JEANS EXAM 1: TEINS AND NUC ACIDS
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
a nucleotide is the blank. it is composed of three parts:
basic building blocks for nucleic acids, repped as a repeating struct unit of dna and rna. phosphate group, 5 carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base
what is the dna backbone made of
sugar and phos group
purine vs pyrimidines : name which nitro base is under which one
cytosine, thymine, uracil= pyrimidine
guanine and adenine= purine
what is the struct difference tween pyrimidine and purines
purines = a 6 ring and 5 ring bonded together
pyrimidine= just one 6 sided ring
deoxyribose vs ribose
deoxyribose= no OH at the carbon 2 and is seen w/ dna
ribose= carbon 2 has hydroxyl (basically will have two oh’s at the base)
thymine and adenine have blank ammt of H bonds while guanine and cytosine have blank ammt of H bonds
t/a = 2
g/c = 3
the phosphodiester bond is made of blank and blank. it is (covalent or ionic). what is being connected?
phos and sugar
covalent
phos connects to the 5c of a NT to the other NT’s 3C
what bond allows for 5 to 3 directionality? what does this mean
phosphodiester. 5 prime to 3 prime means
which functional group attached to the 3 carbon is important in allowing NTs to form covalent links w eachother
OH
in a single NT, the base is attached to which carbon?
which carbon does phosphate group attachment
carbon 1
carbon 5 for phosphates
5 to 3 directionalitty happens cuz
in a strand all sugar molc are oriented in the same direction and orientation. this is just the chem direction of the strand based on the numbering of carbon atoms. the 5 end is the side with the phos group and the 3 end will have a OH group.
How many bases are there within each turn of the DNA molecule?
10 nulceos in each strand per turn
distance tween two consecutive NTs
0.34 nm
length of a complete turn
1 complete turn is 3.4 nm
wut is minor groove and major groove
grooves = to describe the indentations where atoms of the bases are in contact with the water in the surrounding cellular fluid.
The DNA helix has two grooves winding around its outer surface.
a narrow minor groove and a wider major groove.
2. The DNA molecule has directionality; its strands are blank and blank. What does that mean?
The directionality of the DNA molecule is 5’ 3’. Explain why.
directonality meaning that this is the end to end chem orientation. the 5 end and 3 end, 5 end has the phosphate group attached to 5th carbon of the sugar. the 3 prime end has a hydroxyl group on 3rd carbon. this happens cuz a nucleoT can only build on the 3 prime end
anti-parallel and complementary. antipara meaning the two strands run in opp directions. complementary means a BP will always be found
what did Paulin do for DNA
proposed regions of teins can fold into a secondary struct by using large models and linking them tg with simple ball and stick units
what did Watson and crick
used a ball and stick method and the final hurdle was conquered as they both discovered how the nucleotides fit together like a puzzle piece aka how the base pairs are supposed to match up. from there it showed two strands could be side by side - becoming double stranded
chargaffi importance
found out that the biochem comp of DNA means that amounts of A and T are equal. ammounts of G and C are equal too.
wilkins / Franklin mportance
x ray diffraction. this means exposing DNA to x rays- a diffraction pattern can help show the molc struct of the DNA. and it DID! the pic shows a pattern consistent with a two stranded helical struct
this letter DNA is going to be left handed
Z DNA
this letter DNA is right handed
B DNA
which DNA is found more in living things: b or z
B
how many BP per 360 turn in z DNA
12
what can you notice to differ tween z and b DNA? also use Google slides and hit yes if right
b DNA is right handed and has a major and minor groove
z DNA has only one big groove
What are amino acids?
molc that combine to form teins. they r building blocks for polypeptides (short chains of protein)
draw the structure of an amino acid. what are the parts of it and label it. type yes if right
yes
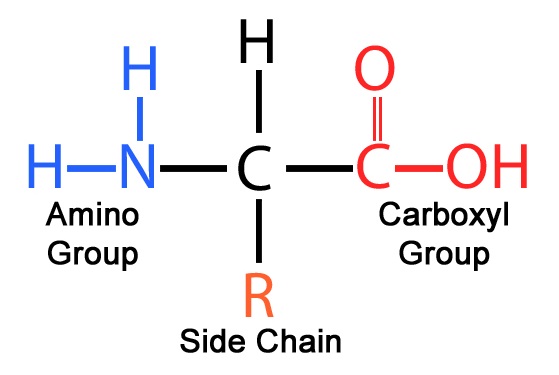
What part of the amino acid molecule is different among all?
the r group aka side chain
traits of a polar amino acid
traits of a charged
where either be found in a protein?
polar will show a O2 (except for cysteine) and FOUND ON SURFACE
charged shows pos or neg ALSO SEEN ON CELL SURFACE
polar, charged and nonpolar
found where
hydrophillic or phobic
any other traits
nonpolar= interior, phobic and composed of cs and hs
polar= either inside cell or on cell surface. phillic. will see Os
charged= will see pos or neg charge. surface only location. phillic
What is a peptide bond?
covalent bond that links AA tg to form polypeps and then teins
how is peptide bond formed
dehydration synthesis where two H’s of amino group of AA 1 and then one O of the carboxyl group of AA 2 get taken away (aka h2o is removed). whats left is a connection of carboxyl group to the amino group
What is a peptide backbone?
the cahin of atoms the runs the length of the tein. will only include the amino group the central C, and the carboxyl group
The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of the amino acids. How does the primary structure of a protein affect the secondary and tertiary structures?
this is cuz the primary struct is the blueprint meaning that the folding will be dictated by the amino acid seq of the polypeptide in primary form. esp with chemical properties assc to each side chain, something is bound to happen
Name two types of secondary structures in proteins. plus describe forces that maintain these structs
The α-helix is a right-handed helical coil, while the β-sheet consists of extended polypeptide chains arranged in a sheet-like structure. Both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds formed between different parts of the polypeptide backbone
Describe the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins
tert= struct determined by hydrophobia, ionic interactions, H bonds and disulfide bridges that form among atoms that make up the side chain of AA
quat= teins made up of two or more polypeps
which struct will be the final conformation of proteins that are composed of a single peptide
secondary
primary
quat
tert
none
tert. eg is myoglobin. this is cuz its a single peptide. no need to go into quat mode
myoglobin is part of what struct while hemoglobin is part of
tertiary
quat
t or f: having more t/a pairs in a dna strand would make it harder for dna molc to seperature and denature (thru breaking h bonds)
false. actually having more g c bonds make it harder. this is cuz g and c have 3 h bonds.
if theres 64 percent g and c content, what are the percentages of each - a t g and c
first use ur given. remember g and c will be the same number. just divide by 2.
g is 32 cent and so is c
now think about it. if theres a whole unit contained with 100 percent of g c t and a- with 64 percent being both g/c- what can you do to get the other percent of t and a? just do 100-64 (since t and a will have the same answer)
100-64=36 cent of t and a.
36/2= 18. each will have 18 cent
length of pitch means
height of full turn
ds has 560 nts. how many complete turns would be found in this double helix
if know that there are 10 bps per every turn. so you're given the total ammts of NT. but you know that there are 10 bps every turn. so figure out how many of the NTs pair together. figure out by doing 560/2. this equals to
theres 560 nts all together. i need to discover how many would be on one strand.
560/2=280. so there's 280 BP. each group of 10 contributes to a turn. so how many 10 groups need to happen/ do 280/10= 28 turns
A DNA duplex is 200 nm long. How many nucleotides does it have?
do 200 nm / 0.34 nm = 588.2 BP. just always divide it so it is able to cancel out. then do 588.2 times 2 so you can figure out how many NTs exist in all.
the final answer is 1176
when given NT, needingg to find how many turns there are use
10 nt per every turn
when given length of DNA duplex, and must find how many NTs there are
you should use
the 0.34 = distance tween bps .
Chromosome X is composed of 153 million bp while chromosome Y is composed of 50 million bp.
If the DNA of these two chromosomes is extended so that only the helical structure remains, determine their length in nm
just do bp number times 0.34 to find the length of chrom x and of chrom y.
x will be 52,020,000 nm
y wil be 17 mill
this gene has 2.4 mill base pairs. what is length and what is turns
do 2.4 times 0.34 = 816,000
to find turns just do 2.4 BP/ 10 = 240,000 turns
if 46 chroms compose the genome of a diploid human cell become extended and lined up, it would measure to 2 meters. so how many BP would there be
1- turn 2m to nm. this would be 2e9 nm
2- now just do 2e9 divided by 0.34 = 5.9e9.