Chapter 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
Belived that atoms were invisible and they moves and combined in different ways. Purely speculative
Democritus

2
New cards
Believed that all matter was composed of the four basic elements, earth, wind, fire, and water. More influencial then Democritis. The theory survived until science and expiriments came around.
Aristotle

3
New cards
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change
Law of Conservation of Mass
4
New cards
A chemical compound contains the same elements in the same proportions of mass.
Law of Definite Proportions
5
New cards
Concluded that matter could be explained in terms of atoms
Dalton's thoughts on matter
6
New cards
1) elements are composed of atoms. 2) atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements. 3) elements can mix together 4) atoms only change when mixed with other elements
Dalton's Atomic Theory
7
New cards
measured the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. Discovered that atoms are divisible! and discovered the electron
Thomson's Cathode Ray Experiment
8
New cards
Positive
Protons charge
9
New cards
Negative
Electrons charge
10
New cards
Atom
Thomson's Plum Pudding Model of the _______
11
New cards
Discovered that all positives are concentrated into the center (nucleus).
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment discoveries
12
New cards
Alpha-particles were directed at a thin sheet of gold foil; most passed through the foil, but a few were deflected; this led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
13
New cards
Sprayed oil droplets between electrically charged plates
Milikan's Oil Drop Experiment
14
New cards
Discovered the charge of electron, and ues dimensional analysis and calculated the mass of electron
Milikans Oild Drop expiriment discoveries
15
New cards
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic number
16
New cards
On top
Where is the atomic number located on the Periodic table?
17
New cards
The basic unit of a chemical element. The smallest unit
Atom
18
New cards
Atomic Number
How to determine an atoms identity?
19
New cards
neutral. The number of protons minus the number or neutrons.
Charge of an atom
20
New cards
1 amu
Mass of proton
21
New cards
1 amu
Mass of neutron
22
New cards
0 amu
Mass of electron
23
New cards
Strong neuclear force
How is the neuclus held together?
24
New cards
Holds the protons and neutrons together in the neucleus
Role of Strong Nuclear Force
25
New cards
Contain the same number of protons
Isotope Similarities
26
New cards
Contain different numbers of neutrons
isotope differences
27
New cards
Same as atomic number
Determine the number of protons in an isotope
28
New cards
Protons minus the charge
Determine the number of electrons in an isotope
29
New cards
Protons minus electrons
Determine the number of neutrons in an isotope
30
New cards
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
Isotope
31
New cards
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
Ion
32
New cards
A solid sphere of matter that was uniform throughout
Daltons model
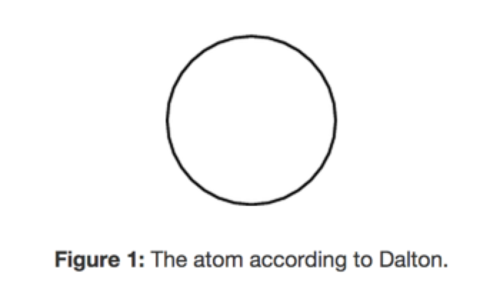
33
New cards
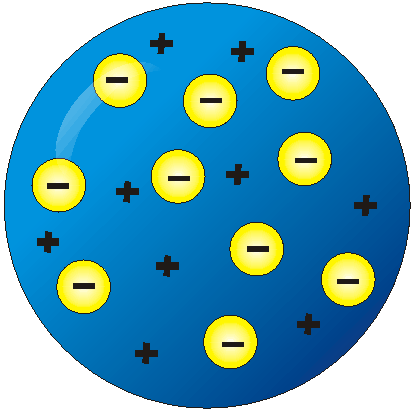
Plum Pudding. Electrons in a sea of positive goo.
Thompsons model
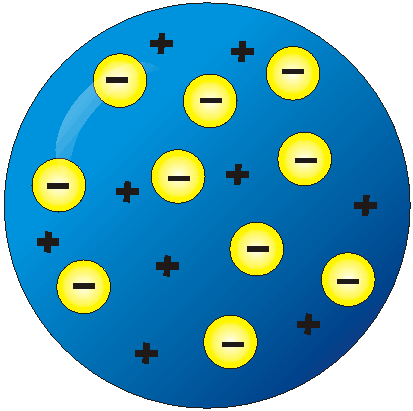
34
New cards
Concluded atoms consist mostly of empty space where electrons move and also have a positively charged molecule in the center
Rutherfords model
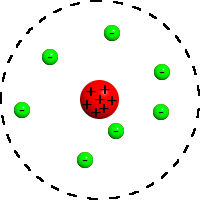
35
New cards
The atomic weight of any atom can be found by multiplying the abundance of an isotope of an element by the atomic mass of the element and then adding the results together.
Calculating atomic weight of an element given the weight of each isotope and relative abundance
36
New cards
(g) (1 mole/# g)
Mass to moles
37
New cards
(moles) (6.022 x 10^23/ 1 mole)
Moles to particles
38
New cards
atoms, molecules, formula units
Particles
39
New cards
6.022 x 10^23
Avagadro's number
40
New cards
Theory is testable
Idea vs. Theory
41
New cards
1) elements are composed of atoms.
Daltons Theory Principle 1
42
New cards
2) Atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements.
Daltons Theory Principle 2
43
New cards
atoms only change when mixed with other elements
Daltons theory principle 4
44
New cards
3) Elements can mix together
Daltons theory Principle 3
45
New cards
When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers
Law of Multiple Proportions (Dalton)
46
New cards
Negative electrode
Cathode
47
New cards
positively charged particle, found in the neuclues
Proton
48
New cards
A small particle in the nucleus of the atom, with no electrical charge
Neutron
49
New cards
electron and proton
The subtomic particles that are least massive and most massive, respectivly are the...
50
New cards
Neutral charged
Atom
51
New cards
Balance of the proton and electron
Why is an atom neutral?
52
New cards
Chlorine- 37 ion
Given the # protons is 17 and the # neutrons is 20, with a 1- charge. What is the name of the ion?
53
New cards
17
Given the # protons is 17 and the # neutrons is 20, with a 1- charge. What is the atomic #
54
New cards
37
Given the # protons is 17 and the # neutrons is 20, with a 1- charge. What is the mass #
55
New cards
37
Given the # protons is 17 and the # neutrons is 20, with a 1- charge. What is the # of particles in the neuclues?
56
New cards
21
Given the # protons is 17 and the # neutrons is 20, with a 1- charge. What is the # of electrons?
57
New cards
Mass number
When writing the symbol which number goes at the top left?
58
New cards
Atomic number
When writing the symbol which number goes at the bottom left?
59
New cards
Charge
When writing the symbol which number goes at the top right?
60
New cards
False, it depends on the number of electrons
T or F: In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of neutrons.
61
New cards
True
T or F: When an atom loses or gains electrons, it is called an ion
62
New cards
False, it depends on your neutron.
T or F
atoms with the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons are called isotopes.
atoms with the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons are called isotopes.
63
New cards
atomic mass unit, 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
AMU
64
New cards
the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
Atomic mass
65
New cards
the amount of a substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12
Mole
66
New cards
the mass of one mole of a pure substance
Molar mass
67
New cards
Mass number on periodic table
g=