Biology - C6
1/218
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nervous/endocrine systems, negative feedback/homeostasis and thermoregulation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Homeostasis
The maintenance of the bodies internal environment despite changes in the external environment or the bodies rate of activity.
Homeostasis
Concentration of CO2 and ions, pH of blood, temperature, blood glucose and water controlled by…
Negative feedback
How is homeostasis controlled?
Negative feedback loop
A deviation from normal creates a set of responses that bring the system back to normal / a change which reverses the effect of a particular stimulus to maintain stability.
Effectors
Organs, glands, muscle or any other structure that responds to bring the variable back to the set point - told by control centre to counteract the deviation/correct imbalance.
Receptors/sensors
Respond to light, heat, pain or other external or internal stimulus - detects change /imbalance and sends message to control centre.
Control centre
Compares factor (change/imbalance) against the set point in homeostasis.
Stimulus
A change in the internal or external environment - detected by receptor/sensor.
Electromagnetic receptors
Photoreceptors (light) and thermoreceptors (heat) are both … - neural receptors.
mechanoreceptor
Detects sound, touch, pressure, balance - neural receptor.
chemoreceptors
Detected from food/environment - neural receptor.
Nocireceptors
Detects pain - neural receptor.
Central nervous system
Made up of brain and spinal cord which contains ‘interneurons’ which are relay neurons.
Skull and vertebrae
What protects the central nervous system.
Somatic nervous system
Part of the PNS - voluntary movements and sensory perceptions - what we experience - system
Peripheral nervous system
Part of the nervous system that lies outside the brain and spinal cord and communicates between the brain and body - somatic or autonomic
Autonomic nervous system
PNS: parasympathetic (rest and digestion), sympathetic (fight or flight) and enteric (gastrointestinal) - what is the system
Sensory/afferent neurons
Neurons that carry information from the receptors to the central nervous system.
Motor/afferent neurons
Neurons that carry information from the central nervous system to effectors - muscles/organs/glands.
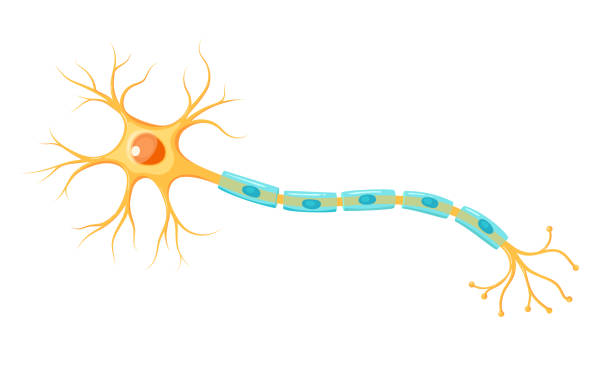
Neuron
Electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body - electrical or chemical components - connects to effector organs (+ synapse stuff) - nerve cell
Sensory neurons
After a stimulus which is used first, motor or sensory neurons?
Motor neurons
Which neuron (sensory or motor) is used by the central nervous system to control effectors and cause response to a stimulus.
Interneurons
CNS: a neuron which transmits impulses between other neurons.
Dendrites
The ‘branches’ of the neuron that collect information from other cells and sends it into the cell body.
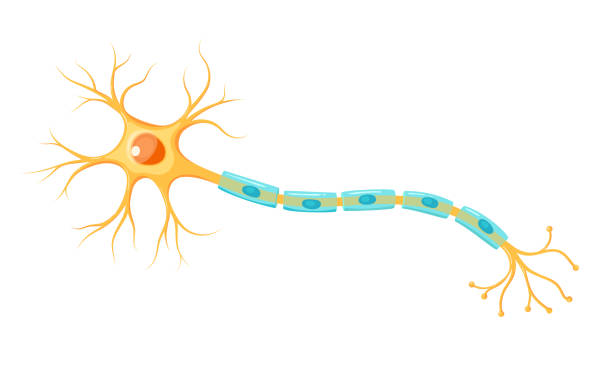
Cell body/soma
Keeps the cell alive and contains nucleus and organelles - main section (circle)
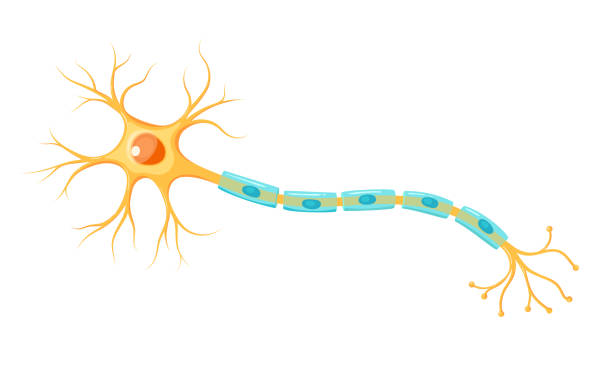
Axon
Part that transmits information from cell body via action potential to the axon terminal - long section
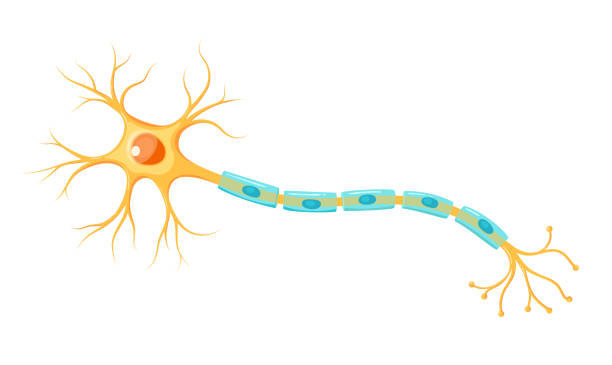
Schwann cells
Produce myelin sheath
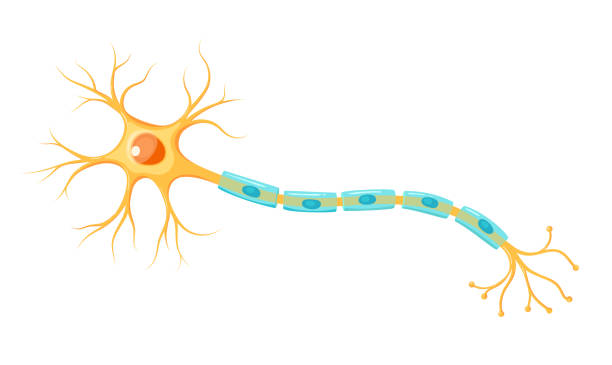
Myelin sheath
Fatty tissue surrounding axon fibre, acts as an insulator that allows faster transmission of electrical impulses - goes faster as it stops the diffusion of action potential out of the axon
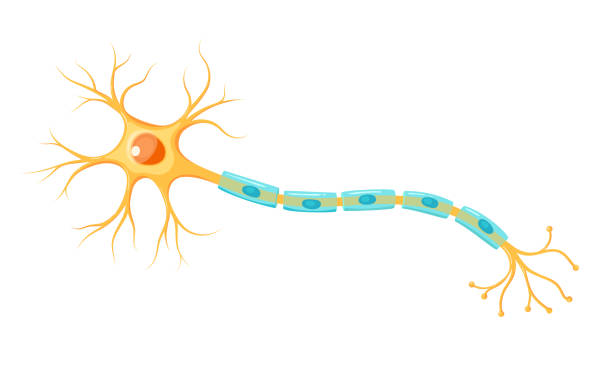
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath, contain voltage gated Na+ and K+ channels - rejuvenates action potential between jumps (saltatory conduction)
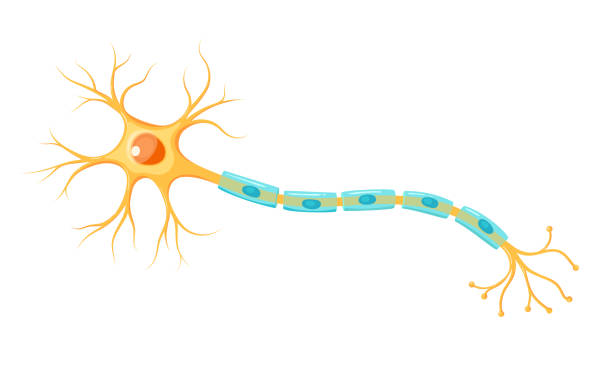
Axon terminal
End of axon, leads to synapses and contains neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical that carries messages/signals from one neuron to the next cell
Action potential
A rapid sequence of changes in the potential difference across a membrane to transmit information from one part of the body to another.
-70mV
The resting potential of a neuron (volts)
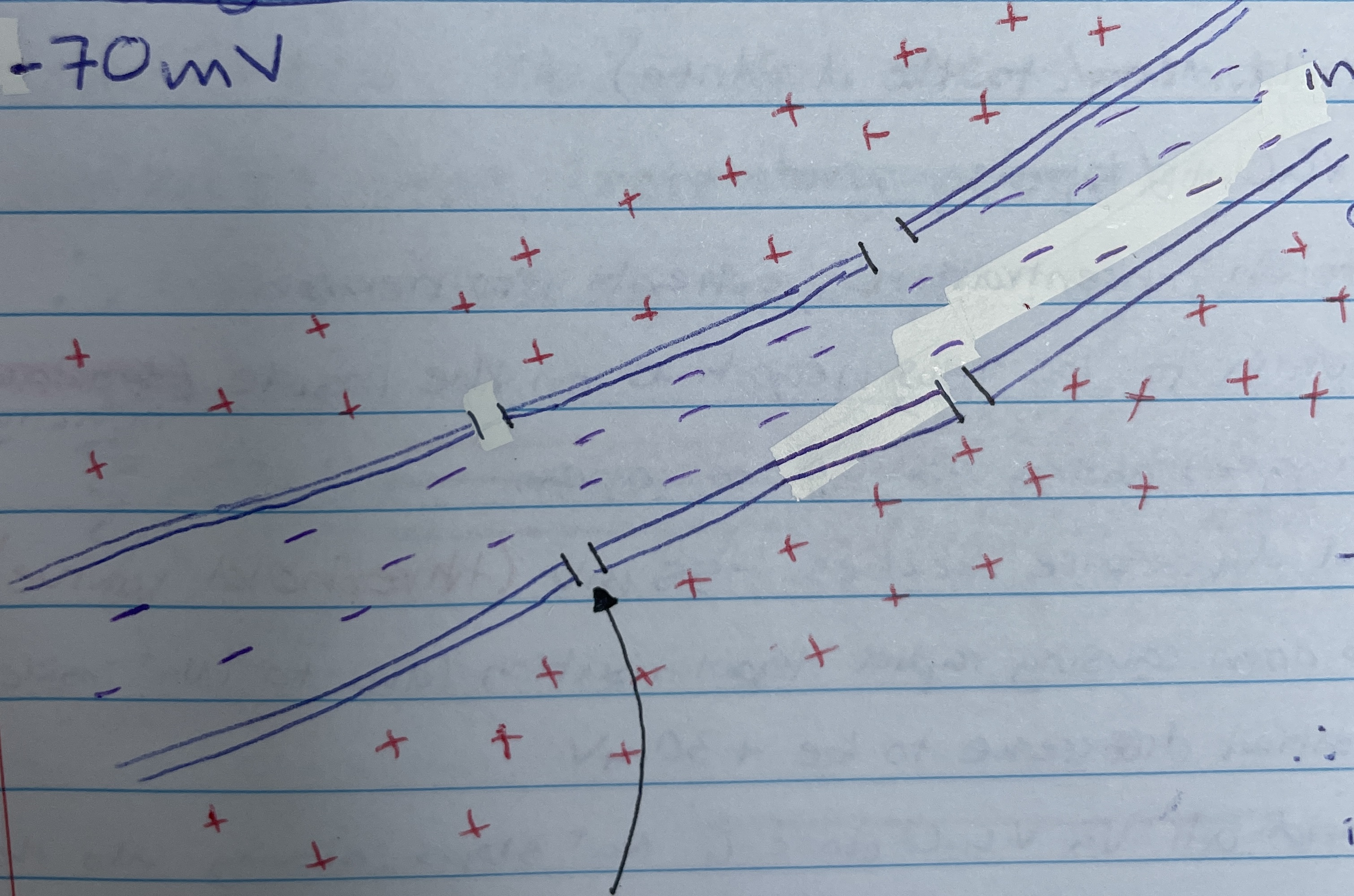
Electrochemical gradient
The difference in charge between the outside of a neuron, which is more positive, and the inside, which is more negative - in the axon
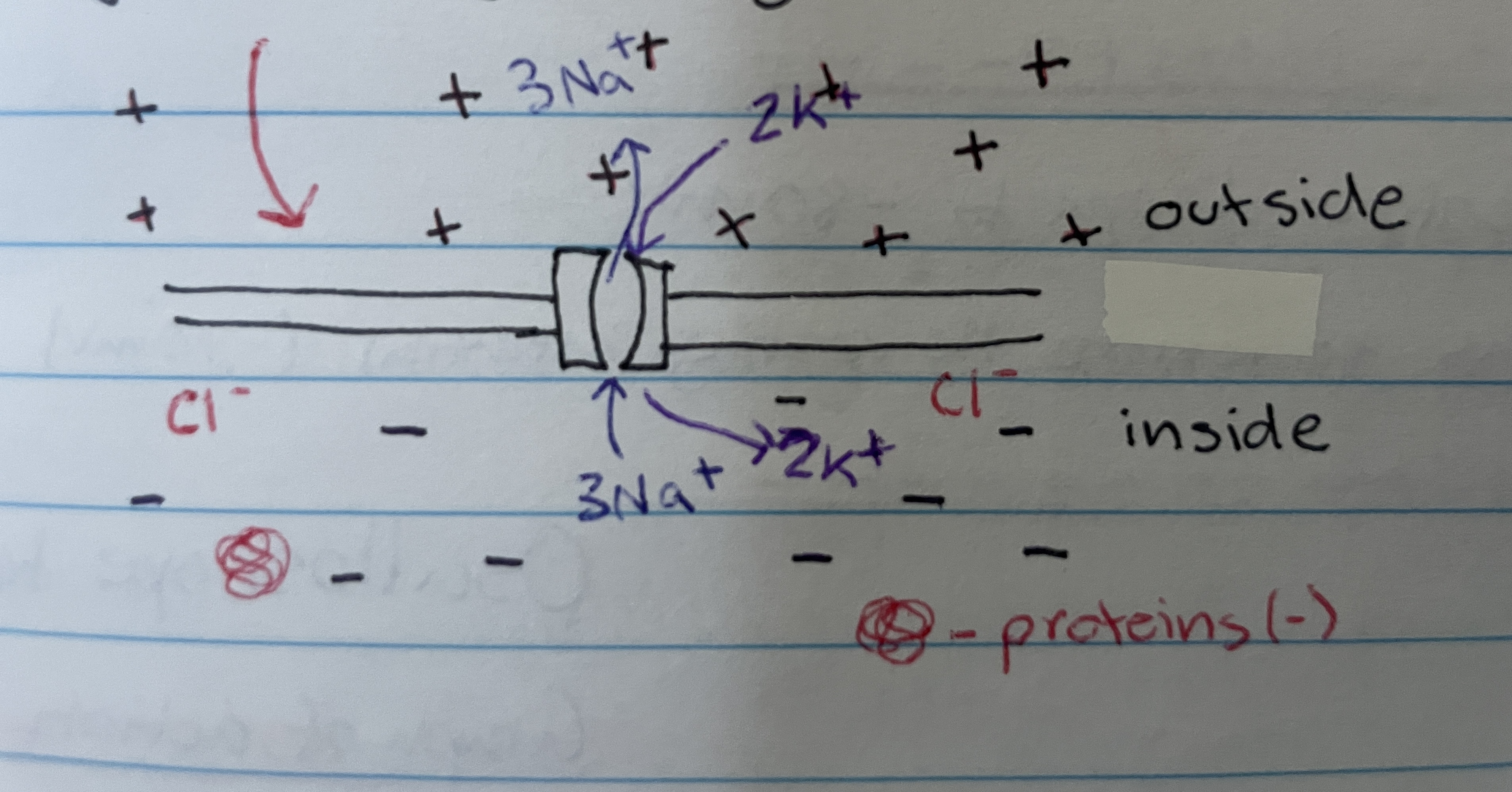
Sodium-potassium pump
When in a resting state it maintains the concentration gradient/electrochemical gradient by pumping 3 Na⁺ out and 2 K⁺ in
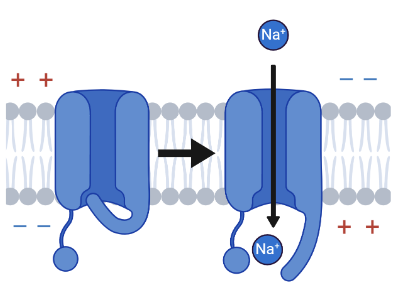
Voltage gated channels
Protein channels in the neural membrane that are closed at -70mV and open during a change in the electrical potential across the membrane - Na+ and K+ have them
Negative
Is it more positive or negative inside a neutron at resting potential.
Positive
Is outside of the neuron more positive or negative at resting potential.
Axon stimulation
Causes sodium voltage gated channels to open so Na+ goes into the neuron so it becomes less negative (-70mV to -55mV) - can be environmental stimulus or neurotransmitter binding to dendrite.
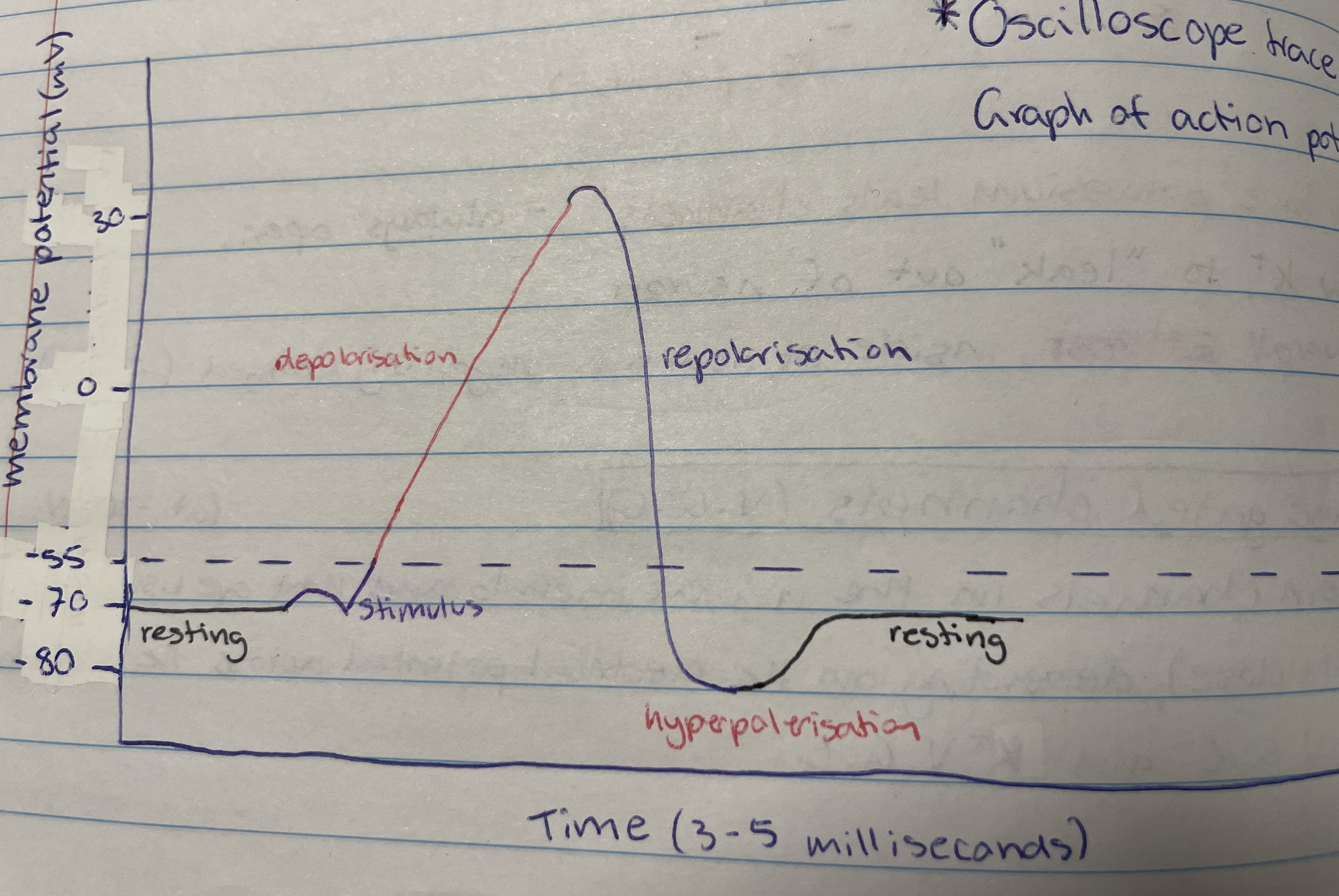
Depolaristion
When the potential difference reaches -55mV more Na V.G.C open to cause rapid ___ and causes potential difference to be +30mV - more Na+ in neuron
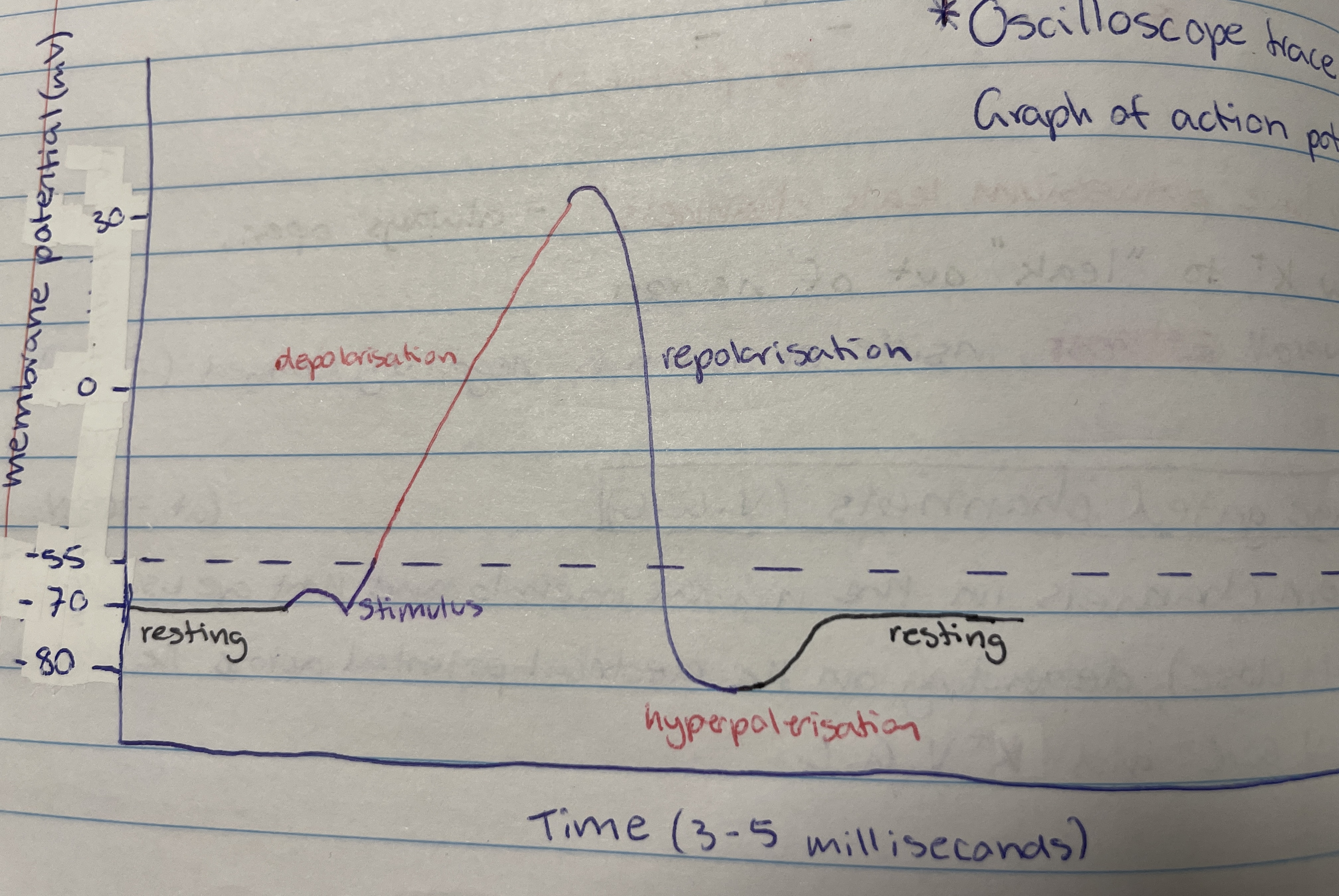
-55mV
The threshold value
Repolarisation
After about 1 millisecond all Na V.G.C close and Ka V.G.C open so Ka+ diffuse out of axon/neuron - potential difference drops to -80mV
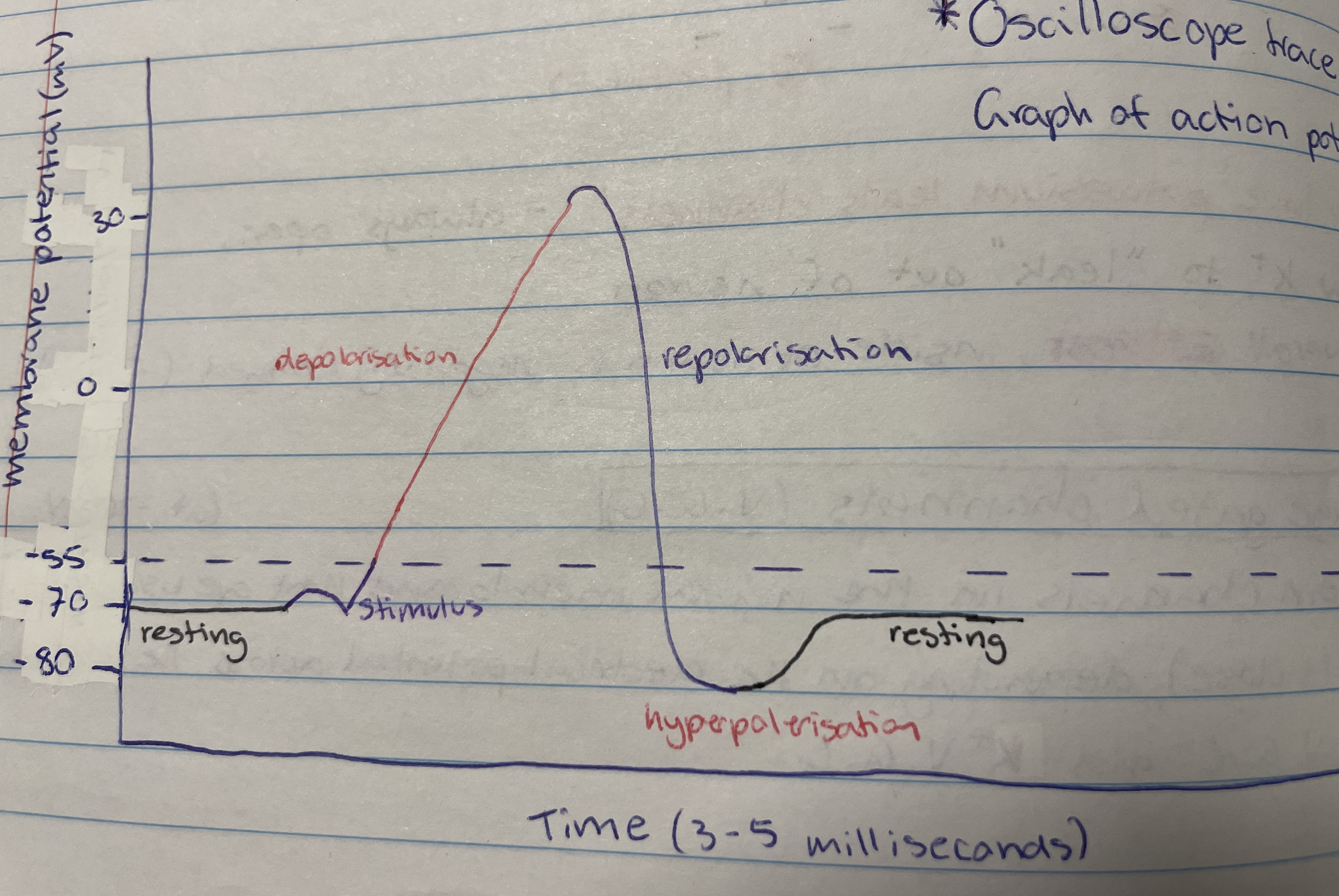
Hyperpolarisation
Occurs due to lag in closing K V.G.C - membrane potential is at -80mV so sodium-potassium pump brings it back to -70mV (resting)
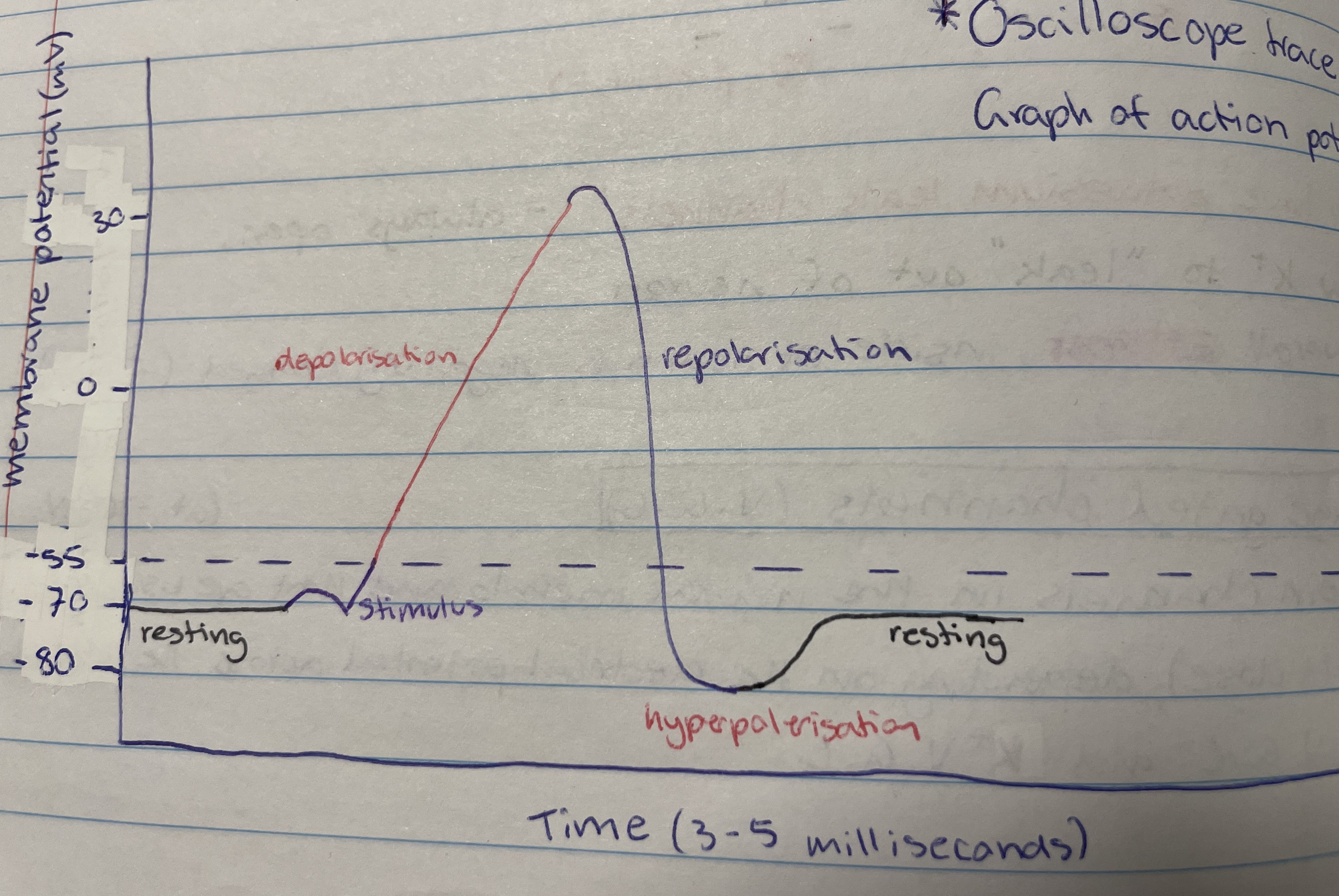
Action potential
What travels down the neuron as the -55mV potential difference triggers depolarisation in one section which then triggers it in the next - wave movement

Resting, axon stimulation, depolarisation, repolarisation, hyperpolarisation and resting
Order the stages of action potential (including resting)
Nodes of Ranvier
Where are the Na and Ka V.G.C on the neuron
x100
By how much does having myelin sheaths increase the transmission speed of action potentials
refractory period
Action potential travels in one direct in the axon (dendrite to synapse) due to the…
repolarisation
The refractory period occurs because the voltage gated channels close due to the potential difference not being -55mV after ___ which is -80mV
sensory neuron
The nature of stimulus (light/heat/pain) is deduced due to the position of the ___ ___ on the body
strength
The brain interprets the ___ of a stimulus due to the frequency of the action potential and the number of neurons
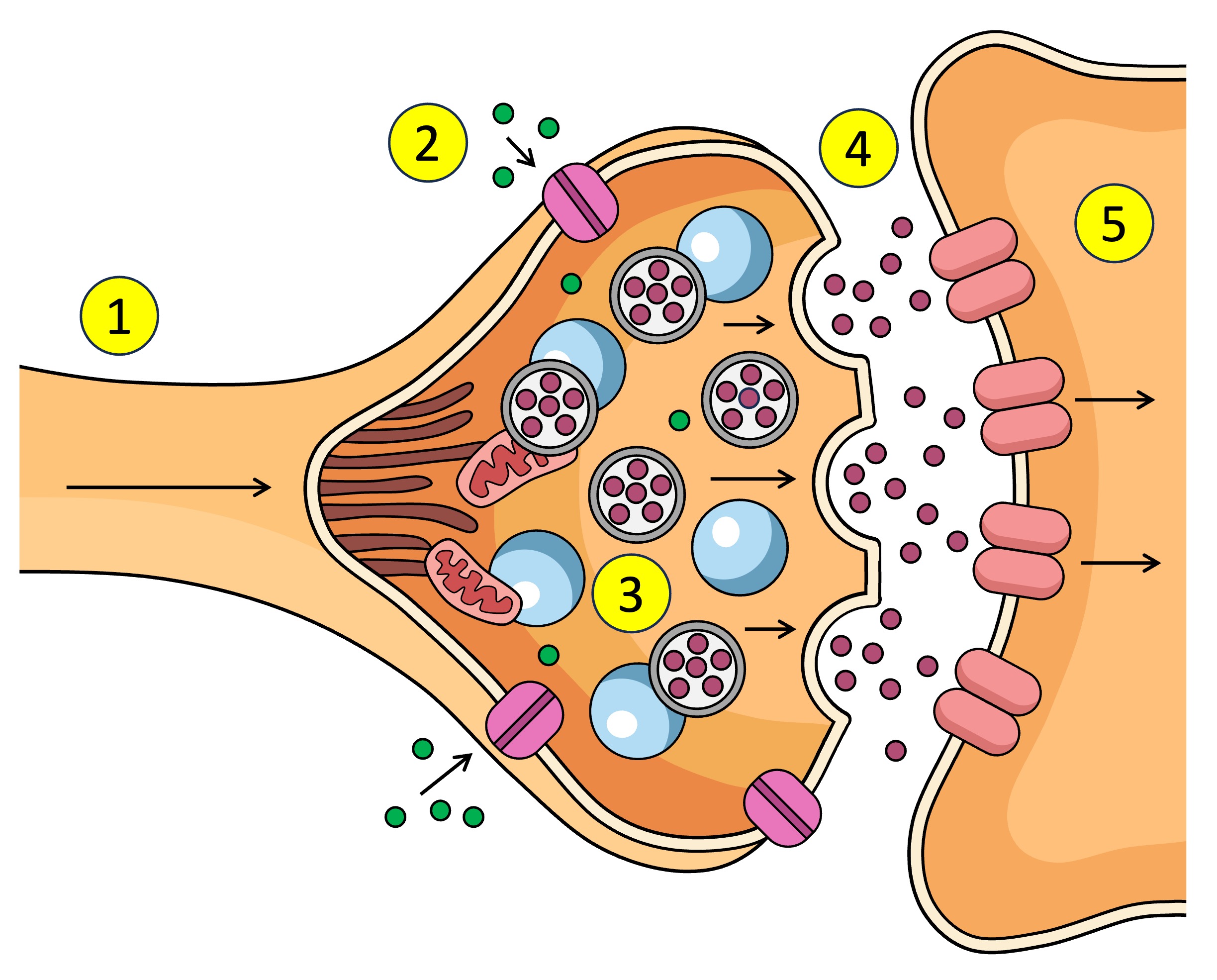
Synapse
The gap between the axon terminal and the next neuron
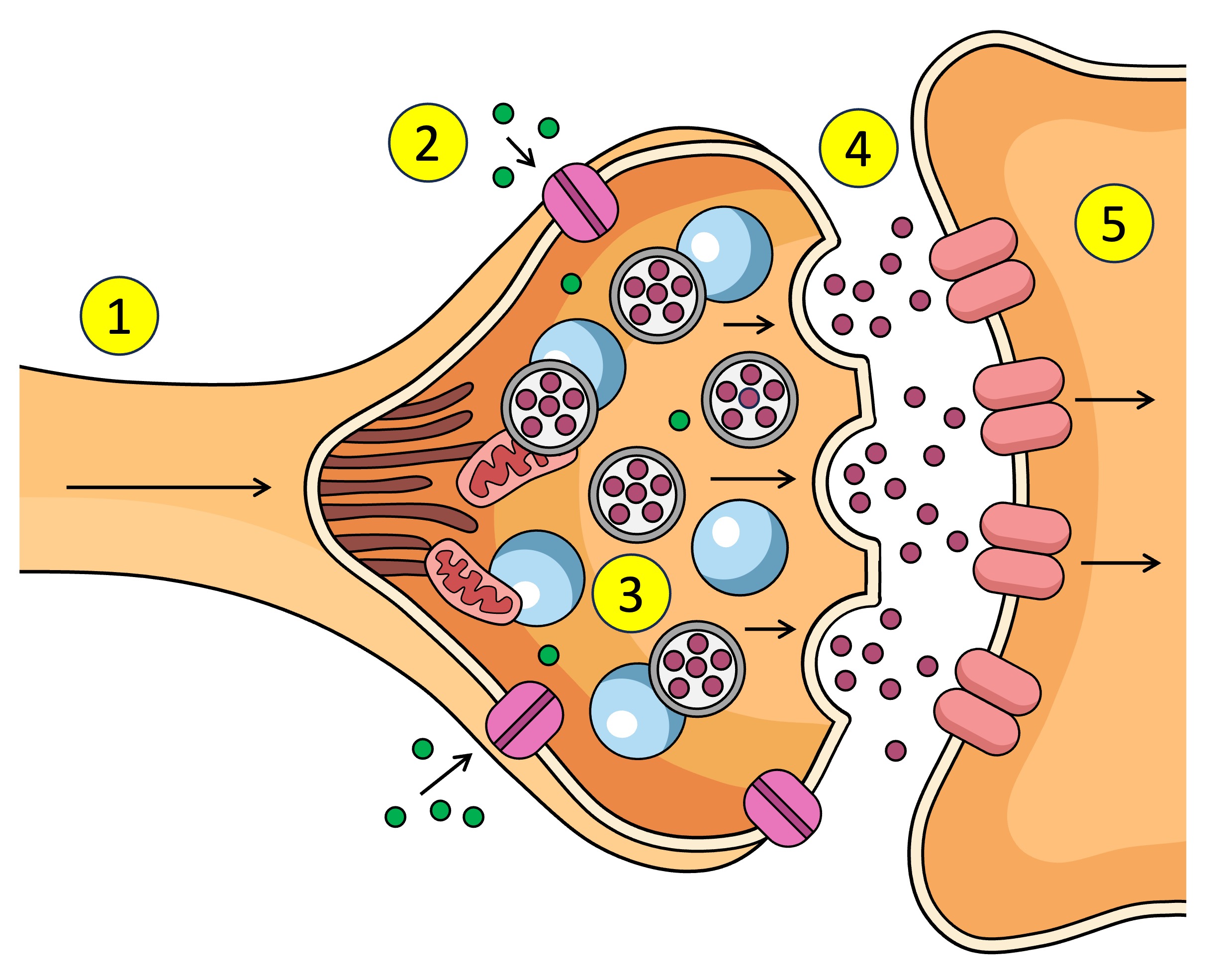
neurontransmitters
What is the action potential converted to in the synapse - chemical messages
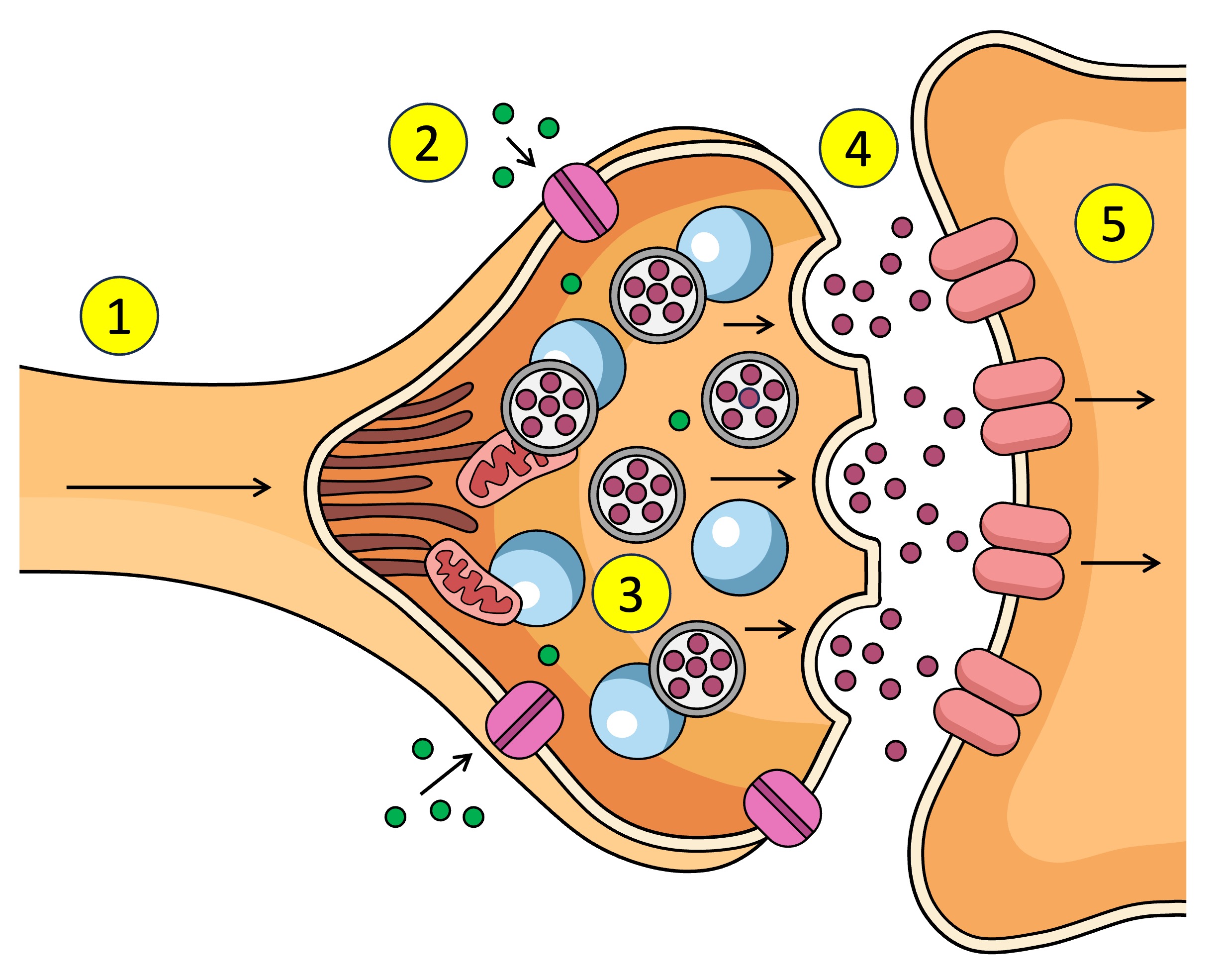
Action potential depolarisation in the membrane
What causes the Ca2+ V.G.C to open in the synapse.
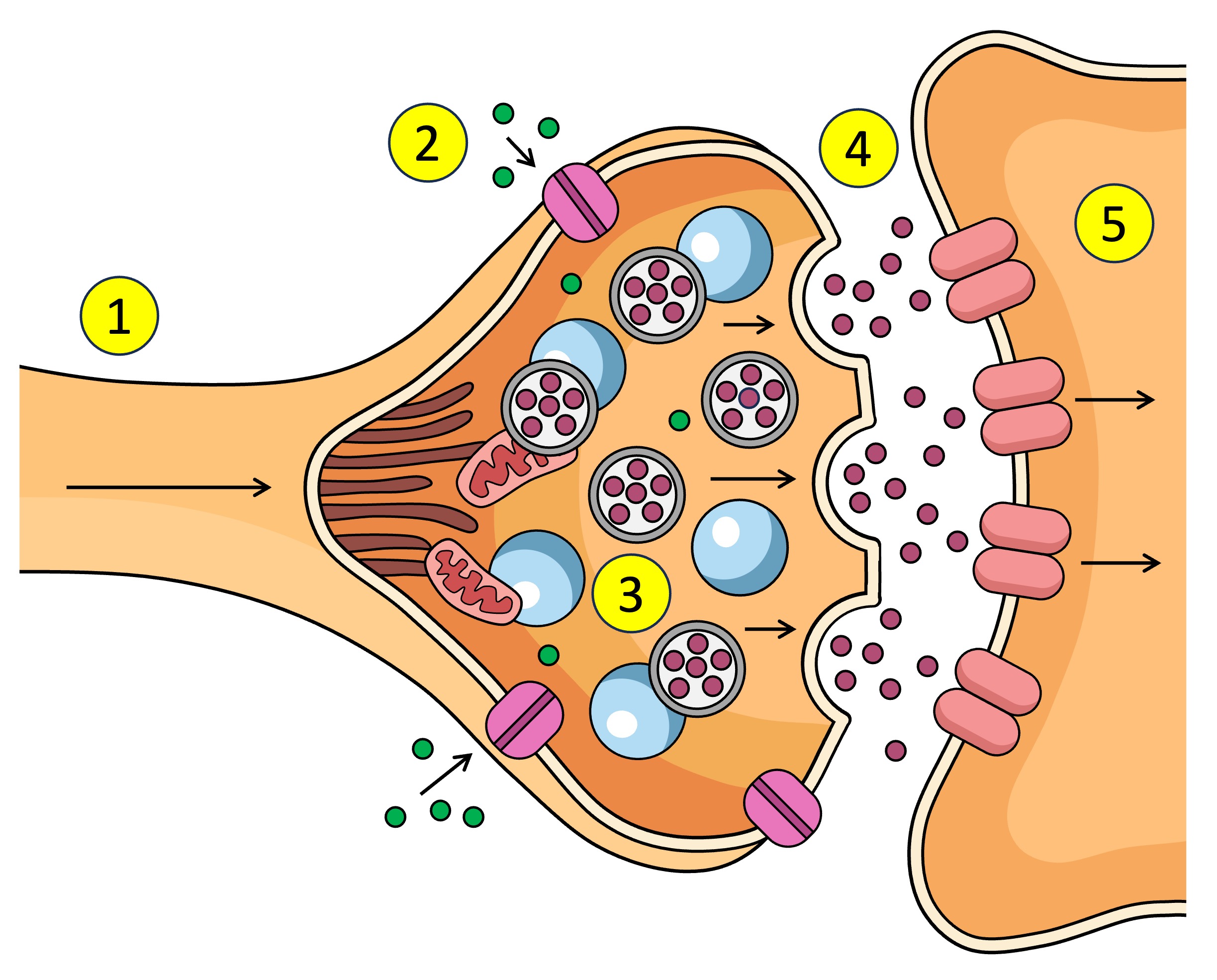
pre-synaptic neuron
The ___ neuron sends chemical messages to the post-synaptic neuron across the synapse
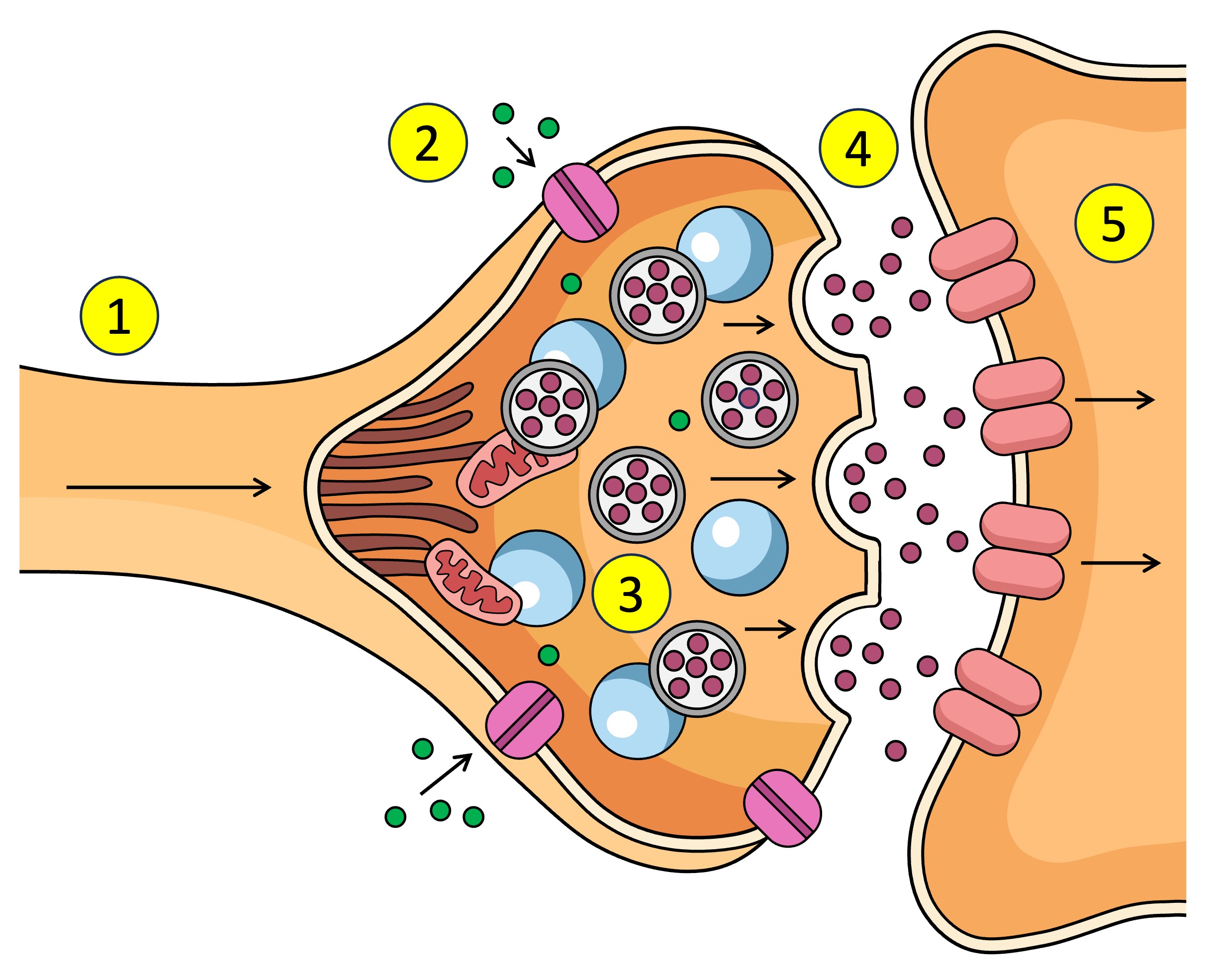
post-synaptic neuron
The pre-synaptic neuron sends chemical messages to the ___ across the synapse
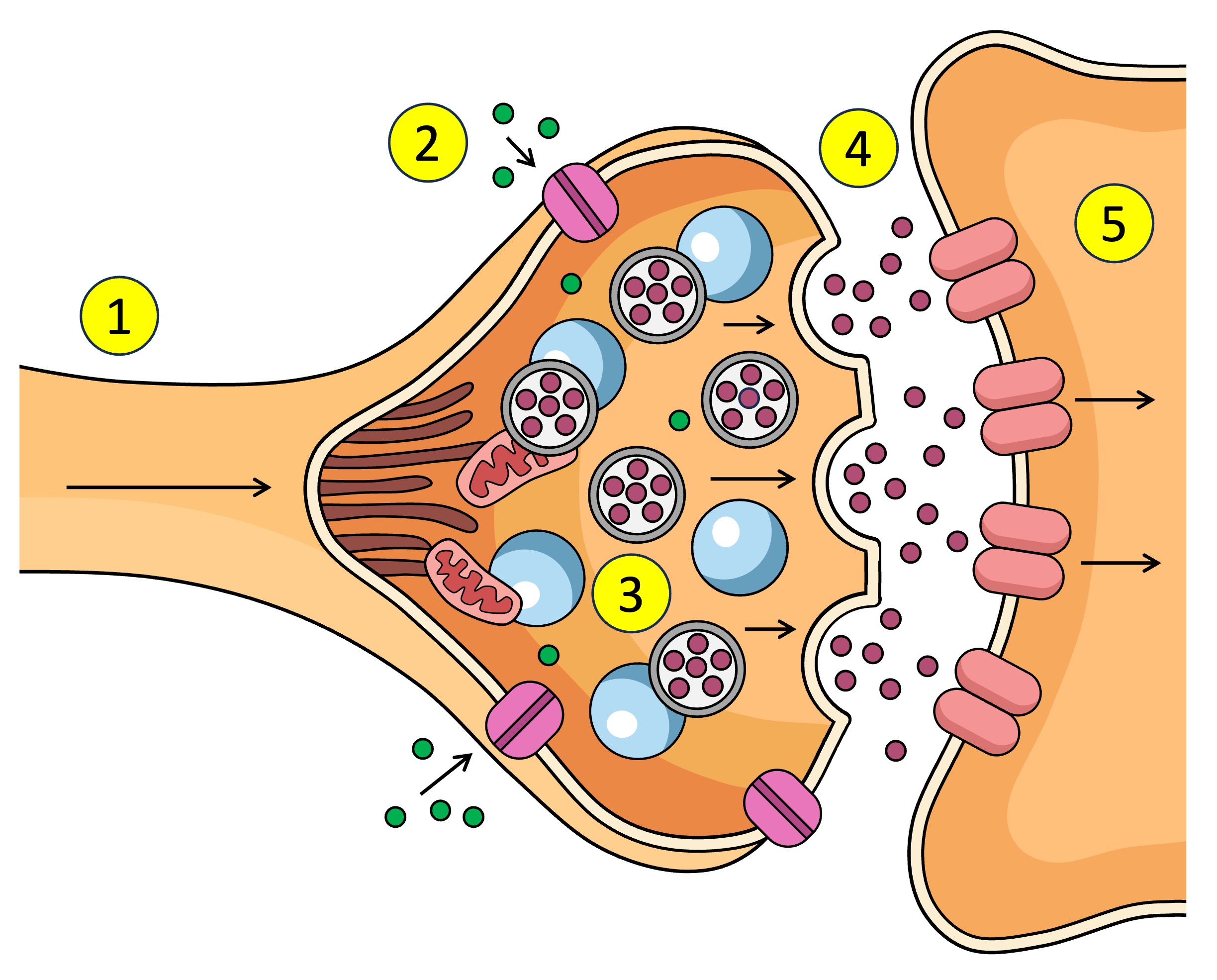
synaptic vesticles
What are the neurotransmitters inside in the pre-synaptic neuron.
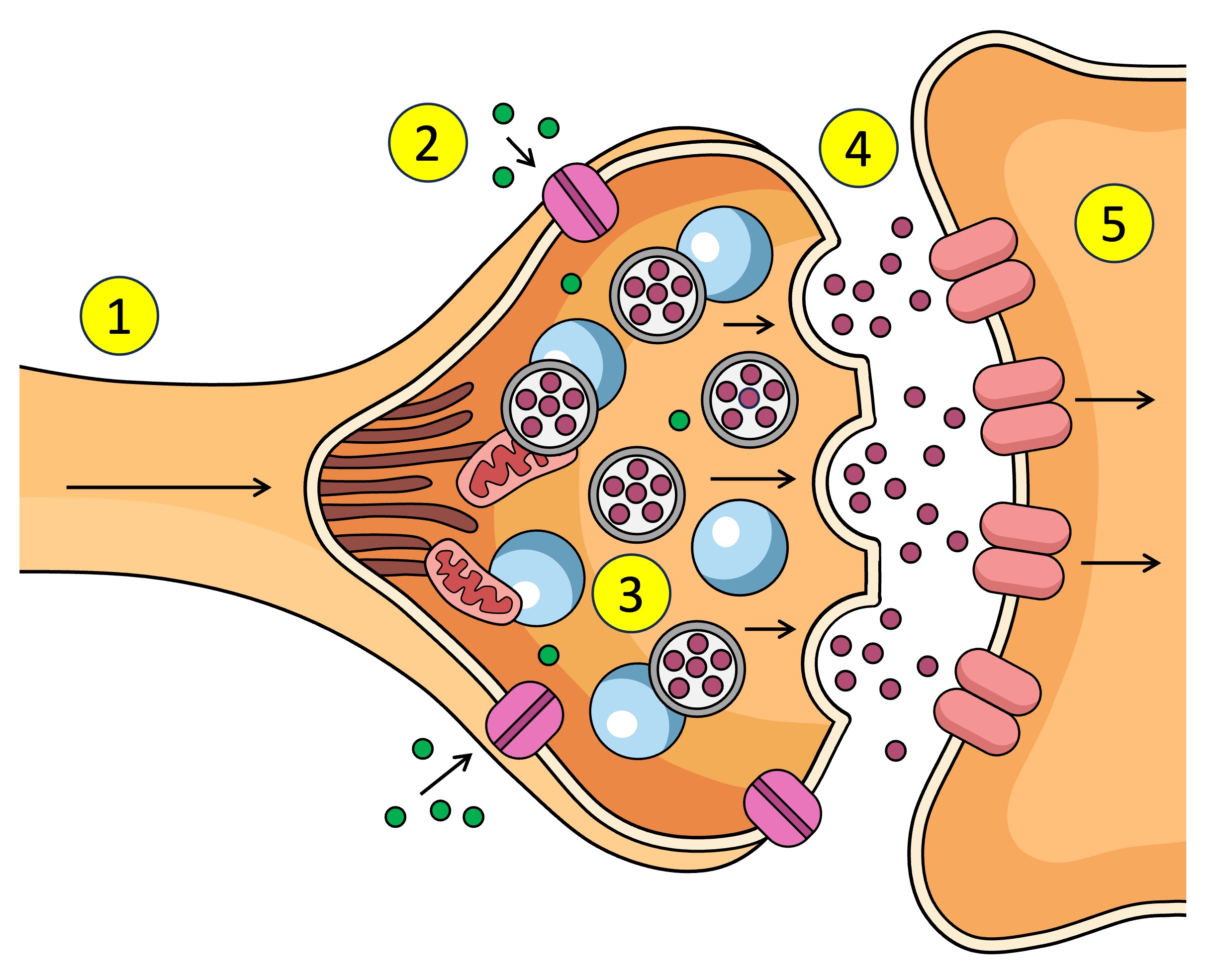
terminal bud
other name for axon terminal
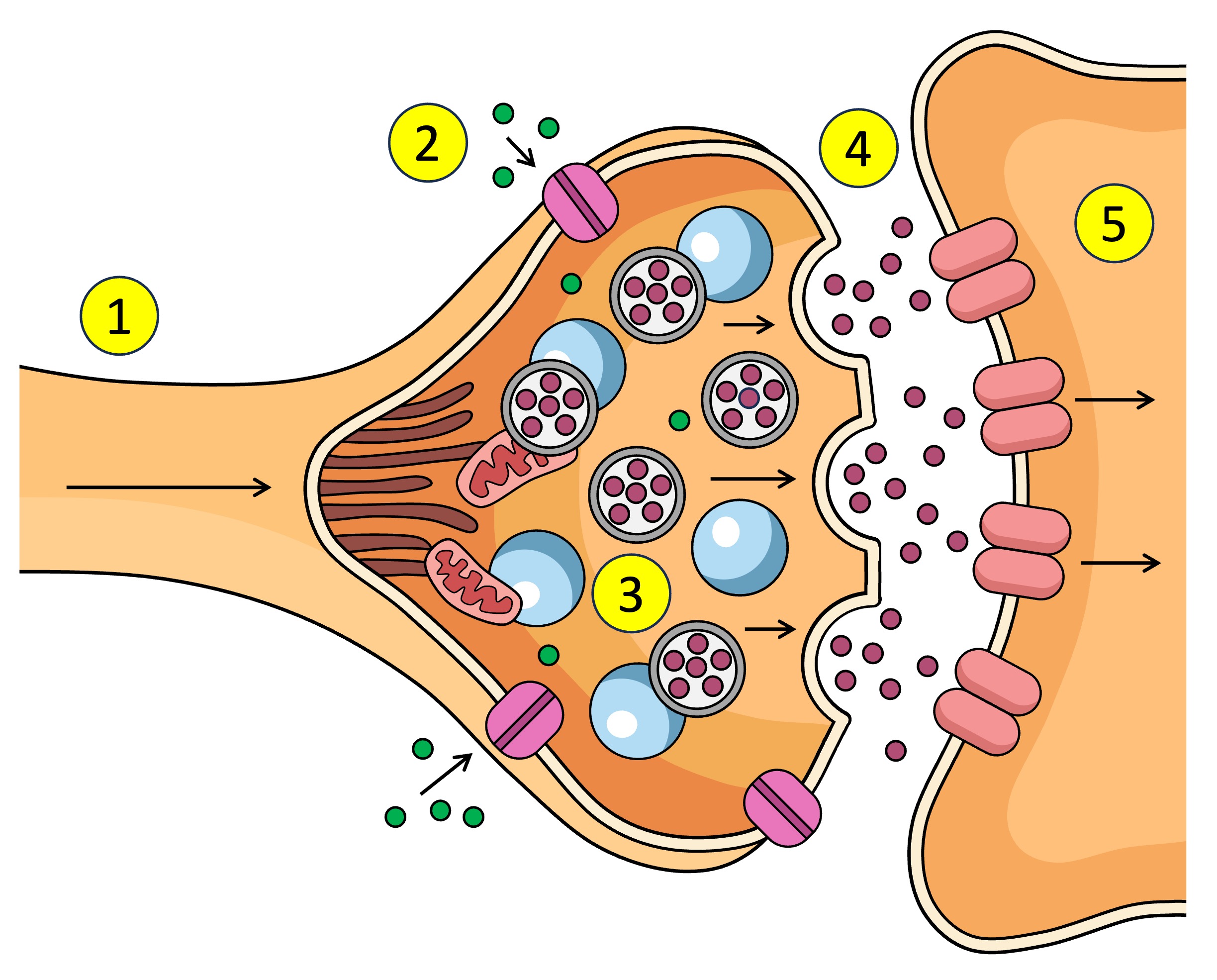
synaptic vesticles
After Ca2+ enters the pre-synaptic neuron what does it interact with.
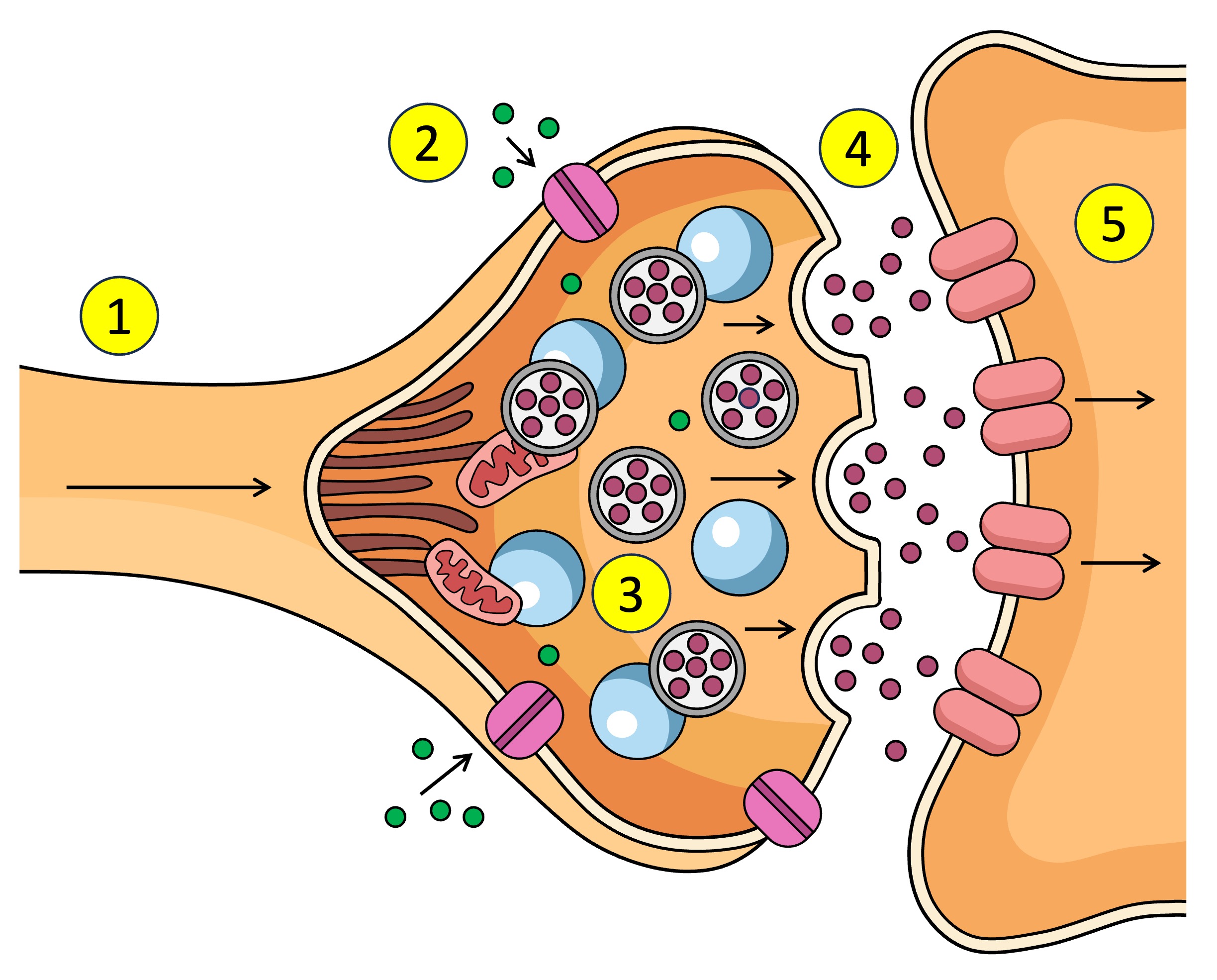
dock
What does the synaptic vesticle do at the membrane after interacting with the Ca2+
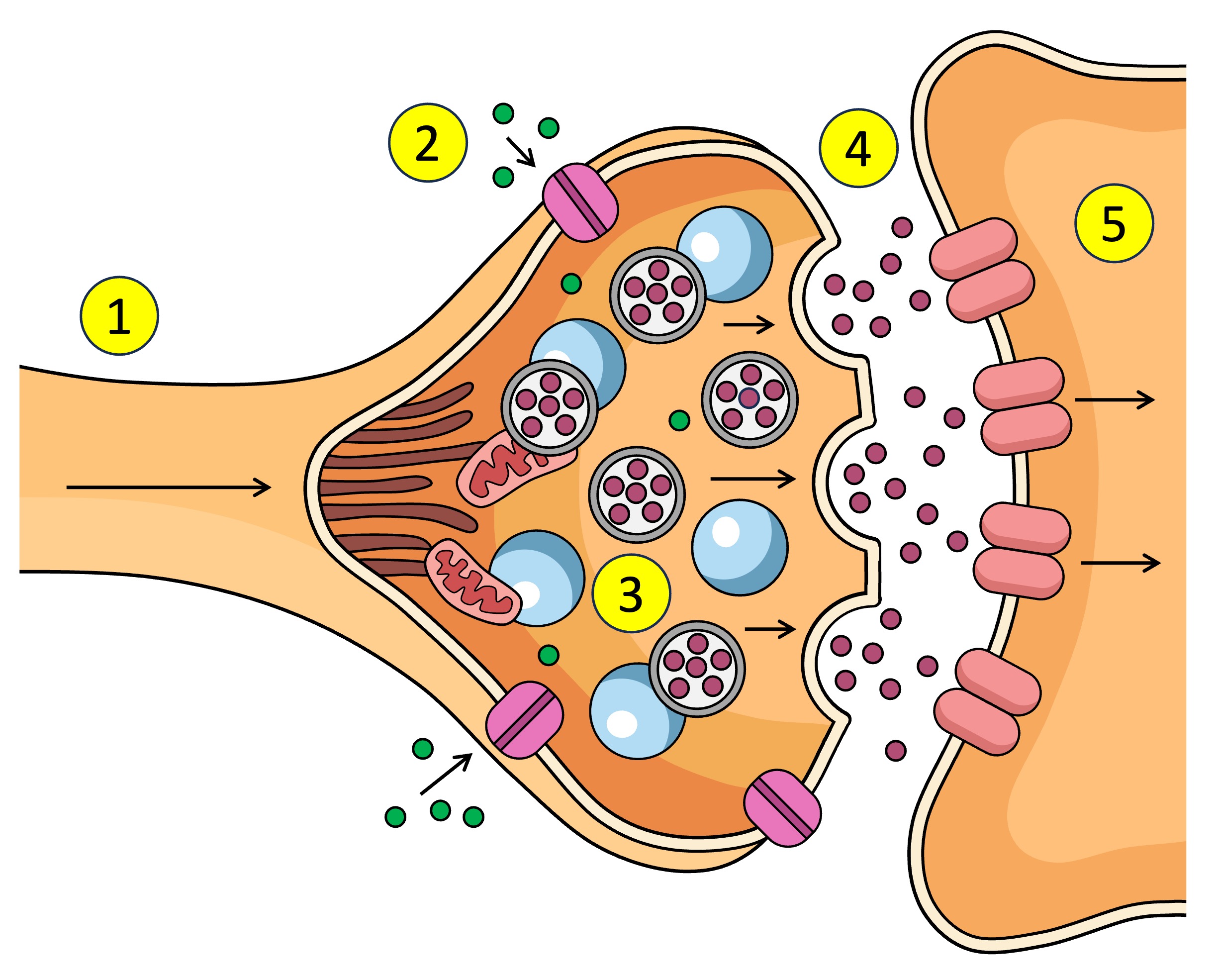
neurotransmitters
What is released into the synapse when the vesticle docks at the membrane of the pre-synaptic neuron.
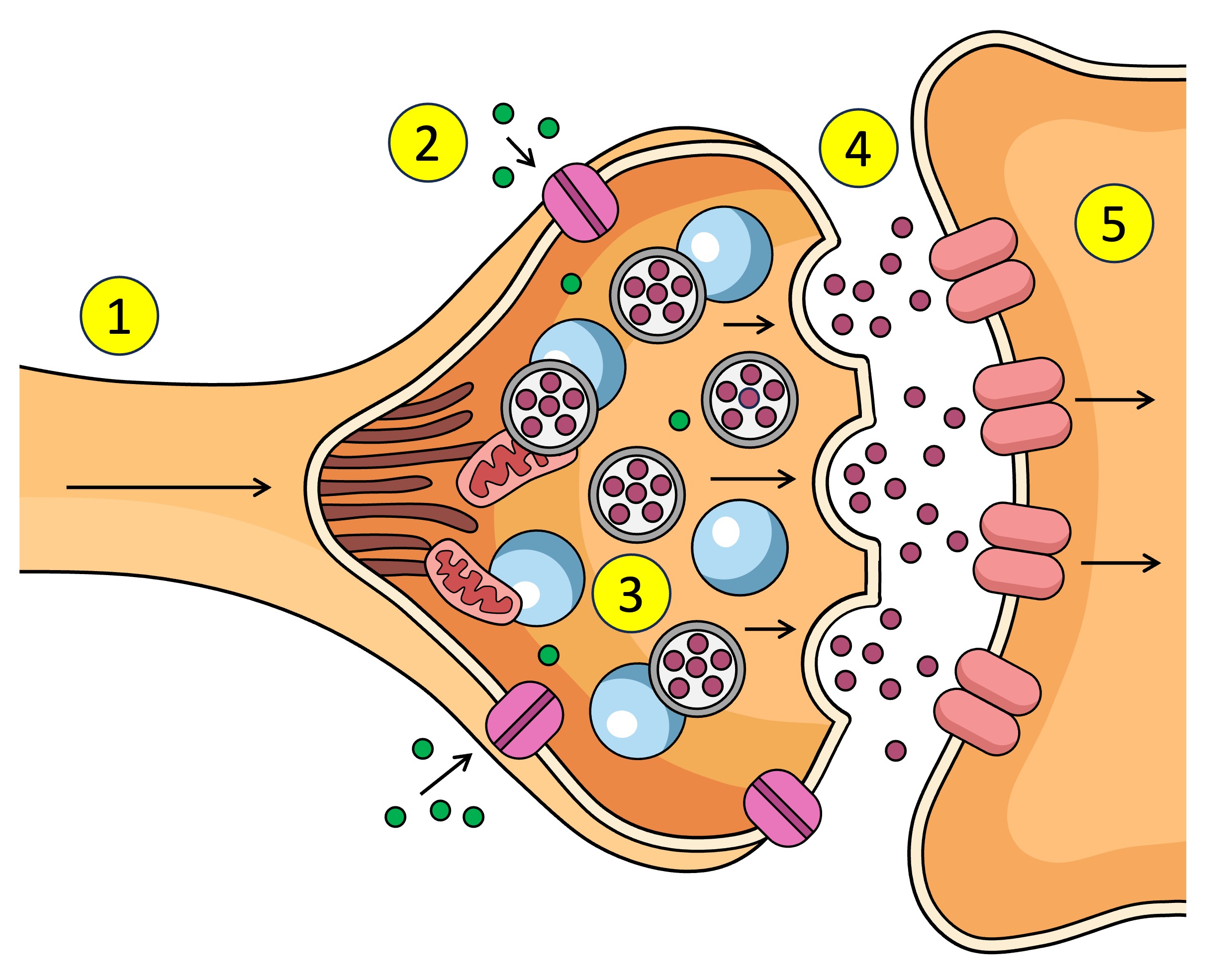
target cell
other name for post-synaptic neuron
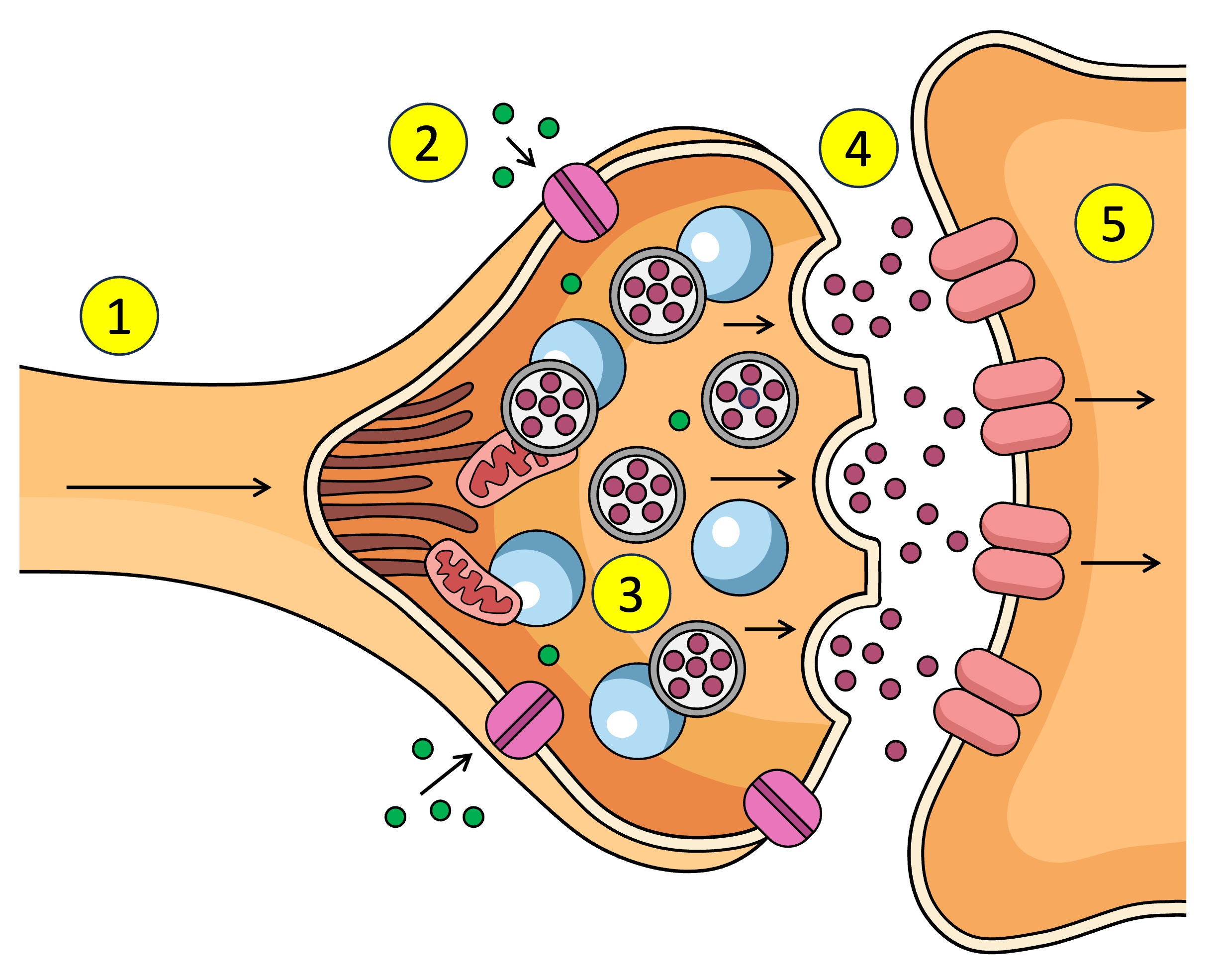
receptors
What do neurotransmitters bind to after being released from the pre-synaptic neuron across the synapse to the post-synaptic neuron.
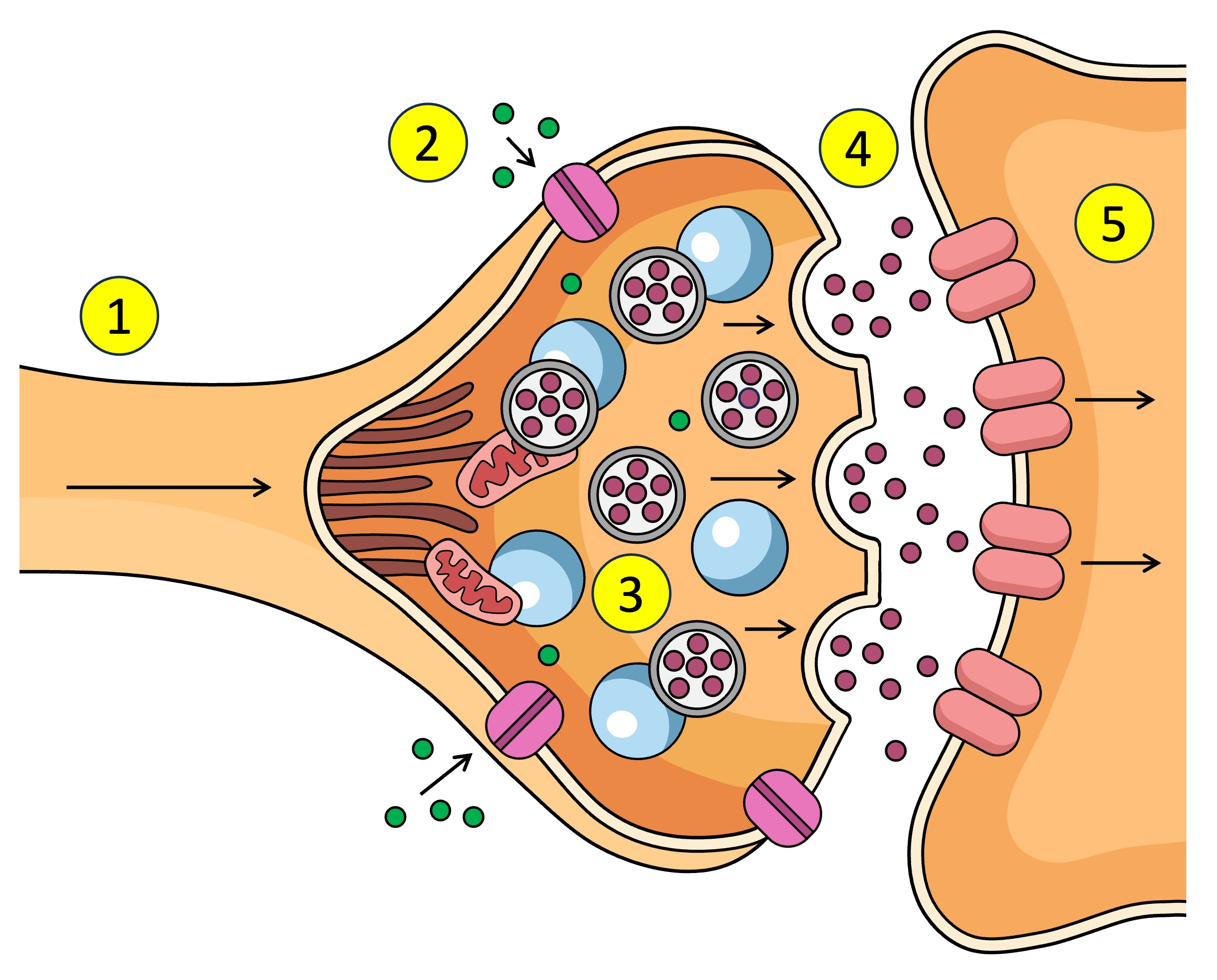
Action potential
Receptors (5) receive the neurotransmitter (4) which affects what? (increase or decrease)
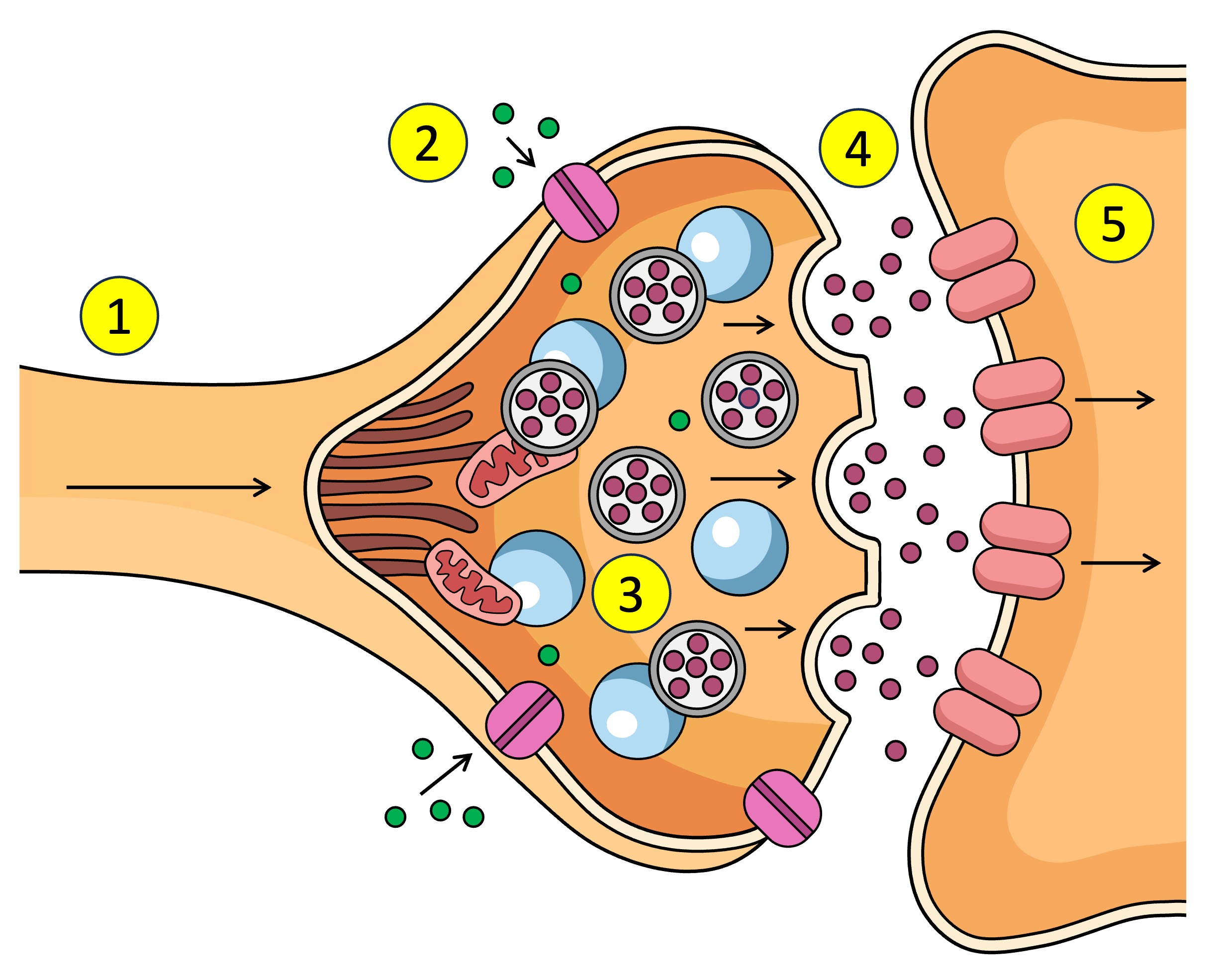
Ligand-gated channels
Other name for receptors on the post-synaptic neuron / open after neurotransmitters bind to receptors???
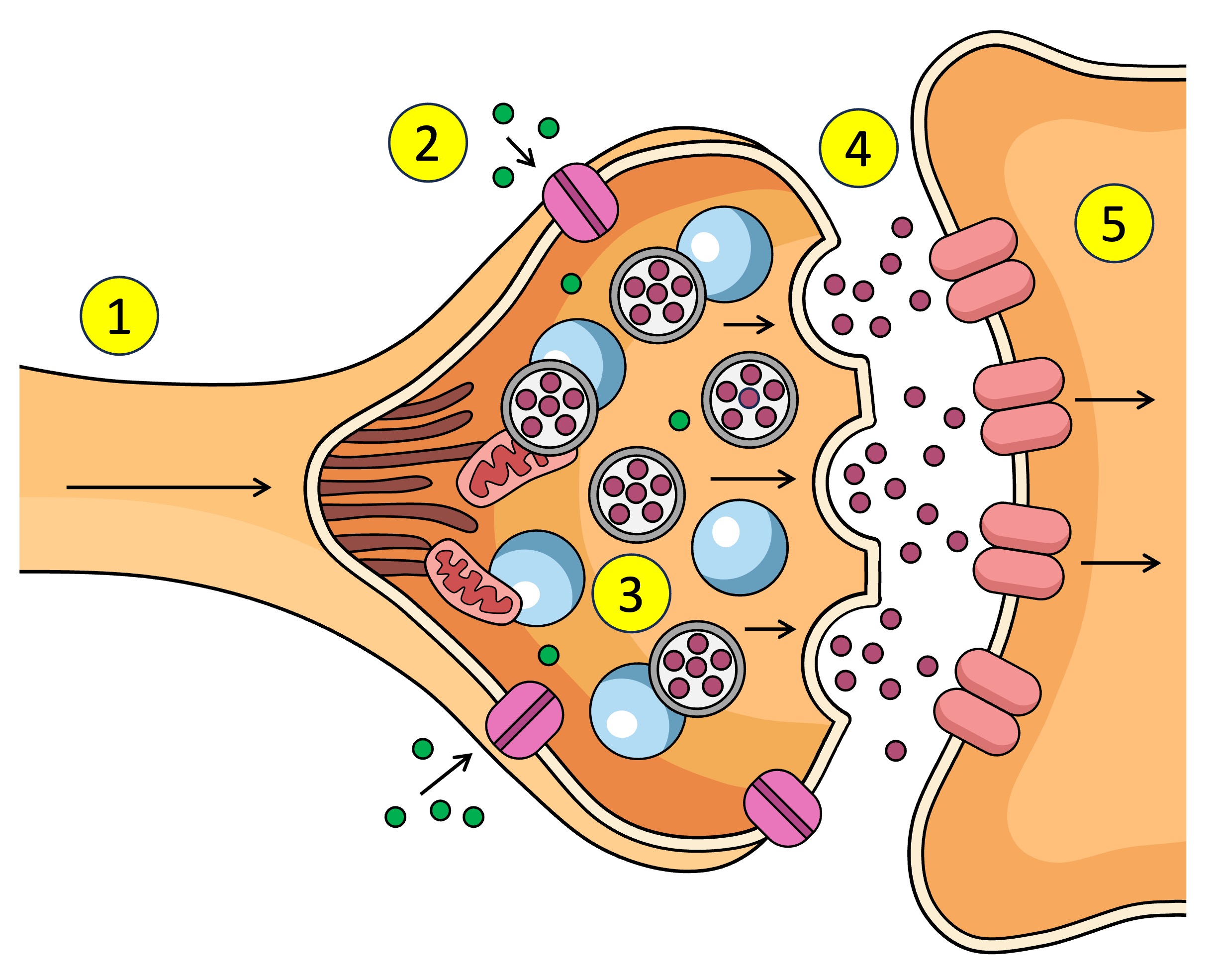
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Chemical message that stimulates an action potential (depolarisation) or tiggers action in the cell - more positive in cell = action potential
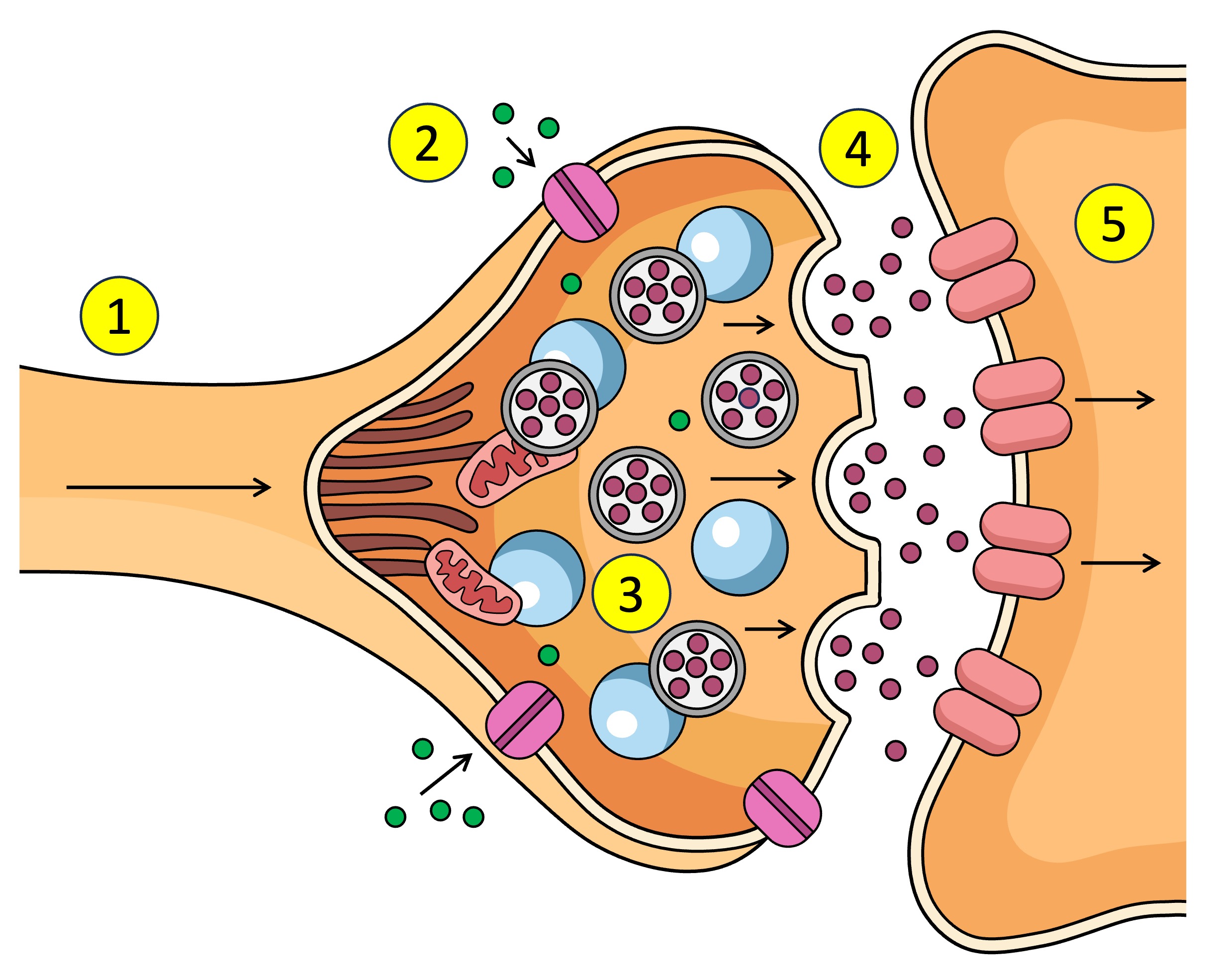
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
Chemical message that causes hyperpolarisation (flow of K+ and Cl+ out of cell) to reduce the message - more negative = resting
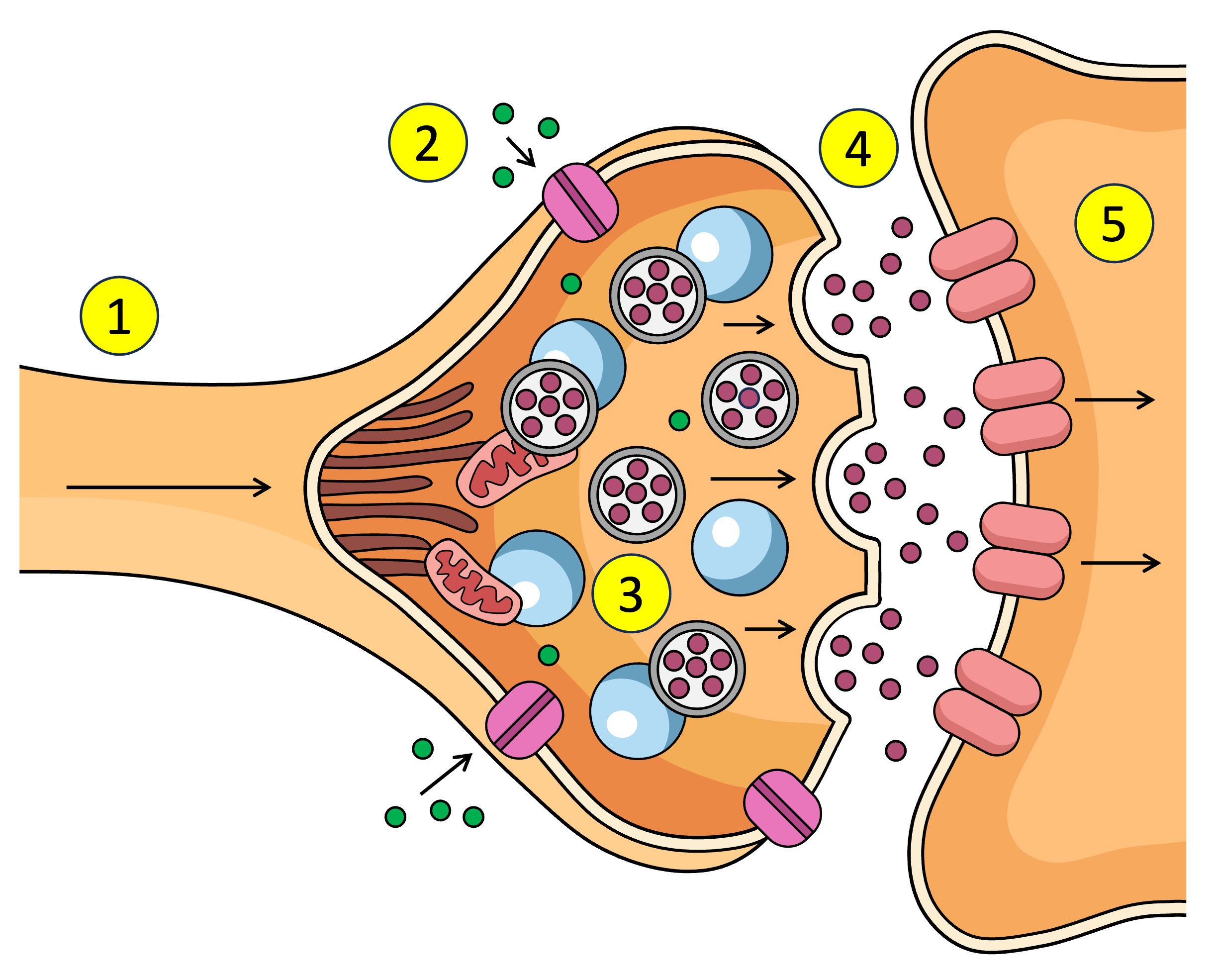
Reabsorbed, diffused, broken down
After neurotransmitters are used by the receptor what three things can happen? ___ back into the post-synaptic neuron, ___ away from site or ___ by enzymes.
The endocrine system
A collection of glands that produce hormones to regulate metabolism, growth and development, sexual function, reproduction, mood, sleep, etc.
Hypothalamus, pituitary glands and pancreas
Three organs in the endocrine system.
neurohormones
Hormone produced by the hypothalamus
pituitary glands
Target of neurohormones from the hypothalamus
Antidiuretic hormone
Hormone produced by the pituitary glands
kidneys
Target of antidiuretic hormones from the pituitary glands
glucagon and insulin
Hormones produced by the pancreas
liver
Target of glucagon from the pancreas
Liver and most cells
Target of insulin from the pancreas
Through the bloodstream
How do hormones travel to cells after they are excreted from the organ.
Nervous system
Which is more fast acting endocrine or nervous?
Endocrine system
Which message lingers nervous or endocrine?
Nervous system
Is nervous or endocrine sent electrically via neurons?
Endocrine system
Is nervous or endocrine sent chemically via hormones?
Increase water reabsorption
What do the pituitary glands instruct the kidneys to do using antidiuretic hormones?
Increase the blood glucose levels
What does the pancreas instruct the liver to do using glucagon?
Glycogen
What does the glucagon convert into glucose to increase blood glucose levels?
Decrease blood glucose levels
What does the pancreas instruct the liver and most cells to do using insulin?
Glycogen formation
What does the insulin simulate in the kidneys to decrease blood glucose levels?
binds to receptors
To affect target cells hormones ___ to ___ on the cell
stimuli
What controls the release of particular hormones? - pressure, light, etc
stimuli, hormones
Presence of metabolic products and other hormones and stimulation by the autonomic nervous system are all ___ that control the release of ___
permeability, enzymes, cell organelles, gene production
Hormones influence target cells by changing the ___ of a membrane, affecting ___ in a membrane, affecting the ___ ___ or activating ___ ___
link, control homeostasis
The role of the hypothalamus is to ___ nervous and endocrine systems and ___
Pituitary glands
What other organ in the endocrine system is controlled by the hypothalamus (using hormones)?
control centre
The hypothalamus can be call the ___ of the endocrine system
hormones, chemicals, blood
Hypothalamus collects information from other parts of the brain by monitoring ___ and ___ in the ___ passing through.
master gland
The pituitary gland is also called ___ because it produces many hormones and controls the function of some other endocrine glands.
Thermoregulation
The maintenance of internal body temperature
36.1-37.2
Average internal body temperature for an adult human
38.5
Fever
35
Hypothermia - body temperature