neurotransmitters + hormones involved in psychiatry - lecture
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
what are the main 2 types of ways that neurotransmitters signal?
- G-protein linked receptors e.g. Gs, Gi, Gq
- ligand gated ion channels
which signalling pathway is most important in psychiatry?
G-protein linked receptors
how do ligand-gated ion channels work?
- flux of ions causes an action potential
- calcium channels open and calcium acts on calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase
how do G-protein linked receptors work?
- through secondary intracellular messenger cAMP
- stimulates 'early genes' in nucleus to cause subtle changes activity of the neurone (rather than stimulating an action potential)
what type of receptor are muscarinic receptors?
G-protein coupled
what do G-proteins coupled to?
adenylate cyclase
are G-protein coupled receptors excitatory or inhibitory?
can be both
what happens when G-proteins are bound to adenylate cyclase in an excitatory state?
- increases cAMP
- increase gene expression of the cell
what happens when G-proteins are bound to adenylate cyclase in an inhibitory state?
- decreases CAMP
- decreased gene expression of the cell
what is epigenetics?
the study of how the environment affects which genes are expressed
what are some of the main neurotransmitters in psychiatry?
- amino acids - glutamate + GABA
- ACh
- monoamines
- neuropeptides - opioids
are glutamate receptors excitatory or inhibitory?
excitatory
are GABA receptors excitatory or inhibitory?
inhibitory
what are some examples of monoamines?
- histamine
- dopamine
- noradrenaline
- 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin)
- melatonin
what is dopamine activated from?
L-tyrosine
what is L-tyrosine converted to and by what?
converted to L-DOPA by tyrosine hydroxylase (this is the rate-limiting step)
what is L-DOPA converted to and by what?
converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase
what can dopamine also be converted into?
noradrenaline
what can noradrenaline be converted into?
adrenaline
what happens in the pre-synaptic neurone after dopamine has been produced?
packaged into vesicles by vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) and released into synaptic cleft
what are the options for what happens to dopamine in the synaptic cleft? (4)
1) bind to D1-D5 receptors (Gs on postsynaptic neurone)
2) bind to D2-D3-D4 receptors (Gi/o on postsynaptic neurone)
3) bind to D2-D3 autoreceptor on presynaptic neurone
4) broken down by monoamine oxidase A or B (MAO-A or B) or COMT
what happens if dopamine binds to D1-D5 (Gs) receptors on the postsynaptic neurone?
EXCITATORY:
- increases adenylate cyclase expression
- increases cAMP expression
- increases gene expression
what happens if dopamine binds to D2-D3-D4 (Gi/o) receptors on postsynaptic neurone?
INHIBITORY:
- decreases adenylate cyclase expression
- decreases cAMP expression
- decreases gene expression
what happens if dopamine binds to D2-D3 autoreceptors on presynaptic neurone?
self-regulating - acts as a negative feedback loop to reduce dopamine vesicle production
what happens if dopamine is broken down by MOA-A or B?
gets transported to presynaptic neurone to be reused
what are the options for noradrenaline when it enters the synaptic cleft? (5)
1) bind to α1-adrenergic receptors on postsynaptic neurone
2) bind to α2-adrenergic receptors on postsynaptic neurone
3) bind to β-adrenergic receptors on postsynaptic neurone
4) bind to α2-adrenergic autoreceptors on presynaptic neurone
5) gets taken up into presynaptic neurone by noradrenaline reuptake transporter (NET)
what happens when noradrenaline binds to α2-adrenergic receptors on postsynaptic neurone?
INHIBITORY:
- decreases adenylate cyclase
- decreases cAMP
- decreases gene expression
what happens when noradrenaline binds to α1 or β-adrenergic receptors on postsynaptic neurone?
EXCITATORY:
- increases adenylate cyclase
- increases cAMP
- increases gene expression
which parts of the presynaptic neurone can neurotransmitters bind to for autoregulation?
- axon terminal (presynaptic end)
- somatodendritic end
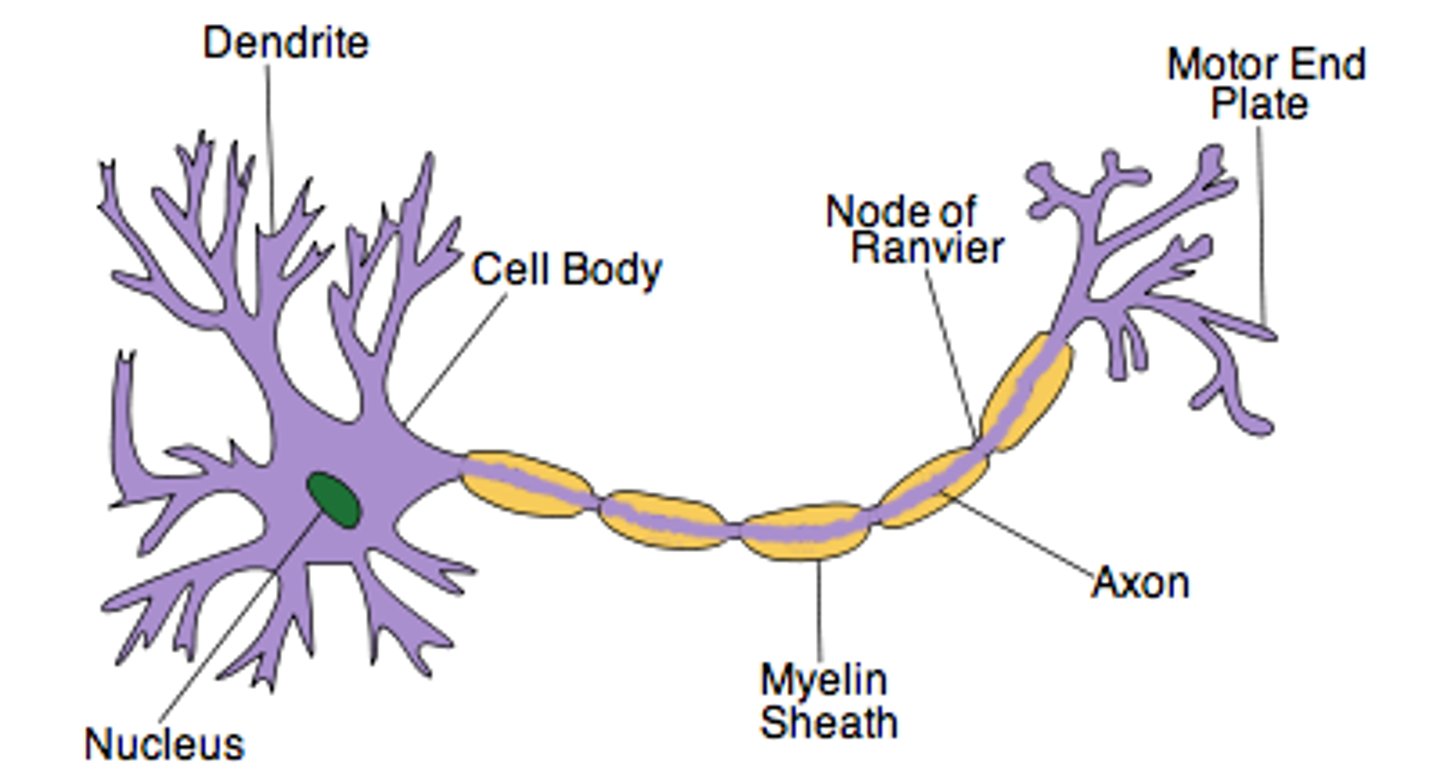
what happens with autoregulation at the axon terminal?
binding autoreceptors causes decreases release of the neurotransmitter
what happens with autoregulation at the somatodendritic end?
binding to autoreceptors causes a reduced likelihood for the neurone to fire
what is 5-HT derived from?
tryptophan
what are the options for 5-HT when it is released into the synaptic cleft?
1) bind to 5-HT1 receptors on postsynaptic neurone
2) bind to 5-HT2 receptors on postsynaptic neurone
3) bind to 5-HT3 receptors on postsynaptic neurone
4) broken down by monoamine oxidase (MAO)
5) binds to 5HT1 autoreceptors on presynaptic neurone
what happens when 5-HT binds to 5-HT1 receptors on postsynaptic neurone?
INHIBITORY
what happens when 5-HT binds to 5-HT2 receptors?
EXCITATORY (LHD and magic mushrooms)
what happens when 5-HT binds to 5HT1 autoreceptors on presynaptic neurone?
INHIBITORY - autoregulation via a negative feedback loop
what happens when 5-HT binds to 5HT3 receptors on postsynaptic neurone?
EXCITATORY - linked with nausea
what is an example of monoamines regulating each other?
when noradrenaline (na) and 5-HT neurones are laid close to each other, the na neurone can interact with the 5-HT neurone in the raphe nucleus of the brain
where are the α1 and α2-adrenergic receptors found on the 5-HT neurone?
α1 - found on cell bodies in the raphe nucleus
α2 - found on nerve terminals in the cortex
what happens in this interaction between na neurones and 5-HT neurones?
- when there is increased na release at cell body end, they bind to α1 receptors and cause EXCITATION of 5-HT neurones
- when there is increased na release at the nerve terminals in the cortex, they bind to α2 receptors and cause INHIBITION of 5-HT neurones
where do dopamine projections originate from?
ventral tegmentum (midbrain)
where do noradrenaline projections originate from?
locus coeruleus (pons)
where do 5-HT projections originate from?
raphe nucleus (medulla)
what are the general functions of dopamine? (6)
- cognition and memory
- mood
- motivation
- motor control
- reward (addictions)
- sexual function
what are the general functions of noradrenaline? (6)
- cognition and memory
- anxiety
- sympathetic ns
- wakefulness and attention
- hunger
- emotional memory
what are the general functions of 5-HT? (7)
- appetite
- mood
- emotion
- arousal
- body temp regulation
- sensory perception
- sleep
what circuits are useful to view in neuroimaging for depression?
- amygdala - emotions
- nucleus accumbens - rewards
- ventromedial prefrontal cortex - processing emotion
- dorsolateral prefrontal cortex - cognition
what neuroimaging technique can be used to see which circuits are activated?
FMRI - function MRI
what happens to the HPA axis in chronic stress?
excessive glucocorticoid release from zona fasciculata
what does excessive glucocorticoid release cause?
hippocampus atrophy
what does the hippocampus normally do in the HPA axis?
negative feedback loop to the hypothalamus when glucocorticoid release is high
what does hippocampus atrophy cause?
chronic activation of HPA axis - no negative feedback loop
what eventually happens to glucocorticoid receptors?
become desensitised to ACTH
what happens when glucocorticoid receptors become desensitised?
increased serum cortisol - leads to chronic inflammation
why is some stress good?
to develop resilience
why is significant stress e.g. child abuse negative?
can sensitise brain circuits, leaving them more vulnerable rather than resilient
what is a CTSC loop?
corticothalamostriatocortical
what is the CTSC loop running between?
- dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
- striatum
- thalamus
what is the anxiety theory linked with the CTSC loop?
in anxiety this loop is overloaded and it leads to worry
what is the CTSC loop regulated by?
- 5-HT
- GABA
- dopamine
- noradrenaline
- glutamate
- voltage gated ion channels
what is the stress-diathesis model?
- some individuals have a genomic predisposition (risk genes) to psychiatric disorders
- normal life stressors can cause activation of these risk genes leading to over or under reactivity of circuits
what does hyperactivation of these circuits lead to?
anxiety
what does hypoactivation of these circuits lead to?
depression