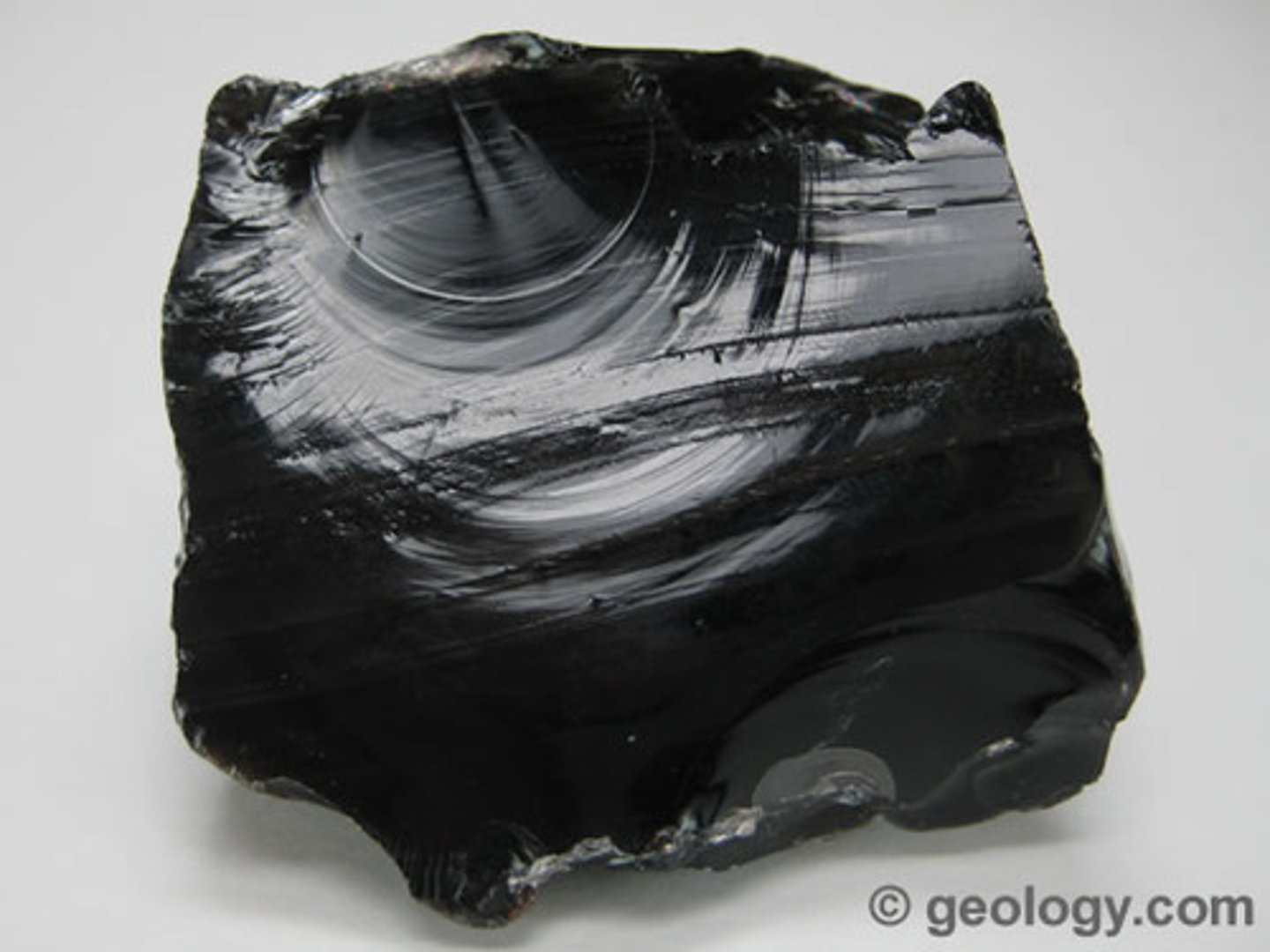

Intrusive Igneous rock
Igneous rock that forms from magma freezing beneath Earth's surface.
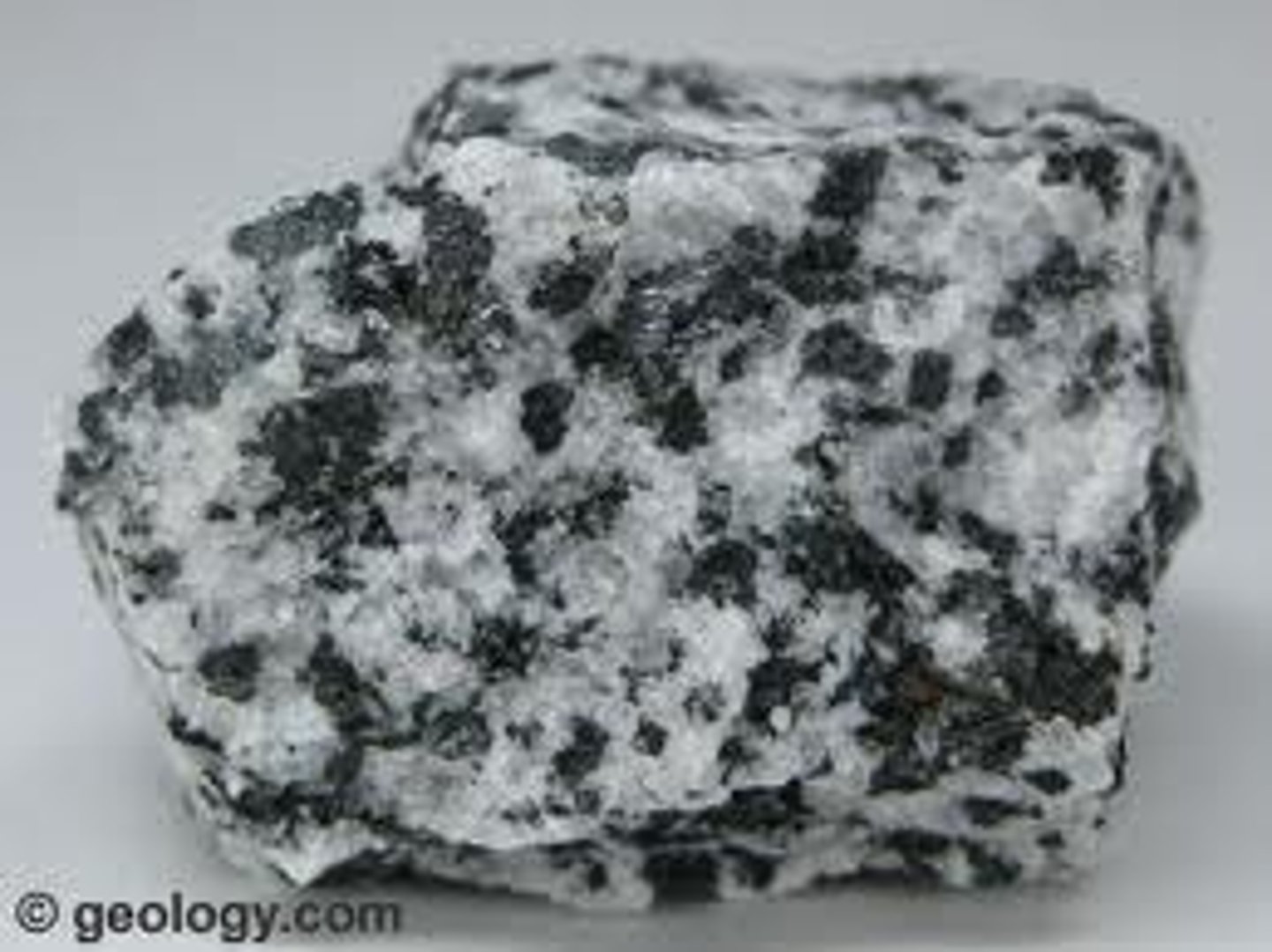

Sediment
Small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms.
Erosion
The process in which water or wind carries away fragments of rock.
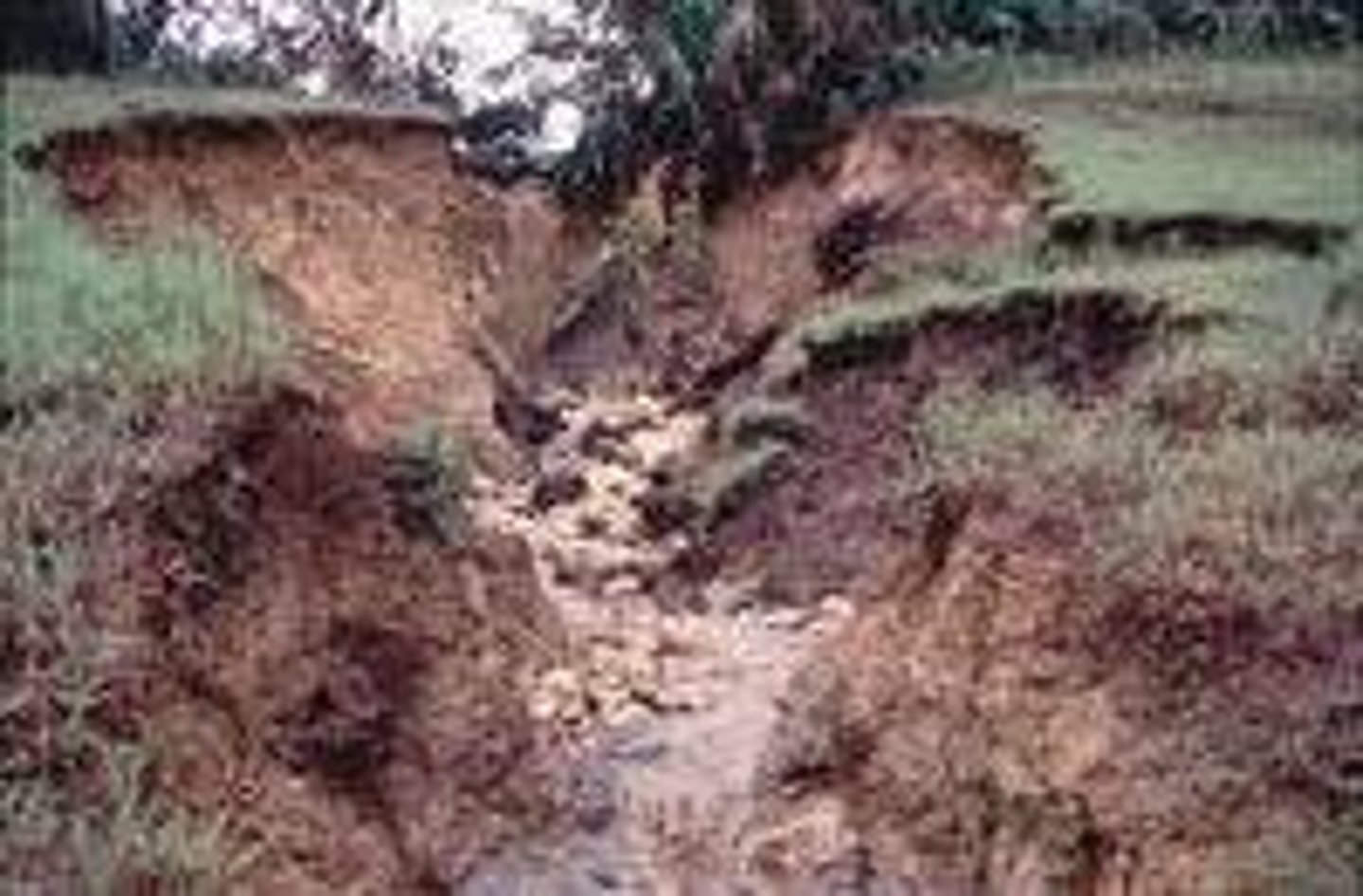

Deposition
The process by which sediment settles out of the water or wind that is carrying it.
Compaction
The process by which sediments are pressed together under their own weight.
Cementation
The process by which dissolved minerals crystallize and glue particles of sediment together into one mass.
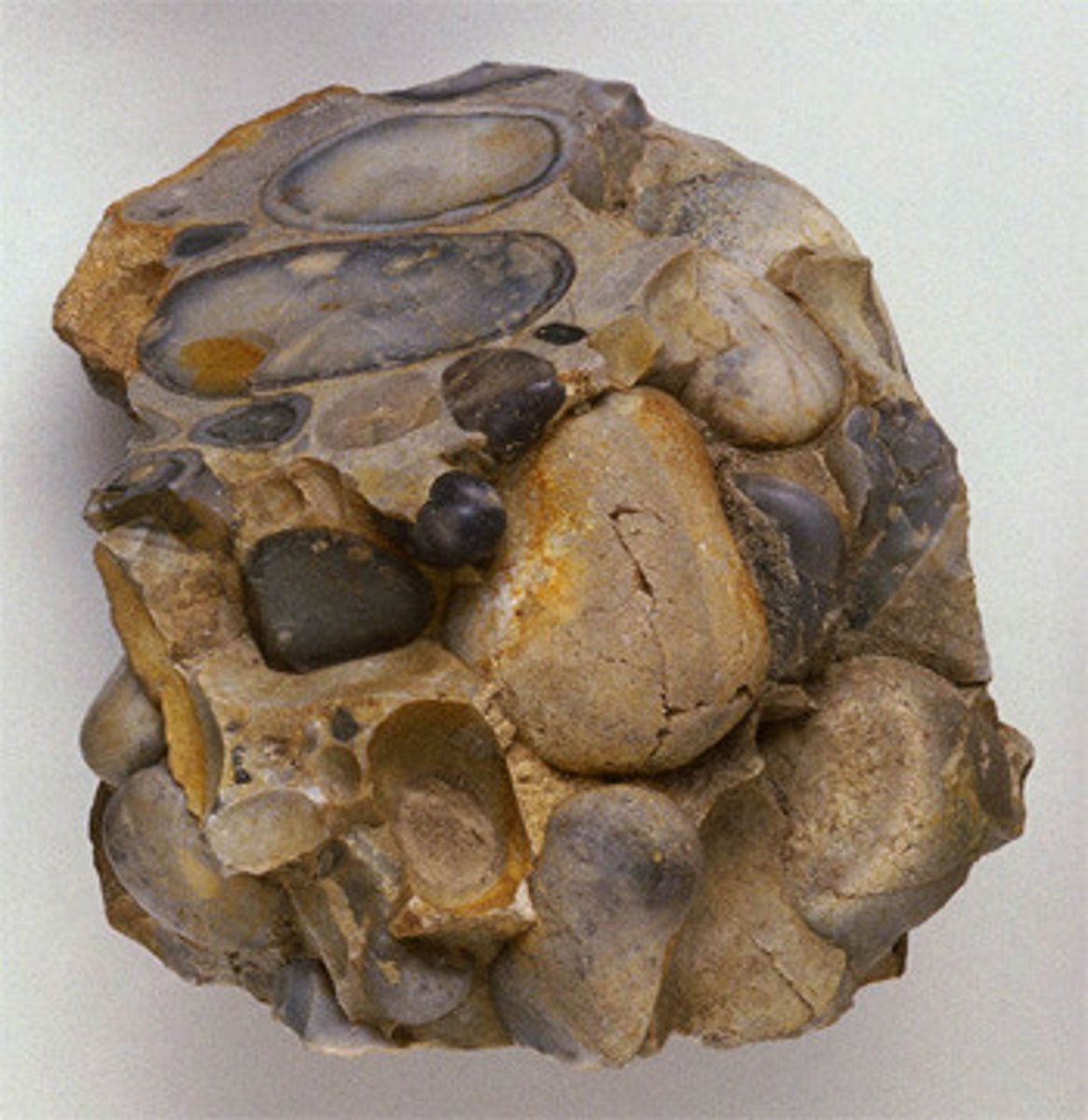
Clastic sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock that forms when rock fragments are squeezed together under pressure.

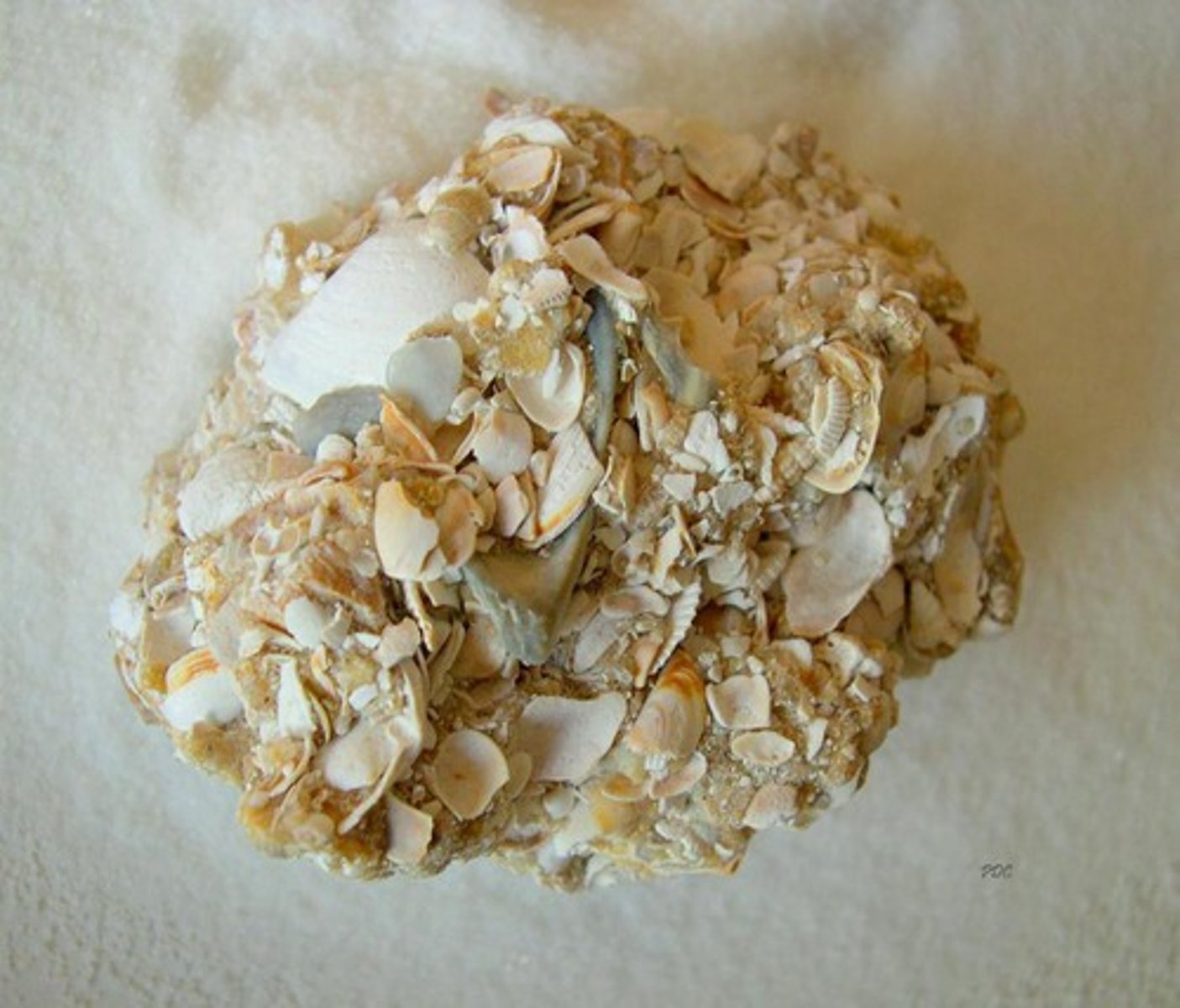
Organic sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock that forms from remains of organisms deposited in thick layers.

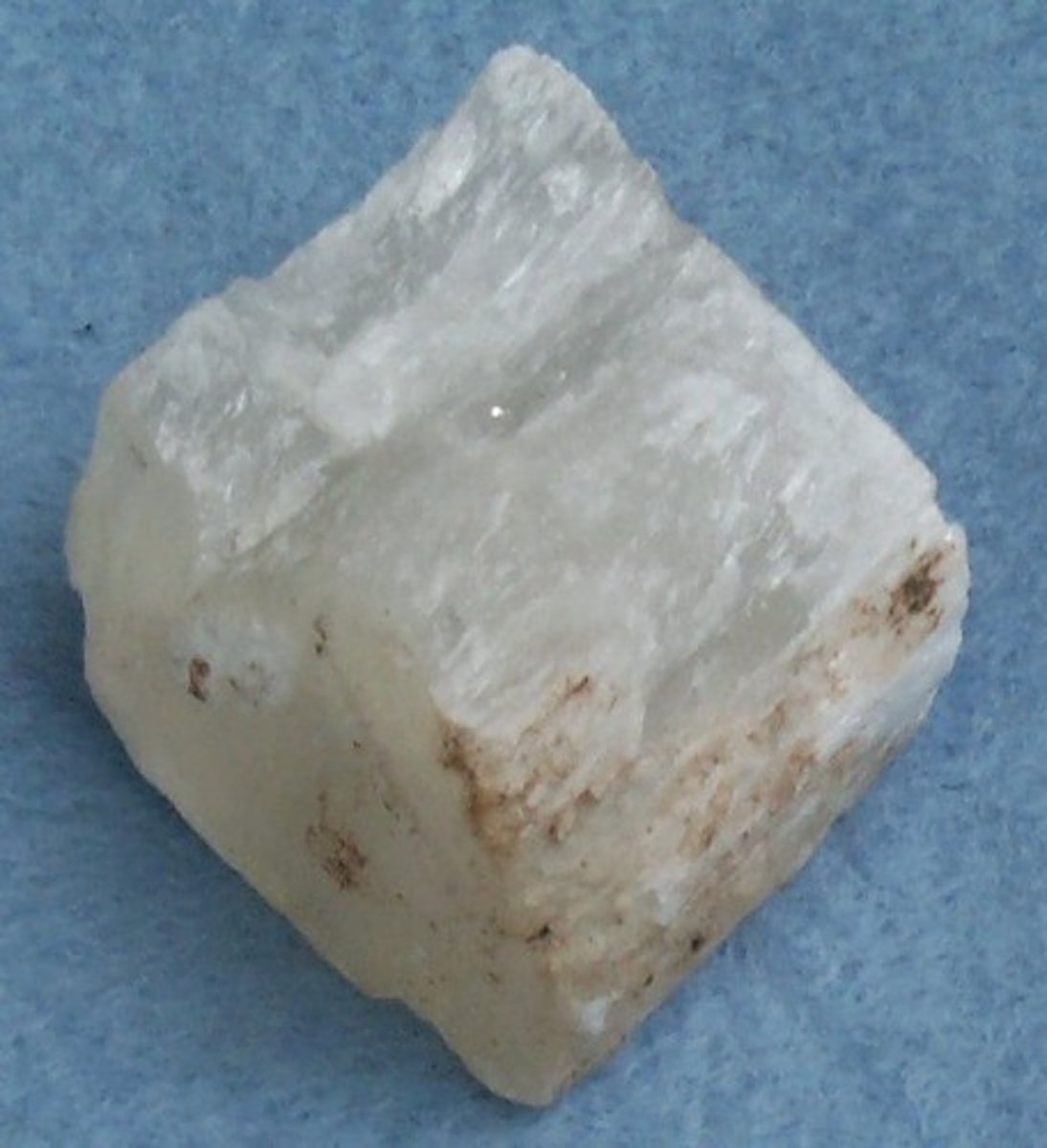
Chemical sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock that forms when minerals crystallize from a solution.

Foliated metamorphic rock
Term used to describe metamorphic rocks that have grains arranged in parallel layers or bands.

Nonfoliated metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock that doesn't have grains arranged in parallel layers or bands.

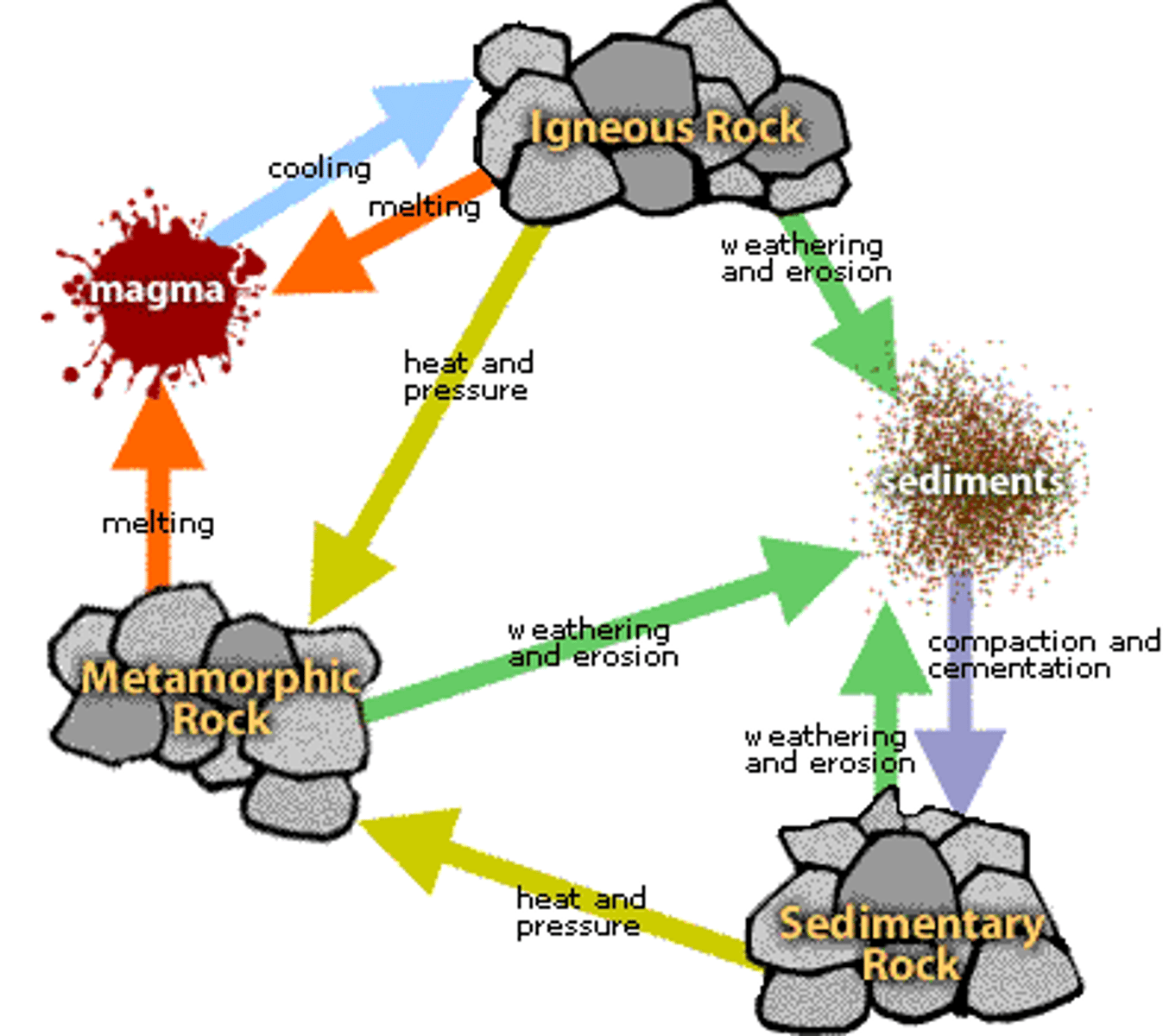
Rock cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another.
Mineral Composition
Along with texture and color, geologists use this characteristic to help classify rock.
Breccia
Sedimentary rock made up of rock fragments with sharp edges.
Marble and slate
The two most useful metamorphic rocks.
Mantle
This is where the heat that changes a rock into metamorphic rocks comes from.
Heat and pressure
Deep beneath Earth's surface these can change rock into metamorphic rock.
Conglomerate
A sedimentary rock made up of rock fragments with rounded edges.
Size, shape, and pattern
These are used to describe a rock's texture which geologists use to determine a rock's grain.
Weathering
When heat, cold, rain, snow, freezing etc. break down rock into smaller pieces of rock.