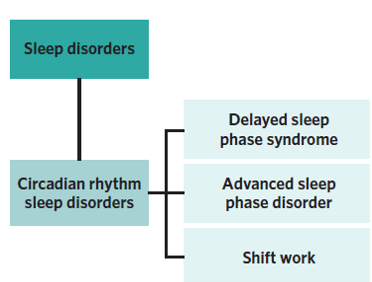
Circadian and rhythm sleep disorders
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is a sleep disorder
A condition where sleep problems cause distress, deviate from normal sleep-wake patterns, or disrupt daily functioning
Are sleep disorders limited to one type of problem
No, they are broad and include many different types of sleep-related problems
What are circadian rhythm sleep disorders
Sleep disorders that disrupt the normal regulation of the circadian rhythm, altering the sleep-wake cycle
Which specific circadian rhythm sleep disorders will be discussed
Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome (DSPS)
Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD)
Shift work disorder
What fundamentally causes circadian rhythm sleep disorders
A disruption to the typical sleep-wake cycle
What are examples of causes of circadian rhythm sleep disorders
Biological issues (like adolescent sleep-wake shifts) and lifestyle changes (such as shift work)
What common outcome do circadian rhythm sleep disorders tend to cause
Sleep deprivation
What are some emotional and physical effects of circadian rhythm sleep disorders
Amplified emotional responses, fatigue, irritability, and reduced ability to concentrate
How can circadian rhythm sleep disorders disrupt an individual’s lifestyle
By causing late arrivals to commitments and feeling sleepy at abnormal times, making daily tasks difficult
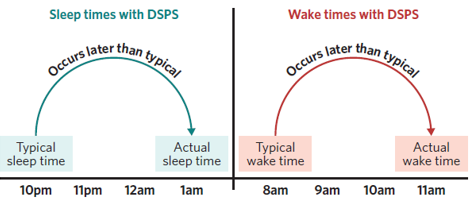
What is Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome (DSPS)
A circadian rhythm sleep disorder where sleep and waking occur later than usual
How does DSPS affect the typical sleep-wake cycle
The sleep-wake cycle is delayed, so sleep and wake times shift later than normal
Give an example of how DSPS changes sleep times
Instead of sleeping from 10pm to 8am, a person with DSPS may sleep from 1am to 11am
What causes DSPS
Misalignment between external cues (like light) and internal biological cues regulating the circadian rhythm
How does melatonin secretion relate to DSPS?
Melatonin is secreted later than usual, causing later sleep and wake times
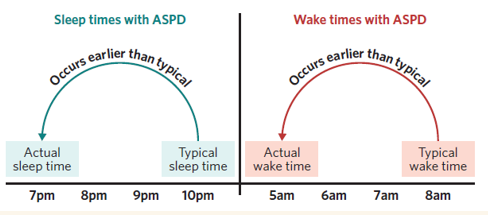
What is Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD)
A circadian rhythm sleep disorder where sleep and waking occur earlier than usual
What causes ASPD
Misalignment between external cues (received appropriately) and internal cues, causing early melatonin secretion
How does melatonin secretion affect ASPD
Melatonin is secreted earlier, leading to earlier sleep and wake times
What is the key difference between DSPS and ASPD
DSPS involves later melatonin secretion and delayed sleep times; ASPD involves earlier melatonin secretion and earlier sleep times
What is shift work
An occupation that involves working at unusual hours, often outside the typical 9-to-5 schedule
How does shift work affect sleep times
Individuals may need to sleep at unusual times, such as during the day instead of at night
What is rotating shift work
Working different shifts in rotation, such as a week of morning shifts followed by a week of night shifts
Name some occupations that often involve shift work
Nurses, road workers, hotel staff, and drivers
How does shift work impact the sleep-wake cycle
It causes the circadian rhythm to constantly change and adapt, disrupting normal patterns
Is shift work considered a sleep disorder
No, it is considered a cause of sleep problems, potentially leading to circadian rhythm sleep disorders or other issues
What is insomnia
A sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep
How does shift work cause fragmented sleep
Sleeping at unusual hours leads to waking up repeatedly and having multiple short sleep episodes instead of one continuous sleep period
What is a circadian rhythm phase disorder related to shift work
When external environmental cues are out of sync with work requirements, like being in bright light at night
How does shift work affect sleep quality and quantity
Both can be negatively affected because the body is programmed to sleep at night and be awake during the day
What causes ASPD and DSPS compared to shift work disorders
ASPD and DSPS are caused by problems with internal cues, while shift work disorders are caused by problems with external cues (like light exposure)
What is bright light therapy
A method to adjust a person’s circadian rhythm through exposure to a high-intensity light source
How does morning bright light exposure affect the body
It signals the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), promoting wakefulness through cortisol release and triggers earlier melatonin release at night
What role does the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) play in bright light therapy
It acts as a biological clock regulator by receiving light as an external cue to adjust the sleep-wake cycle
How does bright light therapy readjust the circadian rhythm
By ensuring sleeping and waking occur at the desired times through gradual exposure
How long and how often are bright light therapy sessions typically conducted
Sessions last from about 15 minutes to a couple of hours, up to a few times a day, for several consecutive days
Why are bright light therapy sessions done over several consecutive days
To gradually shift the sleep-wake cycle by adjusting exposure time each day to reach the desired waking time
Why is the timing of bright light exposure important
Exposure must occur at the right time to help a person feel awake and adjust their sleep-wake cycle appropriately
Give an example of appropriate timing for bright light therapy
Someone who feels sleepy early (e.g., 5pm) might use bright light in the late afternoon or early evening to stay awake longer
What is important about the amount of light used in therapy
The intensity and length of exposure must fit the person’s disorder and be built up gradually to avoid side effect
Why should bright light exposure be built up gradually
To avoid negative side effects like headaches
What safety measures should be taken during bright light therapy
Do not look directly at the light, and maintain an adequate distance between the face and the light source
How is bright light therapy used to treat Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome (DSPS)
Exposure to bright light in the morning promotes wakefulness and signals earlier melatonin release for an earlier sleep time
How does bright light therapy help Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD)
Exposure to bright light in the evening promotes wakefulness later, delaying melatonin release and shifting sleep time later
How does bright light therapy help with shift work-related sleep disorder
Exposure before a shift promotes wakefulness during work and helps shift sleepiness to a suitable time afterward
What role does the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) play in bright light therapy for these disorders
The SCN receives light as an external cue to regulate cortisol and melatonin release, adjusting sleep-wake timing