3 - Gene Segregation and Interaction
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
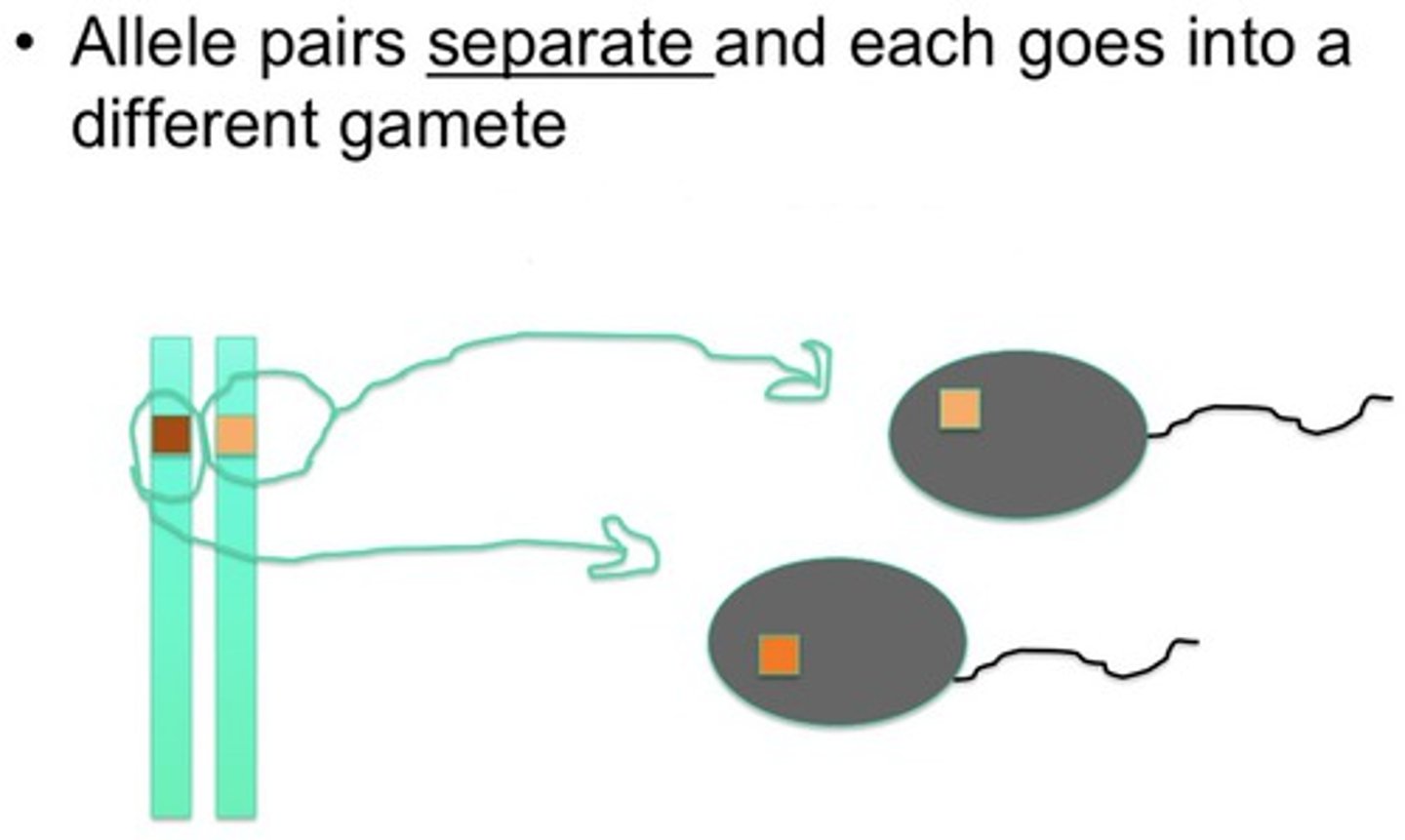
Law of Segregation
When an organism makes gametes, each gamete receives just one copy, which is selected randomly.
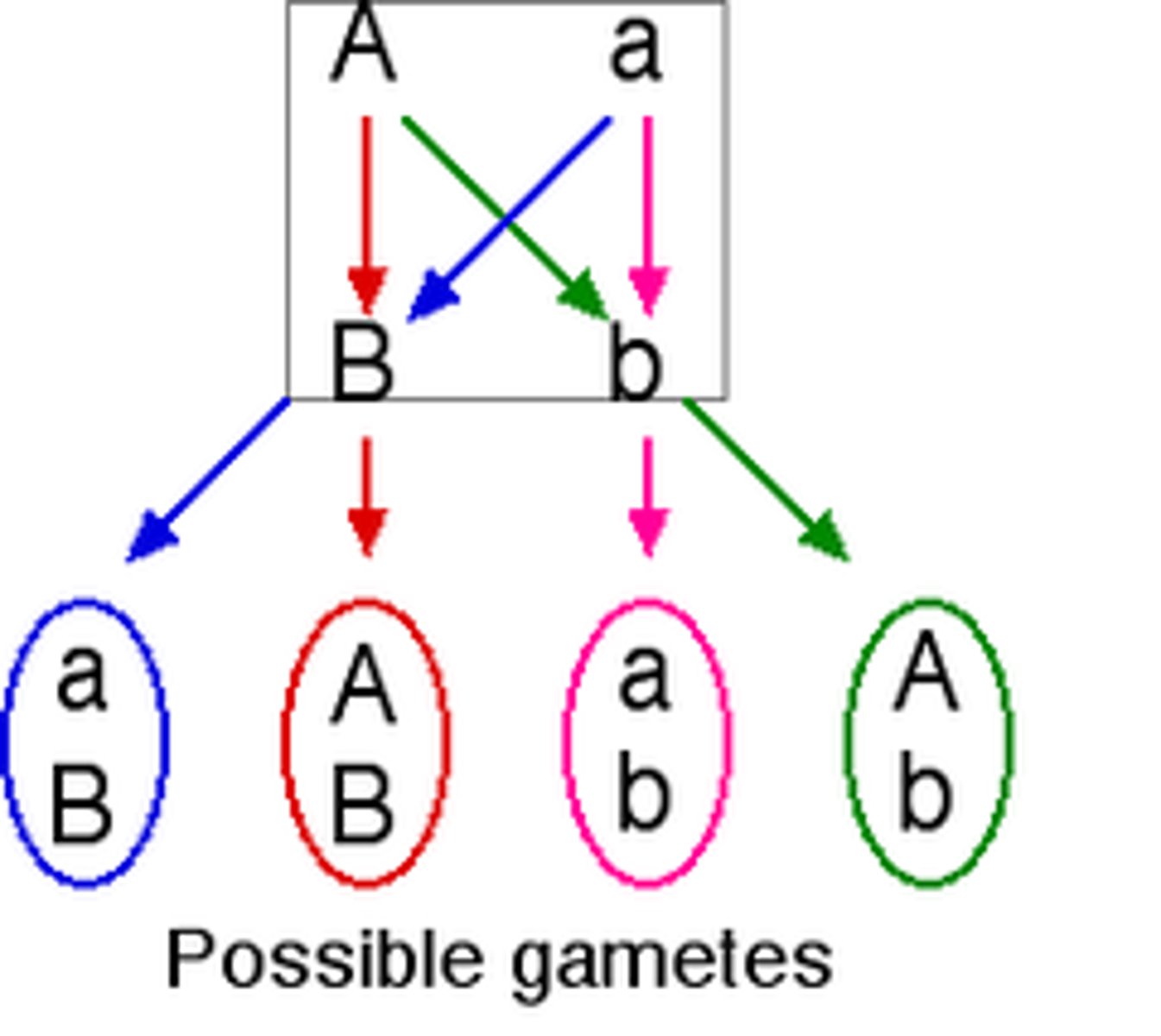
Law of independent assortment
genes do not influence each other with regard to the sorting of alleles into gametes: every possible combination of alleles for every gene is equally likely to occur.
Gene
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and determines some characteristic of the offspring.
Allele
One of two or more versions of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
Locus
The specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or allele is located.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual, representing the alleles inherited from both parents for a specific trait.
Phenotype
The observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an individual, determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a particular gene.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are similar in shape, size, and genetic content, pairing during meiosis.
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations of a genetic cross between two organisms.
complete dominance
offspring has a dominant allele that's what the phenotype shows
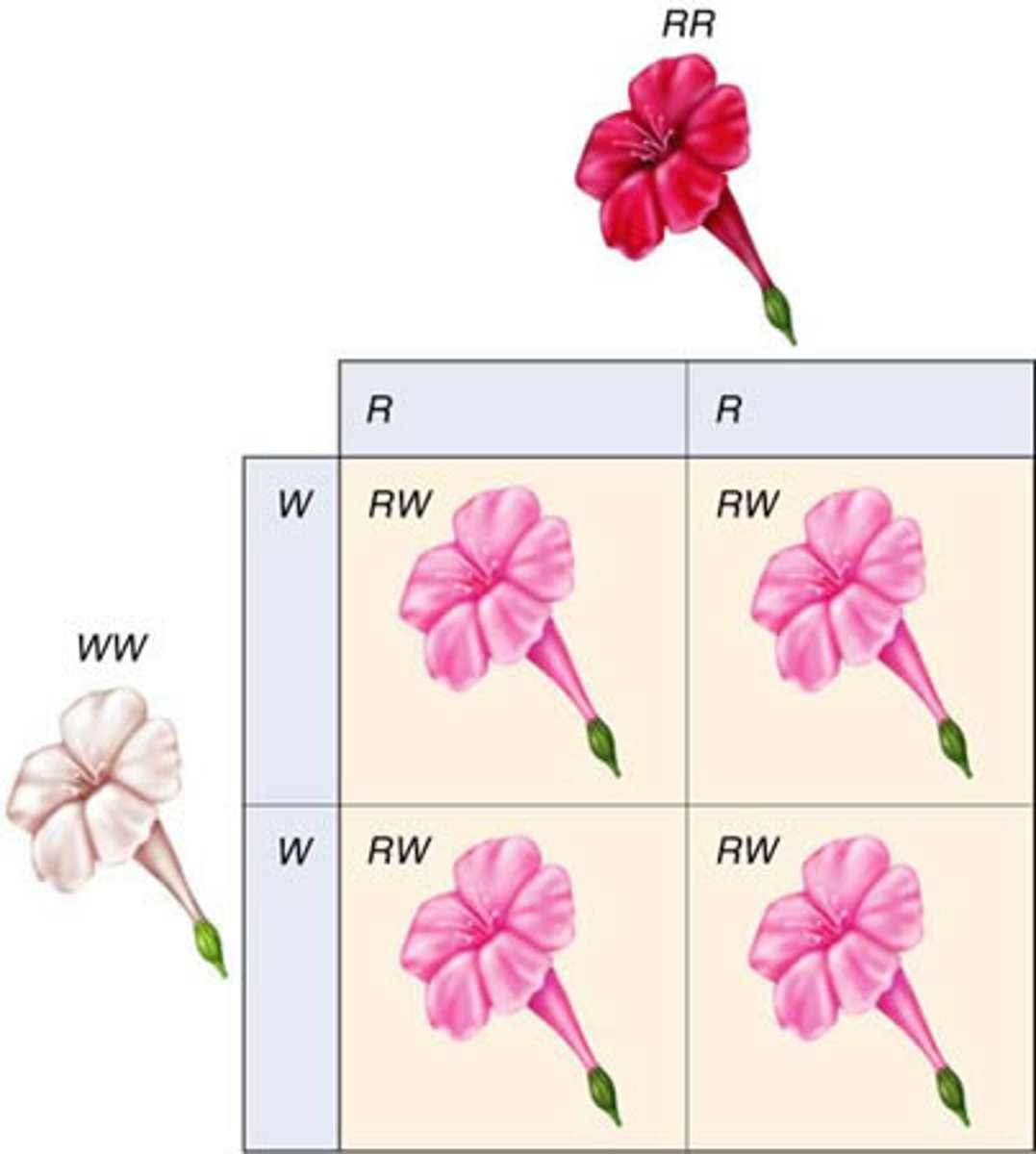
Incomplete Dominance
The trait of both dominant and recessive mixes (ex. purple and white will become pink)
Overdominance
Heterozygotes have higher fitness than homozygotes.

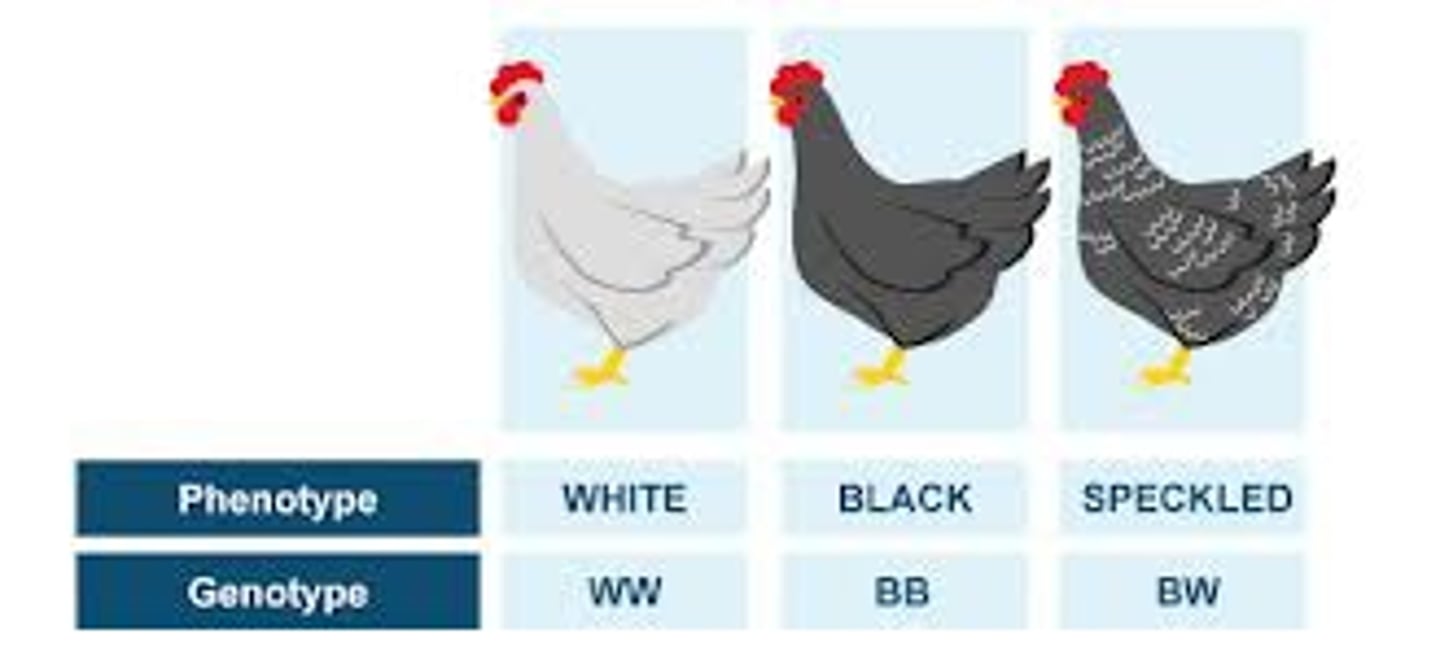
Co-dominance
both traits are expressed
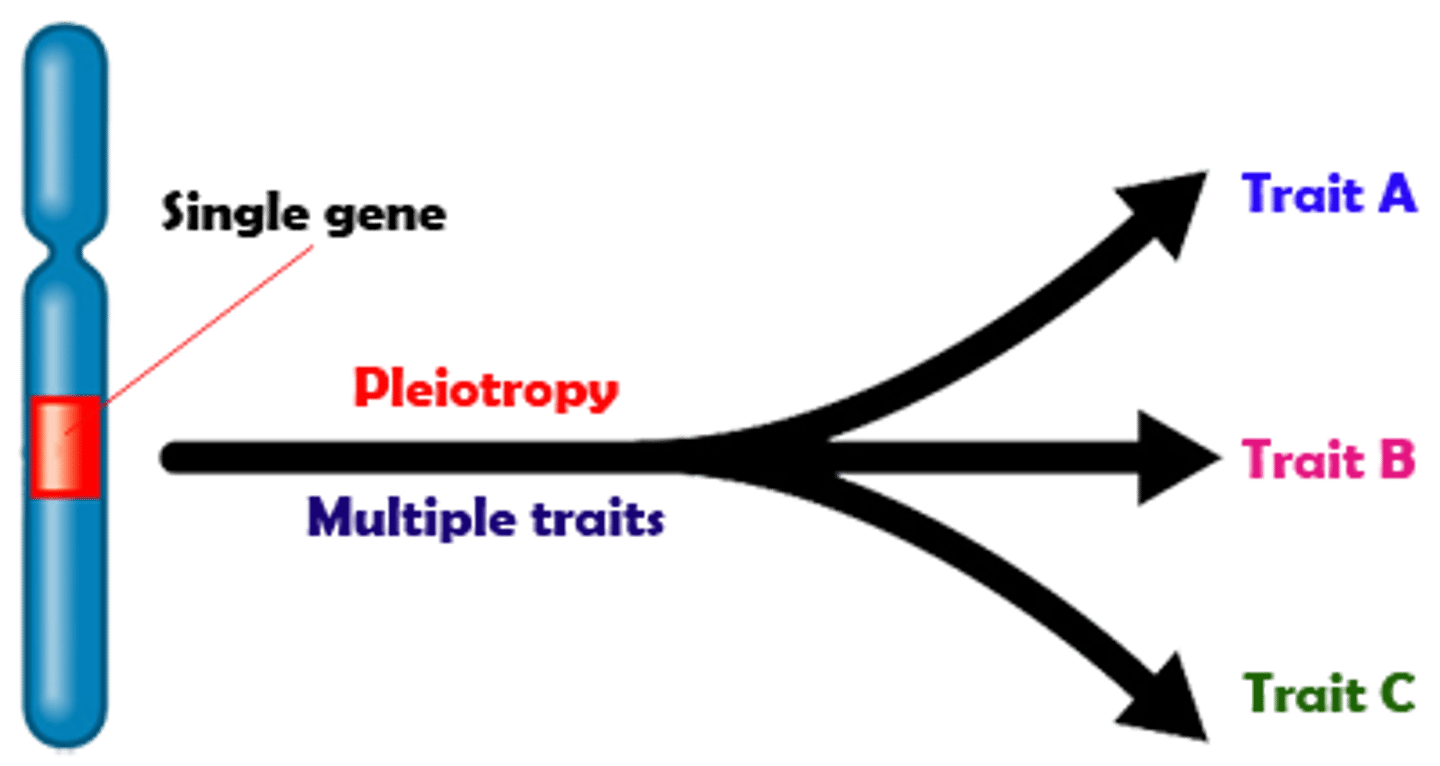
pleiotrophic genes
genes that affect more than a single trait
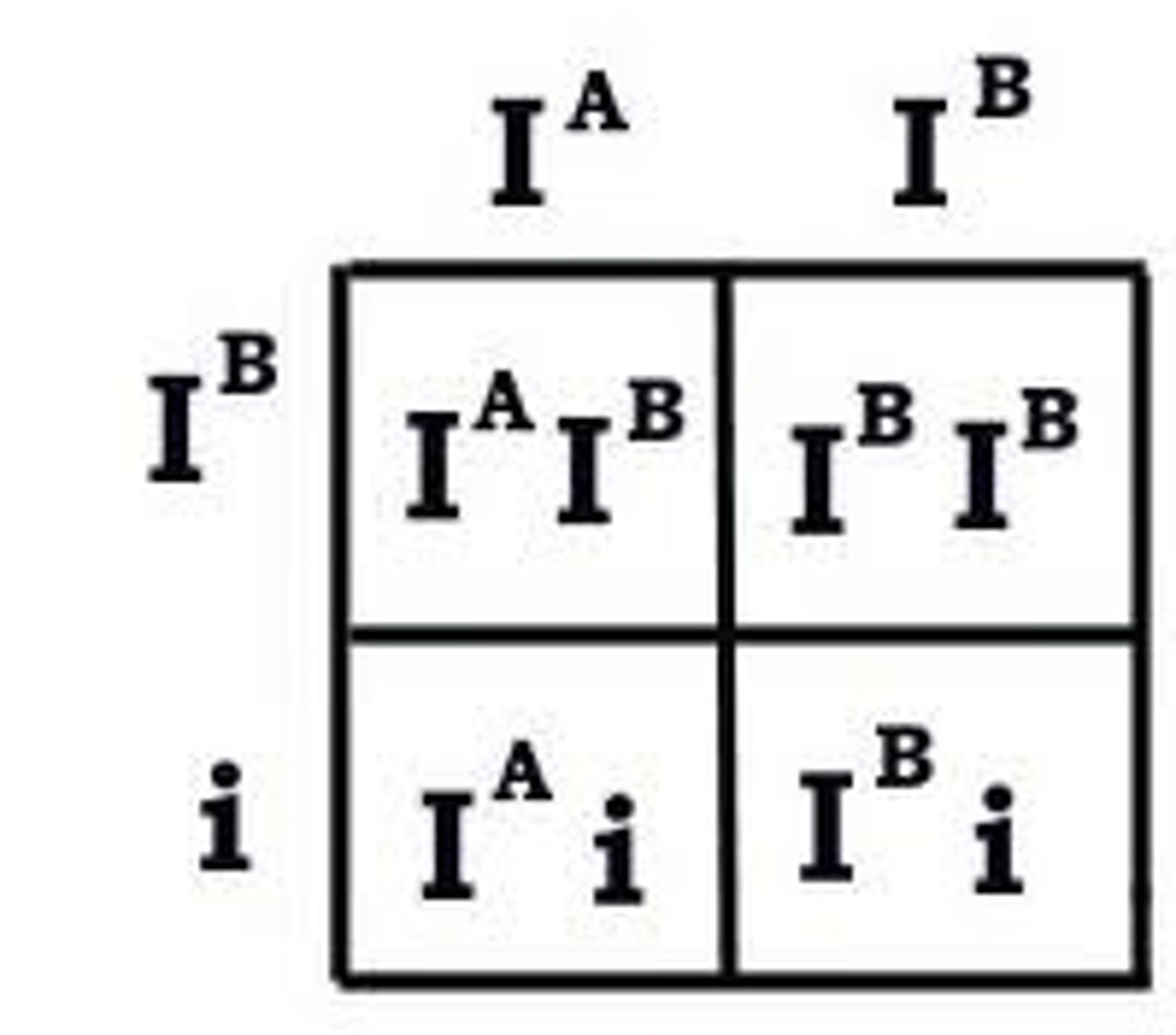
Multiple Alleles
A gene that has more than two alleles
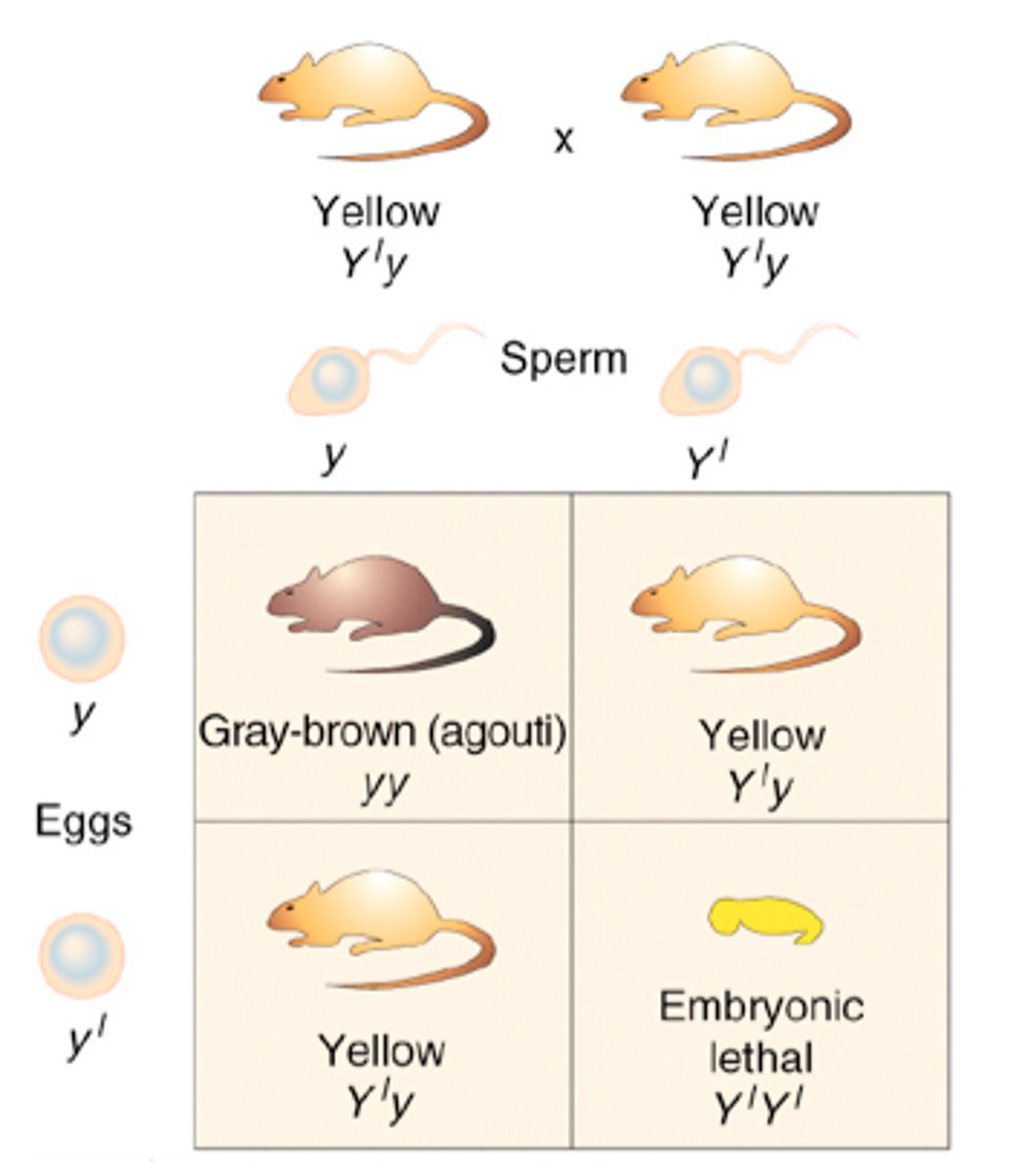
Lethal Genes
genes that causes death
Recessive Lethal
only lethal if homozygous recessive
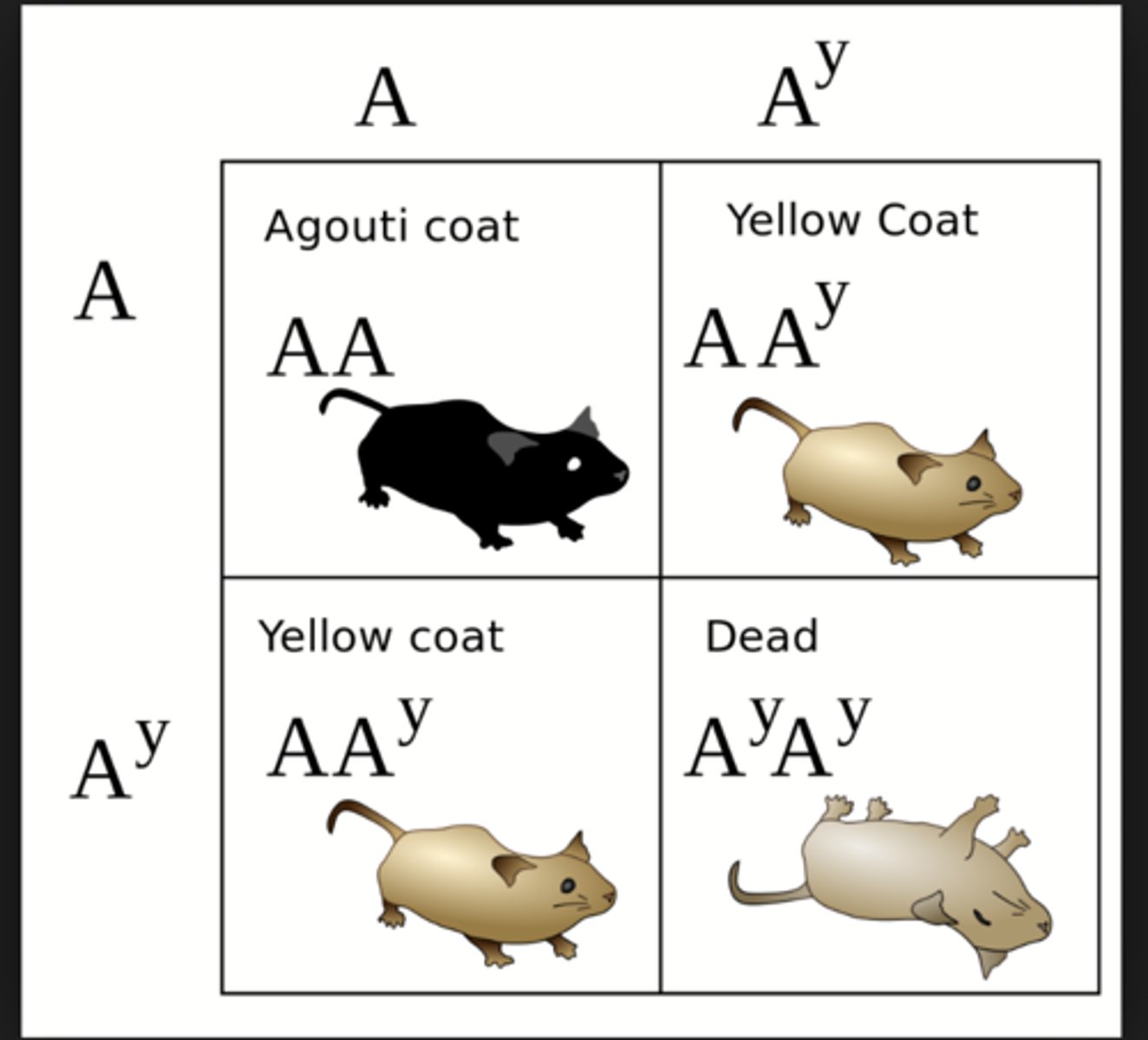
dominant lethal
if it has one dominant, it will die
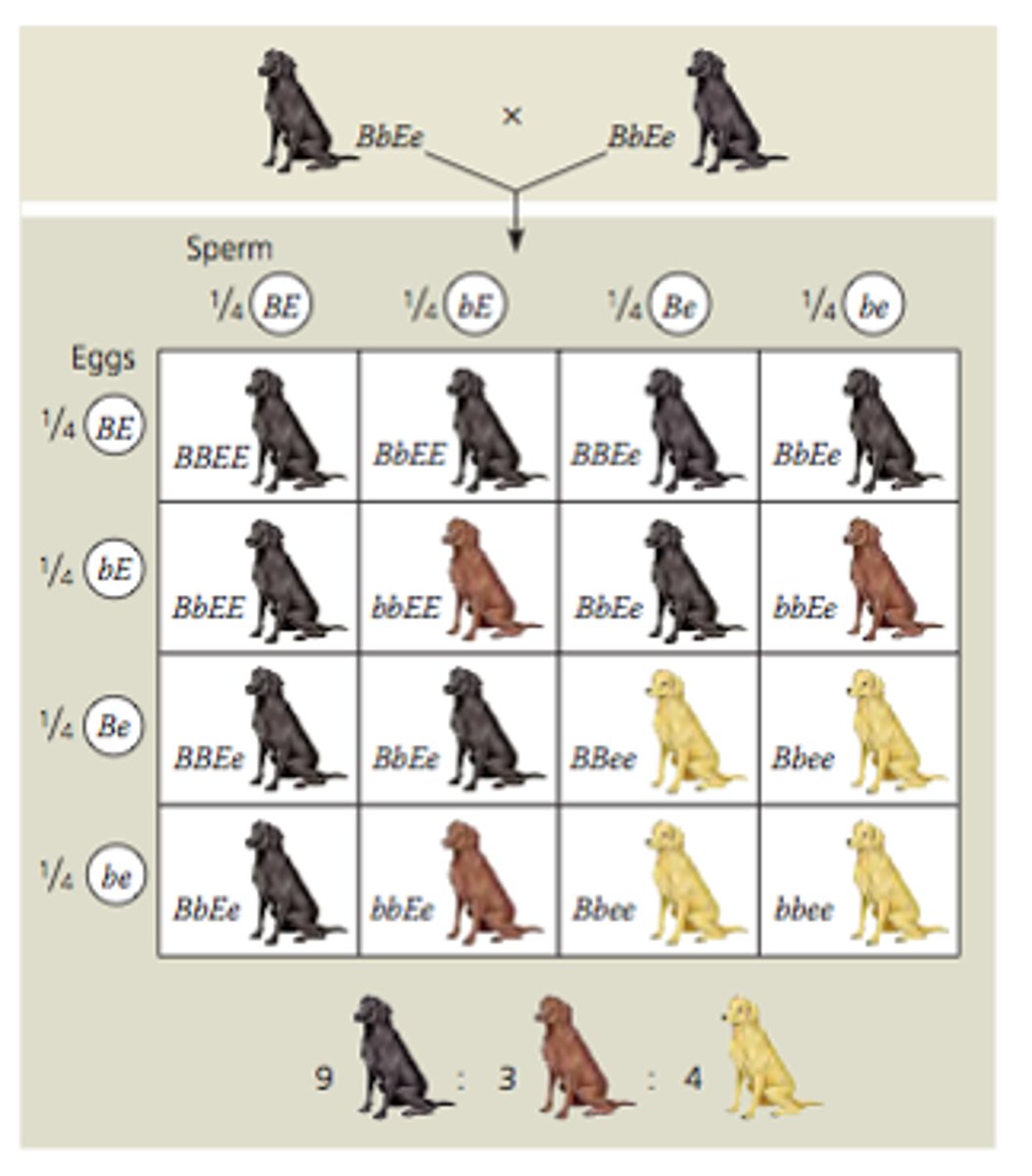
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene mask the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
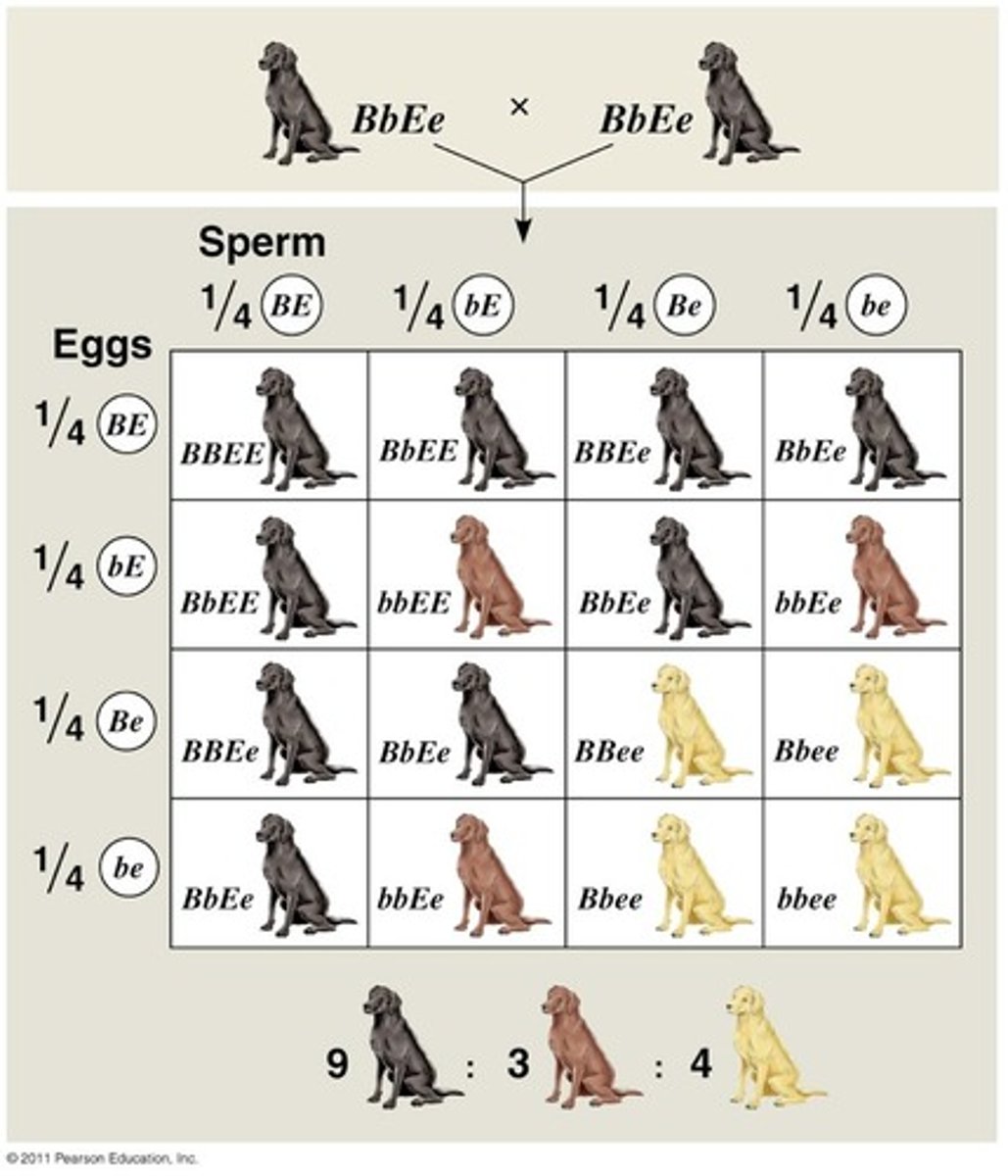
Recessive Epistasis
when a homozygous recessive genotype (aa or bb) at one gene masks the effect of another gene
9:3:4
Dominant Epistasis 1
only one gene acts as the suppressor
A masks B completely
12:3:1
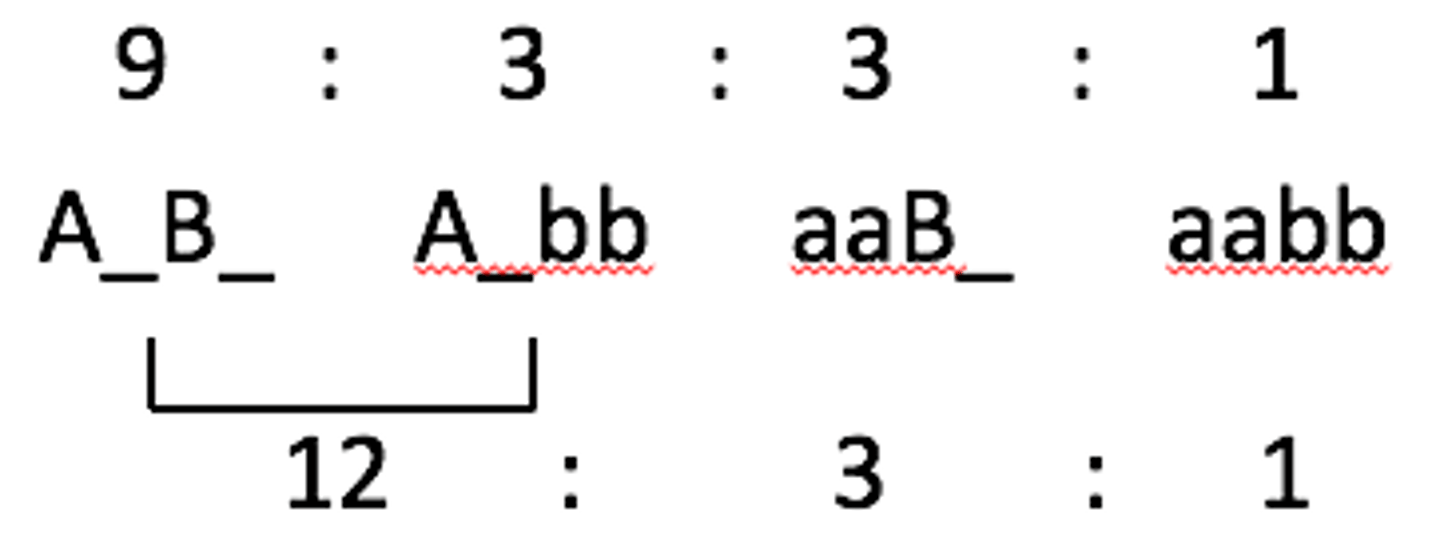
Dominant Epistasis 2
both genes can suppress in different ways
A masks B, but bb also blocks everything (A- and bb is the same)
13:3
Epistatic Gene
the gene that does the masking
Hypostatic gene
the gene whose effect is masked
Complementary Genes
Two genes work together, and BOTH must have at least one dominant allele to produce the trait.
9:7
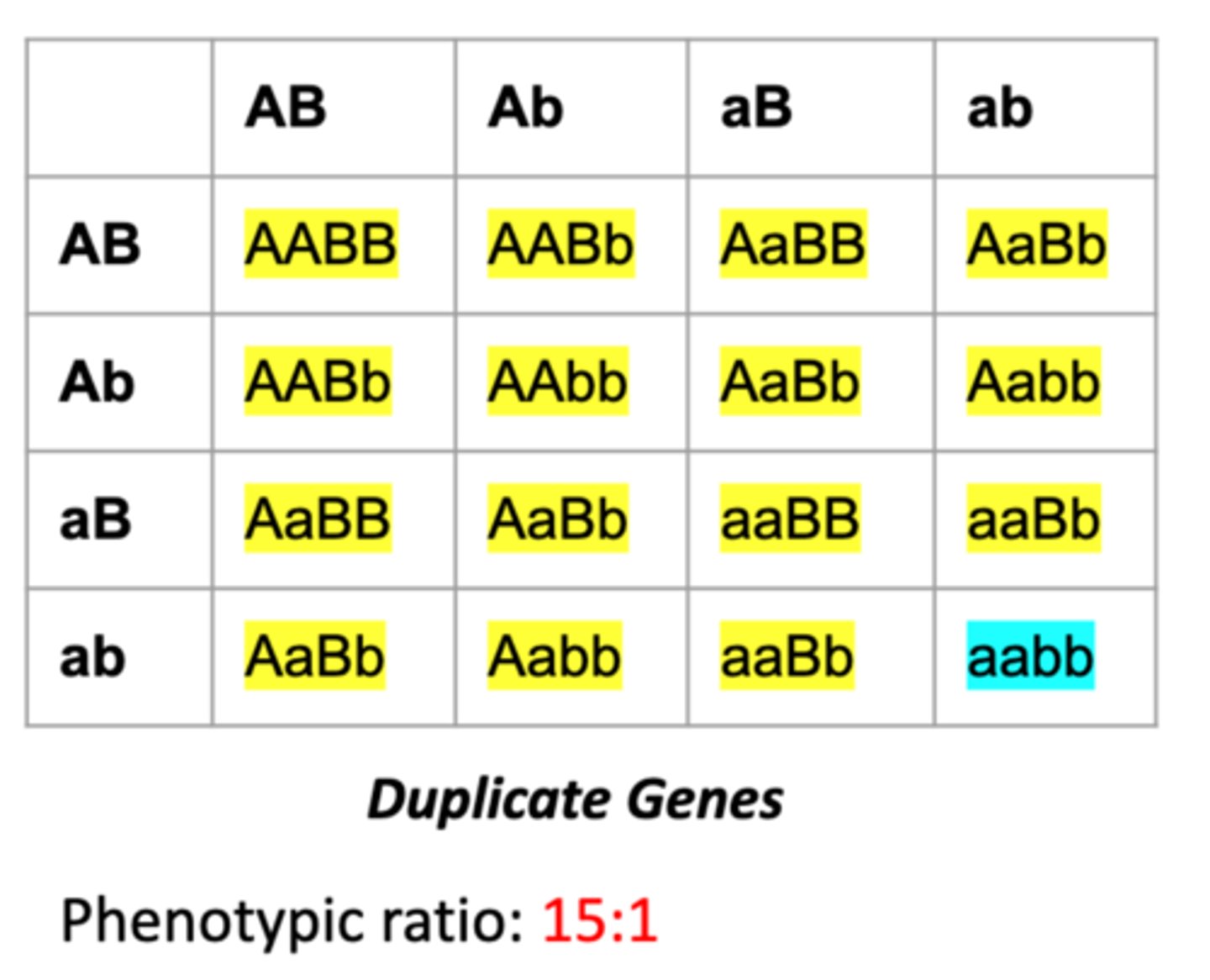
Duplicate Genes
Two different genes control the same trait, and either one alone is enough to produce the dominant phenotype.
15:1
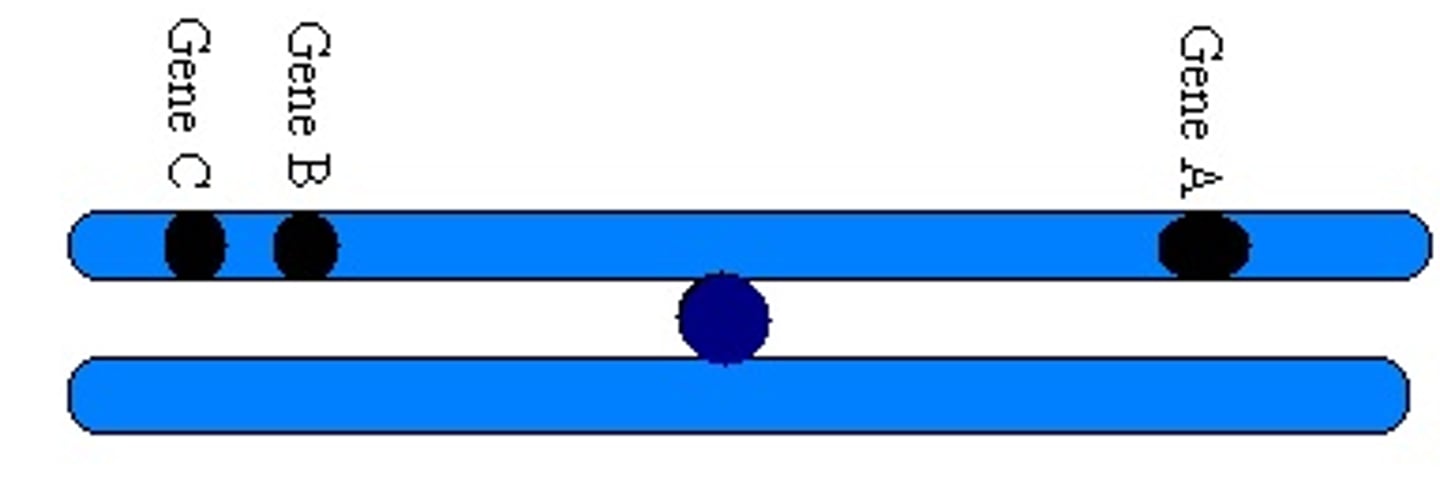
Linked Genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
do not assort independently (violating Mendel’s law of independent assortment).
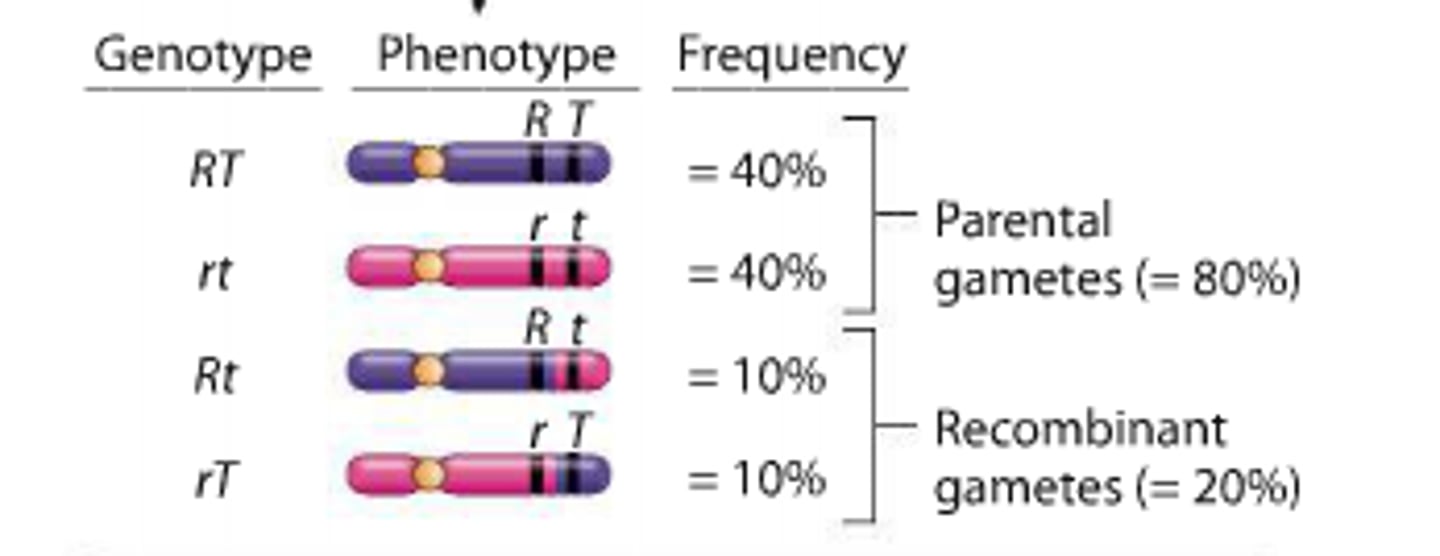
Incomplete Linkage
Genes are on the same chromosome but farther apart, so crossing over can occur between them during meiosis.
Both parental and recombinant gametes are formed
Less than 50% recombinants
Complete Linkage
Genes are very close together on the same chromosome, so no crossing over occurs during meiosis.
Only parental (non-recombinant) gametes are produced
100% Parentals
Cis form
Both dominant alleles are on the same chromosome, and both recessive alleles are on the other chromosome.
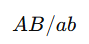
Trans form
Each chromosome has one dominant and one recessive allele, meaning the dominant alleles are on opposite chromosomes.
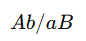
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a specific genotype who actually show the expected phenotype.
If 80 out of 100 people with a dominant gene for polydactyly (extra fingers/toes) actually show the trait, the penetrance is 80%.
Expressivity
The degree or intensity to which a genotype is expressed in an individual.
Some people with polydactyly have fully formed extra fingers, while others have just small skin tags—this variation is due to differences in expressivity.
Pleiotropy
A single gene that affects multiple traits in the body.
Phenocopy
When an environmental factor causes a trait that looks like a genetic condition.
Concordant
When both members of a pair (e.g., twins) show the same trait
Both identical twins have diabetes
Discordant
When only one member of a pair shows the trait.
One twin has diabetes, the other doesn’t