1. STRUCTURE AND BONDING
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
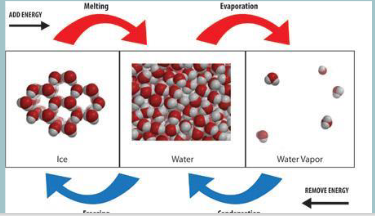
What are the three states of matter?
solid, liquid and gas
What is the particle arrangement in a solid?
fixed shape and volume
cannot be compressed
particles are close together and have no space to move
solid particles vibrate constantly
What is the particle arrangement in a liquid?
take the shape of their container
particles are close together
can move around each other
cannot be compressed
What is the particle arrangement in a gas?
particles move in all directions
particles sread out to completely fill their container
can be compressed
no flixed shape or volume
Why can gases be compressed?
because the particles are far apart
solid to liquid
melting
liquid to solid
freezing
solid to gas
sublimation
gas to solid
deposition
liquid to gas
boiling
gas to liquid
condensing
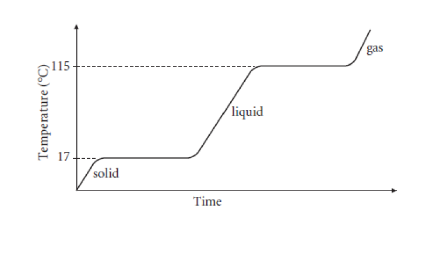
What is the melting point of ice?
0C
What is the boiling point of water?
100C
What is the freezing points of water?
0 degrees celcius
What is the condensation point of water vapour?
100 degrees celcius
What takes place at the melting point?
melting and freezing
What takes place at the boiling point?
boiling and condensing
What does the amount of energy needed to change state depend on?
the strength of the forces between the particles of the substance
What do stronger forces result in?
more energy needed to break the bonds
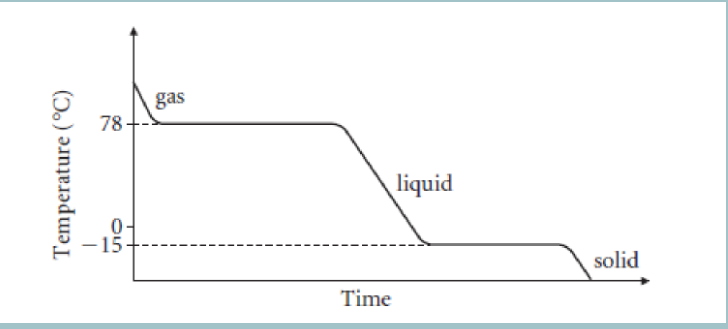
What happens to the temperature when the substance is undergoing a change of state?
it remains constant
What happens to the energy when something is melting or boiling?
all the energy from the surroundings is going towards breaking the forces between particles
What happens to the energy when something is condensing or freezing?
all the energy is transferred from the substance to the surroundings as stronger forces form between particles
What is an ion?
an atom that has lost or gained electrons to become postively or negatively charged
How is a positive ion formed?
when a metal atom loses electrons
Why does losing an electron form a positive ion?
because electrons have a negative charge, so when they get taken away, they are left with a more positive charge
How is a negative ion formed?
when a non metal atom gains electrons
Why does gaining an electron form a negative ion?
electrons have a negative charge, so an atom gaining an electron leads to a more negative charge overall
Why do atoms bond?
to gain a full outer shell of electrons
Why do atoms want to gain a full outer shell of electrons?
for stability
What is ionic bonding?
when electrons are transferred from one atom to another
What substances does ionic bonding take place with?
metal and non metals
How does ionic bonding work?
a metal atom donates an electron to a non metal atom, so that they can both have a (stable) full outer shell
What is electrostatic attraction?
the strong attraction between positive and negative ions
What is an ionic bond?
an electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
What is an ionic substance?
a substance made of oppositely charged ions held in a fixed position by strong ionic bonds, held together in a giant ionic lattice
What is an ionic latice?
a giant 3d structure formed of millions of ions in an ionic compound packed together in a regular cubic arrangement, joined by ionic bonds.
How long will an ionic latice continue to build itself?
until there are no more ions left to add
What does giant mean in regards to ionic substances?
very large structure
What is lattice?
regular repeating arrangement
How are these ions held together in their lattices?
the opposite charges of the positively and negatively charged ions holds them together

What are the properties of ionic compounds?
very high melting and boiling points
can conduting electricity but not in a solid form
brittle
soluble in water
Why do ionic compounds have very high melting and boiling points?
the giant lattice structures are held together by strong electrostatic forces which require large amounts of energy to break
What is an example of an ionic compound having a high or low melting and boiling point?
Sodium chloride has 1+ and 1- ions while magnesium oxide has 2+ and 2-
There is a larger attraction between the stronger charges of MgO so more energy is needed
Therefore magnesium oxide has an even higher melting and boiling point
What is needed for a substance to conduct electricity?
charged particles that are free to move and carry the charge
Why can’t solid ionic compounds conduct electricity?
ions in a solid state can’t move and movement is needed to conduct electricity
Why can molten/dissolved in water ionic compounds conduct electricity?
the ions are free to move and carry a charge
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
ions with the same charges are lined up together, so when a force is applied they slide against each other and snap
What substances does covalent bonding occur between?
non metals
What does covalent bonding involve?
a shared pair of electrons between atoms
Why do covalent bonds occur?
to achieve a full outer shell
How strong are covalent bonds?
very strong
How do you draw a dot and cross diagram?
When drawing Dot & Cross diagrams, we only draw the outer shell of electrons:
1. Fill up the outer shell of electrons by spacing the first four as far apart as possible, then pair the last four.
2. The electrons that are unpaired are the ones involved in the covalent bonding.
3. Re-arrange the electrons so the unpaired electrons are facing each other
4. Now join the two atoms together so that the unpaired electrons are being shared
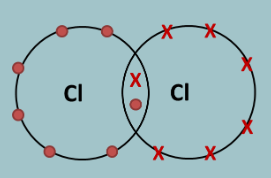
What is a covalent compound?
compounds formed from non metals consisting of molecules
How are two or more atoms held together?
strong covalent bonds
How are molecules held together?
weak intermolecular forces
What are the two possible structures for covalent compounds?
simple molecular structures
giant covalent structures
What are examples of simple covalent molecules?
water
butane
methane
carbon dioxide
oxygen
hydrogen
What are the covalent bonds between atoms like in simple covalent structures?
strong covalent bonds between atoms
What are the covalent bonds between molecules like in simple covalent structures?
weak intermolecular forces
What are the melting and boiling points like for simple covalent molecules?
low melting and boiling point
Why do simple covalent molecules have a low melting/boiling point?
not a lot of energy is needed to overcome the weak intermolecular forces
What happens to the covalent bonds between atoms during melting?
they are not broken
Can simple covalent molecules conduct electricity?
no because there are no charged particles that are free to move and carry the charge
What are giant covalent structures?
millions of atoms joined together by covalent bonding
What are the bonds like in giant covalent structures?
very strong
What are the melting and boiling point like in giant covalent structures?
high
What is an allotrope?
structures that have the same chemical properties but different physical properties due to differences in structure and bonding
What are allotropes of carbon?
diamond and graphite
What does carbon form to achieve a full outer shell in diamond?
four covalent bonds
What is each carbon bonded to in diamond?
four other carbons, forming a giant covalent structure
What are some key properties of diamond?
hard and strng
What does carbon form in graphite?
three covalent bonds
What happens when covalent bonds are formed with graphite?
leaves on delocalised electron
Why can graphite conduct electricity?
delocalised electrons can move between the layers allowing it to conduct electricity
How does graphite arrange itself?
layers
What are the properties of graphite?
soft and slippery
What are the forces between ions called?
electrostatic forces
What are the forces between atoms called?
covalent bonds
What are the forces between molecules?
intermolecular forces
What type of structures are graphenes, fullerenes and nanotubes?
giant covalent structures
What is graphene?
single sheet of hexagonal rings of carbon atoms
How thick is grphene?
only one atom thick
Wht is graphene a single layer of?
graphite
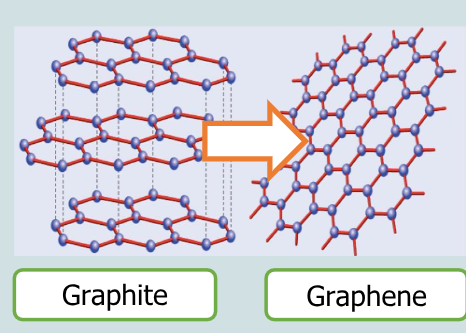
What dimenson is graphene?
the worlds first 2d material
What are the properties of graphene?
• excellent thermal and electrical conductor
• very low density (lightweight)
• flexible
• transparent
• most reactive form of carbon
• very strong for its mass (over 200x stronger than steel)
What are the potential uses of graphene
quicker and more powerful computer chips, electric circuits and solar cells
flexible and durable electronic display screens
What is an allotrope?
a new form of an element
When was Buckminister Fullerene discovered?
1985
Have other fullerenes been discovered since?
Yes
What are the names of other fullerenes that have been made?
C70, C76 and C84
What are fullerenes?
molecules of carbon atoms joined together to make hollow cages of different shapes, usually hexagonal rings of carbons atoms but can be pentagonal or heptgonal
What are Buckminister Fullerenes made of?
molecules of C60
What bonds are between each carbon atom in a Buckminister Fullerene?
strong covalent bonds
How is each fullerene molecule attracter to each other?
weak intermolecular forces
How big is the fullerene molecule?
1nm in diameter
What are the uses of fullerene?
cages to trap smaller molecules inside them.
carrying drug molecules around the body
lubricants because they are spherical with weak intermolecular forces so can roll over each other
What are nanotubes?
hollow, culindrical tubws of carbon atoms
What are the properties of nanotubes?
very strong/high tensile strength
very good electrical and thermal conductors
What are the uses of nanotubes?
can be used to reinforce materials like tennis rackents due to their strength
can be used as catalysts because they have a large surface area to volume ratio