General Chemistry 1: Exam 1
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Majority of the things are conceptual and not the actual math equations Also, for the SI conversions, I the exponents appear as subscripts for some reason, but they’re not. The numbers should be exponents.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
tera (T)
1×1012
giga (G)
1×109
mega (M)
1×106
kilo (k)
1×103
hecto (h)
1×102
deka (da)
1×101
deci (d)
1×10-1
centi [c]
1×10-2
milli (m)
1×10-3
micro (µ)
1×10-6
nano (n)
1×10-9
pico (p)
1×10-12
femto (f)
1×10-15
ºCelcius to Kelvin
K = ºC + 273.15
Kelvin to ºCelcius
ºC = K - 273.15
ºCelcius to ºFarenheit
ºF = (ºC × 9/5) + 32
ºFarenheit to ºCelcius
ºC = (ºF - 32) × 5/9
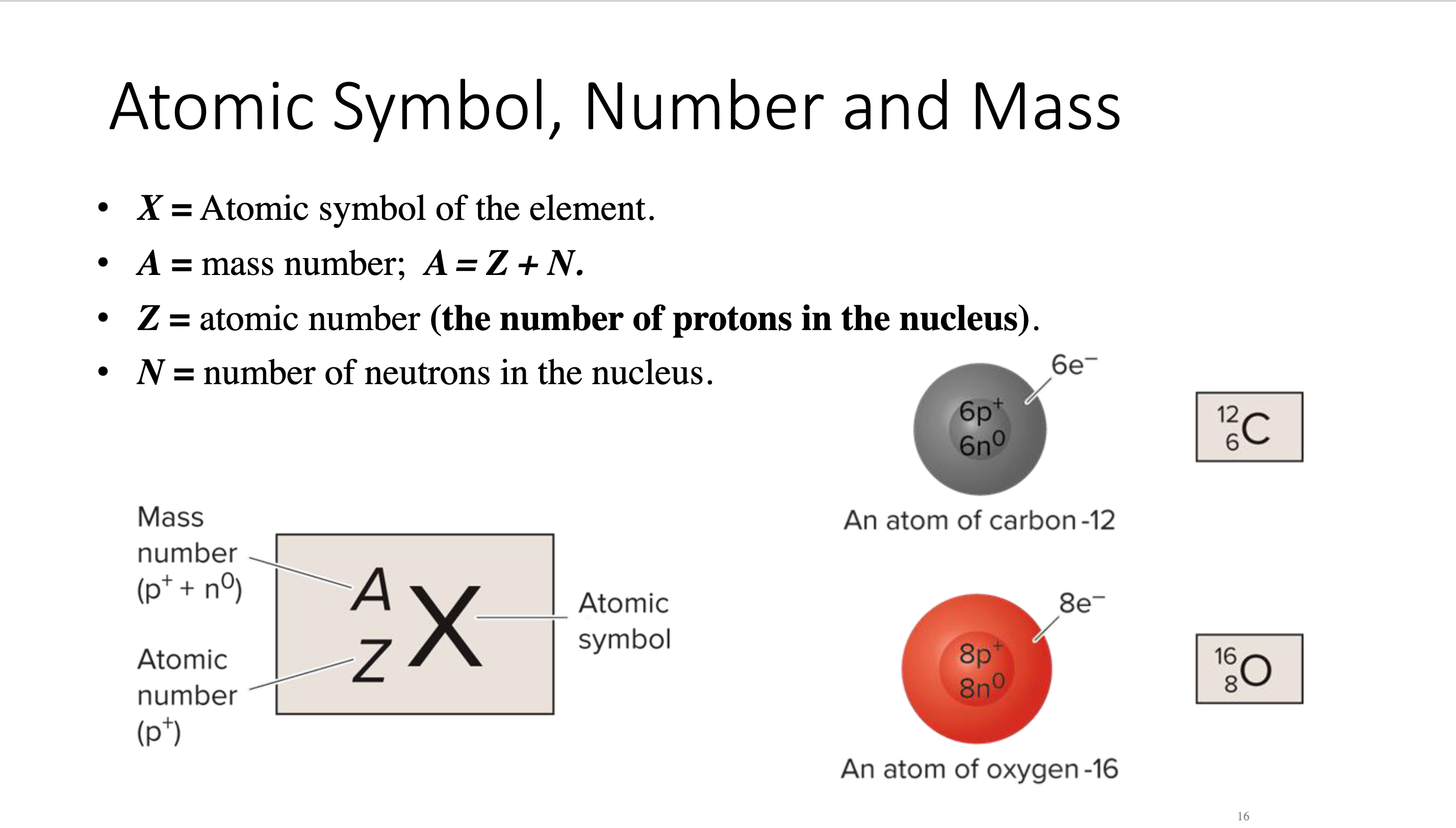
Atomic symbol, number, and mass
X = Atomic symbol of the element
A = mass number; A = Z + N
Z = atomic number (number of protons in nucleus)
N = number of neutrons in nucleus
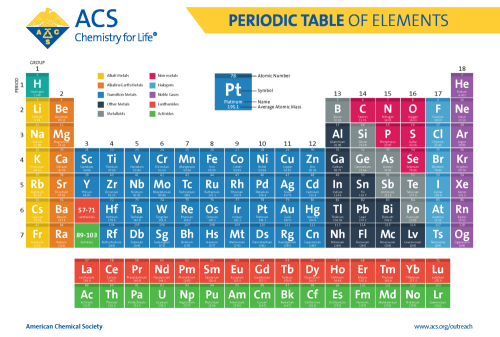
Periodic Table Information
Rows = periods (electron shells)
Columns = Groups (valence electrons present)
Yellow = Akali Metals
Orange = Akali Earth Metals
Blue = Transition Metals
Navy = Post Transition Metals
Gray = Metalloids
Pink = Nonmetals
Light Blue = Halogens
Purple = Noble Gasses
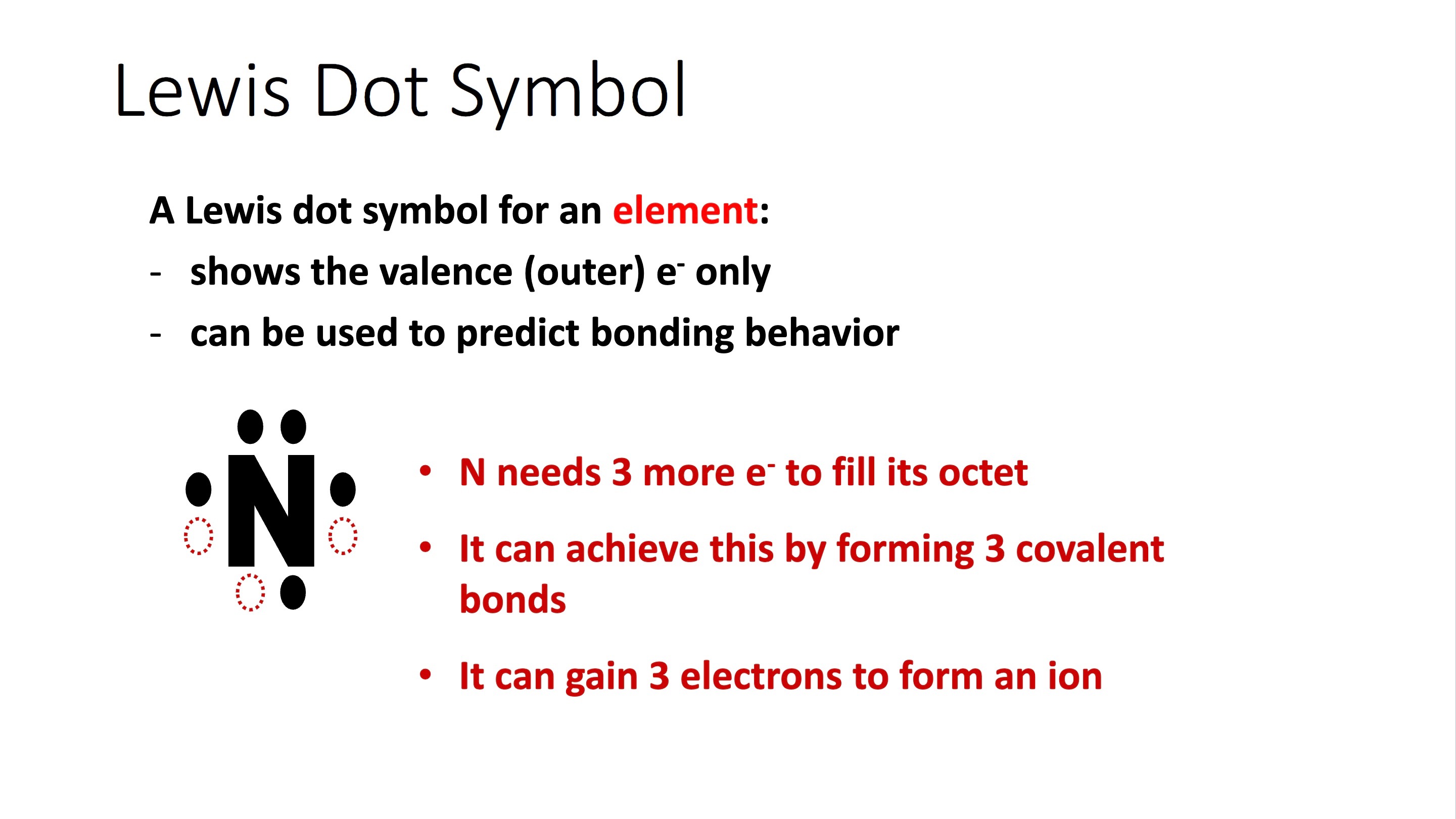
Lewis Structure Example
Two dots = lone pair
One dot = covalent bonds possible
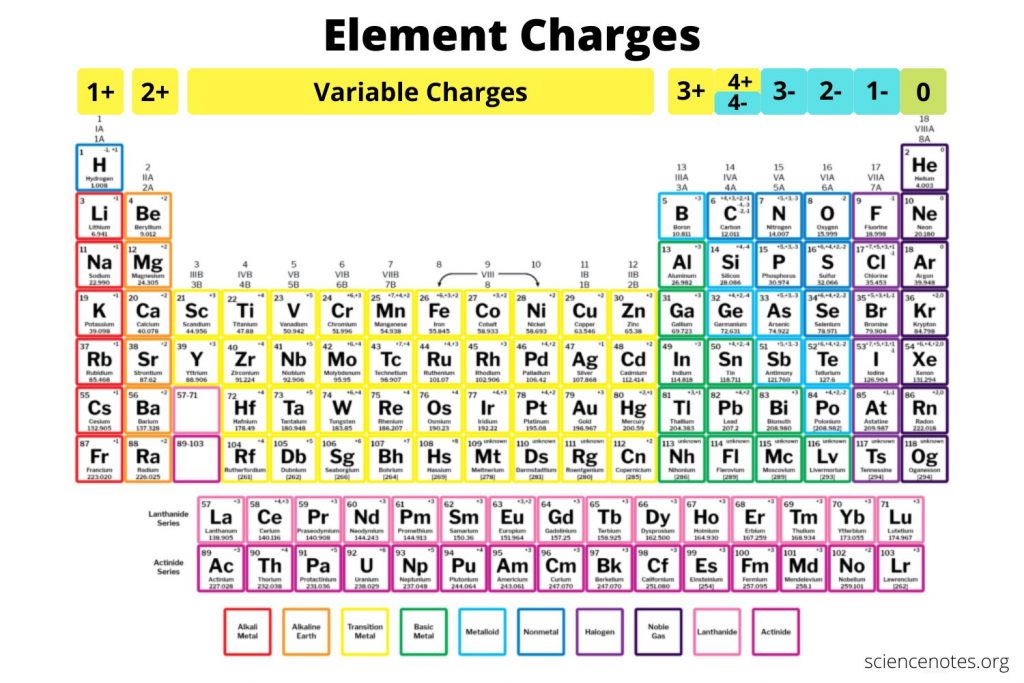
Periodic Table with Charges
Polyatomic ion
A charged species consisting of two or more atoms covalently bonded together
ammonium
NH4 +
nitrite
NO2 -
nitrate
NO3 -
sulfite
SO32
sulfate
SO42-
hydrogen sulfate (aka: bisulfate)
HSO4-
thiosulfate
S2O32-
oxalate
C2O42-
hydroxide
OH-
peroxide
O22-
cyanide
CN-
phosphite
PO33-
phosphate
PO43-
hydrogen phosphate
HPO42-
dihydrogen phosphate
H2PO4-
perchlorate
ClO4-
chlorate
ClO3-
chlorite
ClO2-
hypochlorite
ClO-
bromate
BrO3-
iodate
IO3-
acetate
CH3COO-
and/or
C2H3O2-
carbonate
CO32-
hydrogen carbonate (aka: bicarbonate)
HCO3-
chromate
CrO42-
dichromate
Cr2O72-
permanganate
MnO4-
cyanate
OCN-
thiocyanate
SCN-
Naming binary compounds
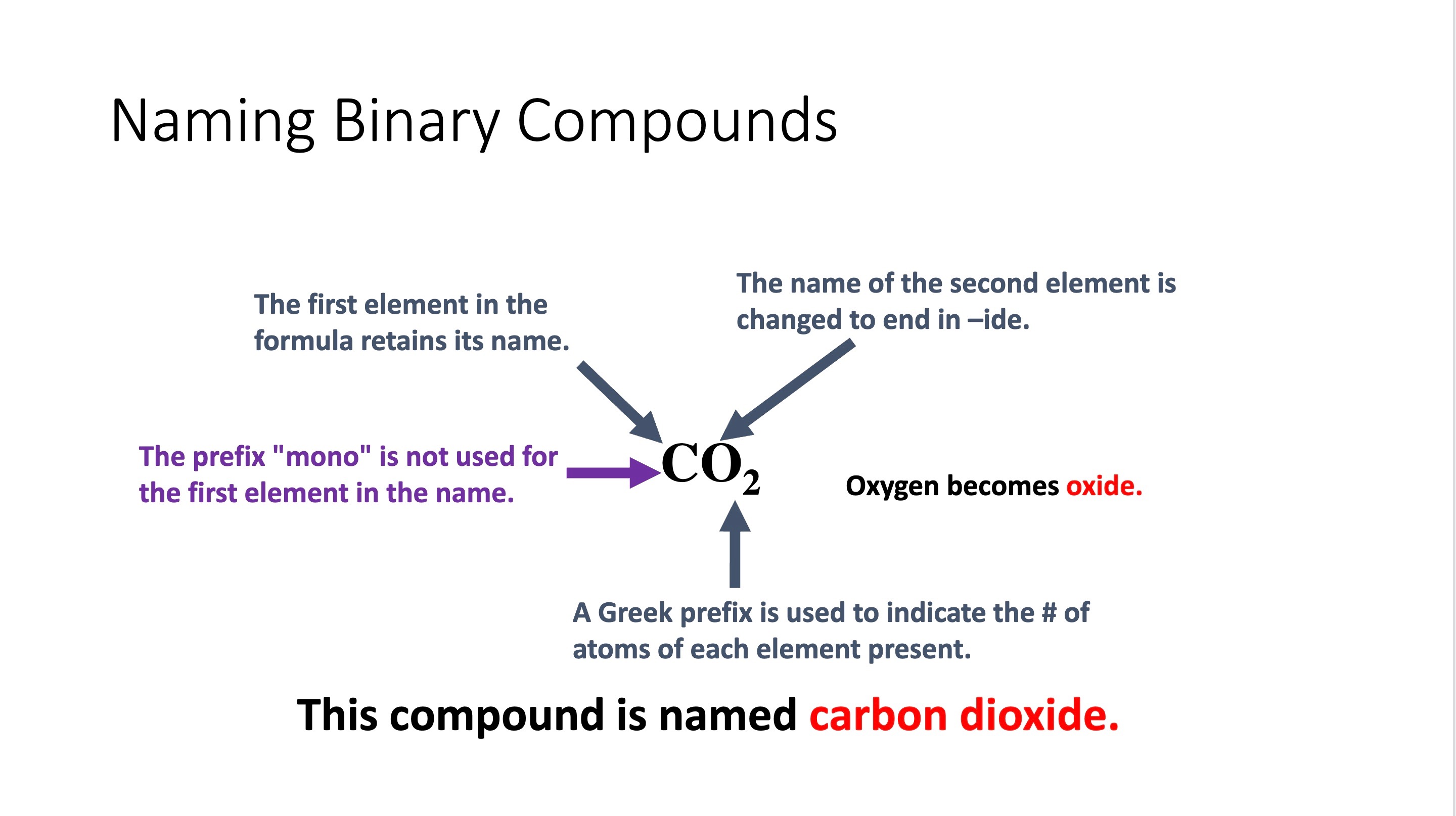
Prefixes and name endings for compounds
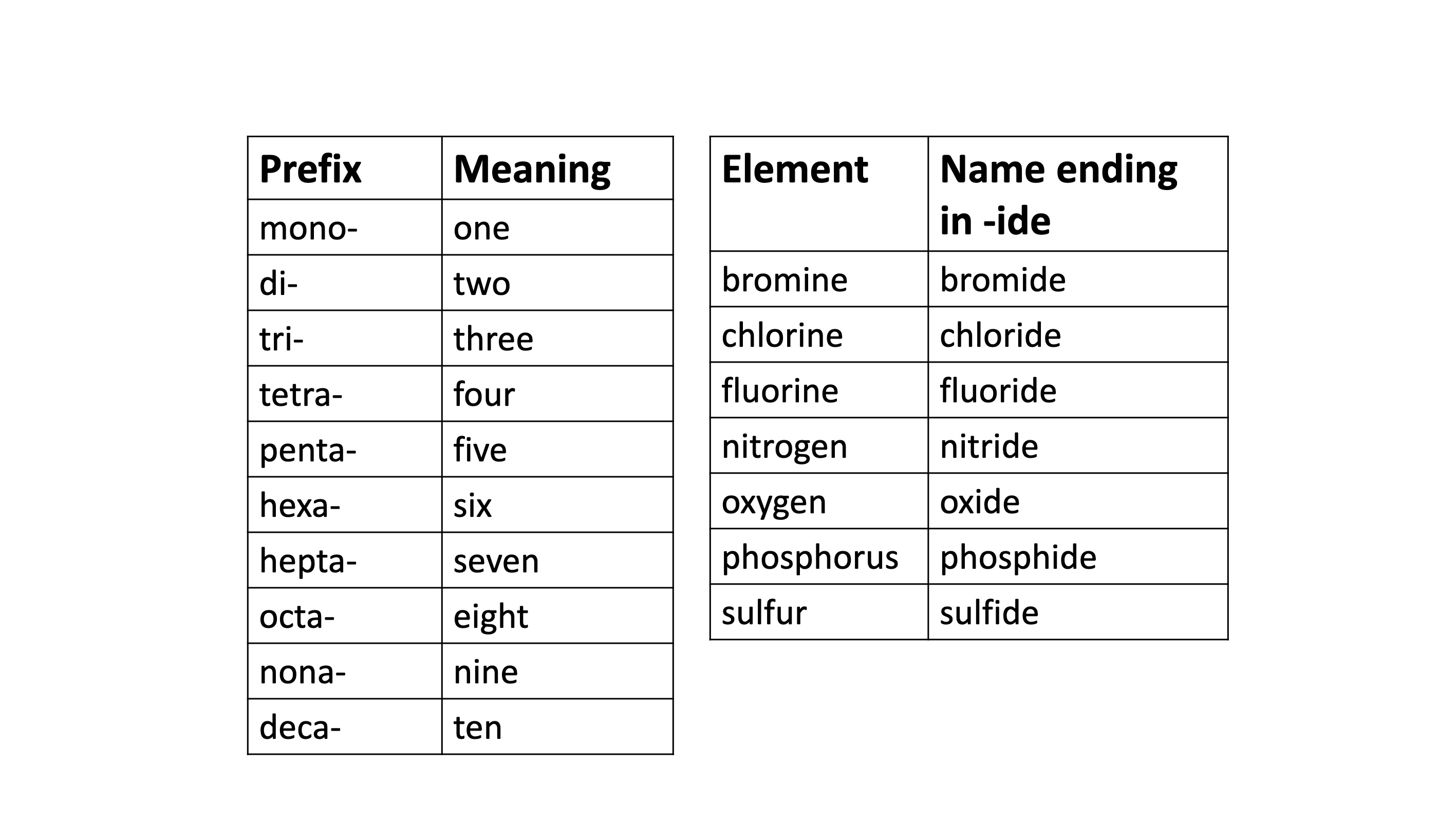
Common names of compounds

Avogadro’s number:
1 mol = 6.022×1023
Calculating % composition
% of element = (mass of specific element/mass of whole compound) x100
Calculating % yield
% yield = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x100
significance of the photoelectric effect experiments on understanding of atomic structure (part 1)
- Electrons ejected when frequency over a threshold frequency
- Size of current is proportional to the intensity of incident light
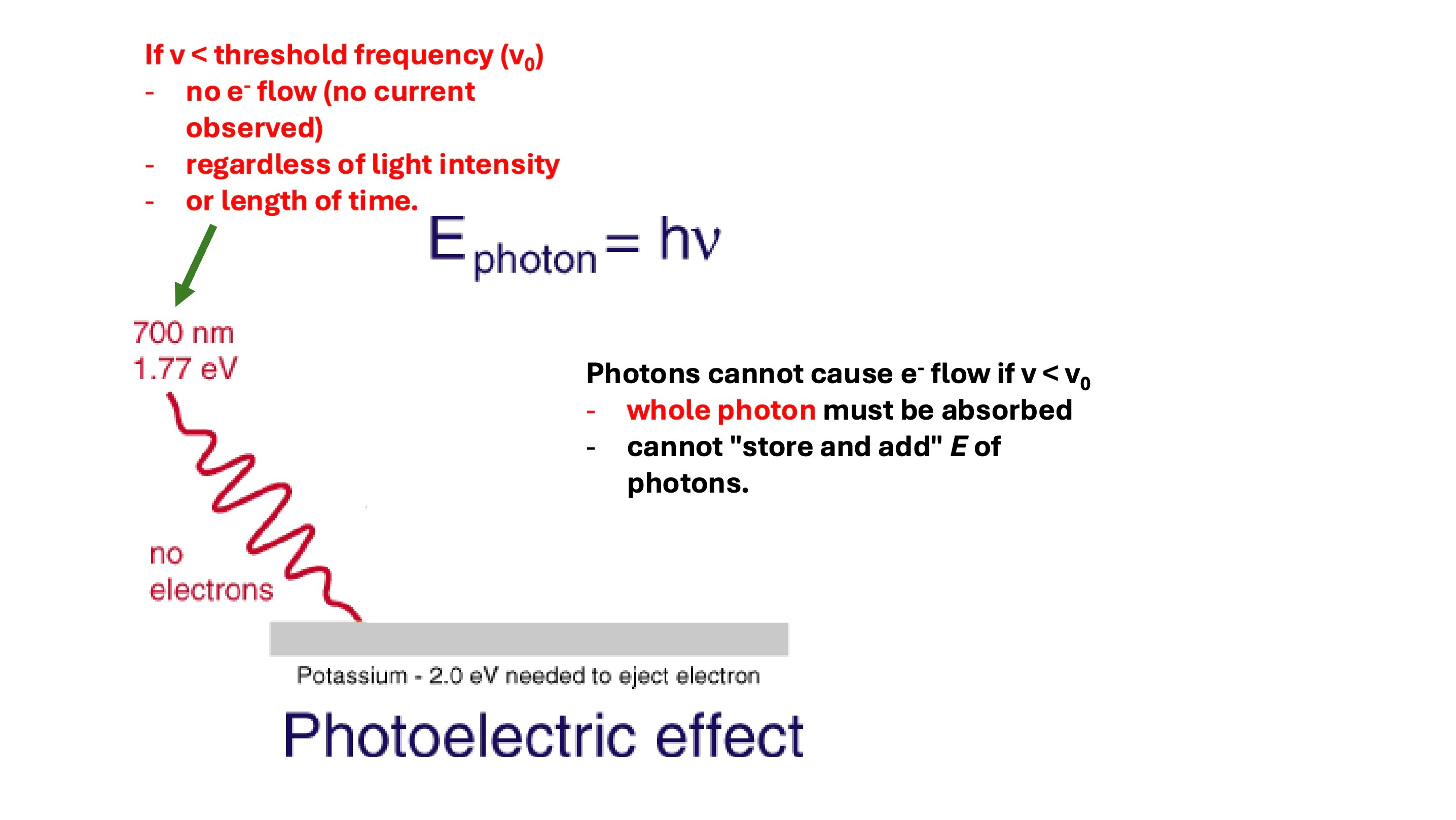
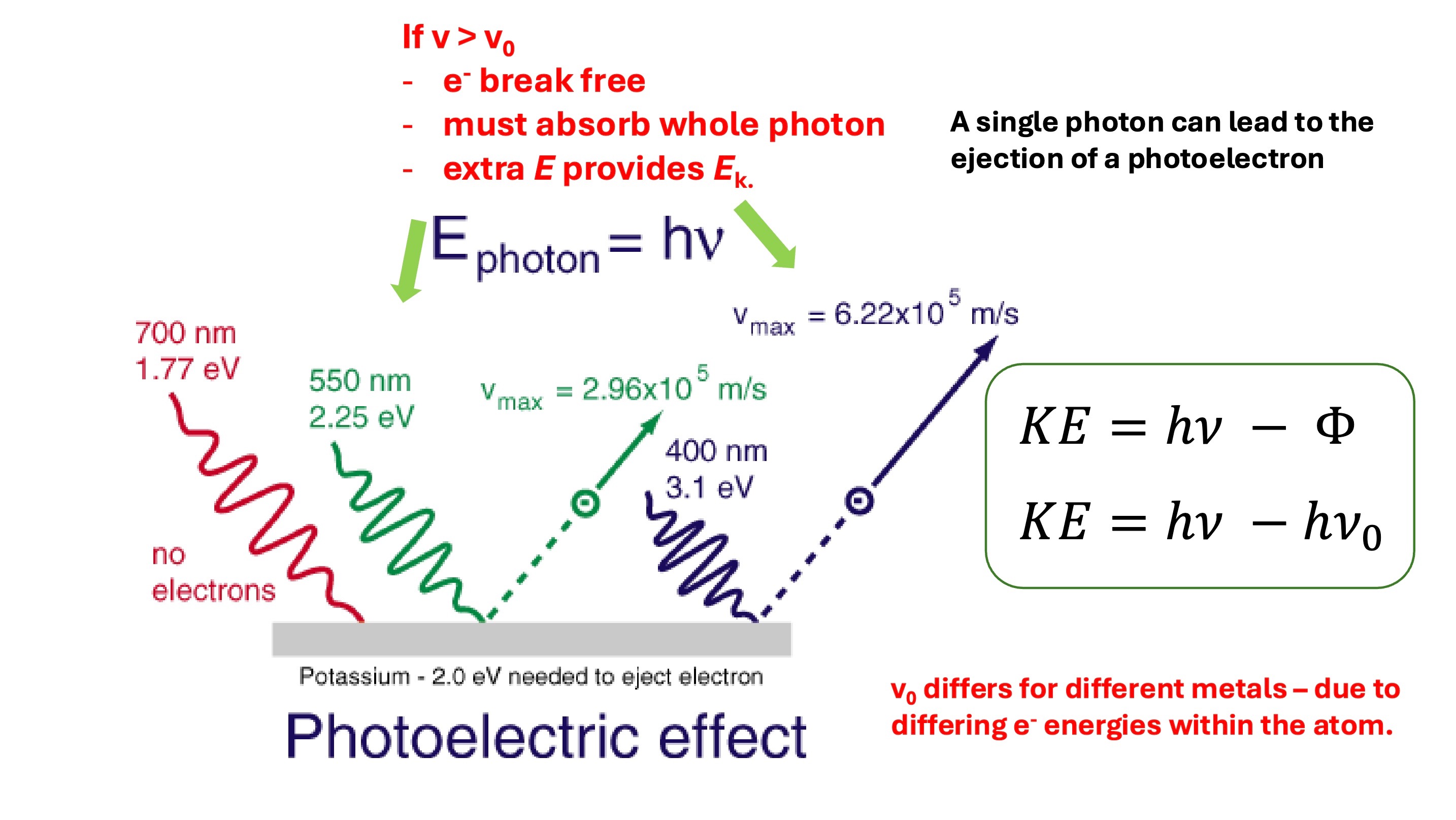
significance of the photoelectric effect experiments on understanding of atomic structure (part 2)
Electrons ejected when frequency over a threshold frequency
Size of current is proportional to the intensity of incident light
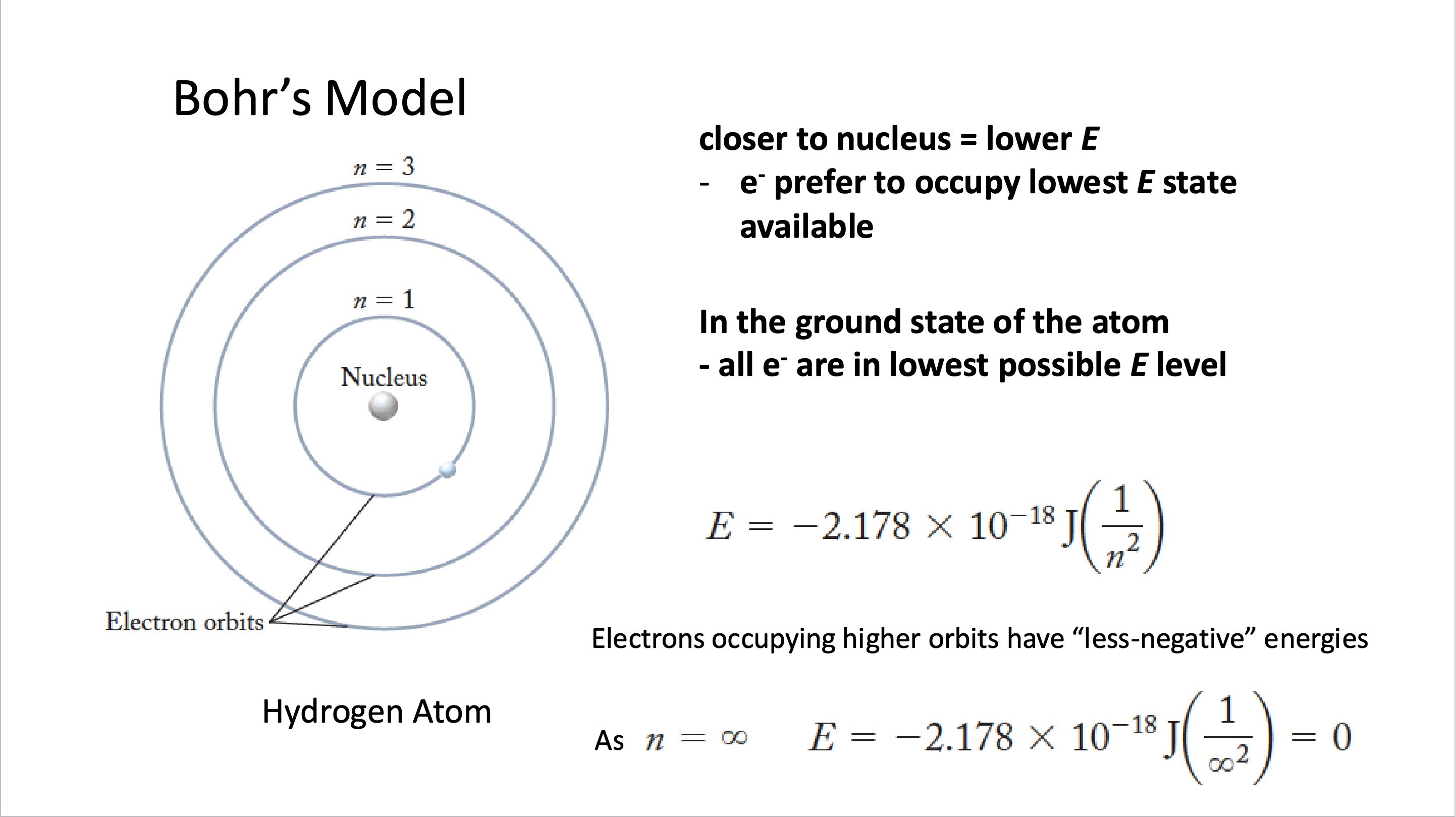
Describe the electronic structure of the atom in terms of energy levels
Closer to nucleus = lower E
e- prefer to occupy lowest E state available
In the ground state of the atom
all e- are in lowest possible E level
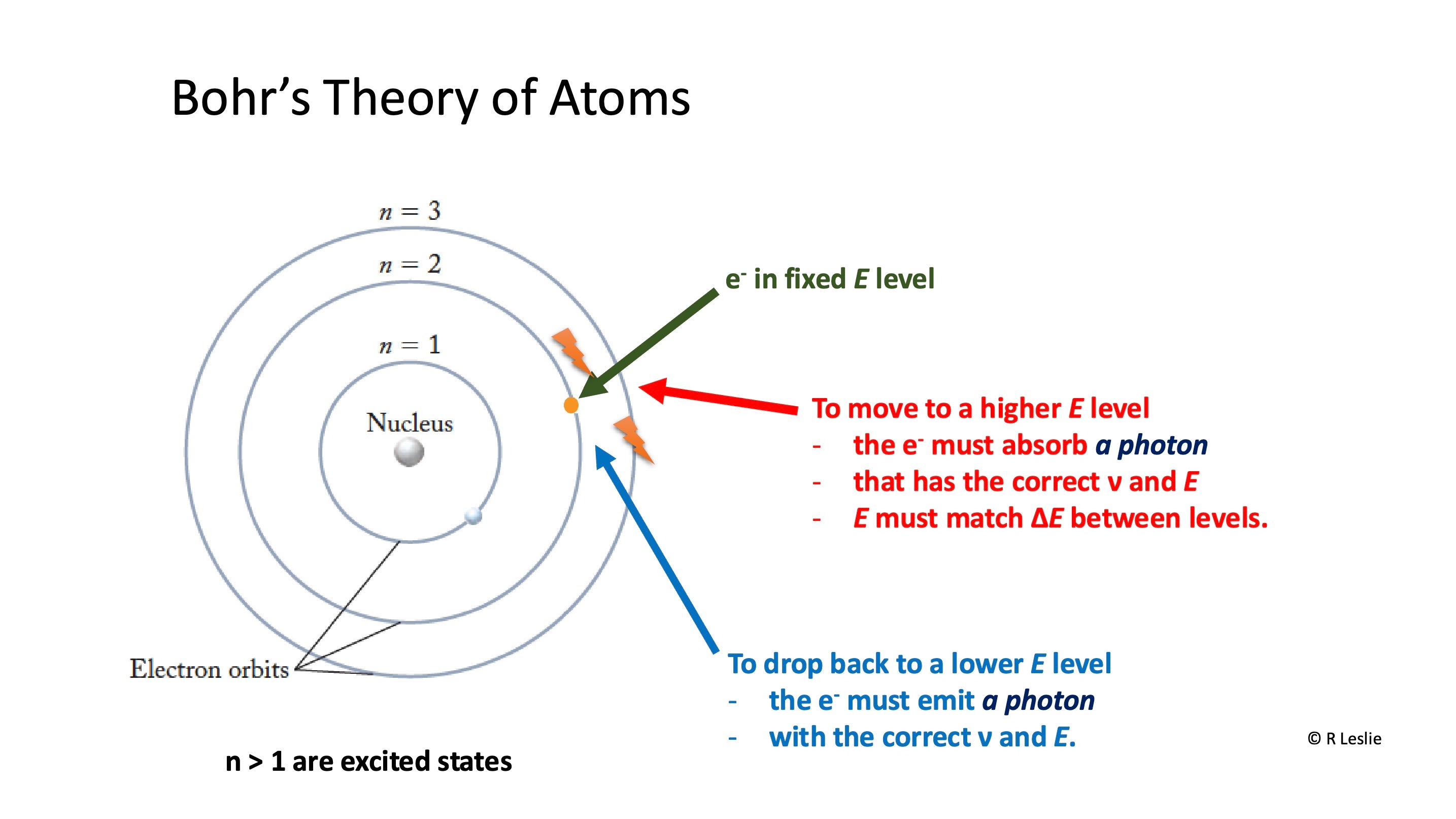
How do electrons move between energy levels within the atom
To move to a higher E level
the e must absorb a photon
that has the correct v and E
E must match ΔE between levels.
To drop back to a lower E level
the e must emit a photon
with the correct v and E.
What is C?
speed of light
2.998×108 m/s (constant)
c = ⋎*λ
What is ⋎?
frequency
⋎ = c/λ
What is λ?
Wavelength
λ = c/⋎
What is h?
6.626 × 10-34 J*s (constant)
How do you find E?
E = (h x c)/(λ)
( 6.626 × 10-34J*s x 2.998 × 108m/s )/(λ)