2.1 + 2.2 + 2.3
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is economic growth
an increase in the long term productive potential of a country
What is GDP
Measures the total value of all goods and services produced within an economy over a year
What is the formula for GDP per capita
GDP/population
Distinction between real and nominal GDP
Real GDP is adjusted for inflation
What are other measures of national income
gross national income - income earned domestically in addition to income earned overseas
Gross national product - value of total goods produced domestically in addition to goods produced abroad
What are PPPs
Purchasing Power Parities - compares the value of currencies by measuring how much of one currency can buy a basket of goods in comparison to another country
for example the Big Mac index
Why are PPPs beneficial
Useful to compare living standards by measuring the cost of living
What are the problems of using GDP to compare standard of living
Inaccuracy of data
inequalities
quality of goods and services
types of spending - for example GDP in the UK was a lot higher in WW2 due to defence spending
Why can the inaccuracy of data be a problem of using GDP to compare standards of living
black market
the subsistence economy
What is national happiness and how is it measured
Societal and personal wellbeing, looking beyond GDP to areas such as health, life expectancy
measuring national wellbeing report - updated quarterly and asks 4 questions about life satisfaction, anxiety, happiness and worthwhileness
What is an example of national happiness in the UK
In 2012-2016 life satisfaction, happiness and worthwhile have continued to rise whilst anxiety levels fell but began to rise slightly
this could be due to falling unemployment but concerns over global security could be causing anxiety
What is the Easterlin Paradox
Happiness and income are positively related at low incomes, but higher levels of income aren’t associated with increases in happiness
once basic needs are met an increase in consumption won’t increase long term happiness
What are the different directions of inflation
inflation - a sustained increase in the GPL
deflation - sustained fall in the GPL
disinflation - GPL is still increasing but not as significantly
How to work out index numbers
New figure/base year figure x 100
What is the CPI and how is it calculated
Consumer price index
ONS survey
Create a consumer basket of most popular goods and services with prices
Prices of these goods and services are weighed as a % of income
Weighted prices are added to give total weighted price of the basket
What are the limitations of using CPI
not completely representative
does not include the price of housing
difficult to make comparisons with historical data as it’s only been used since 1996
What is RPI
retail price index
includes housing costs such as mortgage and interest payments
takes into account that when prices rise people switch to the product which has gone up by less
excludes the top 4% of earners and low income pensioners as they aren’t average households
What are the different types of inflation and what are the diagrams
demand pull - AD increasing and AD shifting outwards
cost push - increase in costs of production causing firms to push their prices up and SRAS shifting inwards
growth of money supply - more money but not enough goods and services to supply increase in demand
What is the impact of inflation on consumers
fall in living standards (if wages don’t rise with inflation)
those in debt (either benefit or loose)
consumers saved will suffer
What is the impact of inflation/deflation on firms
If expected, deflation causes people to postpone their purchases and are likely to save - fall in demand and business confidence
What is the impact of inflation on workers
if wages don’t rise they are worse off
deflation could cause staff to loose their jobs due to lack of demand
What is the impact of inflation on governments
If the government fails to excise taxes in line with inflation then real gov revenue will fall
however if they fail to change personal income tax allowances real gov revenue will rise and taxpayers will have less money
How can negative impacts on inflation be reduced
If it’s anticipated negative impacts can be reduced through indexation
wages and taxes increase in line with inflation eg: workers can negotiate with employers for wage rises in line with the predicted CPI
What is the definition of unemployment
The number of people above working age who are not currently working but seeking a job
What are the ways of measuring unemployment
the claimant count - the number of people receiving benefits for being unemployed
ILO survey sent to 60,000 people every quarter of a year, respondents self determine whether they are unemployed
Comparisons between the claimant count and LFS
some people may not be included in ILO survey but would be included in the claimant count eg: those who fraudulently claim benefits
some people would be in the ILO survey but not the claimant count as they are eligible for benefits
What is under employment
Those who work below their skill set qualifications or who are working less hours
tends to increase during recessions because firms will reduce staff hours - can reduce AD as they have lower incomes
What is frictional unemployment
Short term - moving between jobs
What is structural unemployment
Long term decline in a demand for an industry leading to unemployment
What is seasonal unemployment
Only prominent during certain times in a year
What is cyclical unemployment
Due to a lack of demand of goods and services - caused by a recession
What is real wage inflexibility
When wages are above their market clearing level
What are the impacts on unemployment on workers
loss of income
long term unemployed have difficulties gaining jobs as they lose skills
Impact of unemployment on firms
decrease in demand for their goods
long term unemployment can lead to a loss of skills - smaller amount of people to employ
Impacts of unemployment on the government
reduced income due to a fall in tax revenue and higher welfare spending (opportunity cost)
can result in a budget deficit
What is the impact of an increase in migration
Increased jobs and lower wages
What components make up the balance of payments
current account
capital account
financial account
What components make up the current account
balance of trade - goods and services
primary income - earnings from ownership of FOP
secondary income - one way payment
What are the macro economic objectives
T - trade
I - inflation
G - growth
E - employment
R - redistribution of income
S - sustainability
B - balanced budget
What are the 4 causes of globalisation
increased individual trading
more assets owned internationally
higher migration
more technology being shared
What is the definition of aggregate demand and what are its components
The total planned expenditure of a countries goods and services at a given price level in a given time
Formula : C+I+G+(X-M)
Consumption - 60%
Investment - 15-20%
Government spending - 18-20%
Net trade - 5%
What is MPC and MPS
marginal propensity to consume - how much a consumer changes spending following a change in income
marginal propensity to save - the proportion of each additional pound of household income that is used for saving
Added together they equal 1
What are influences on consumer spending
Interest rates - impacts saving, mortgage payments and taking out loans
consumer confidence/animal spirits - job security/unemployment
wealth effects - negative and positive
How does the wealth effect impact consumer spending
If houses prices increase consumers experience a rise in equity so they might be paying less on their mortgage than the house is worth on the market, making them feel wealthier so more willing to spend + take out more loans
What is an evaluation point for the wealth effect
Ricardo Sousa found that the wealth effect is not significant in the UK because 50% of people rent, this means that as house prices increase people will pay more rent and therefore consume less
What is the distinction between gross and net investment
gross - total amount of investment
net - gross investment - capital depreciation
What are influences on investment
spare capacity
buisness expectations and confidence
interest rates - cost of borrowing/rate of return (higher opportunity cost of interest rates are high for not saving money)
access to credit - either more expensive or not possible
government regulations- corporation tax or subsidies
Influences of net trade
real income - during economic growth consumers can afford to import goods
exchange rates - WIDEC and SPICED
protectionism - tariffs, quotas… (uk may increase protectionism to decrease imports but this may cause retaliation)
Evaluation for impact of exchange rates on net exports
Depends what currency the pound depreciates against - if it’s not one of UKs major trading partners it won’t be as significant
What is the distinction between SRAS and LRAS
SRAS - short run (when atleast one factor of production if fixed)
LRAS - long run (when all factors of production are variable, and maximum output when all factors of production are fully employed)
What factors influence SRAS
cost of production
exchange rates
productivity
What is the Keynesian LRAS
Suggests the price level is fixed until all factors are fully employed, horizontal section shows the output and price when there is spare capacity in the economy (here output can be increased without impacting the price level)
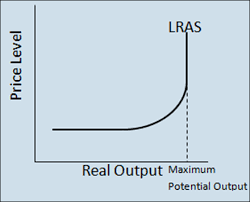
What is the classical LRAS
Suggests output is fixed at each level - in the long run all factors of production are fully employed
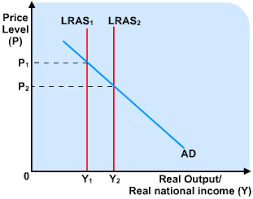
Factors influencing LRAS
Quantity or quality of factors of production
technological advancements
relative productivity
education and skills
government regulation
migration