2 - pH & Buffers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
⬇pH = __ Proton concentration
⬇pH = ⬆️ Proton concentration
what’s the formula regarding pH and H+?
pH = -log[H+] / [H+] = 10-pH
mM = 10 _
μM = 10 _
nM = 10 _
mM = 10-3
μM = 10-6
nM = 10-9
at lower pH values, more __ are present to __ different functional groups
at lower (⬇) pH values, more H+ are present to protonate different functional groups
what does pKa values measure?
what is the formula for pKa?
measures the strength of an acid (HA), tells the pH at which a functional group loses/gains H+
pKa = -log Ka, where Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA]
Ka = acid dissociation constant
[H+] = concentration of H+
[A-] = concentration of conjugate base (deprotonated form of acid)
[HA] = concentration of undissociated acid
if pH < pKa:
if pH > pKa:
if pH = pKa:
if pH < pKa: mostly protonated
if pH > pKa: mostly deprotonated
if pH = pKa: equal probability of protonated/deprotonated species
strong acids have _ Ka and _ pKa
strong acids have ⬆ Ka (high dissociation) and ⬇ pKa → donate protons readily, it will be deprotonated @ physiological pH
which functional groups are neutral when protonated at pH = 1.0?
pH = 1.0 is highly acidic, most groups with pKa values > 1 will be protonated
e.g. -COO- → COO, -NH2 → NH3+
one can also be protonated multiple times & have multiple pKa values
What is Isoelectric Point, what does it measure?
What’s the formula?
Isoelectric point (pl) is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge → a zwitterion is present. (+ & - charges on the molecule are balanced)
pl = (pKa1 + pKa2) / 2
(pKa1 + pKa2) = the average of 2 pKas around the neutral species
pKa1 = pKa for 1st proton lost
pKa2 = pKa for 2nd proton lost… so on
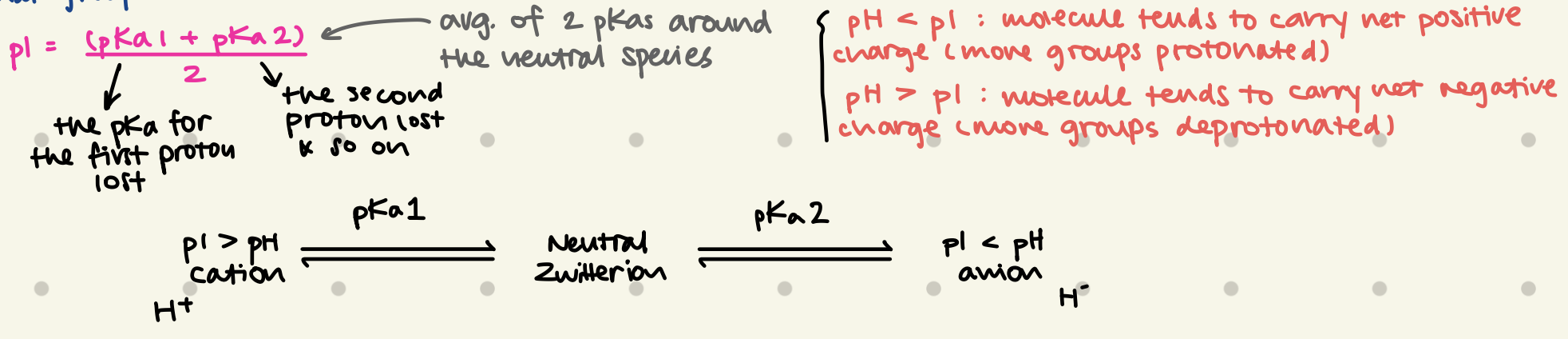
What’s a Zwitterion?
a neutral molecule that has separate + & - charged functional groups
pH < pl:
pH > pl:
pH < pl: molecule tends to carry net positive charge (more groups protonated) - cation
pH > pl: molecule tends to carry net negative charge (more groups deprotonatd) - anion
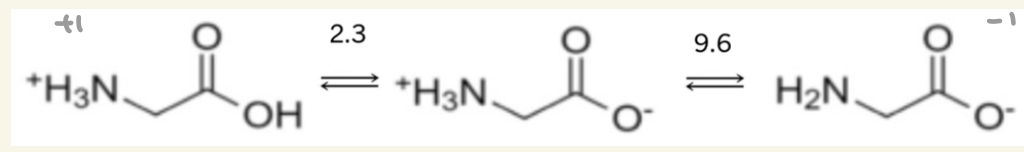
calculate the pl
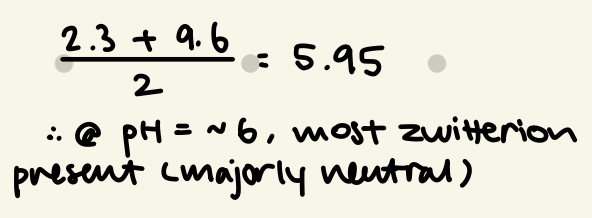
What’s the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation? What does it measure?
pH = pKa + log ([A-]/[HA])
x = log → 10x
determines the pH of a solution depending on the amount of ionization of a weak acid (protonated [HA] vs. deprotonated [A-])
can be used to determine the pH of a mixture of weak acid & conjugate base
![<ul><li><p><strong>pH = pKa + log ([A<sup>-</sup>]/[HA])</strong></p><ul><li><p>x = log → 10<sup>x</sup></p></li></ul></li><li><p>determines the pH of a solution depending on the amount of ionization of a weak acid (protonated [HA] vs. deprotonated [A<sup>-</sup>])</p></li><li><p>can be used to determine the pH of a mixture of weak acid & conjugate base</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cbfda2b7-3072-475b-b1b0-20ec2e1c7878.png)
What’s a Buffer? When are they most effective?
mixture of weak acids & conjugate bases that can resist pH changes, maintaining a protein’s structure/function
by neutralizing small addition/loss of H+, keeping pH stable
most effective at pKa (within range of ±1 pH unit around pKa)
H2O is a poor buffer - lacks significant amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base

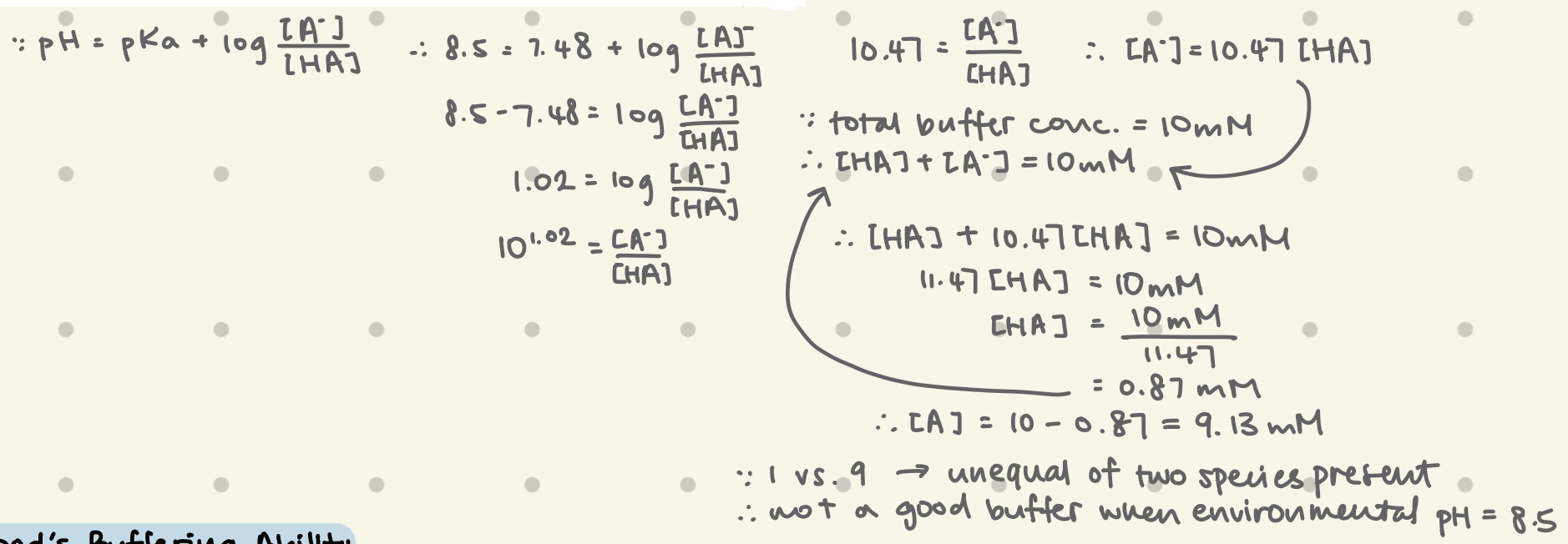
What’s the equation for Total buffer concentration?
Ctotal = [HA] + [A-]
what’s the main buffering species in Blood?
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
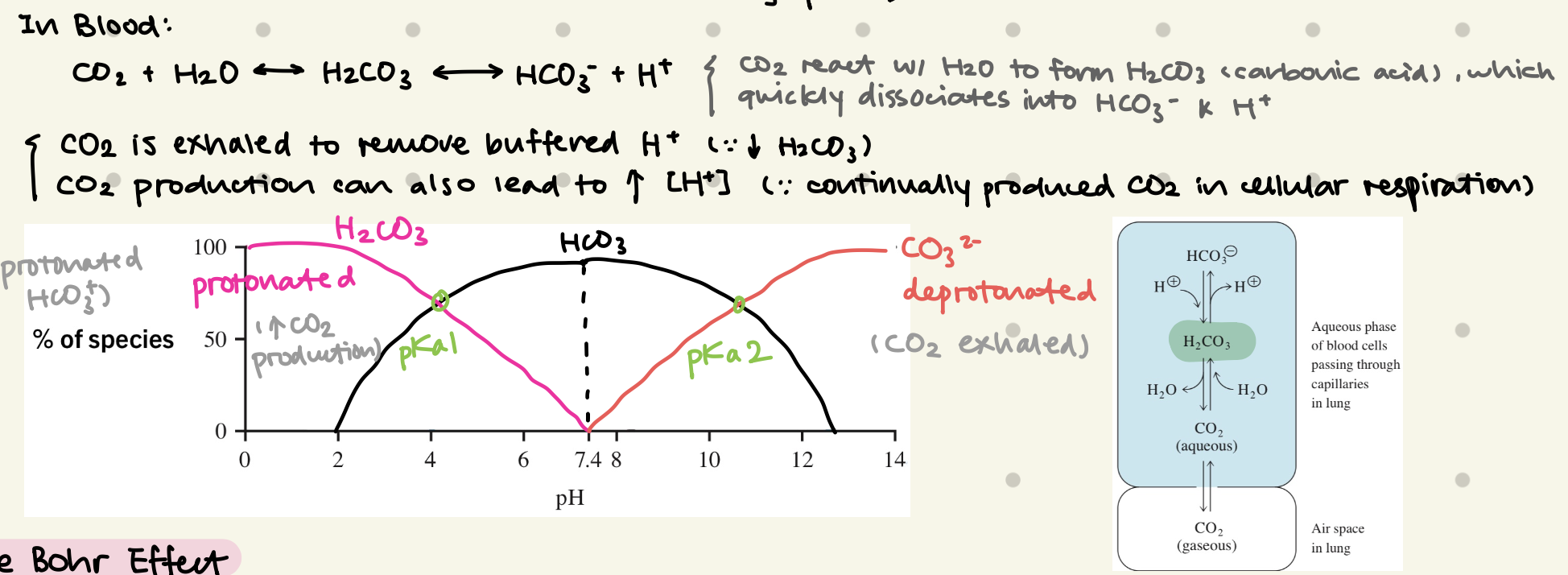
what’s the Bohr Effect?
pH can affect oxygen-carrying ability of Hb (hemoglobin)
⬇ blood pH / ⬆ blood CO2 = ⬇ Hb affinity for O2, therefore ⬆ Hb release O2