Pharmo preg
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
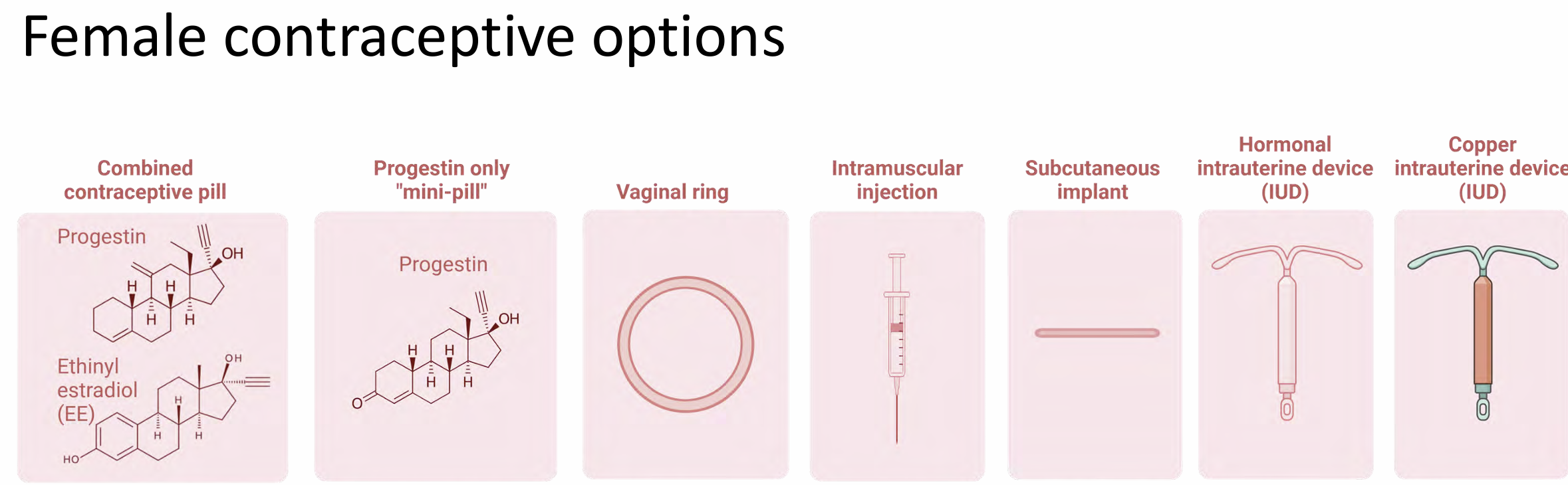
Types of Female contraceptive options
Combined contraceptive pills
Progestin ONLY pill (mini pill)
Hormonal vaginal ring
Intramuscular injection
Subcutaneous implant
Levonorgestrel IUD
Copper IUD
Combined Contraceptive pills (Content, duration, pro, contraindications, adverse reaction)
Contains synthetic estrogen and progestin.
Duration: Consume daily orally for 3 weeks, followed by an insert pill for 1 week.
Pro: Improve acne, regular menstruation.
Contraindications: Breastfeeding, history/risk of thromboembolism, Previous ER+ cancer, cardiovascular disease.
Adverse reaction: Mastalgia, nausea, depression, hypertension, breakthrough bleeding, risk of venous thromboembolism.
Progestin ONLY pill (mini pill)
Contains synthetic Progesterone.
Taken orally daily and must be taken at the same time each day.
Pros: can use while breastfeeding
Contraindications: History/risk of thromboembolism, pregnancy, hepatic disease.
Adverse reaction: Headache, acne, changes in LDL and HDL, breakthrough bleeding. Lower estrogen production, but impact on bone is unclear.
Hormonal vaginal ring
Contains: Etonogestrel (Progestin) and ethinylestradiol (EE) for extended release.
Duration: 3weeks in, 1 week out.
Pros: No need for daily pill and regular menstrual cycle.
Contraindications: Breastfeeding, history/risk of thromboembolism, previous ER+ cancer, cardiovascular disease.
Adverse reaction: Mastalgia, hypertension, depression, risk of venous thromboembolism, nausea and breakthrough bleeding.
Intramuscular injection
Contain: Microcrystalline medroxyprogesterone.
Duration: 3 months
Pro: Can be used while breastfeeding.
Contraindication: History/risk of thromboembolism, pregnancy and hepatic disease.
Adverse reaction: Headache, change of LDL and HDL, breakthrough bleeding. Lower estrogen production and unclear impact on bone.
Subcutaneous implant
Contain: Etonogestrel (Progestin)
Duration: 3 years
Pro: Can be used while breastfeeding.
Contraindications: History/risk of thromboembolism, pregnancy, hepatic disease.
Adverse risk: Headache, changes in LDL and HDL. Lower estrogen production. Unknown effect on bone. Breakthrough bleeding.
Levonorgestrel IUD
Contain: Levonorgestrel (progestin) extended release.
Duration: 5 Years
Pro: Can be used while breastfeeding
Contraindications: History/risk of thromboembolism, pregnancy, hepatic disease.
Adverse effect: headache, changes in LDL/HDL, breakthrough bleeding, lower estrogen production and unknown effect on bone health.
Copper IUD
Contain: Copper, which is spermicidal and prevents fertilization.
Duration: 5-10 years
Pro: Can also be used an emergency contraceptive within 5days of sex.
Contraindications: pregnancy infection, history of heavy menstrual bleeding
Adverse effect: Heavy menstrual bleeding, risk of perforations.
Name the combined contraceptive pills
Ethinyl Estradiol
Desogestrel
Levonorgestrel
Ethinyl Estradiol (MOA, Indications, Contraindications, route of administration, side effect, pharmokinetics)
MOA: Synthetic form of estradiol that provides greater bioavailability & half life.
Indications: Used in combination with progestin for combination contraceptive pills or slowrelease vaginal ring. AND can be used in hormonal release therapy (HRT) to treat menopause symptoms.
Contraindications: ER+ breast cancer, cardiometabolic disease (Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease), smoking - risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)/ Pulmonary embolism (PE)
Route of administration: Oral, subcutaneous implant, vaginal cream, vaginal ring and transdermal.
Side effect: Common: Mastlagia, nausea and headache. AND Long- Term: Impact hepatic production of coagulation and increase risk of DVT
Pharmacokinetic: Half life of 18hours under chronic dosing
Desogestrel
MOA: Synthetic agonist of progesterone receptors (More potent than levonorgestrel)
Indications: Used in combination with estrogen, Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) for combination contraceptive pill.
Contraindication: History/risk of thrombosis, genetic mutation: Prothrombin mutation. And Factor V leiden mutations
Route of a: Oral and subcutaneous implant
Side effect: Increased risk of venous thromboembolism, Pulmonary Embolism, headache, irregular menstrual bleeding.
Pharmacokinetics: Half life of 24-30hrs
Levonorgestrel
Contain: Synthetic agonist of progesterone receptor (Weak androgen receptor)
Indication: Used in combination with estrogen, Ethinyl Estradiol for combined contraceptive pills. Can be used as stand-alone contraceptive “mini-pills” at 30mg/day.
Can be used as emergency contraceptive at 2 750mg/ 1.5mg does 12 hrs apart.Contraindications: History/risk of thromboembolism, Genetic mutation: Prothrombin mutation. And Factor V leiden mutation.
ROA: Orally, subcutaneous implant. Emergency: orally
Side effect: Increased risk of venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, irregular menstrual bleeding and headache.
Acute use due to emergency: Mastalgia, vomitting, nausea.Pharmacokinetics: Half life of 24-26 hours.
Types of oestrogen inhibitors
Clomiphene
Letrozole
Clomiphene
MOA: Selective oestrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Inhibits oestrogen signaling in hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to remove negative feedback to HPO axis during follicular phase, Increase follicle growth and maturation.
Indication: Ovulation induction. Inhibition of oestrogen production blocks oestrogen mediated negative feedback to HPO axi to promote increase follicle growth and maturation.
Patient MUST abstain from unprotected sex & have transvaginal ultrasound to verify presence of single dominant follicle to reduce risk of multiple pregnancies (high risk).Contraindication: Pregnancy, breastfeeding
ROA: Orally bioavailable.
Side effect: Headache, Mastalgia, mood changes, vaginal dryness, hot flushes, abnormal menstrual bleeding, altered sleep and night sweats.
Increased risk of multiple ovulation (Twins)
May develop clomiphene resistance. Might respond better to letrozole.Pharmacokinetics: Half life for 5days
Letrozole
MOA: Aromatase inhibitor. Block oestrogen production by inhibiting enzyme CYP19A1 which converts testosterone and androstenedione into oestrogen.
Indications: Long term treatment to ER+ patients to prevent recurrence.
Helps induce ovulation. Inhibition of oestrogen blocks oestrogen mediated negative feedback to the HPO axis which increases follicle growth & maturation.
Can only be used on patients with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) under close observation of Transvaginal ultrasound every 48hrs.Contraindications: Breastfeeding and pregnancy.
Chronic use before menopause can result in osteoporosis.
ROA: Orally bioavailable
Side effects: Fatigue, headache, abnormal bleeding, hot flushes, mood swings, vaginal dryness and altered sleep.
Pharmacokinetics: Half life of 42hrs normally and 3-4 days in breast cancer paitents.
Types of GnRH receptor inhibitors
GnRH antagonists (cetrorelix, Ganirelix)
GnRH agonist (Nafarelin, Buserelin)
GnRH antagonist (cetrorelix, Ganirelix)
MOA: Inhibits GnRH receptor in pituitary gland, preventing release of FSH & LH
(Required for follicle Maturation & Ovulation)Delivered together with recombinant FSH to replace downregulation of endogenous FSH.
Indications: Used in IVF to block endogenous LH surge, preserving dominant follicle for times HCG trigger & oocyte pickup.
Contraindications: Breastfeeding & Pregnancy
ROA: Subcutaneous injection
Side effects: Chronic use in adolescents impairs bone formation
Cetreorelix half life 30 Hrs
Ganirelix half life 13 Hrs
GnRH agonist (Nafarelin, Buserlin)
MOA: Chronically activate GnRH receptor in pituitary gland, leading to long-term down regulation of FSH & LH production (prevent follicle maturation & ovulation)
Indication: Used in IVF to block Endogenous LH surge, preserving Dominant Follicle for times HCG Trigger & Oocyte pickup.
Treating precocious puberty & as Puberty blocker for Transgender care.
Induce chemical castration in Androgen Dependent Prostate Cancer & in Sex offenders.Contraindication: Breastfeeding, pregnancy.
ROA: Subcutaneous Injection & Implants, Nasal Spray (Nafarelin, Buserlin)
Side effects: Mimics Hypogonadism & acute side effects include hot flushes, decreased sex drive & Fatigue.
Chronic use in adolescents can impair bone formation, gonad & sexual development.
Promote ovarian follicle growth
Recombinant FSH
Recombinant FSH
MOA: Recombinant version of endogenous FSH to promote ovarian follicle growth
Indications: Used to increase number of growing follicles available for collection in IVF.
Contraindications: Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
ROA: Subcutaneous injection
Side effect: Headache, nausea, vomitting, bloating and weight gain.
Pharmacokinetics: half life of 30 hrs
Ovulation Induction in IVF
Human Chronic Gonadotropin (HCG)
Human Chronic Gonadotropin
MOA: Recombinant HCG bind to LH receptor and mimics Endogenous Surge to tripper Ovulation.
Indications: Used as part of Ovarian Stimulation Cycle to collect multiple follicles for IVF
Prepared as one-off injection to trigger final stage of follicle growth & Meiosis in preparation for oocyte pickup MUST OCCUR exactly 34-36 hours later.Contraindication: Polycystic Ovarian syndrome (PSOC)
ROA: one-off injection at the end of IVF
Side effect: Headache, Bloating. Risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) in PCOS patients
Pharmacokinetics: Half life of 2 days.
Recobinant LH half life: 90 min
HCG used instead of LH to reduce need for hourly dosage. Both HCG & LH interact with same receptors.
Induction of Labour
Dinoprostone
Dinoprostone (PGE2)
MOA: Promotes cervical ripening & uterine contraction.
Indications: Softening of cervix includes labour & shortens time from onset to delivery.
Contraindications: Oxytocin Administration
ROA: 0.5mg PGE2 gel every 6 hours, maximum of 1.5mg cumulative 24 hour dose.
Controlled-release vagina insert (10mg PGE2) release over 12 hours.Side effect: Uterine Tachysystole, Fetal Distress and uterine hyperstimulation
Indcution to abortion
Anti-progestin/ Selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRM) e.g. Mifepristone
SERM Mifepristone
MOA: orally active progesterone & glucocorticoid receptor antagonist.
Sensitizes Uterus to action of prostaglandins.Indications: Medical termination of pregnancy (Used in combination with prostaglandin), Crushing syndrome
Contraindications: Chronic Glucocorticoid therapy
ROA: Oral
Side effect: Abdominal pain Nausea, Headache, vomitting, Diarrhea, dizziness and fatigue.
Induction of erection (erectile dysfunction)
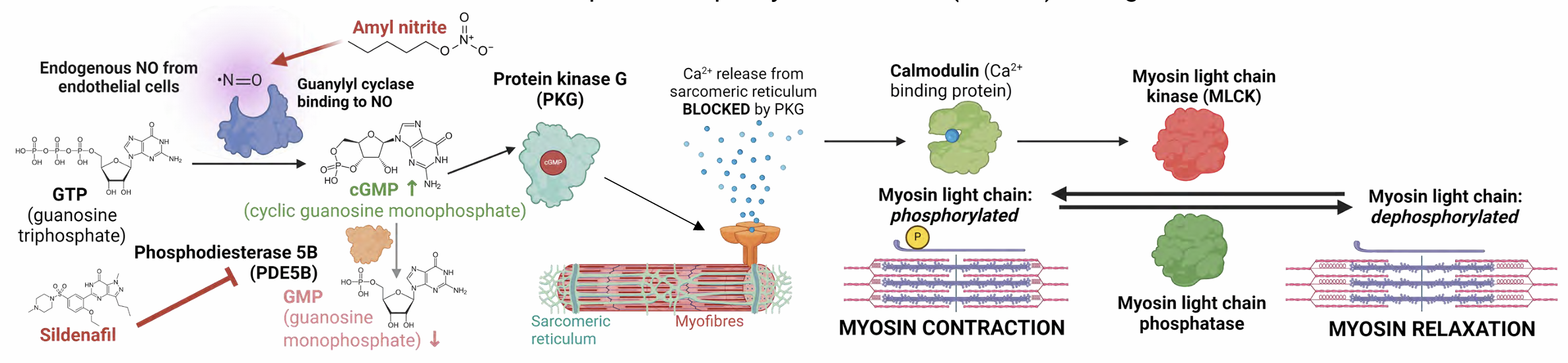
Sildenafil (Viagra)
Sildenafil (Viagra)
MOA: Inhibits enzyme phosphodiesterase 5B to prevent hydrolysis of cGMP into GMP, activating PKG which blocks Ca2+ release & promotes Arterial smooth Muscle relaxation to increase blood flow & stimulate erection.
Indications: Erectile dysfunction in MEN
Contraindications: Any form of nitrates (e.g. Nitrate Glycerine, Amyl nitrate).
Production of cGMP from GTP is mediated by Guanylyl cyclase which is activated by nitric oxide. Nitrates act as Nitrate donor and can cause additional cGMP production leading to potentially hypotensive effect.ROA: orally bioavailable
Side effect: Nausea, headache,dizziness, reduction of blood pressure, associated with non arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)
Pharmacokinetics: Half life of 3-5hours