ETSU Organic Lab 2 Midterm
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
How to Calculate IHD and what does it indicate
IHD=(2x+2-y)/2
where x= carbons
y= hydrogens
for each halogen, add 1 H
for reach N, add 1H and 1C
ignore all Oxygen
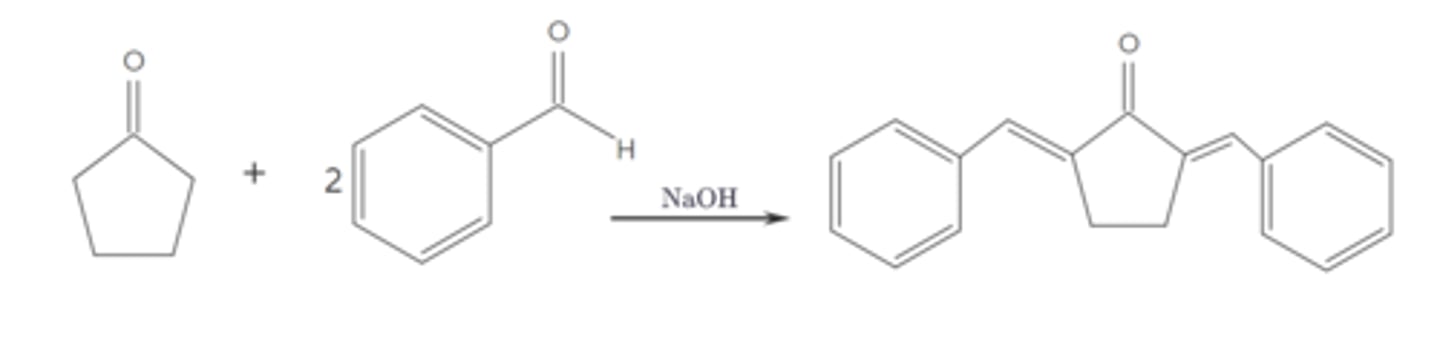
Draw the structure of the aldol condensation between cyclopentanone and two equivalents of benzaldehyde
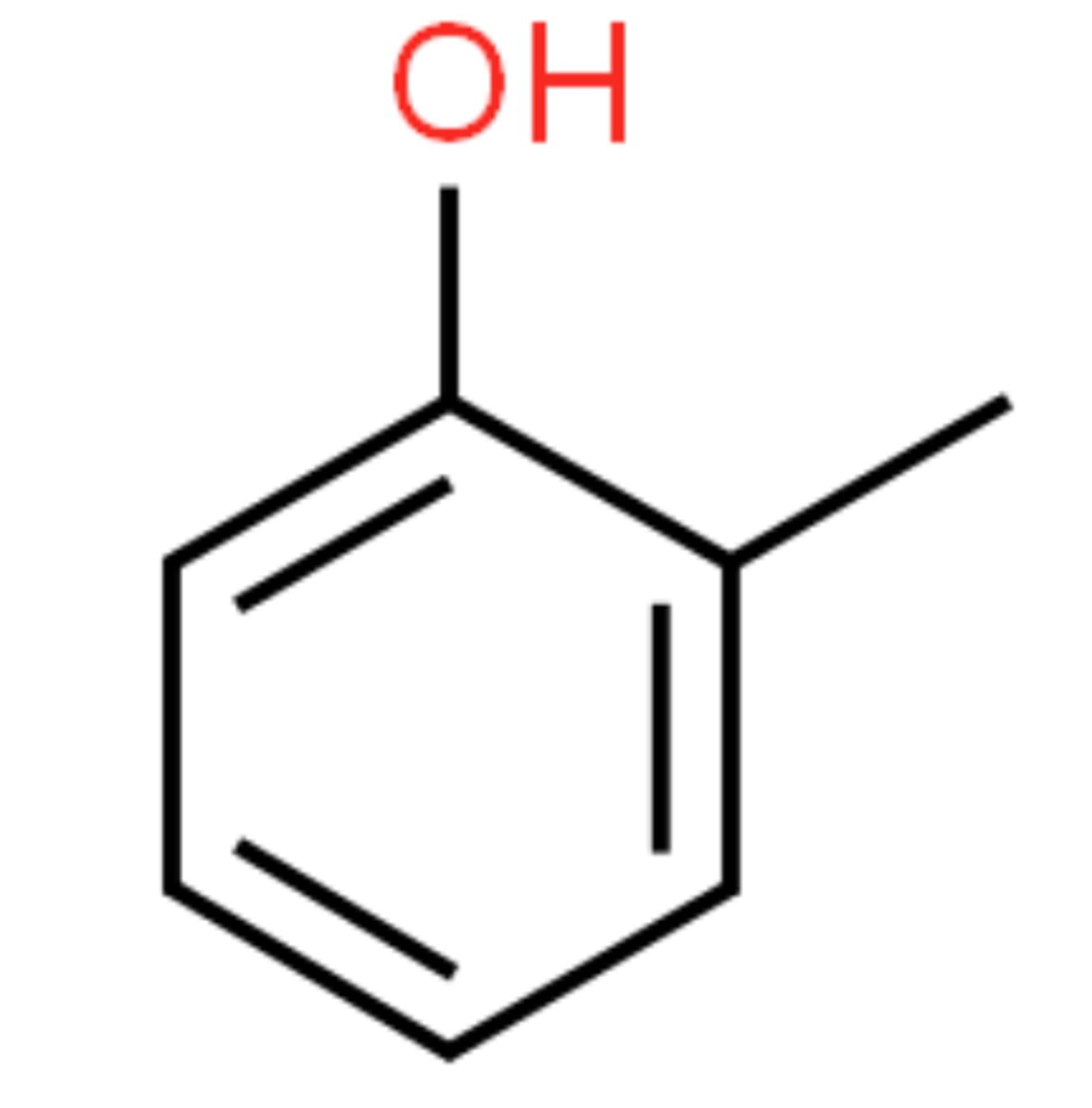
Draw the structure of 2-methylphenol
Explain how infra-red spectroscopy can distinguish between acetone (CH3-CO-CH3) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH).
The functional groups absorb different infrared radiation, therefore their bonds vibrate at different frequencies.
- Functional group OH would be detected in ethanol 3100-3700
- Acetone will signal at 1680 -1750 c=o
What is a non-equivalent hydrogen?
"Equivalent hydrogens are H -atoms that are completely interchangeable as to their role in the molecule"
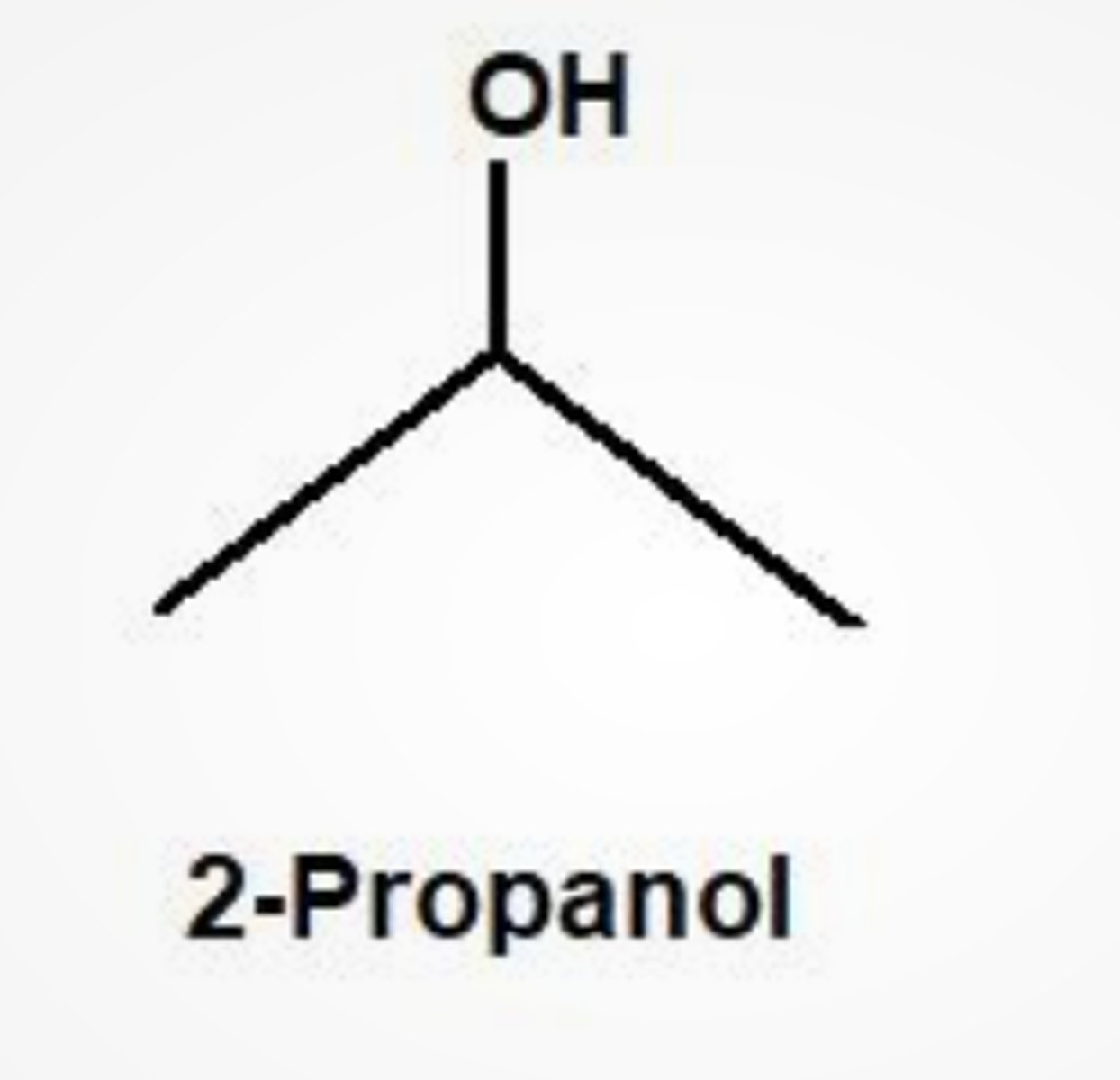
Draw the structure of 2-propanol
.a) how many sets of non-equivalent hydrogens does 2-propanol have?
b) how many 1H NMR signals would 2-propanol give?
a) 3
b) 3
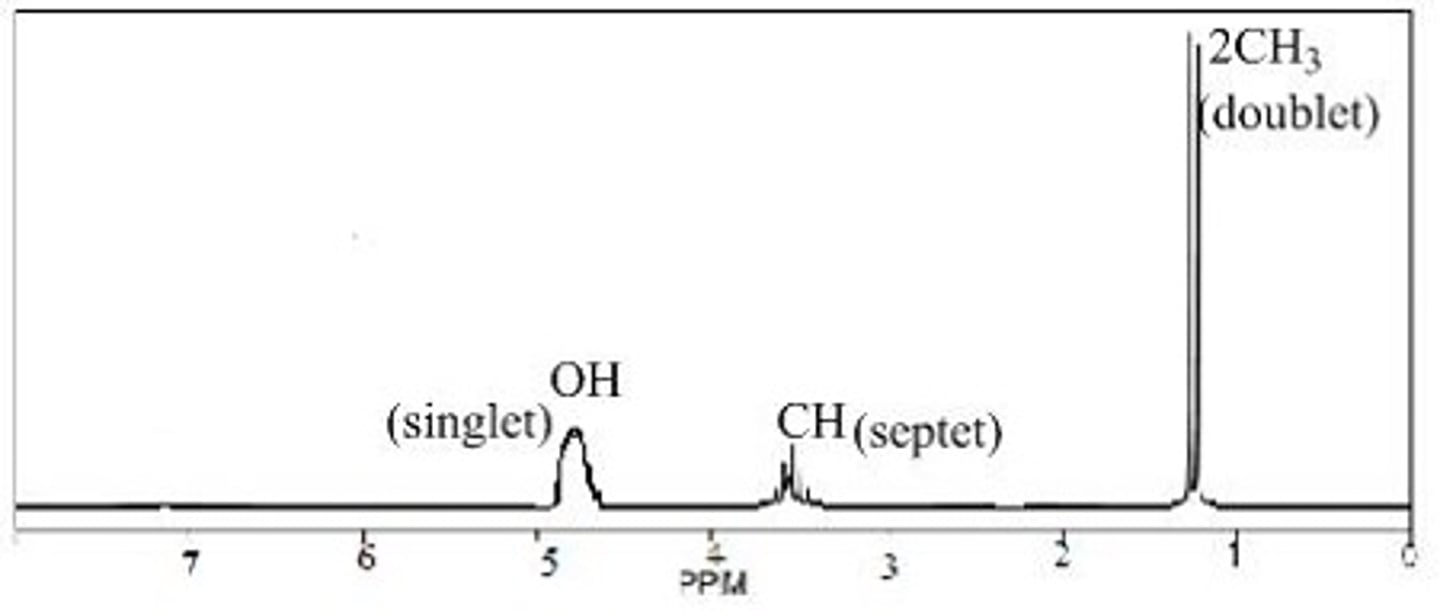
Sketch the H NMR spectrum of 2-propanol.
singlet around 5, around 4 ppm there are 5 short peaks with 4 splits, doublet around 1 for (CH3)2
For each of the following compounds, indicate the number of structurally distinct groups of equivalent carbon atoms and the number of distinct groups of equivalent hydrogens:

Write the structure of the organic product in the tollen's test of benzaldehyde
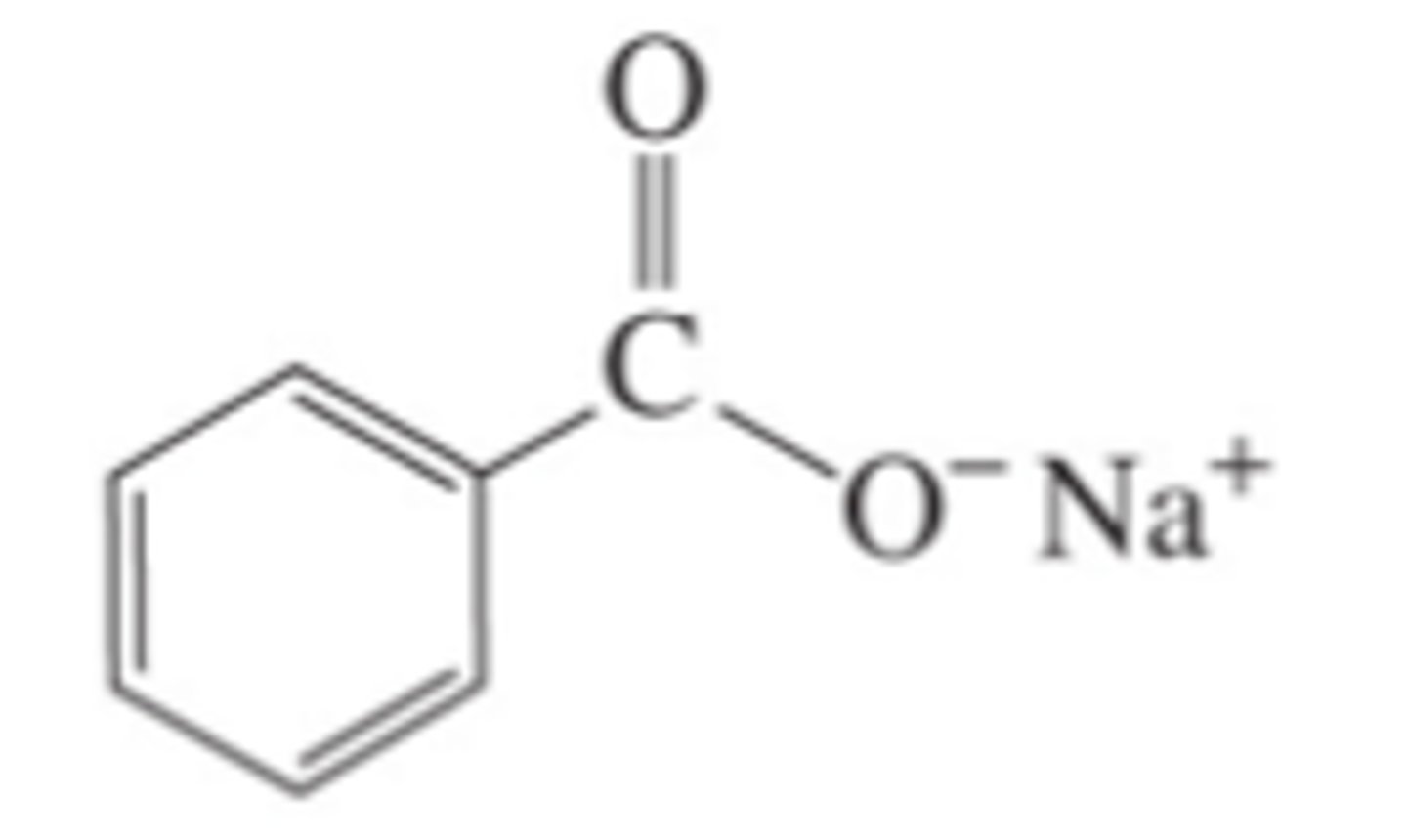
Describe the indication of the positive test of the following:
Tollen's test
Bisulfite test
Schiff test
Iodoform test
T- silver shein forms
B- white, solid, precipitate forms
S- magenta color
I- yellow precipitate forms
Which of the following gives a positive bisulfite test?
Acetone
Propanal
Acetophenone
2-butanone
cyclopentanone
Acetone, propanal, 2-butanone, and cyclopentanone
Will propanol give a positive Schiff test?
Yes
Explain the purpose of preparing derivatives of the unknown
It is easier to accurately compare the values for (MP,BP,etc) to those found in the literature.
What does a positive iodoform test indicate when a it becomes cloudy and yellow?
Ketone present
describe a chemical test that can distinguish between butanal & 2-butanone
butanal is aldehyde, 2-butanone is ketone. use tollen's test
Why do we use sodium carbonate during extraction of caffeine from tea or coffee?
Sodium carbonate ensures that only the caffeine is extracted, leaving all other components water soluble.
Given the solubility of caffeine in water is 2.2 mg/mL at 25 C and 670 mg/ml at 100 C, and given that a 2.4 gram tea bag contains on avg 50 mg of caffeine: calculate the minimum volume of boiling water needed to remove all caffeine from the tea bag.
1 ml/670 mg = x ml/50mg
50 mg/670 mg = 670 mg X ml
x = 0.0746 mL H2O
Percent recovery of caffeine
(weight of purified caffeine after sublimation/weight of crude caffeine) x 100% =
Caffeine content calculation
(weight of purified caff/weight of tea bags) x 100
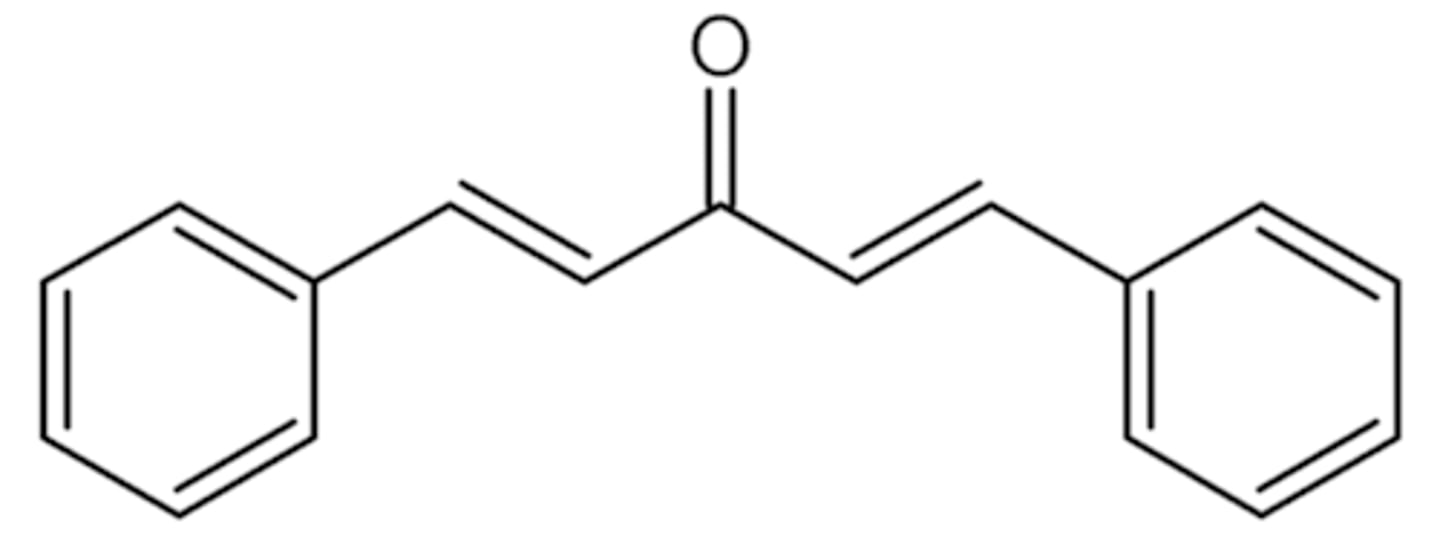
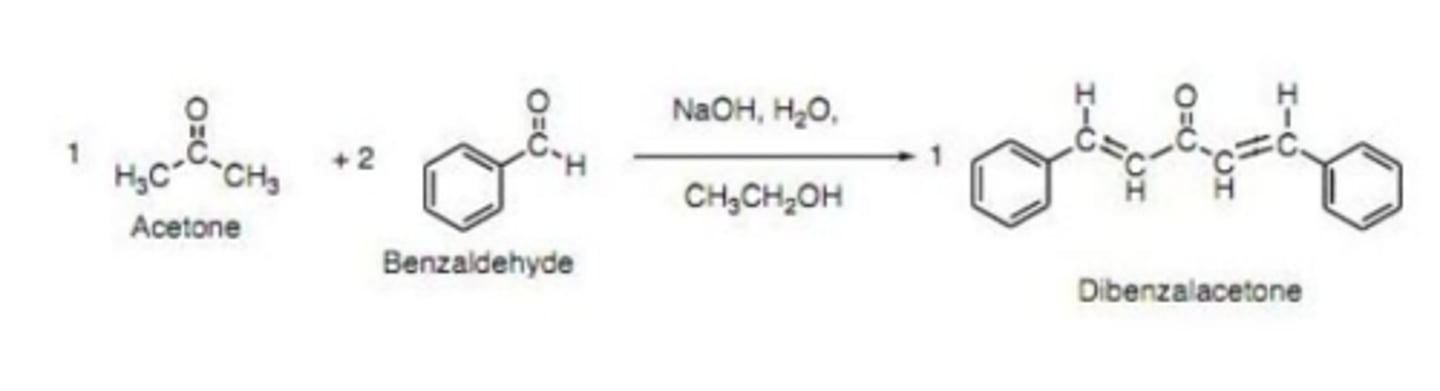
Draw the structure of dibenzalacetone
Write a complete chemical equation of base-catalyzed aldol condensation involving two molecules of propanal:
Enolate Ion
Resonance structure of a carboanion in which the negative change is on an oxygen atom.
Aldol molecule
compound containing an aldehyde and alcohol group
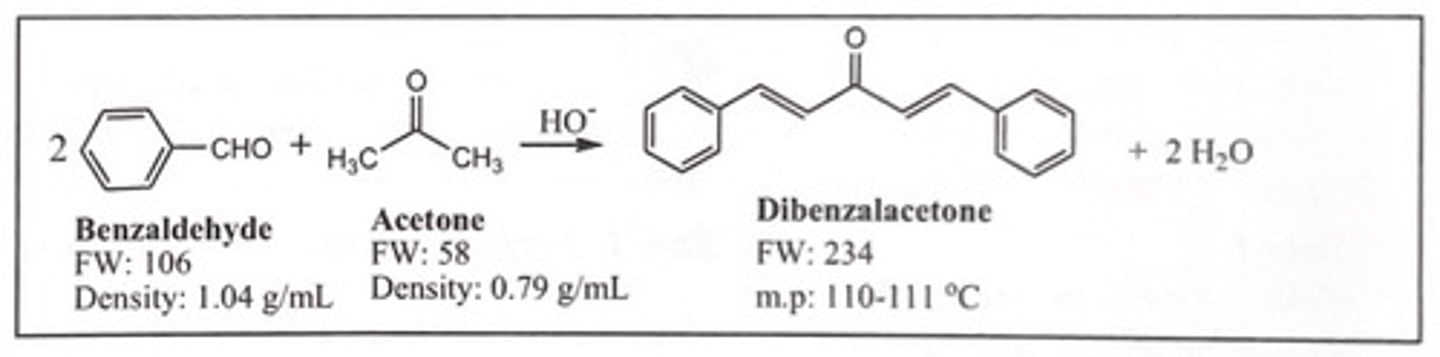
Write a chemical equation of the synthesis of dibenzalacetone
Word document number 5
% yield =
moles product/theoretical yield
Consider the following two compounds:
CH3-CH2-CH3 and CH3-CH2-CHO
a) explain how you can use IR to distinguish between the two compounds:
b) predict the expected splitting pattern for each type of hydrogen in compound II:
c) How many H NMR signals would compound 2 give?
d) How many C NMR signals would compound 1 give?
a) The second compound will have an aldehyde peak at 1740-1690 that the first compound will not.
b) Broad at 9-10, quartet at 2.4-2.5, triplet at 1.05-1.1
c) 3
d) 1
. An unknown compound with a molecular formula C3H7Cl gives two H NMR signals: 1.55 doublet and 4.1 septet. Propose a structure for the unknown; explain your answer:
a) an unknown compound (X) with a molecular formula C4H10O fives four C NMR signals: 10.0, 24.0, 33.0 and at 70.0 ppm. Propose a structure for the unknown; explain your answer:
b) An isomer of compound X (in part a) gives three C NMR signals are 20.0, 30.0, and 70.0 ppm. Propose a structure for this isomer and explain your answer:
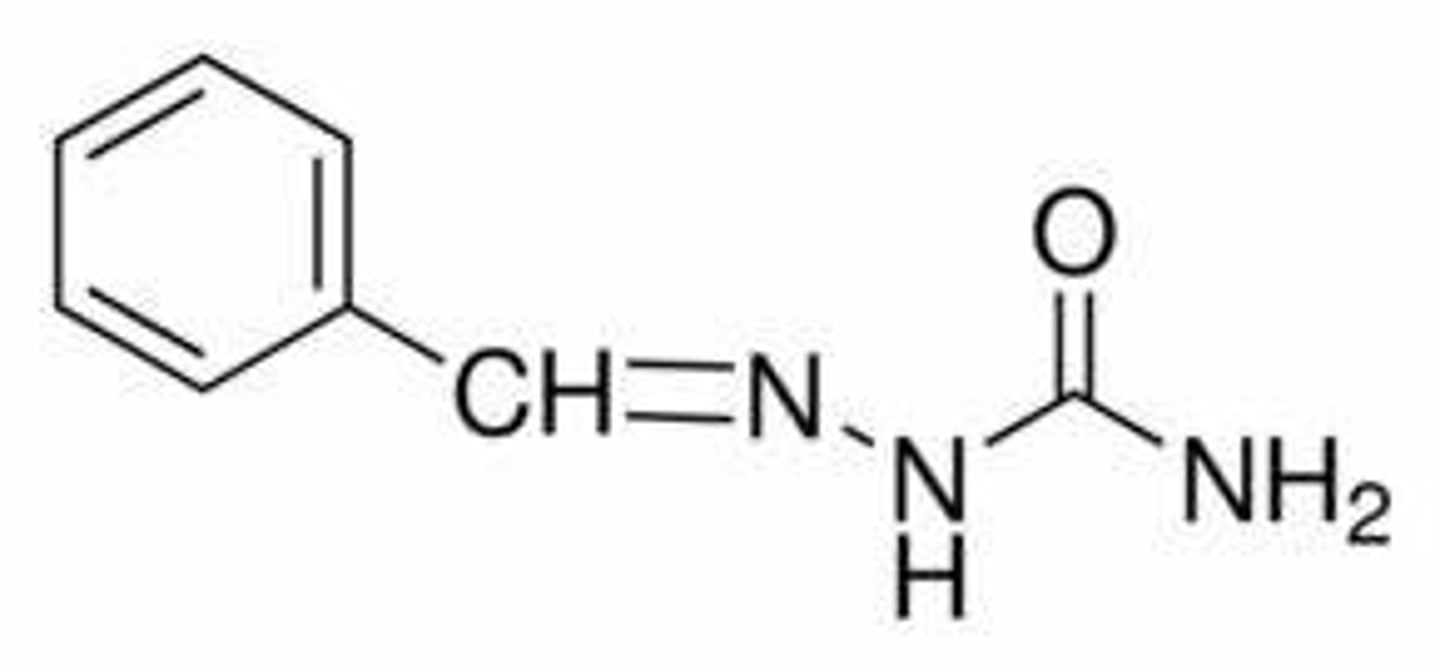
Write the structure of the semicarbazone derivative of benzaldehyde:
Describe a chemical test that can distinguish between butanal, 2-butanone
Tollen and Schiff
Explain how you can confirm if the derivative is pure enough
If melting points are equivalent or close to the values found in literature, the derivative is pure enough.
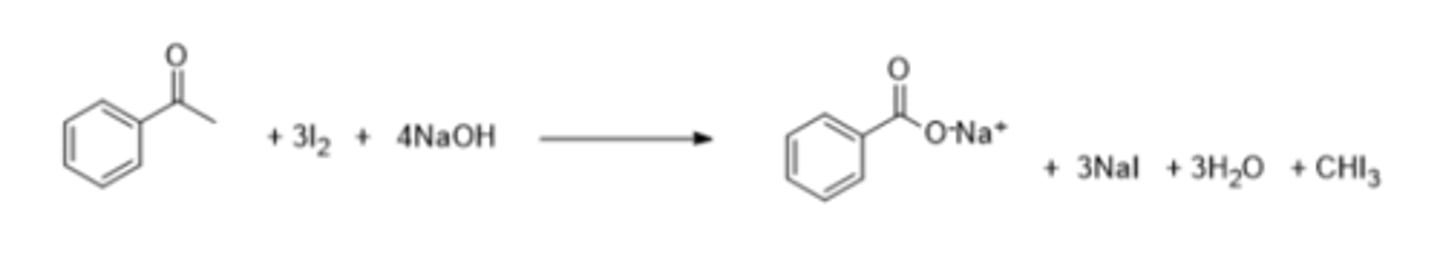
Write a chemical equation for the reaction between iodoform reagents and acetophenone (Ph-CO-CH3):
Why is it important not to shake the two layers vigorously during extraction of the aqueous tea solution with dichloromethane?
To prevent emulsion formation.
Explain why sublimation is performed in a filter with a rubber bulb on the side arm, rather than using an Erlenmeyer flask.
Sublimation converts solid to liquid gas and the rubber bulb can collect these gases, whereas if it took place in an Erlenmeyer flask the gases would escape.
Why did you have to cool the aqueous tea solution before adding dichloromethane?
To prevent evaporation of dichloromethane
Sometimes emulsion is formed during extraction which prevents the two layers from separating. List two things that may cause emulsion formation:
Vigorously mixing the two layers and/or too much drying reagent
Write the structure of monobenzalacetone:
Benzene ring. If the top carbon of the benzene ring is carbon one, move one carbon in the clockwise direction. Here, draw a carbon chain with four additional carbons. Between the second and third carbon in the chain, there is a double bond. On the third carbon there is a double bond to an oxygen atom.
Explain with a chemical equation the role of NaOH in the synthesis of dibenzalacetone:
NaOH removes the alpha proton from acetone to produce the enolate.
What is the purpose of washing the product with cold water?
Remove excess NaOH
IR Absorption C=O Aldehyde
1740 - 1690
IR Absorption C=O Ketone
1750 - 1680
IR Absorption C=O Ester
1750 - 1735
IR Absorption C=O Carboxylic Acid
1780 - 1710
IR Absorption C=O Amide
1690 - 1630
IR Absorption N-H Amide
3700 - 3500
IR Absorption C=N Amine
3500-3300
Tollen's Test
Aldehyde can reduce Ag+ to Ag0
Iodoform Test
methyl ketones
Bisulfite Test
Aldehyde
Schiff's tests for...
aldehydes
explain the purpose of using sodium carbonate during the extraction of caffeine from tea or coffee
tannins are acidic and react w basic sodium carbonate & form their respective salts. these salts remain in the solution and caffeine can be easily extracted by DCM
claisen-schmidt condensation
an aldol condensation between aldehydes and ketones
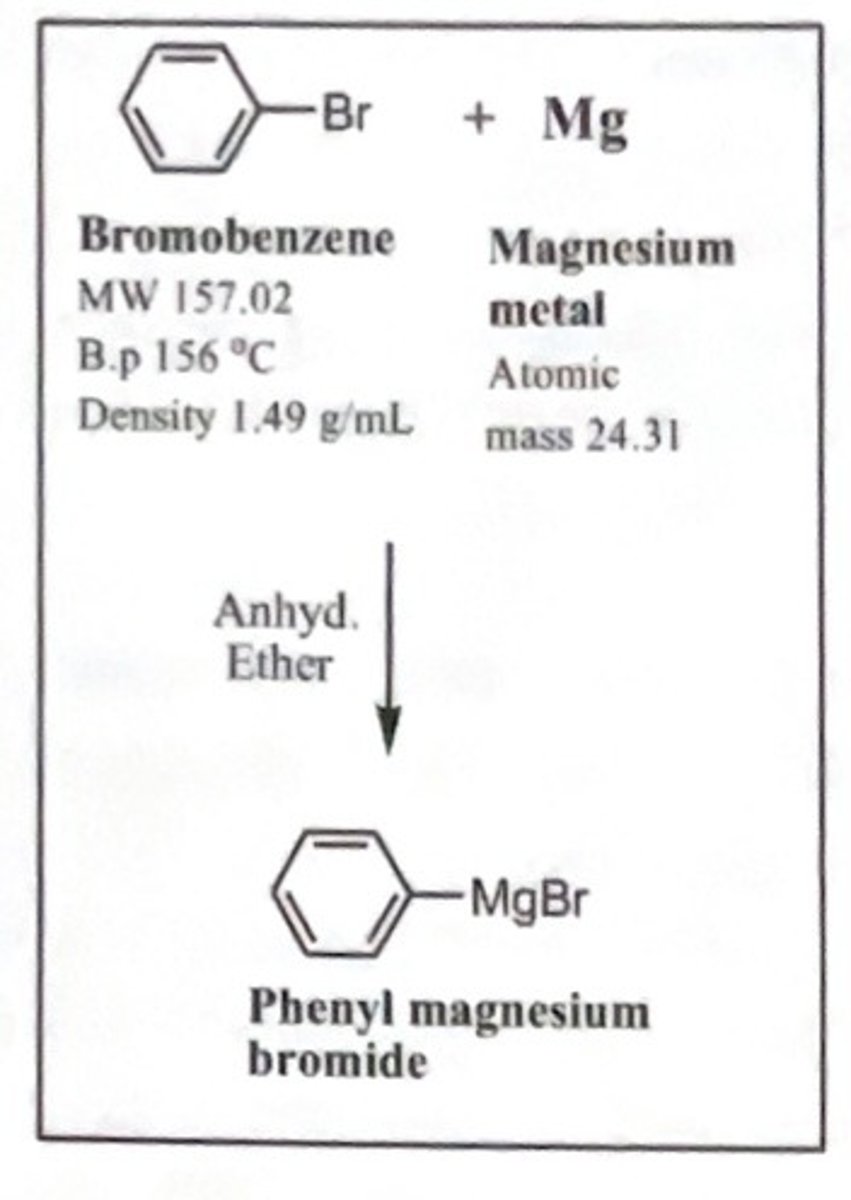
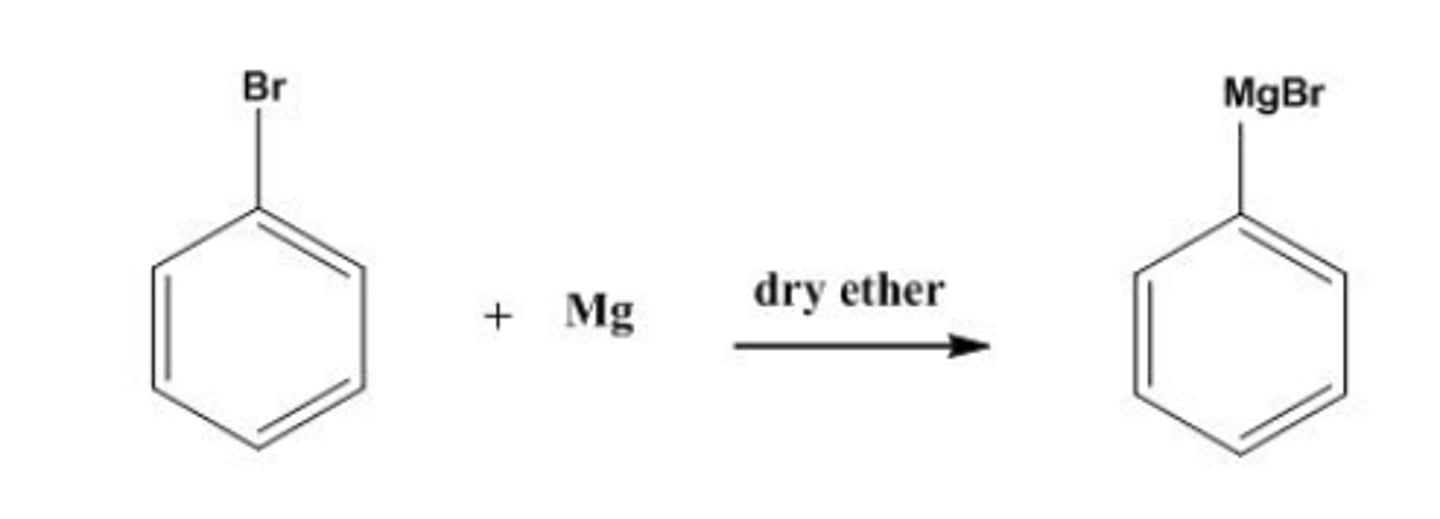
preparation of grignard reagent
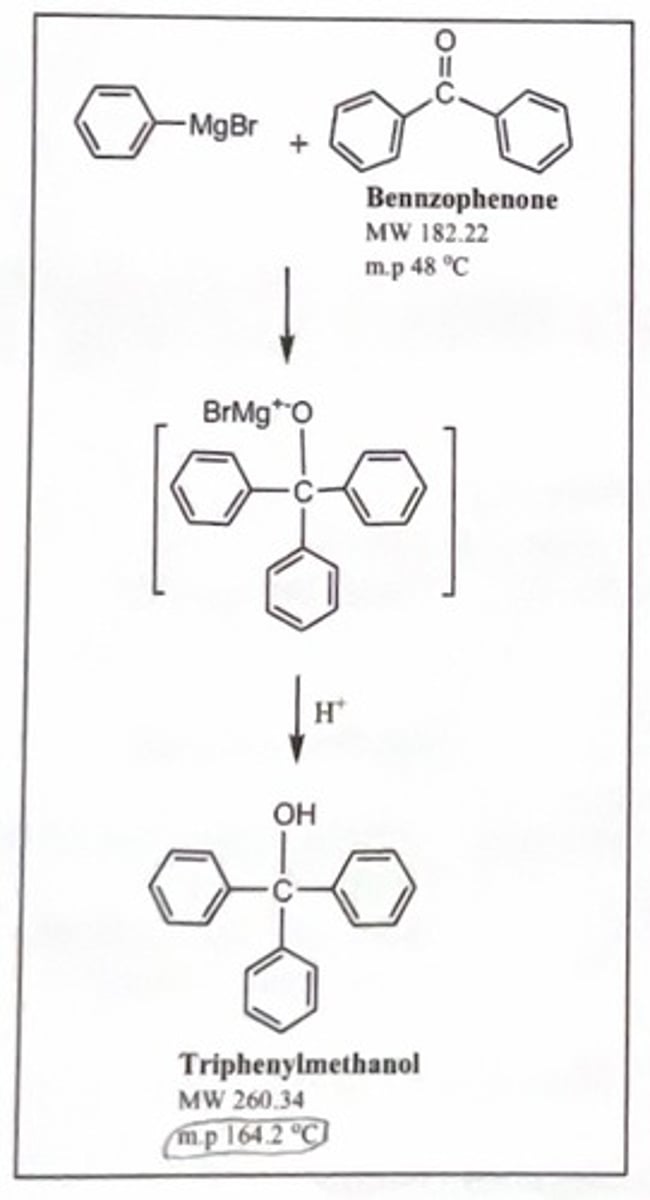
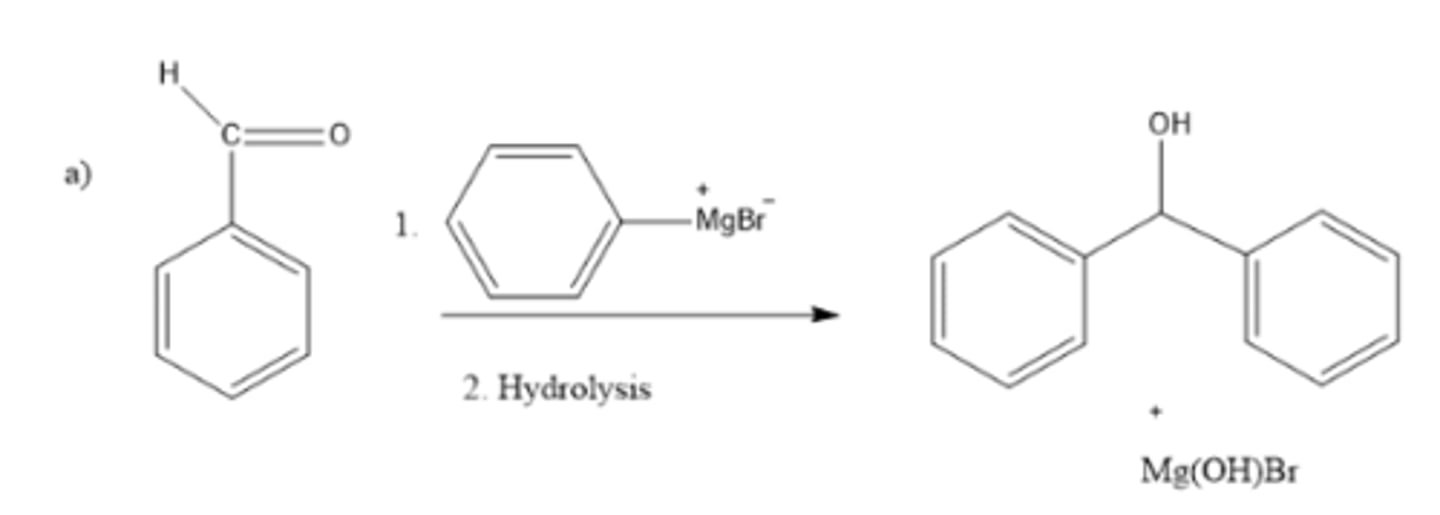
reaction of grignard reagent with benzophenone to form triphenylmethanol
what are the safety hazards of diethyl ether
highly flammable volatile liquid
explain why diethyl ether used in the grignard reaction must be anhydrous
if the solvent used in the synthesis is not anhydrous, the grignard reagent will react quickly with water (and be destroyed) as soon as it is formed
what product would be formed if PhMgBr reacts with ethanol
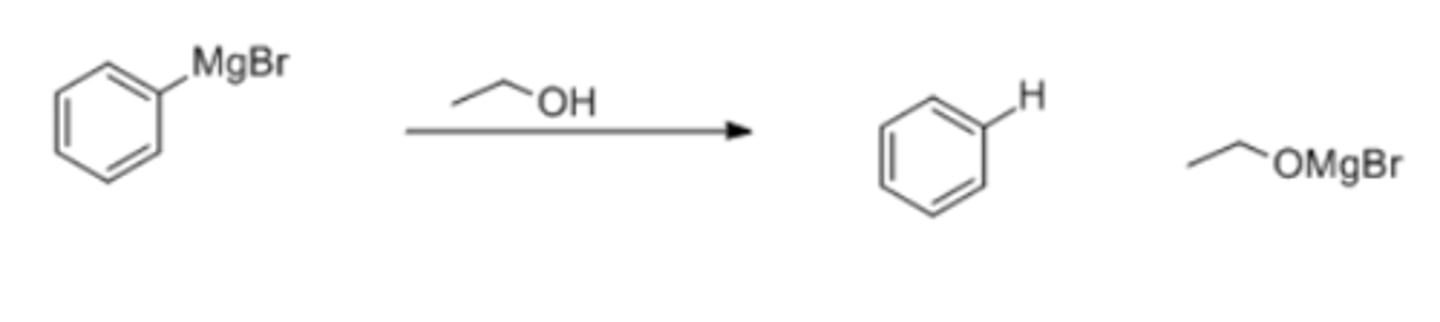
draw structure of grignard reagents formed from rxn of magnesium with chlorobutane

draw structure of grignard reagents formed from rxn of magnesium with bromobenzene
write a chemical equation showing the rxn b/t PhMgBr and benzaldehyde (Ph-CHO) followed by hydrolysis
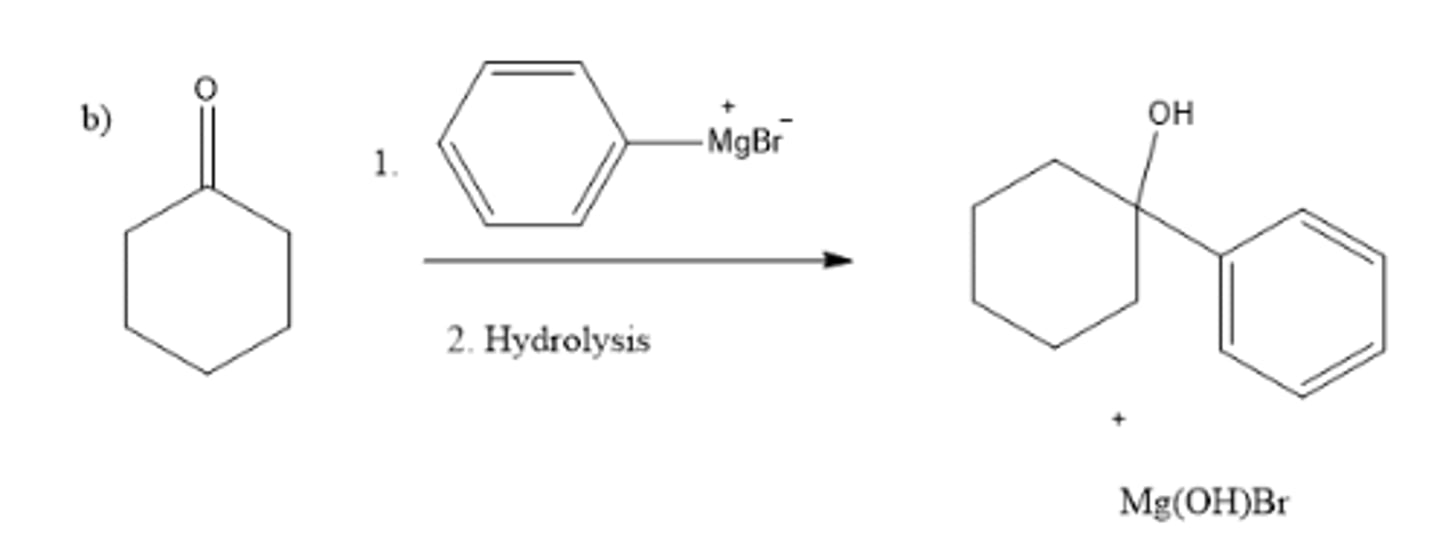
write a chemical equation showing the rxn b/t PhMgBr and cyclohexanone followed by hydrolysis
Endo And Exo - Diels-Alder Reaction
as it involves a transition state w/maximum overlap between pi bonds.