ELA lit terms
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Genre
category or type of literature
protagonist
main character/hero
antagonist
“bad guy”
setting
time and place of the story
theme
overall message of the story/life lesson - universal and can apply to everyone
thematic statement
full sentence
thematic concept
1-2 words
5 ingredients -short story/novel
setting
characters
plot
POV
theme
plot
the storyline/sequence of events in a story
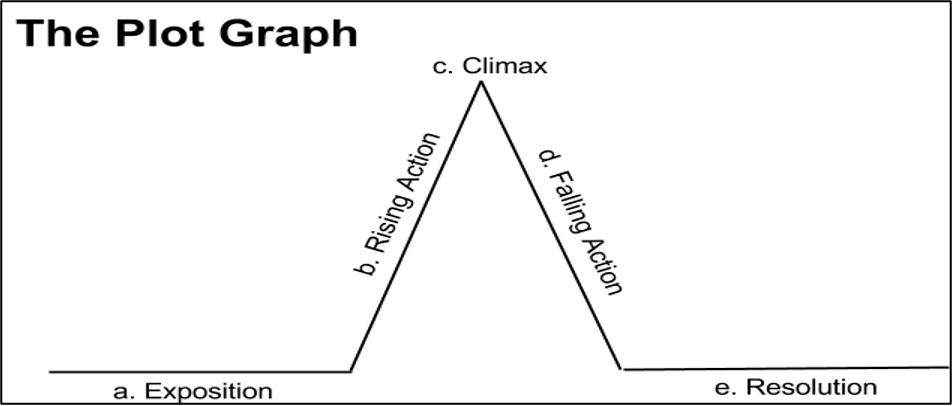
narrator
speaker telling the story
symbol
a person, place, or thing (noun) that represents idea/feeling - EX: statue of liberty is freedom
dramatic irony
when reader knows something important that character does not
situtational irony
a surprise twist/opposite of what you expect to happen
imagery
using 5 senses to describe something
conflict
intense problem faced by character/struggle between 2 opposing forces

characterization
how author brings character to life
A= appearance
T/F= thoughts/feelings
P= personality
O= others treatment of character
S/A= speech/actions
dialogue
convo between characters
dialect
imitating how real people talk (spelled like sound)
mood
atmosphere/ feeling created by literary elements (can change during story)
flashback
when narrator goes back in time to earlier in story
foreshadowing
hints about what happens later in story
diction
vocab/word choice
tone
authors attitude about topic (angry, hopeful, sarcastic…)
denotation
dictionary definition
connotation
emotional feeling the word carries
suspense
tension created by intense conflict - keeps reader engaged
static character
stays same throughout FICTION text
dynamic character
changes drastically due to conflicts and experiences; evolves
alliteration
repetition of sounds at beginning of word - EX: the Lazy Lion Licked his paw/ Can we adopt that Cute Kitten
onomatopeia
sound words
repetition
when word/phrase repeat 2 or more times in a line
rhyme
when words end in the same sound
stanza
section of a poem
synonym
word with similar meaning
antonym
word with opposite meaning
transition words
words that connect ideas within/between paragraphs
NON fiction text patters
time/sequence
cause & effect
problem & solution
compare/contrast
description
mirror moment
when reader see part of identity/experience - helps connect with reader
window moment
when they learna] abt character whose culture/identity is different form theirs
claim
main point the author will prove, topic sentence, TAG
citing vs paraphrasing
taking a quote vs rewording text
source
where the info come from
plagiarism
copying someone else’s work and not citing
anecdote
mini story in 1st or 3rd person
types of evidence
facts, examples, anecdote, quotes, surveys, data, laws, policies…
persuasive techniques
rhetorical question, loaded language, & call to action
loaded language
strong diction with p/n connotation - helps convey tone
counterclaim/argument
claim/argument presented by opposing side
rebuttal
response to counterclaim used to argue opposing side
1st person
uses “I” and “we” - narrarator is in the story
2nd person
rarely used but normally in cookbooks or manuals “you”
3rd objective
narrator is an outside observer and only reports what they can see/hear - sportscaster etc
3rd limited
narrator is limited to one single persons thoughts or feeling
3rd omniscient
narrator is all knowing and can include every characters thoughts & feelings - provides most info
simile
comparison using like/as
metaphor
comparison without like/as
personification
giving inanimate objects human qualities
idiom/figure of speech
a not literal saying
hyperbole
an extreme exaggeration for dramatic effect
oxymoron
2 opposite words are put together
logos
appeals to readers logic
ethos
credibility or expertise of the argument
pathos
emotional and ethics