Comparative Anatomy of Digestion and Circulation in Animals
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Phylum Chordata
Animal phylum including vertebrates with a notochord.
Subphylum Vertebrata
Subgroup of Chordata with a backbone.
Class Mammalia
Warm-blooded vertebrates with hair and mammary glands.
Internal Fertilization
Sperm fertilizes egg inside female body.
Endothermic
Ability to maintain body temperature internally.
Mammary Glands
Glands that produce milk for young.
Differentiation of Teeth
Specialized teeth types for various diets.
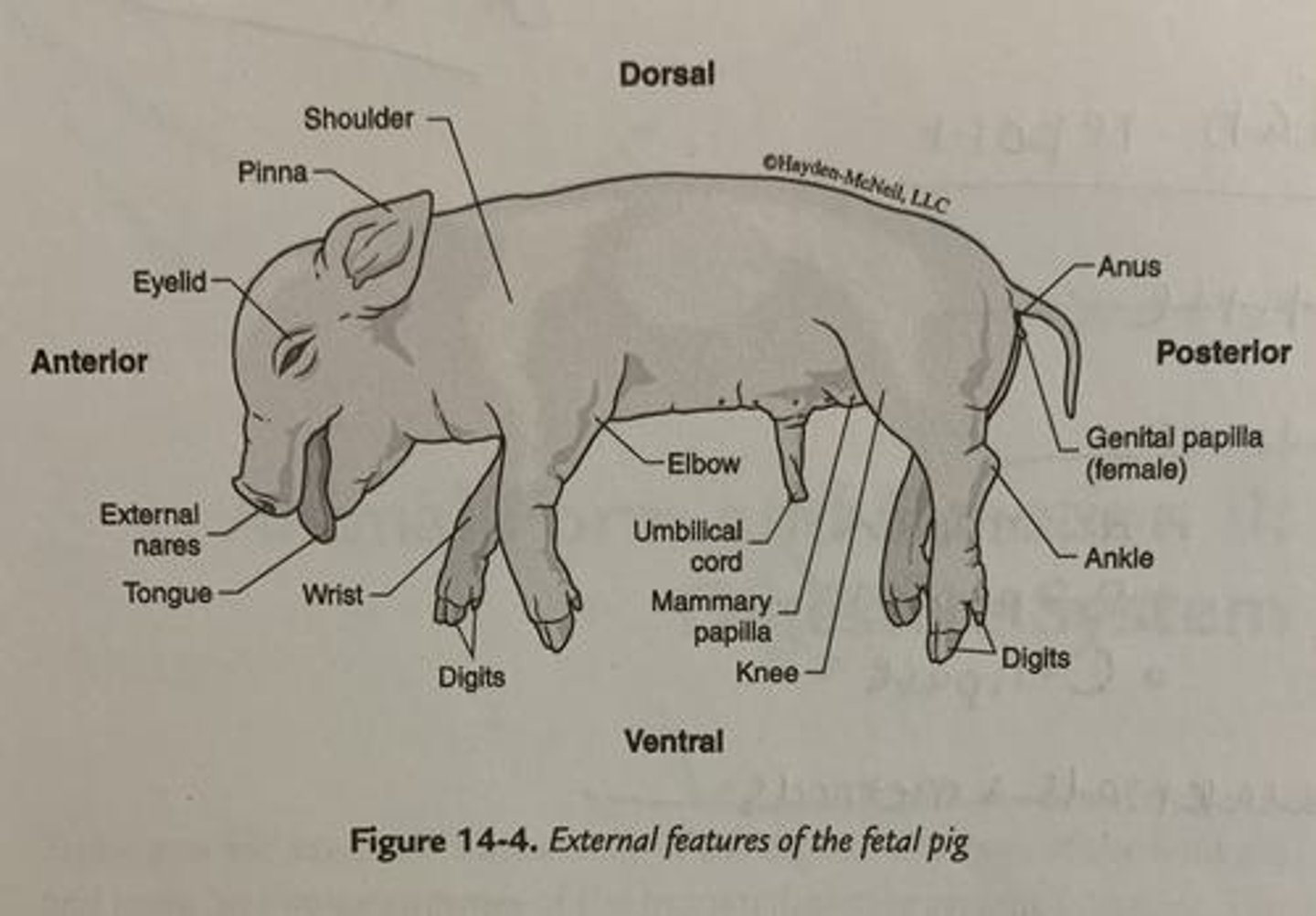
Fetal Pig
Common model organism for mammalian anatomy.
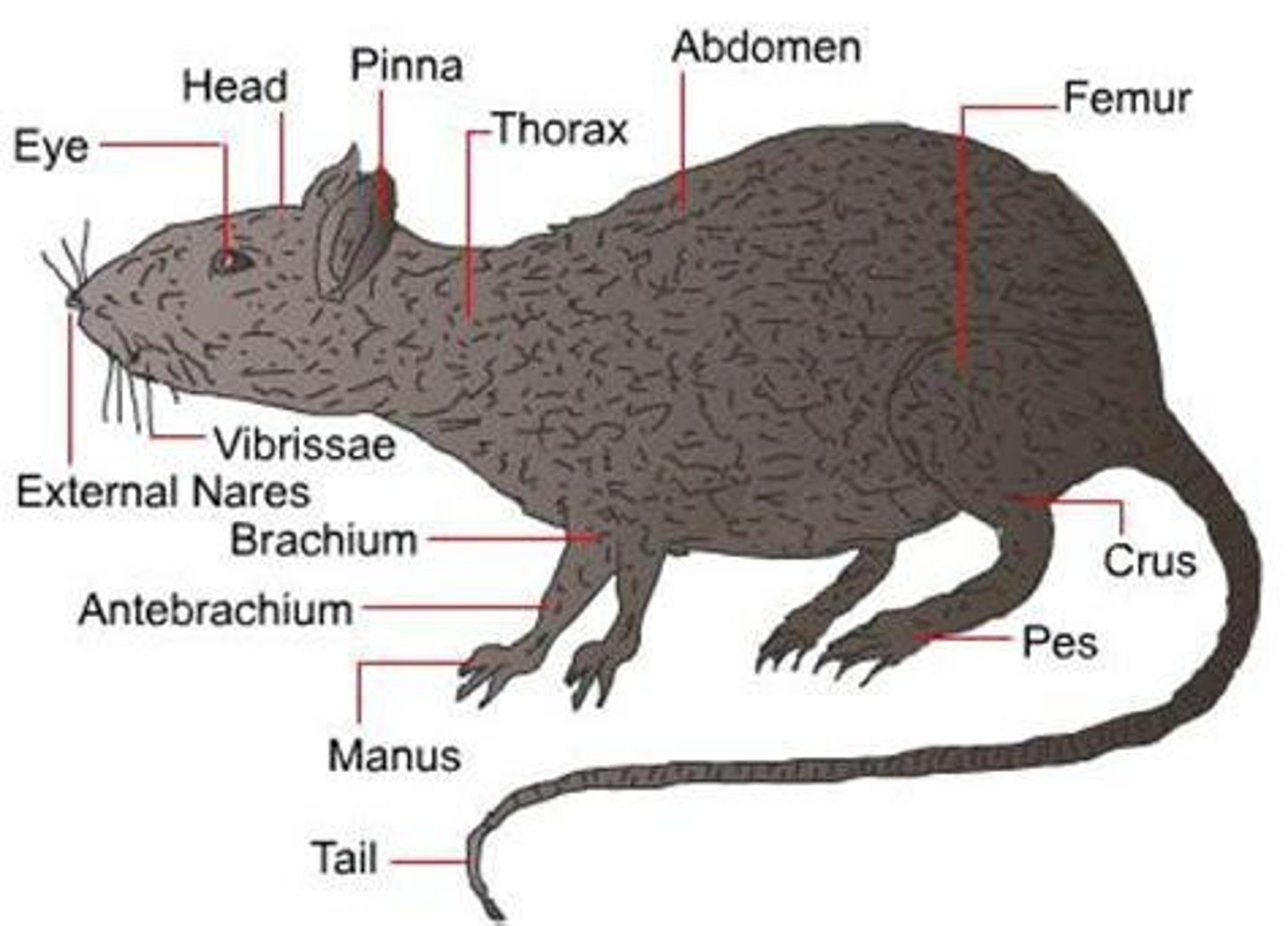
Rat
Another model organism for studying mammals.
Heterotrophic
Organisms that consume food for energy.
Extracellular Digestion
Digestion occurs outside cells in a digestive system.
Gastrovascular Cavity
Digestive cavity with one opening for food and waste.
Complete Digestive Tract
Digestive system with separate mouth and anus.
Crop
Storage organ in some animals for food.
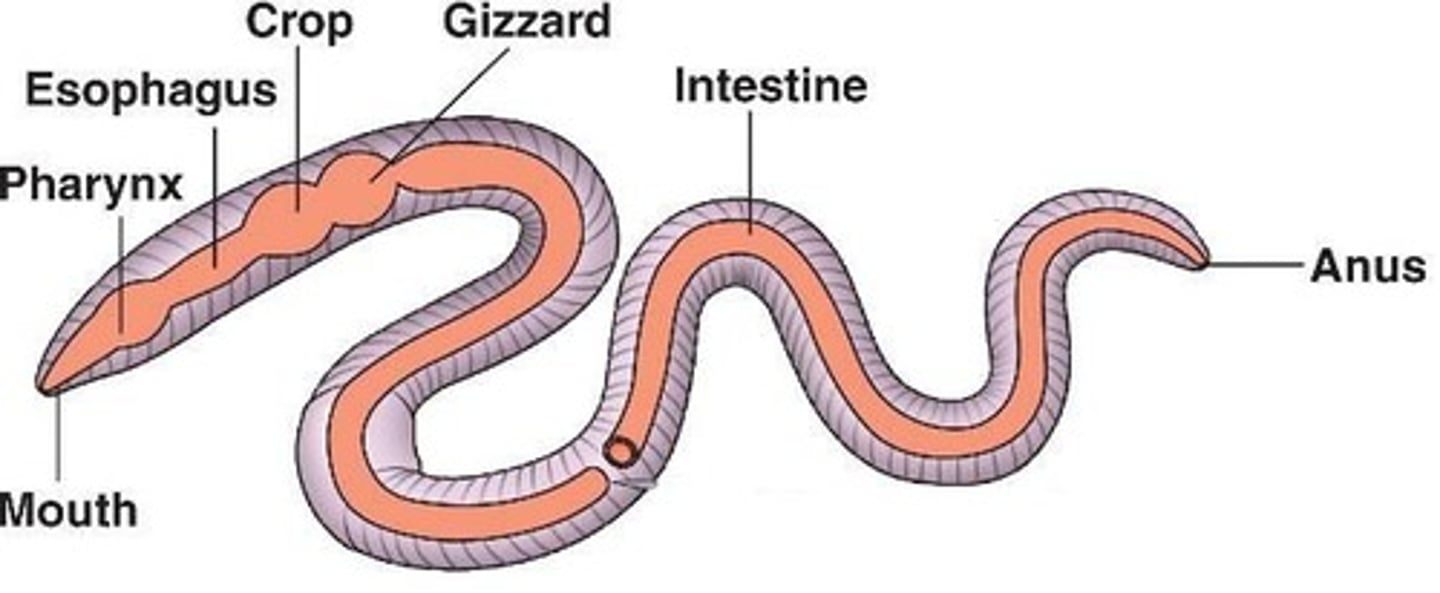
Gizzard
Muscular organ for grinding food mechanically.
Diverticulum
Pouches leading to accessory digestive glands.
Spiral Valve
Structure increasing surface area in digestive tract.
Extendable Tongue
Adaptation in amphibians for capturing prey.
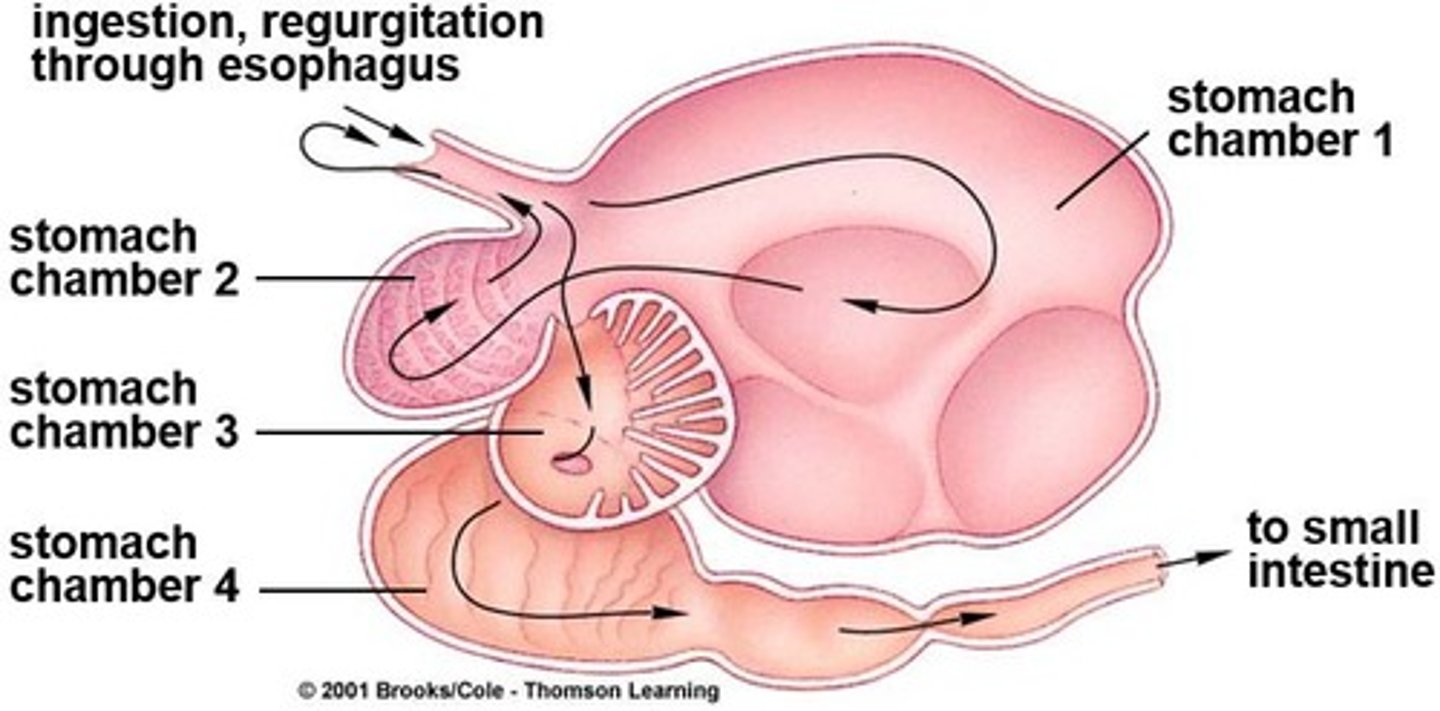
Ruminant Stomach
Specialized stomach for digesting cellulose in herbivores.
Osmoregulation
Regulation of water and solute balance in organisms.
Osmoconformers
Organisms whose internal concentration matches environment.
Osmoregulators
Organisms that actively control internal solute concentrations.
Nitrogenous Wastes
Waste products containing nitrogen from metabolism.
Ammonia
Highly toxic nitrogen waste, requires large water loss.
Urea
Less toxic nitrogen waste, requires moderate water loss.
Uric Acid
Least toxic nitrogen waste, minimal water loss.
Protonephridia
Excretory system in flatworms with flame cells.
Metanephridia
Excretory system in annelids with segmented fluid collection.
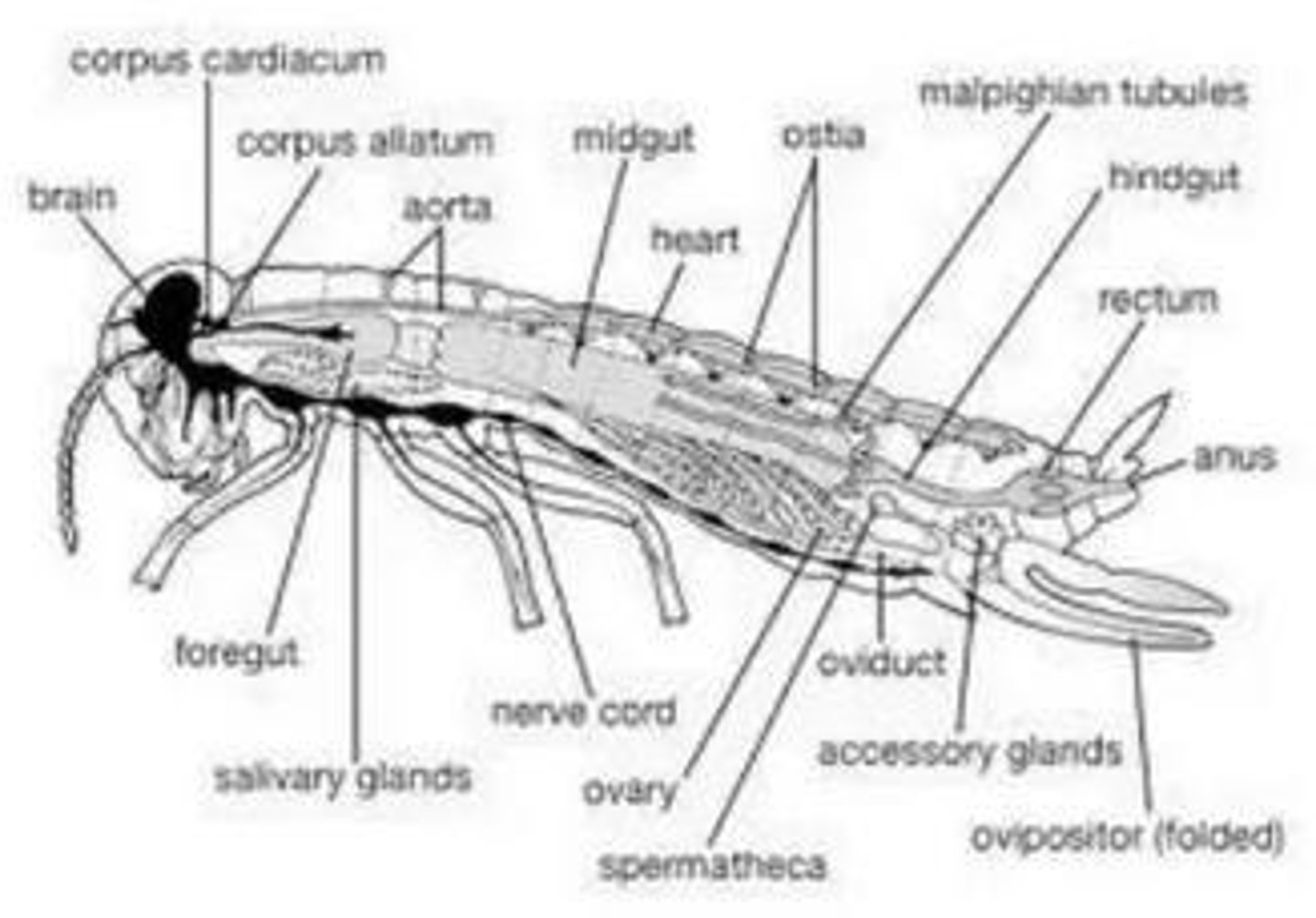
Malpighian Tubules
Excretory system in insects collecting fluid from hemolymph.
Nephrons
Functional unit of kidneys, filters blood.
Systole
Heart contraction phase, maximum blood pressure.
Diastole
Heart relaxation phase, minimum blood pressure.
Sphygmomanometer
Device to measure blood pressure in mmHg.
Sphygmomanometer
Device used to measure blood pressure.
Systolic Pressure
First knocking sound during blood pressure measurement.
Diastolic Pressure
Pressure when knocking sound disappears.
Blood Plasma
Fluid component of blood containing proteins and nutrients.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Leukocytes
White blood cells involved in immune response.
Platelets
Cell fragments that initiate blood clotting.
Respiration
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide for ATP.
Cutaneous Gas Exchange
Gas exchange through skin in some animals.
Trachea
Air passage in terrestrial arthropods.
Spiracle
Opening for air entry in insects.
Gills
Respiratory structures in aquatic animals.
Operculum
Bony flap protecting gills in Osteichthyes.
Countercurrent Exchange
Maximizes oxygen exchange between water and blood.
Lungs
Respiratory organs in terrestrial chordates.
Diaphragm
Muscle that aids in lung ventilation.
Alveoli
Tiny sacs increasing lung surface area for gas exchange.
Tidal Breathing
Regular inhalation and exhalation of air.
Tidal Volume (TV)
Air volume inhaled/exhaled during normal breathing.
Vital Capacity (VC)
Maximum air volume inhaled/exhaled in normal breathing.
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
Total air volume after maximum inhalation.