MILADY CHAPTER 7 + 8
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

72 Terms
alopecia
abnormal hair loss.
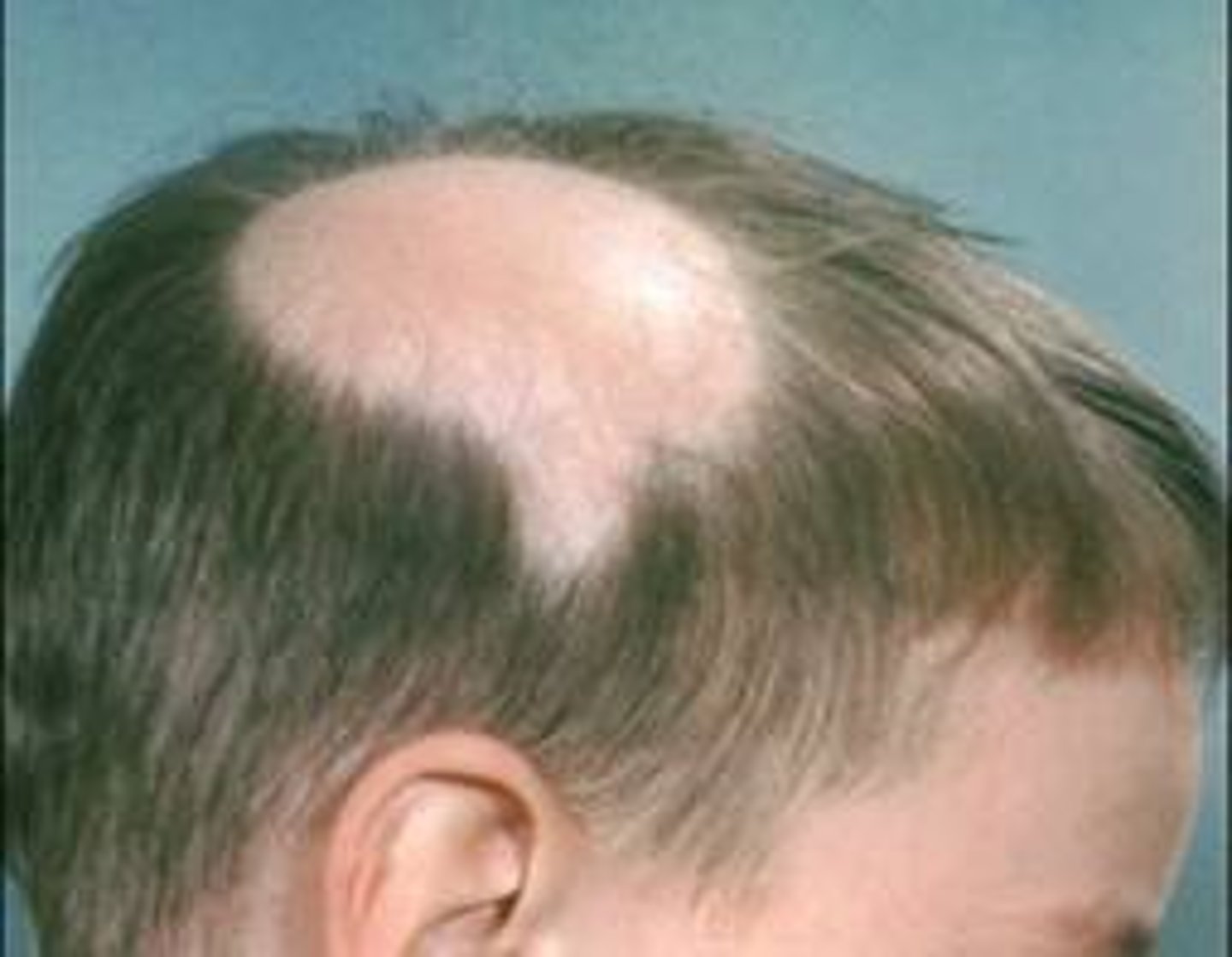
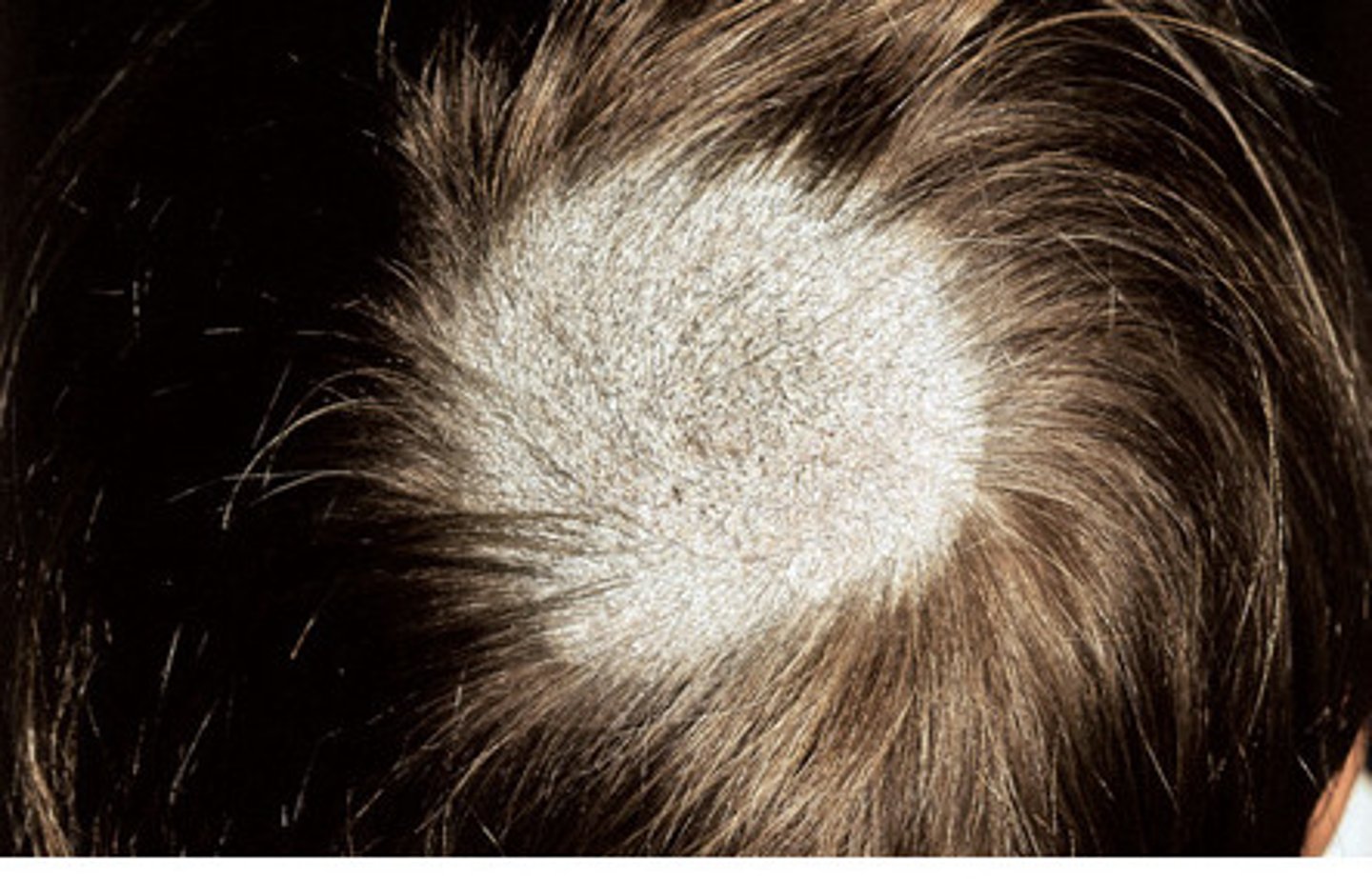
alopecia areata
autoimmune disorder that causes the affected hair follicles to be mistakenly attacked by a person's own immune system; usually begins with one or more small, round, smooth bald patches on the scalp.
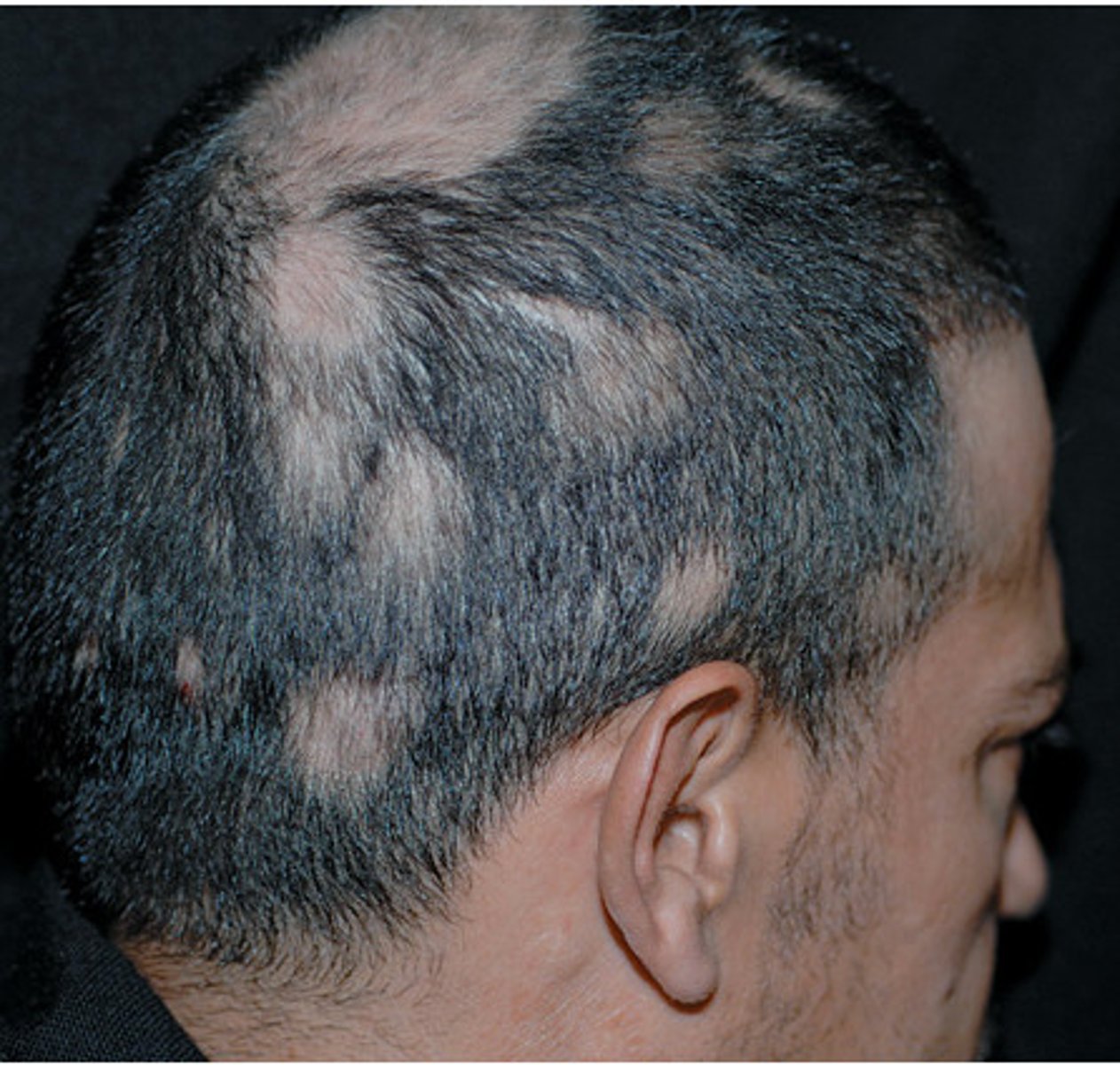
alopecia totalis
total loss of scalp hair.
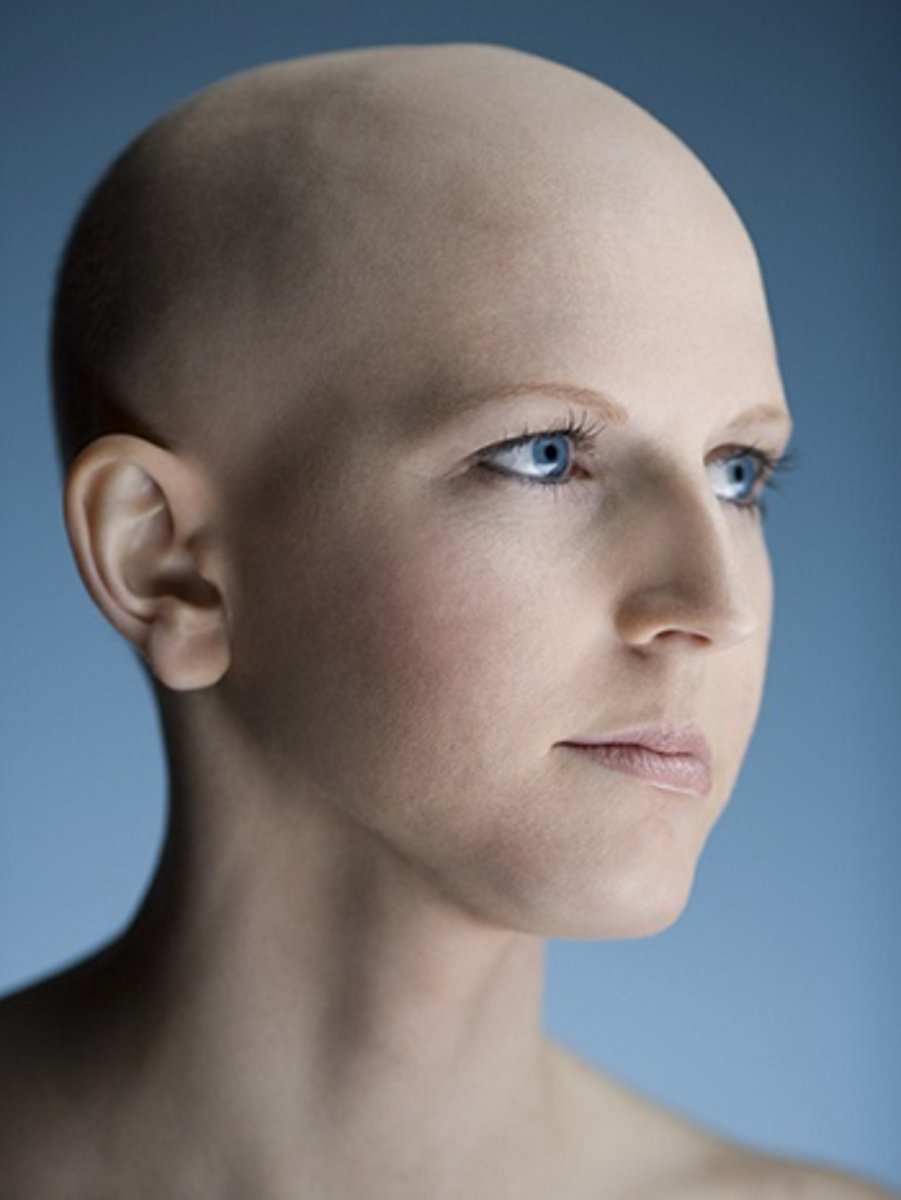
alopecia universalis
complete loss of body hair.

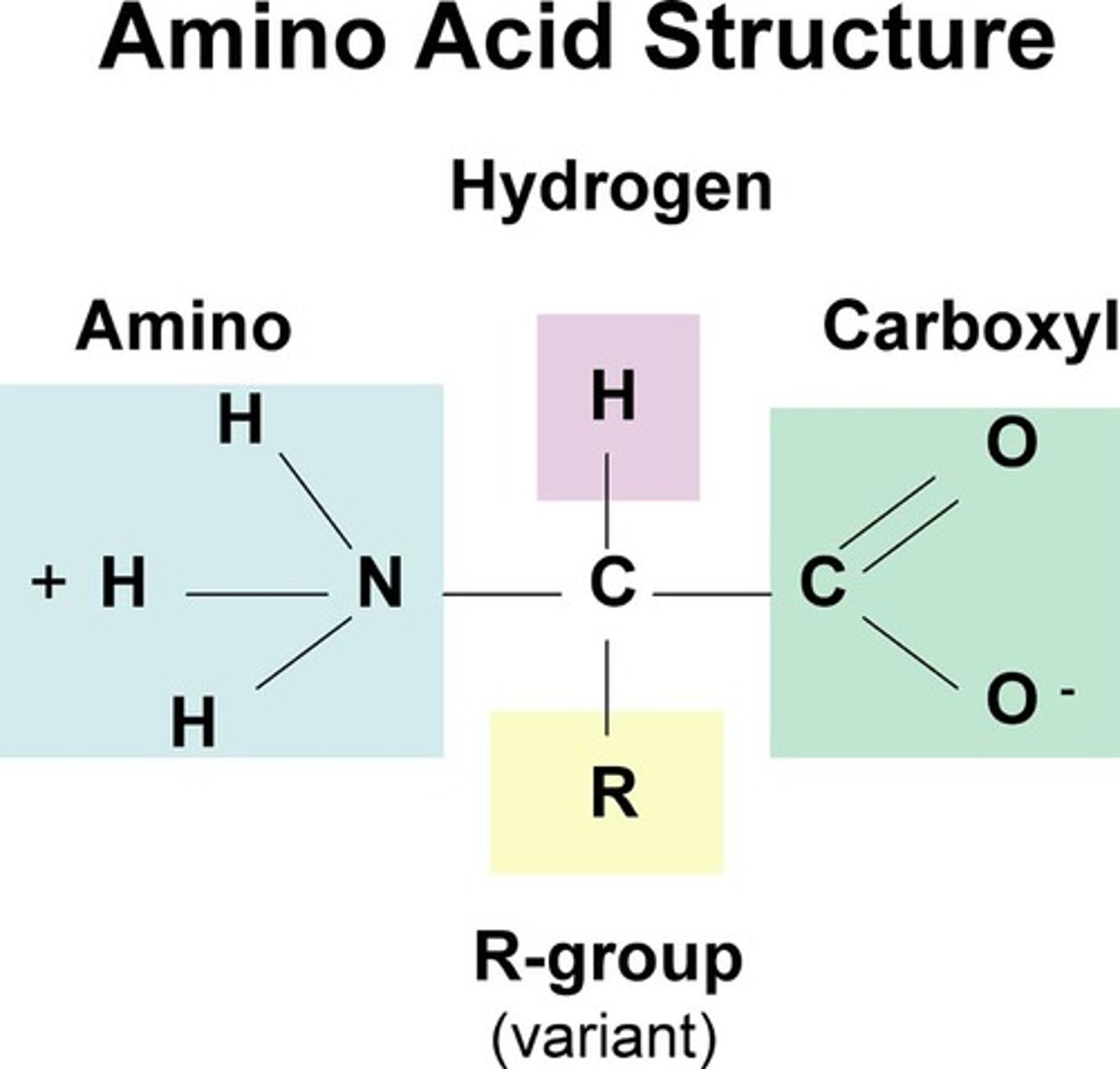
amino acids
units that are joined together end to end like pop beads by strong, chemical peptide bonds to form the polypeptide chains that comprise proteins.
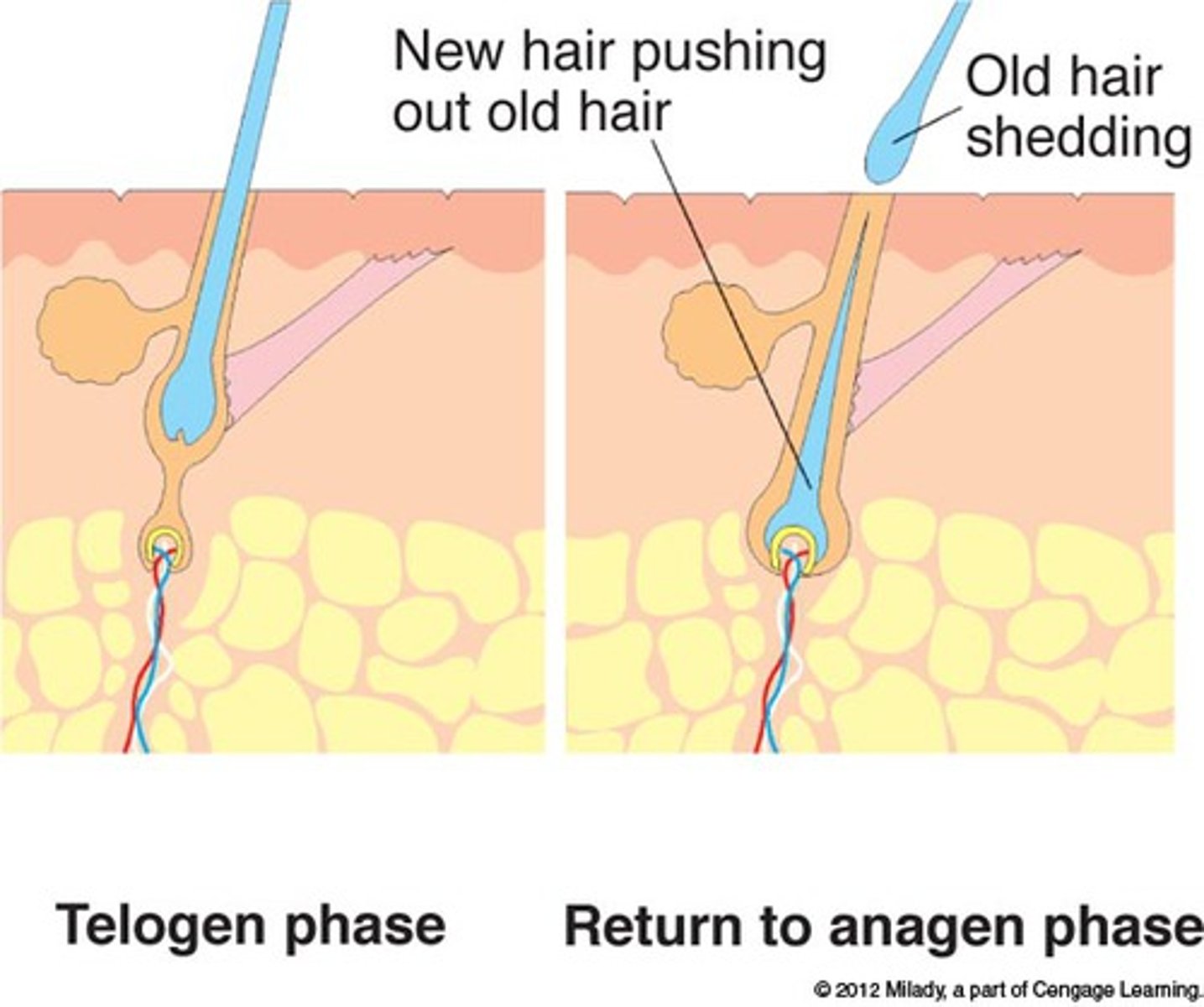
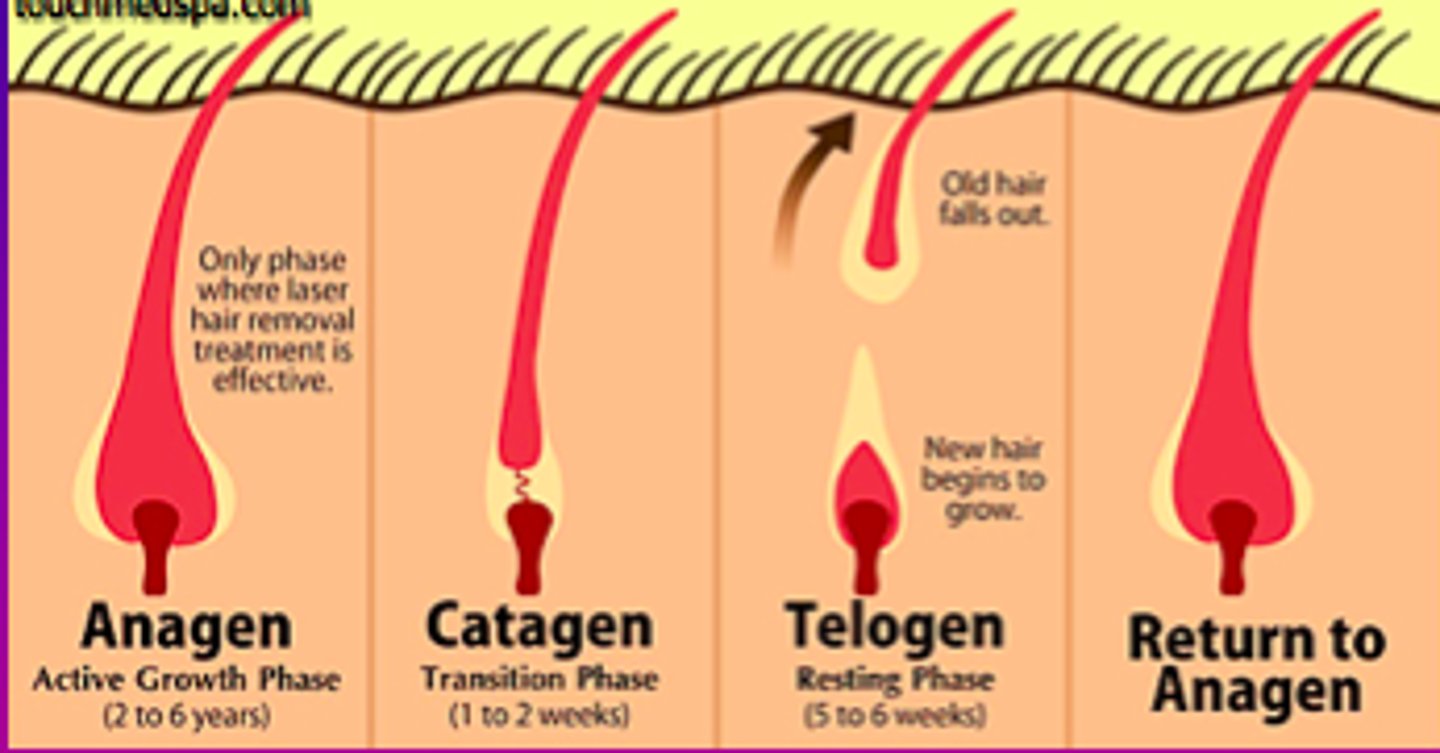
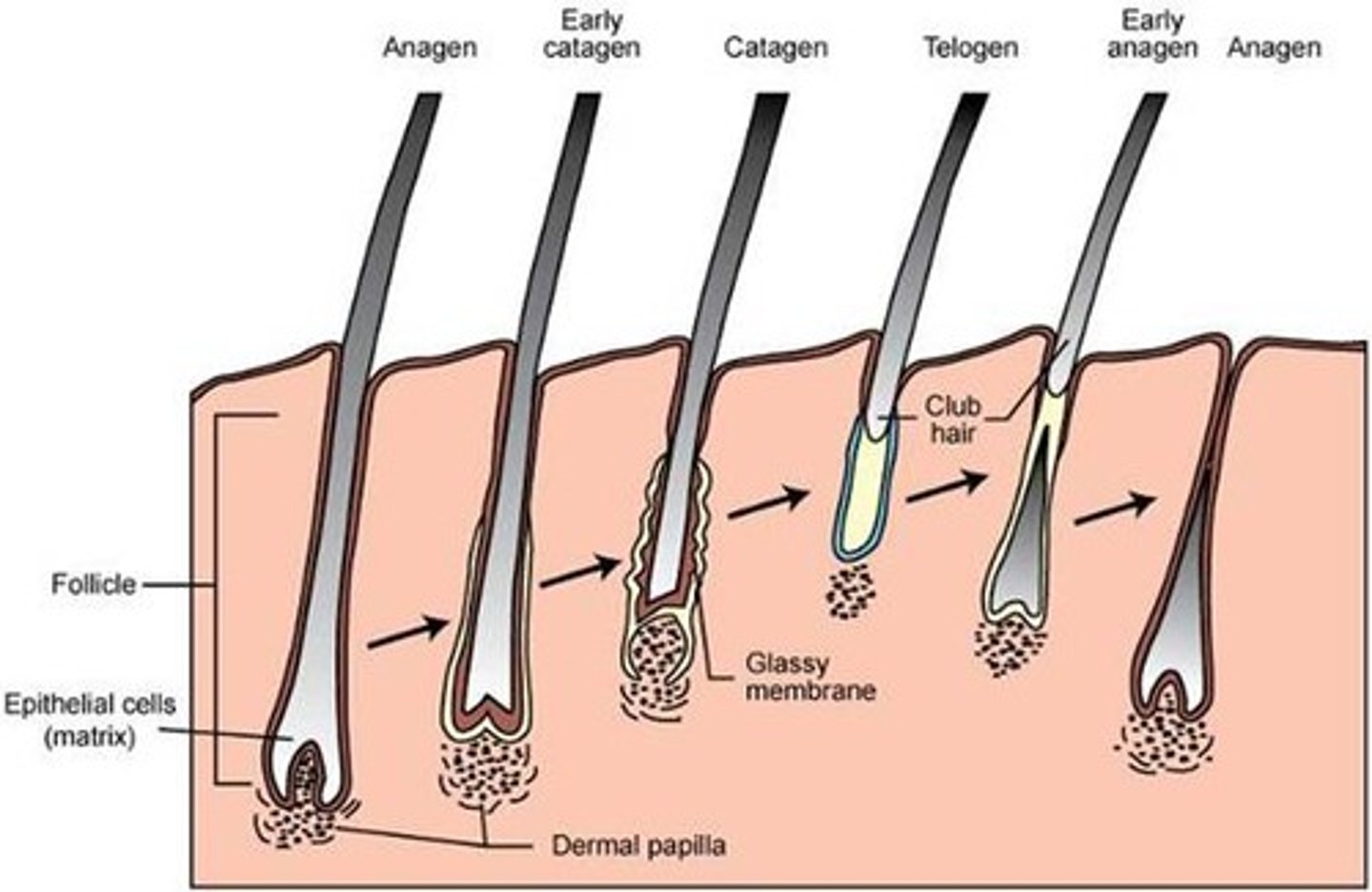
anagen phase
(growth phase) phase during which new hair is produced.
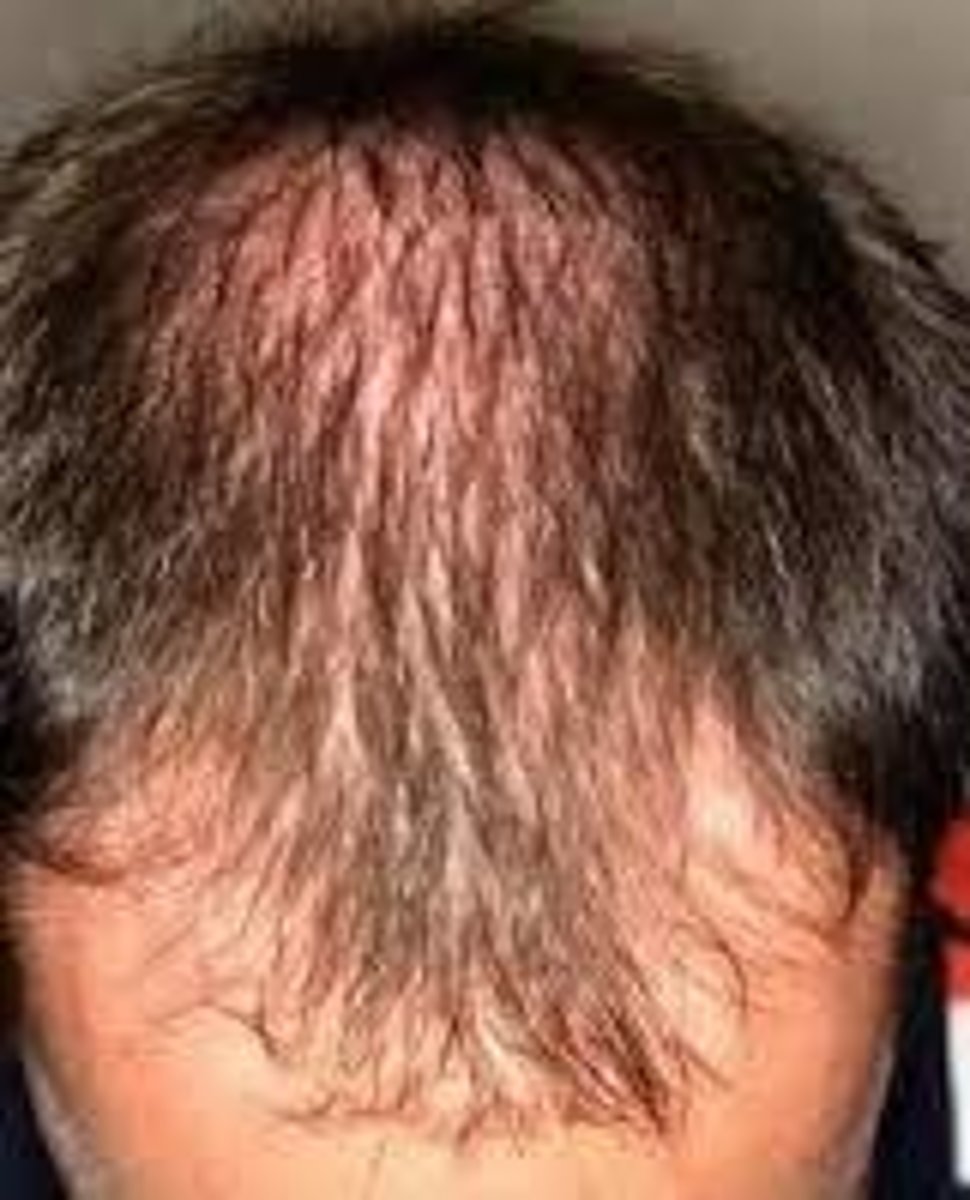
androgenic alopecia
(androgenetic alopecia) hair loss characterized by miniaturization of terminal hair that is converted to vellus hair; in men, it is known as male pattern baldness
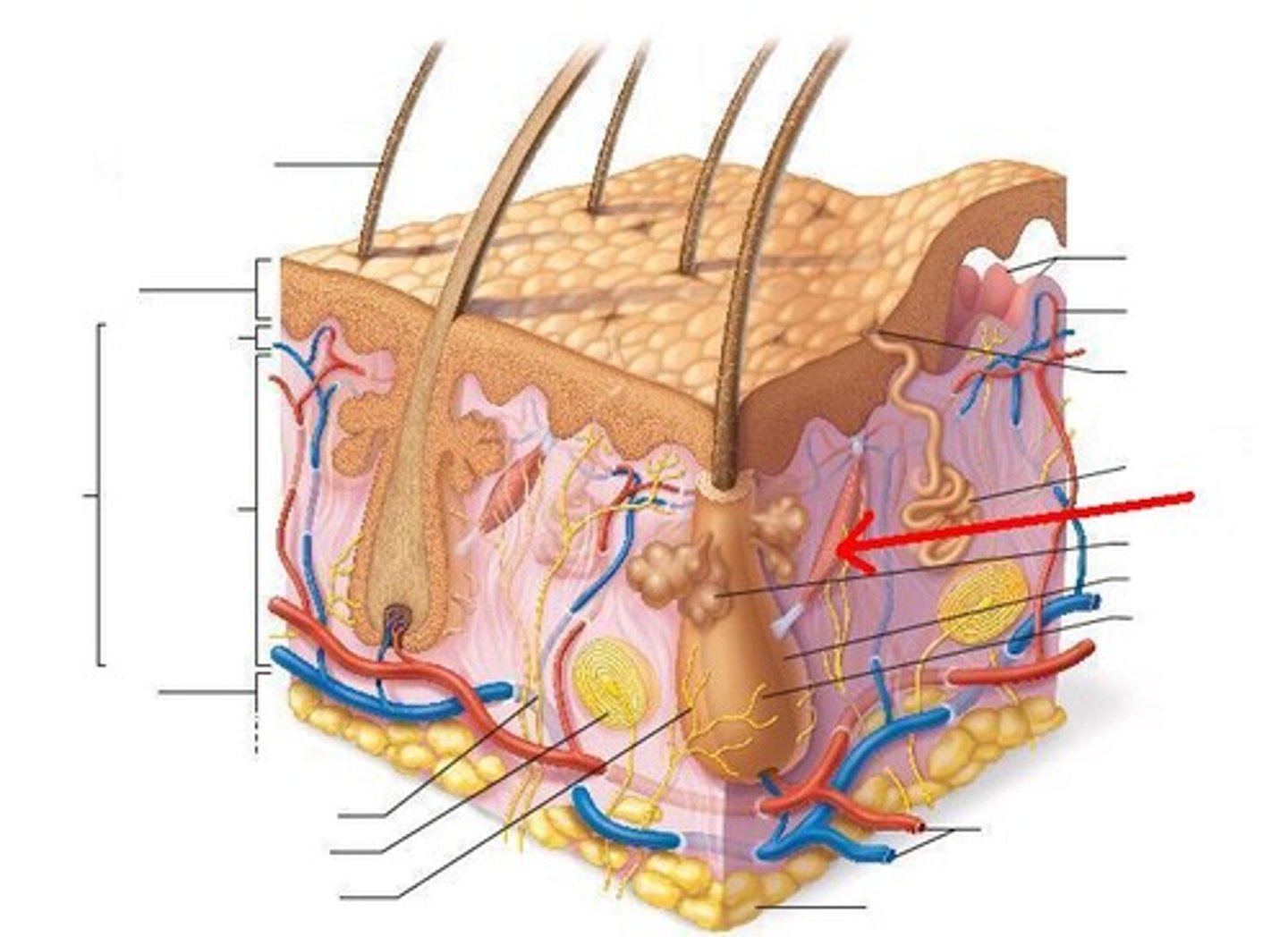
arrector pili muscle
also known as amdrogemetic
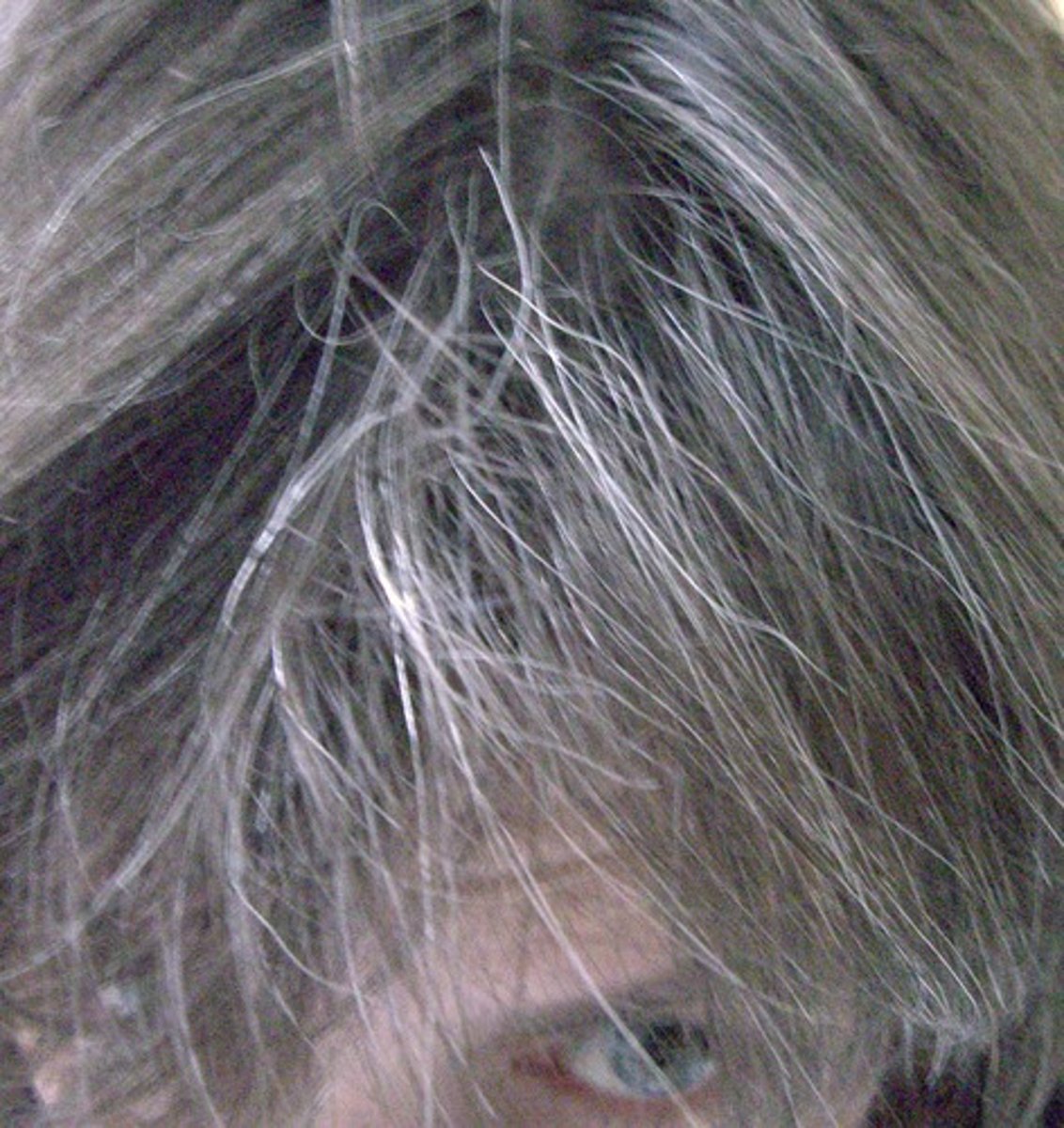
canities
technical term for gray hair; results from the loss of the hair's natural melanin pigment.

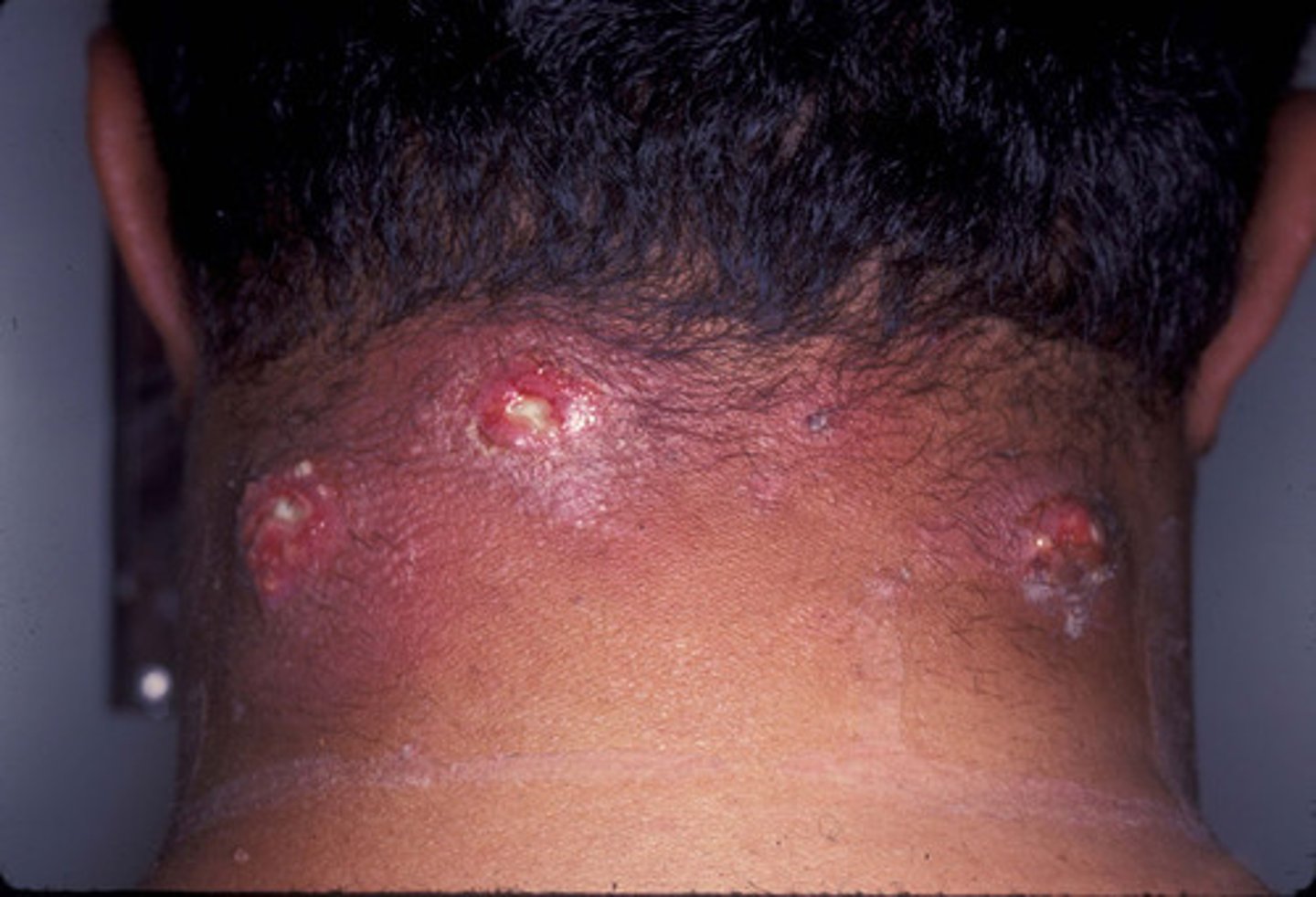
carbuncle
inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue caused by staphylococci; similar to a furuncle but larger.
catagen phase
the brief transition period between the growth and resting phases of a hair follicle. It signals the end of the growth phase.
COHNS elements
the five elements- carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur- that make up human hair, skin, tissue, and nails.
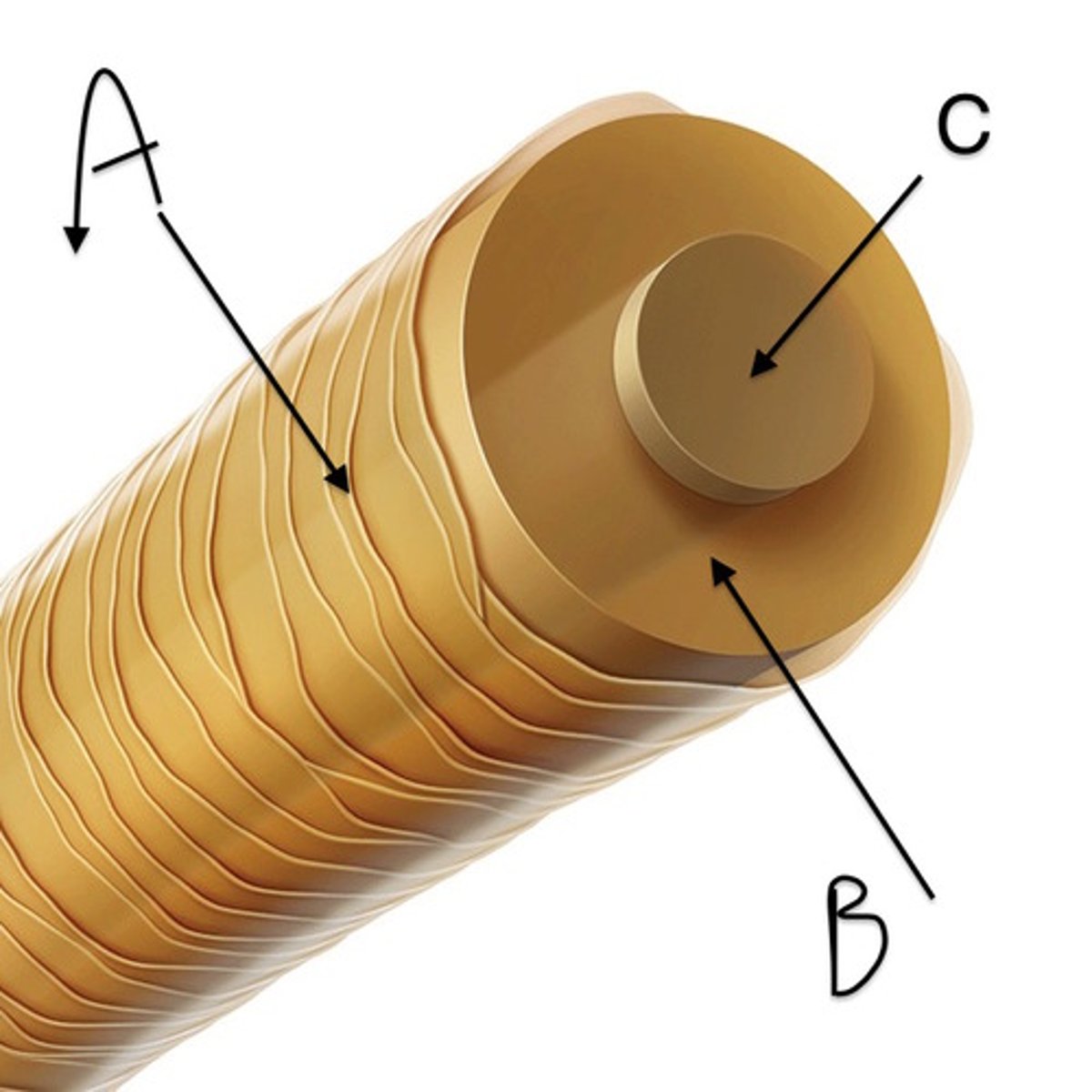
cortex
middle layer of the hair; a fibrous protein core formed by elongated cells containing melanin pigment.
cowlick
tuff of hair that stands straight up.
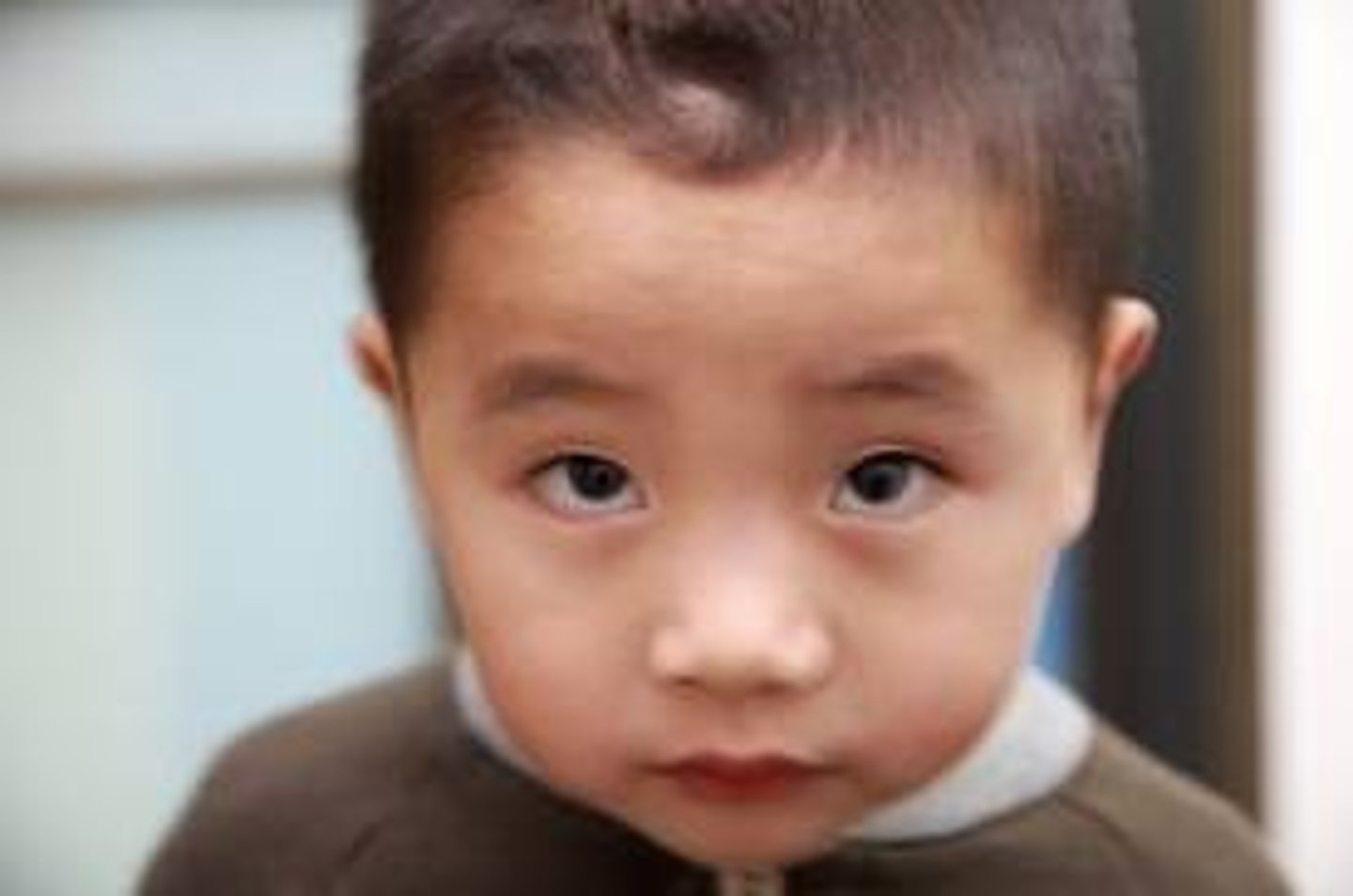

cysteine
an amino acid joined with another cysteine amino acid to create cystine amino acid.
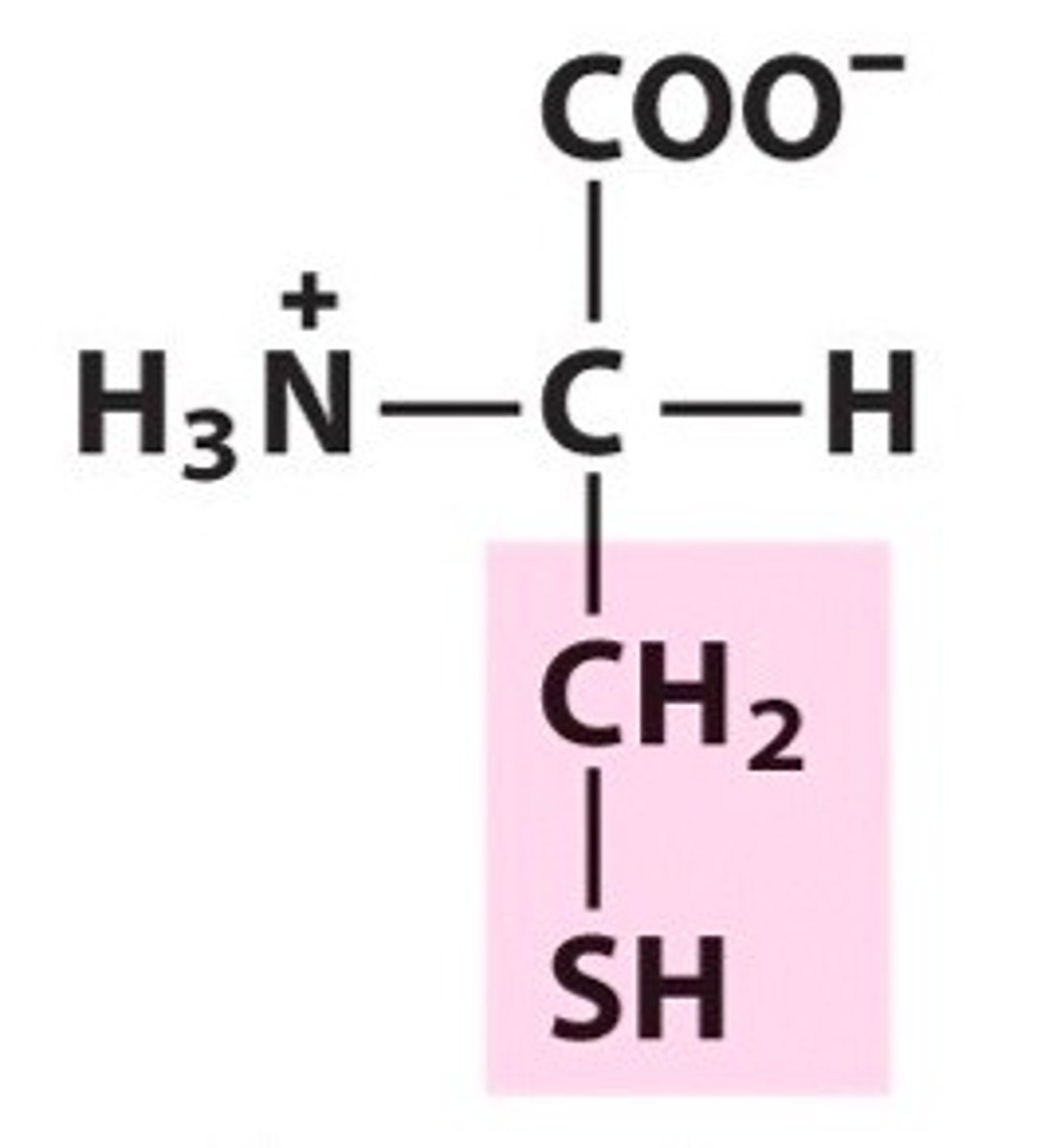
cystine
an amino acid that joins together two peptide strands.
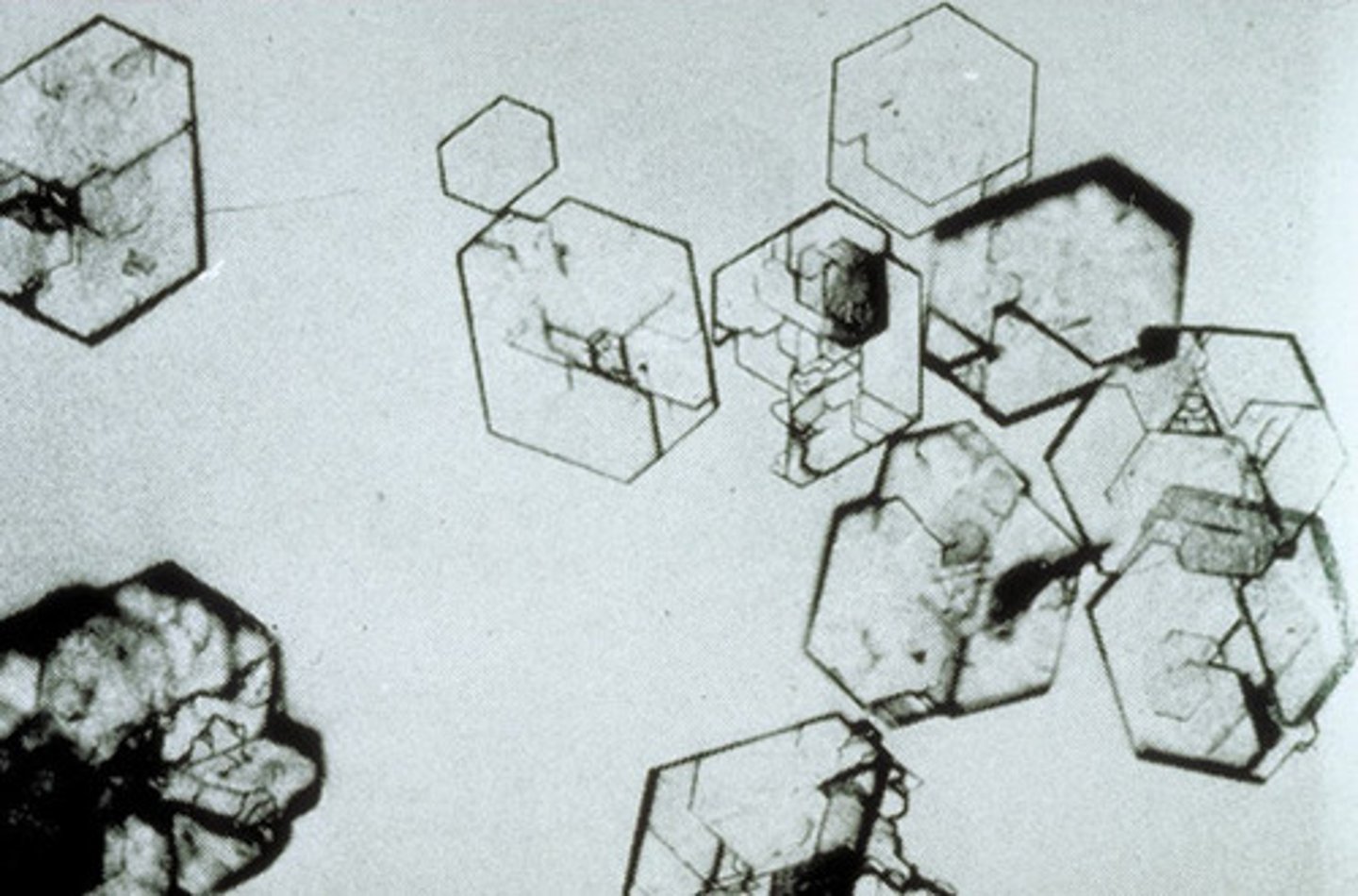
dermal papilla
plural: dermal papilla. A small, cone-shaped elevation location located at the base of the root follicle that fits into the hair bulb.
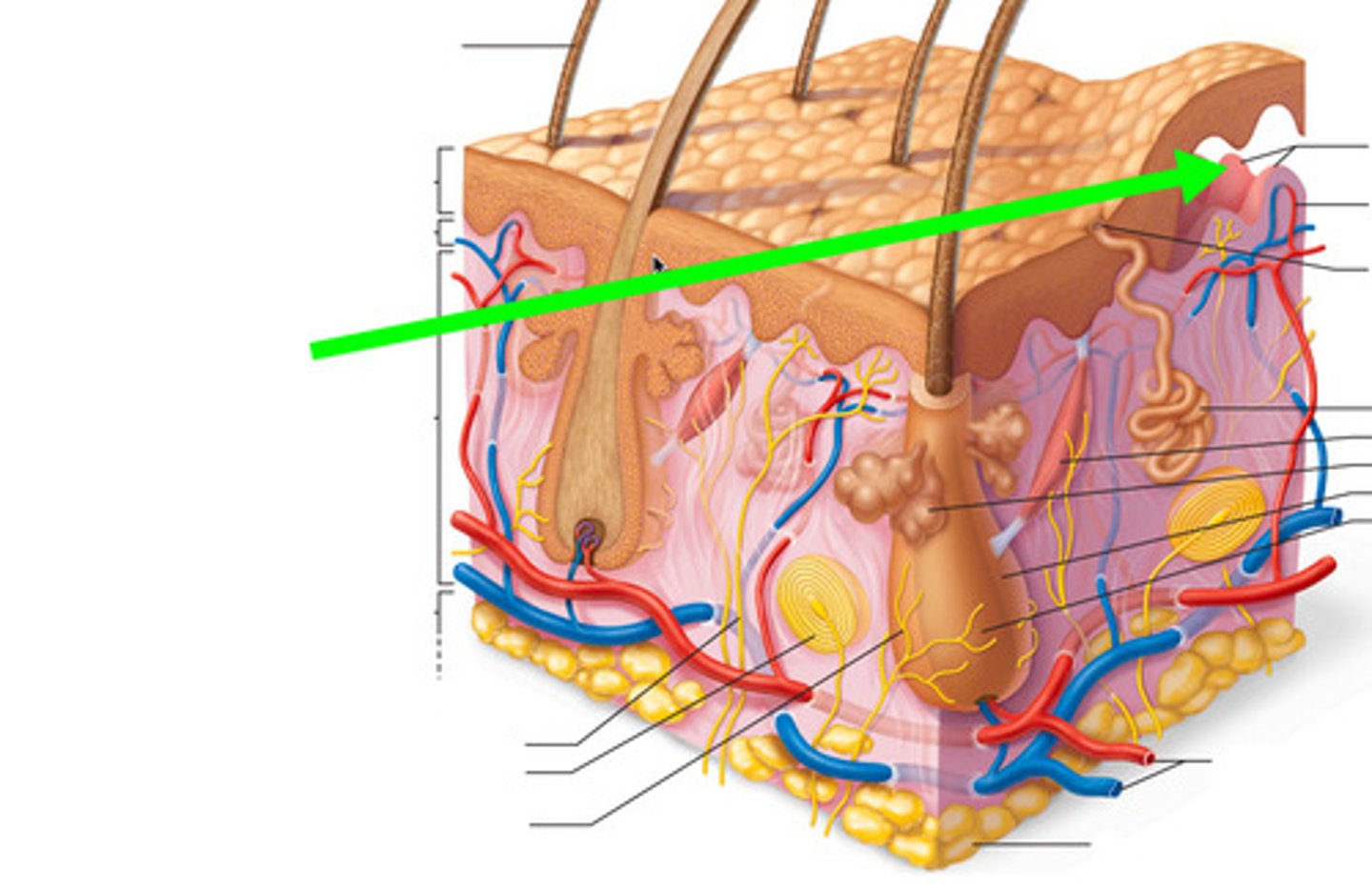
disulfide bond
strong chemical side bond that joins the sulfur atoms of two neighboring cysteine amino acids to create one cystine, which joins together two polypeptide strands like rungs on a ladder.
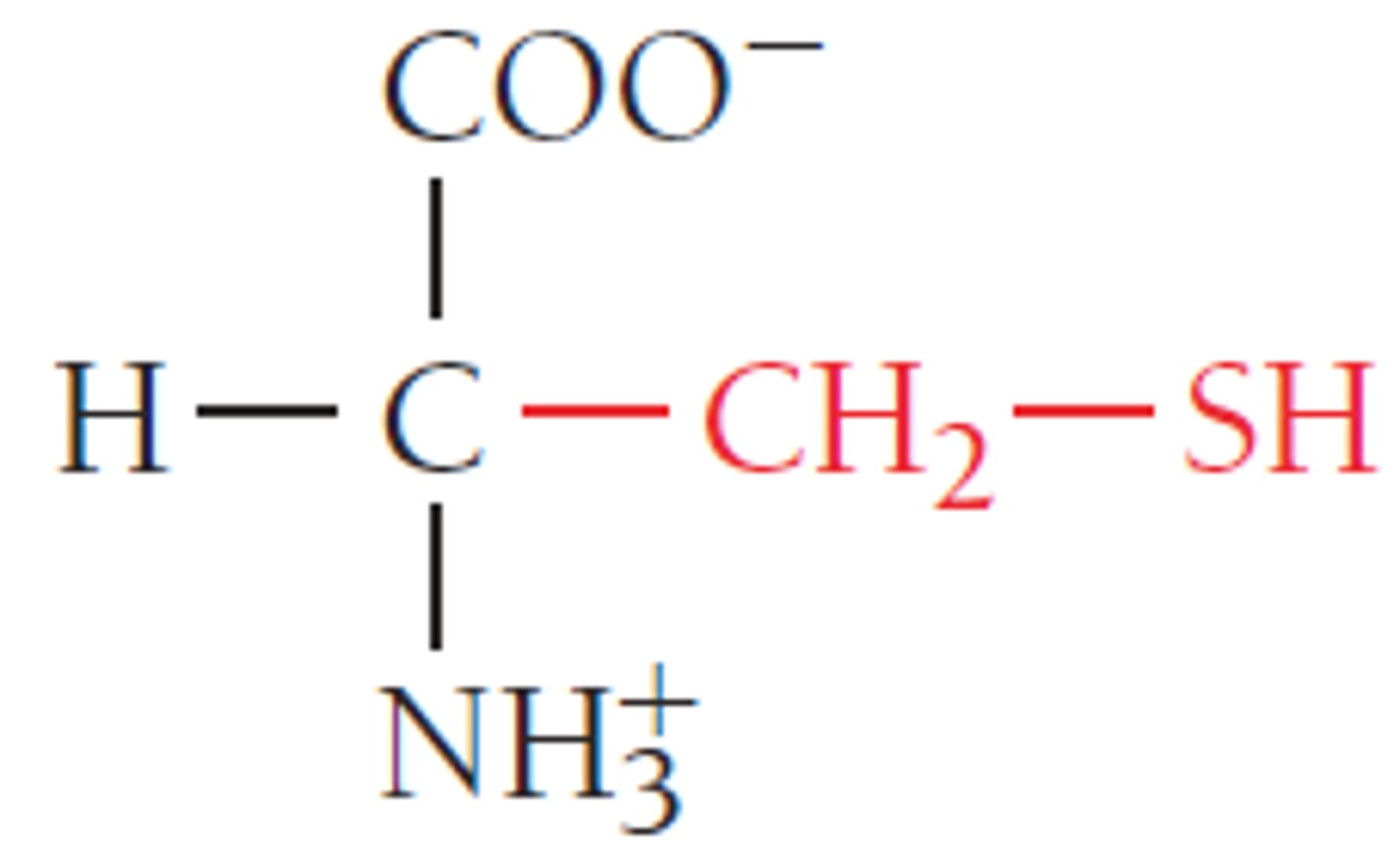
eumelanin
provides natural dark brown to black to the hair and is the dark pigment predominant in black and brunette hair.
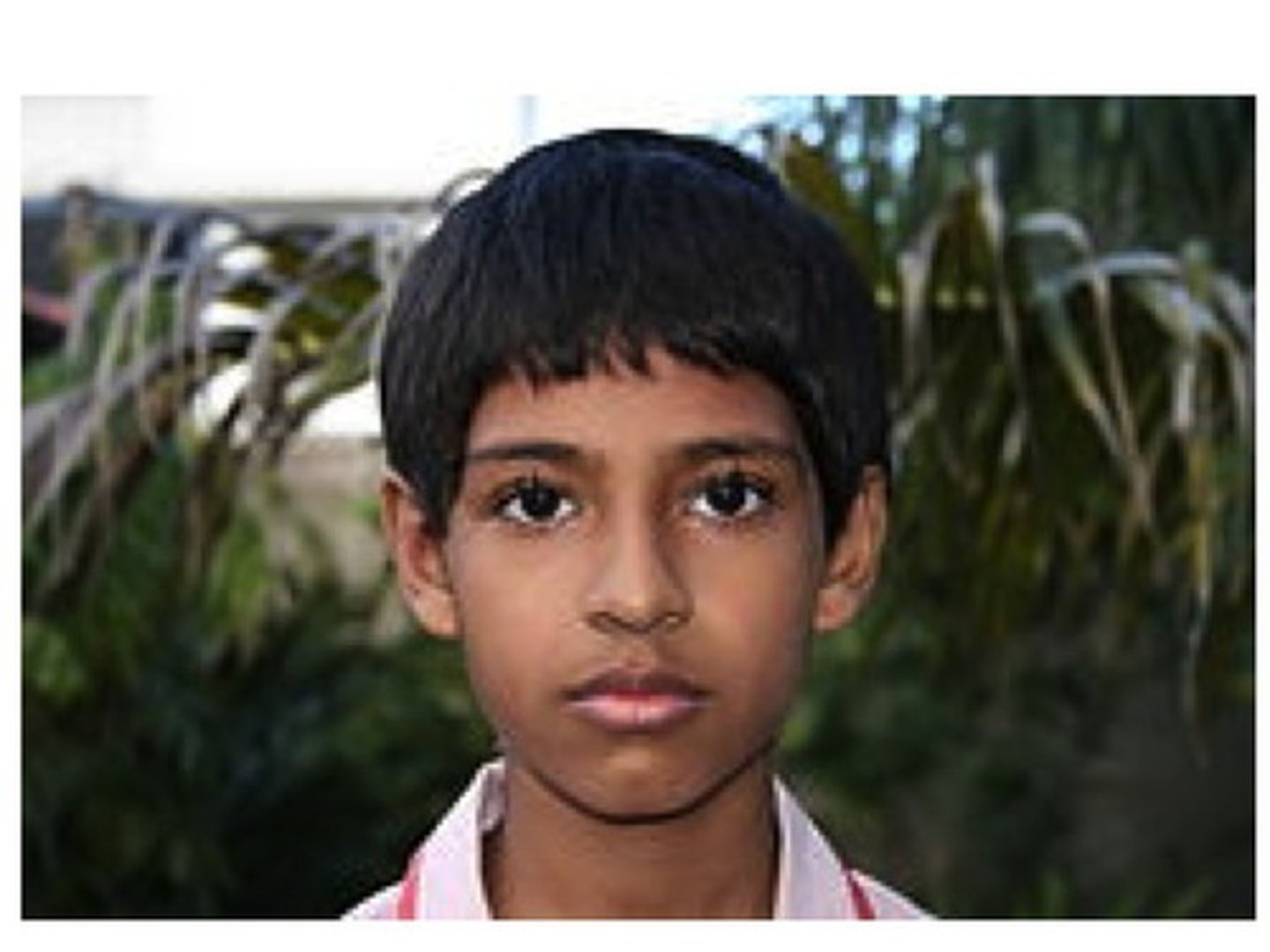

fragilitas crinium
technical term for brittle hair.
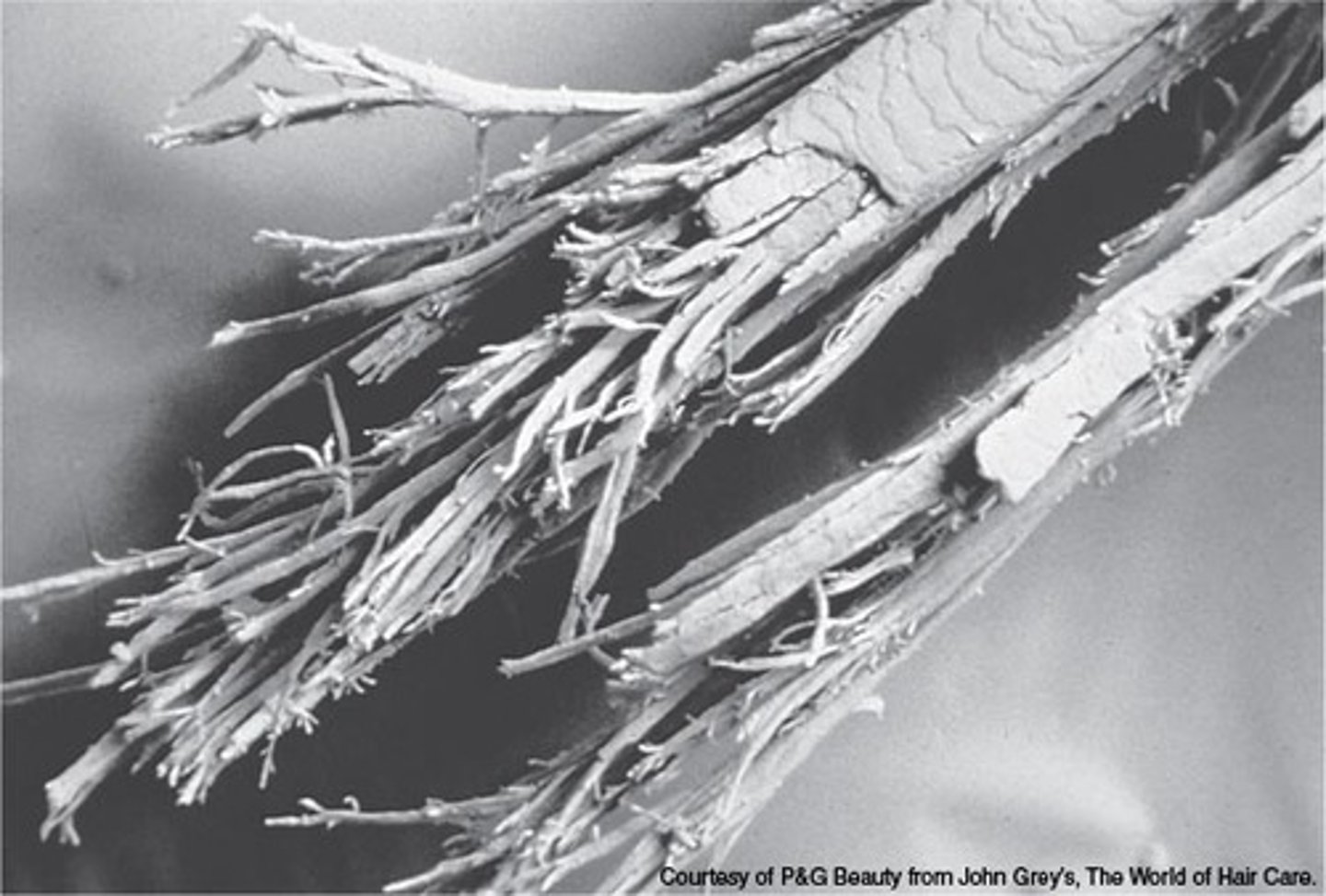
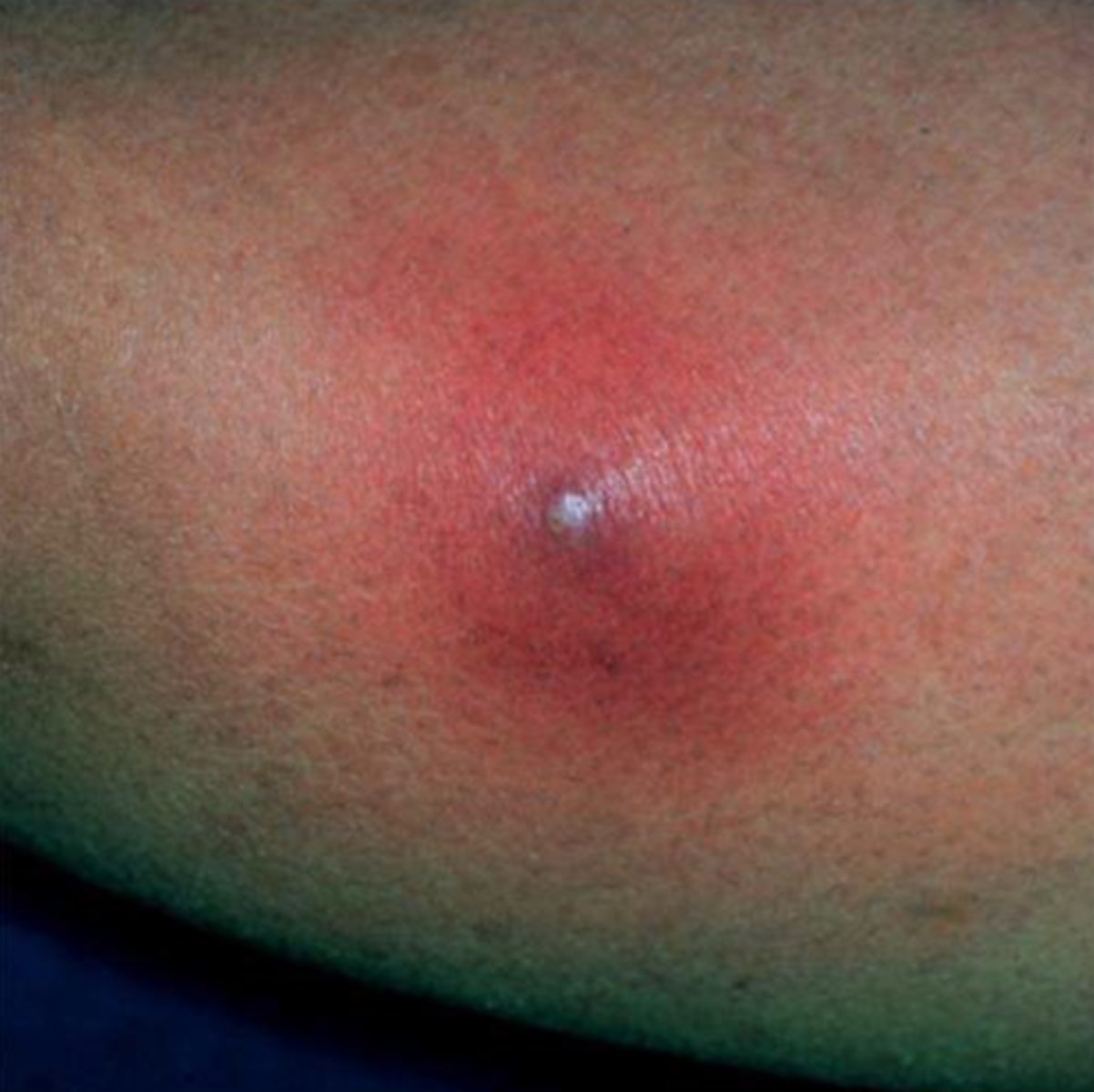
furuncle
boil; acute, localized bacterial infection of the hair follicle that produces constant pain.
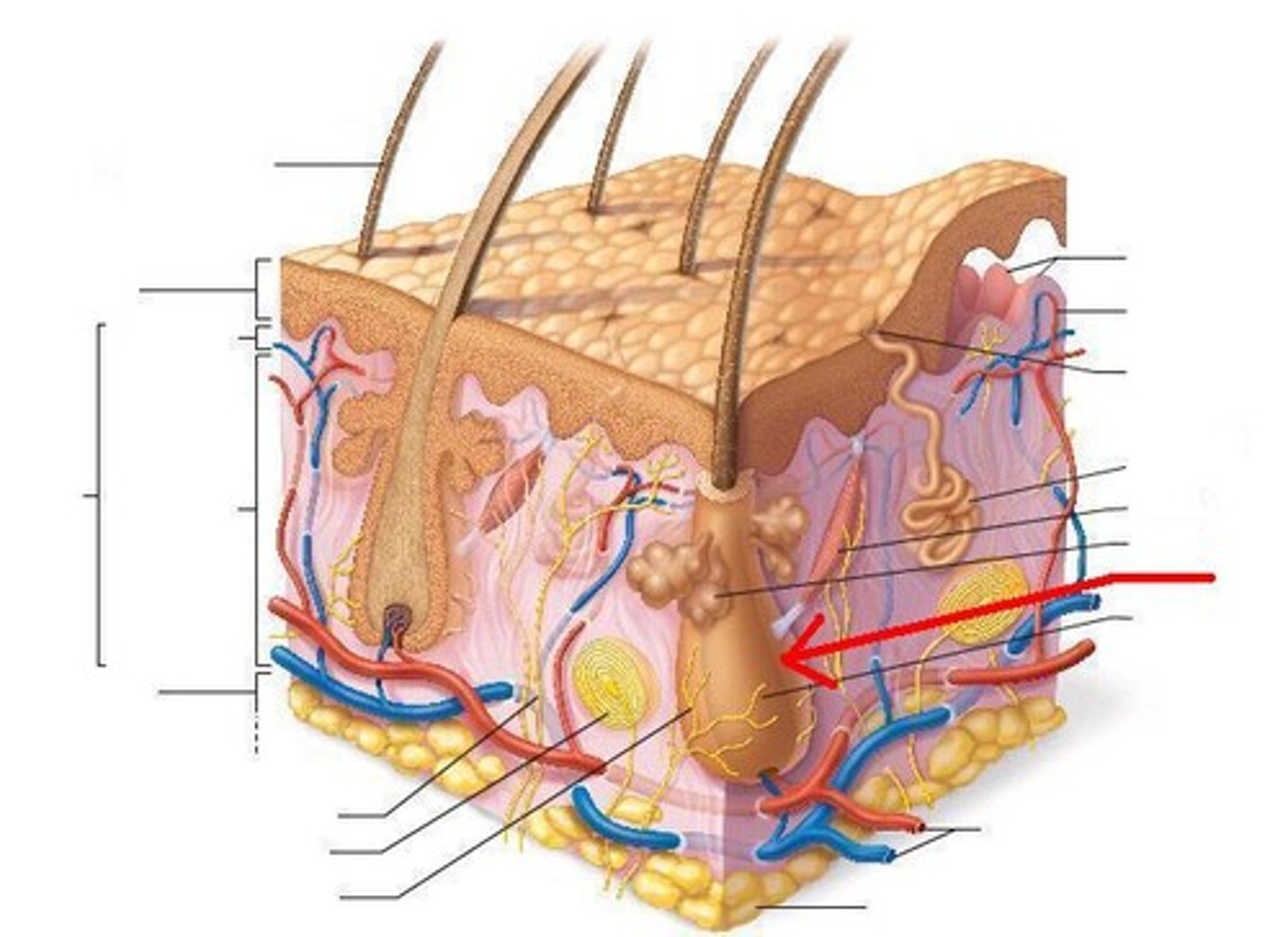
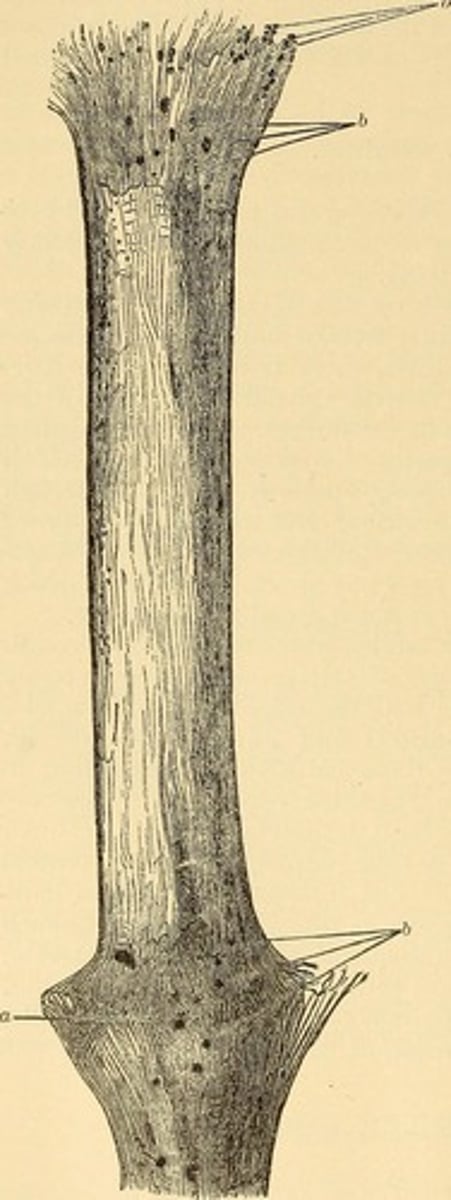
hair bulb
lowest part of a hair strand; the thickened, club-shaped structure that forms the lower part of the hair root.
hair cuticle
outermost layer of hair; consisting of a single, overlapping layer of transparent, scale-like cells that look like shingles on a roof.
hair density
the number of individual hair strands on 1 square inch (2.5 square centimeters) of scalp
hair elasticity
ability of the hair to stretch and return to its original length without breaking.
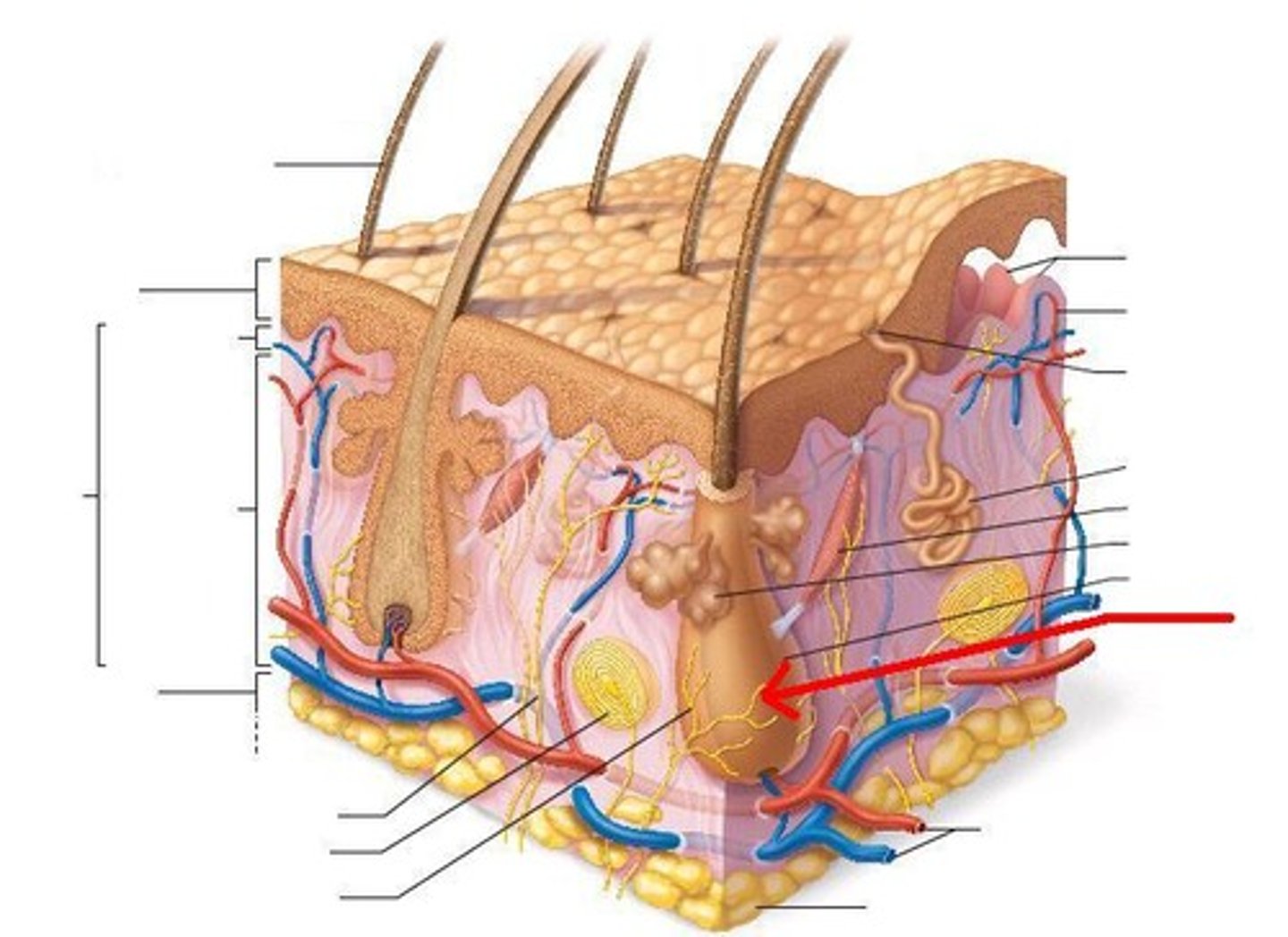
hair follicle
the tube-like depression or pocket in the skin or scalp that contains the hair root.
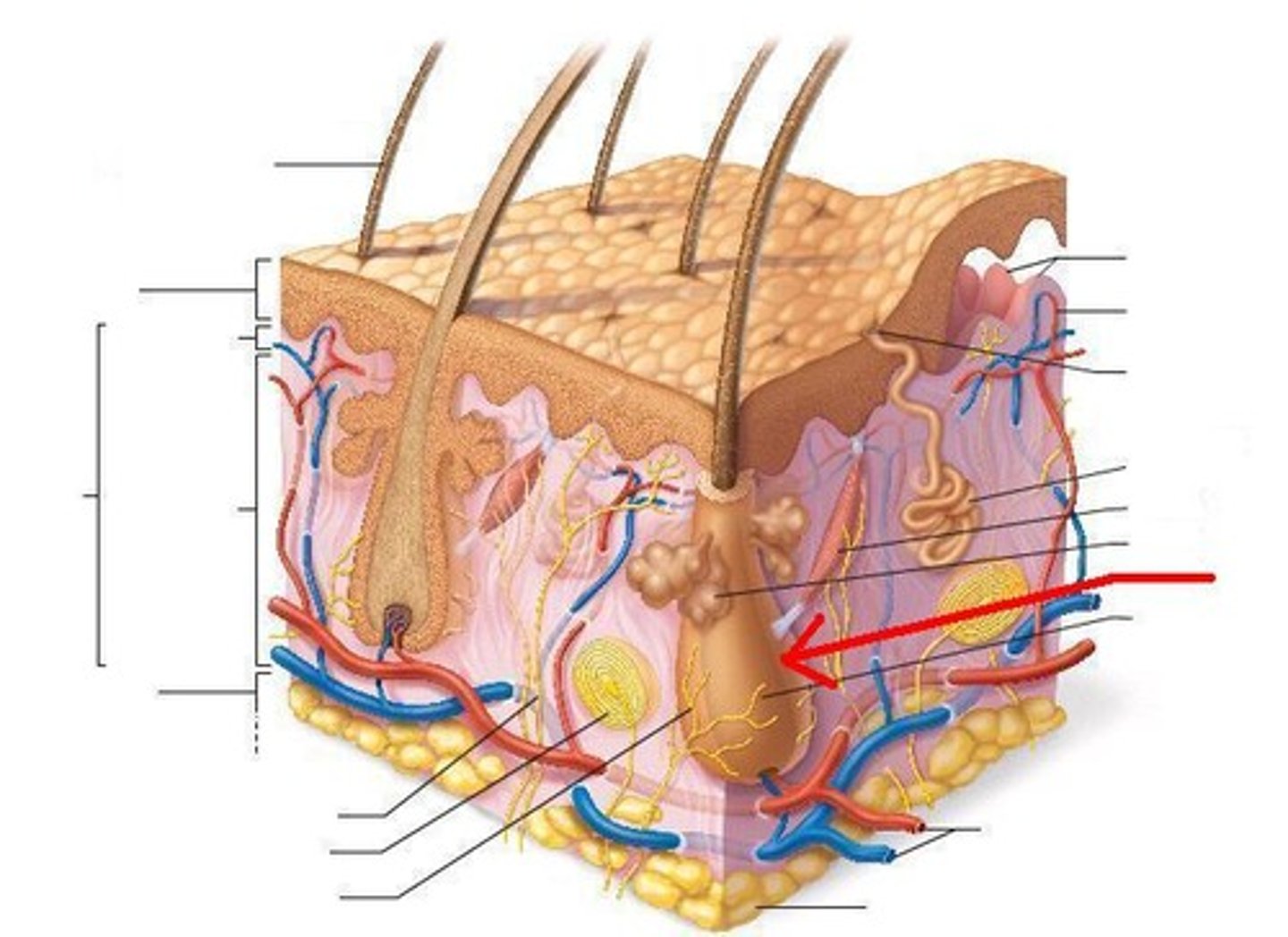
hair porosity
ability of the hair to absorb moisture.
hair root
the part of the hair located below the surface of the epidermis.
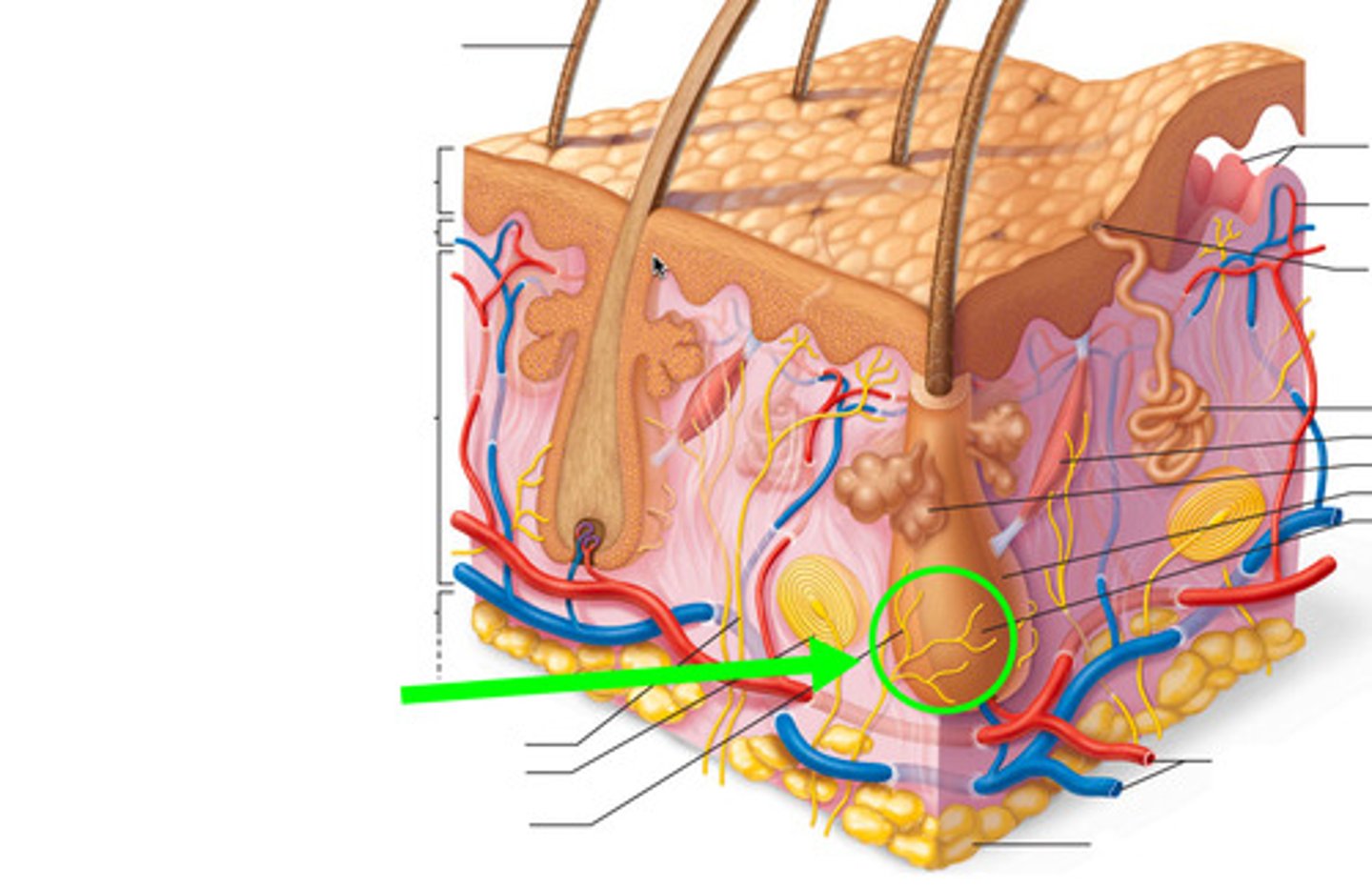
hair shaft
the portion of hair that projects above the epidermis.
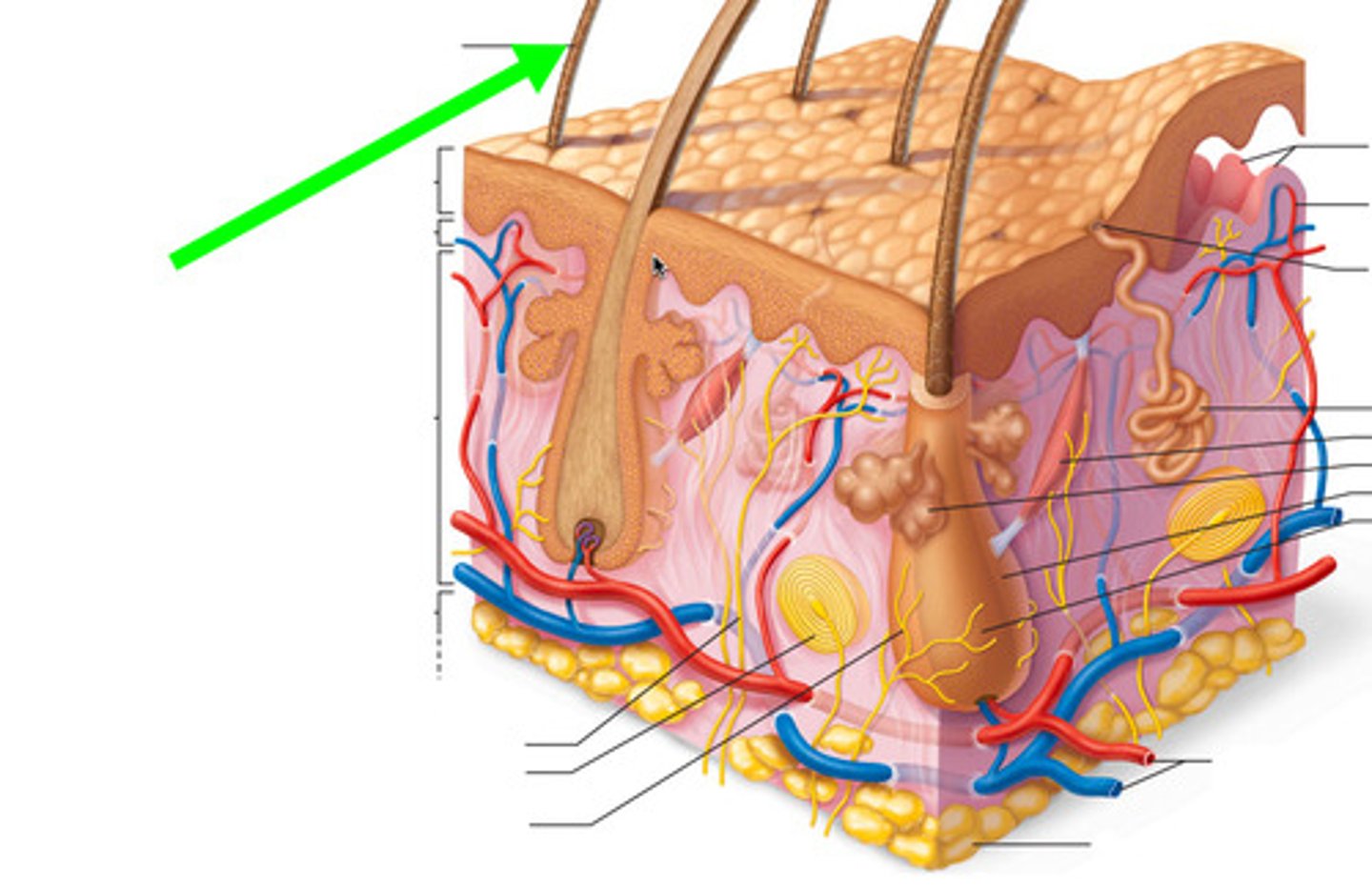
hair stream
hair flowing in the same direction, resulting from follicles sloping in the same direction.
hair texture
thickness or diameter of the individual hair strand.
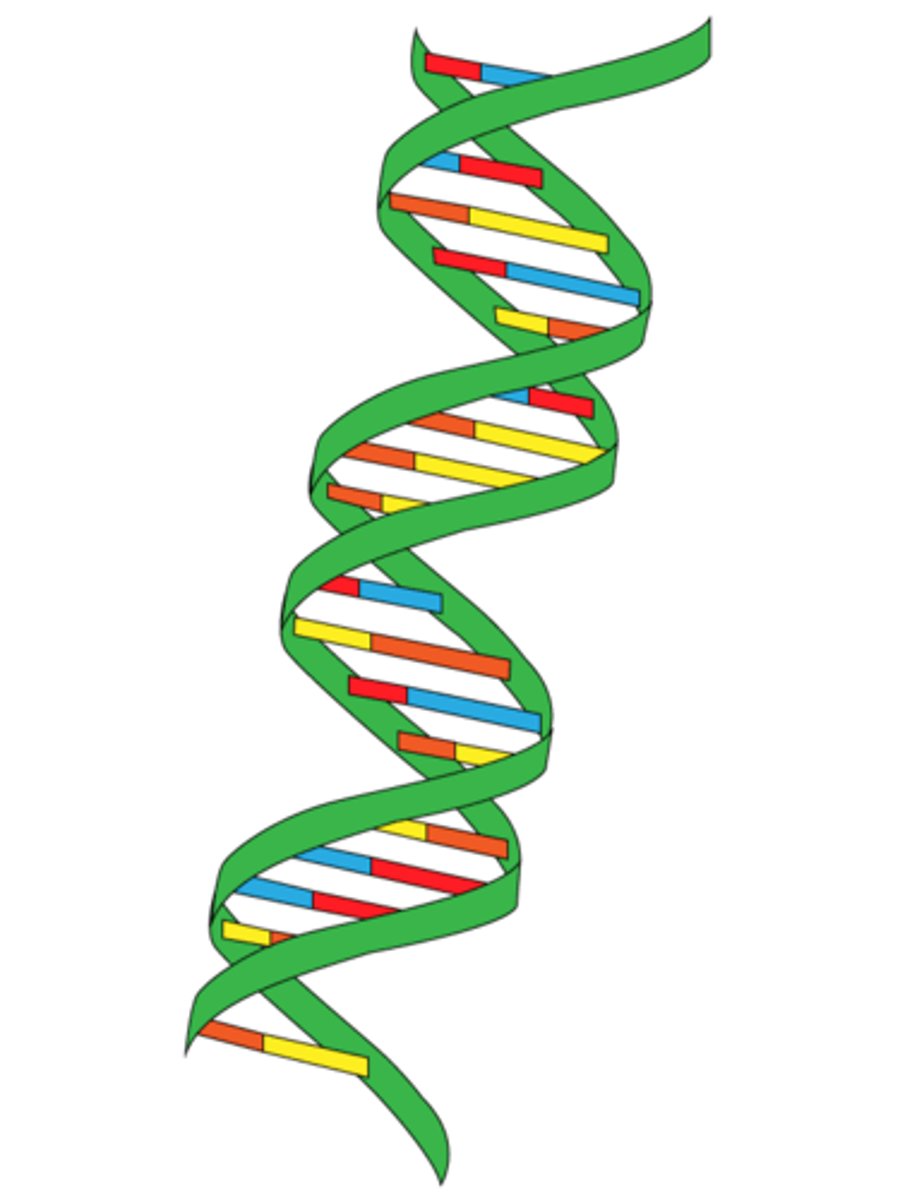
helix
spiral shape of a coiled protein created by polypeptide chains that intertwine with each other.
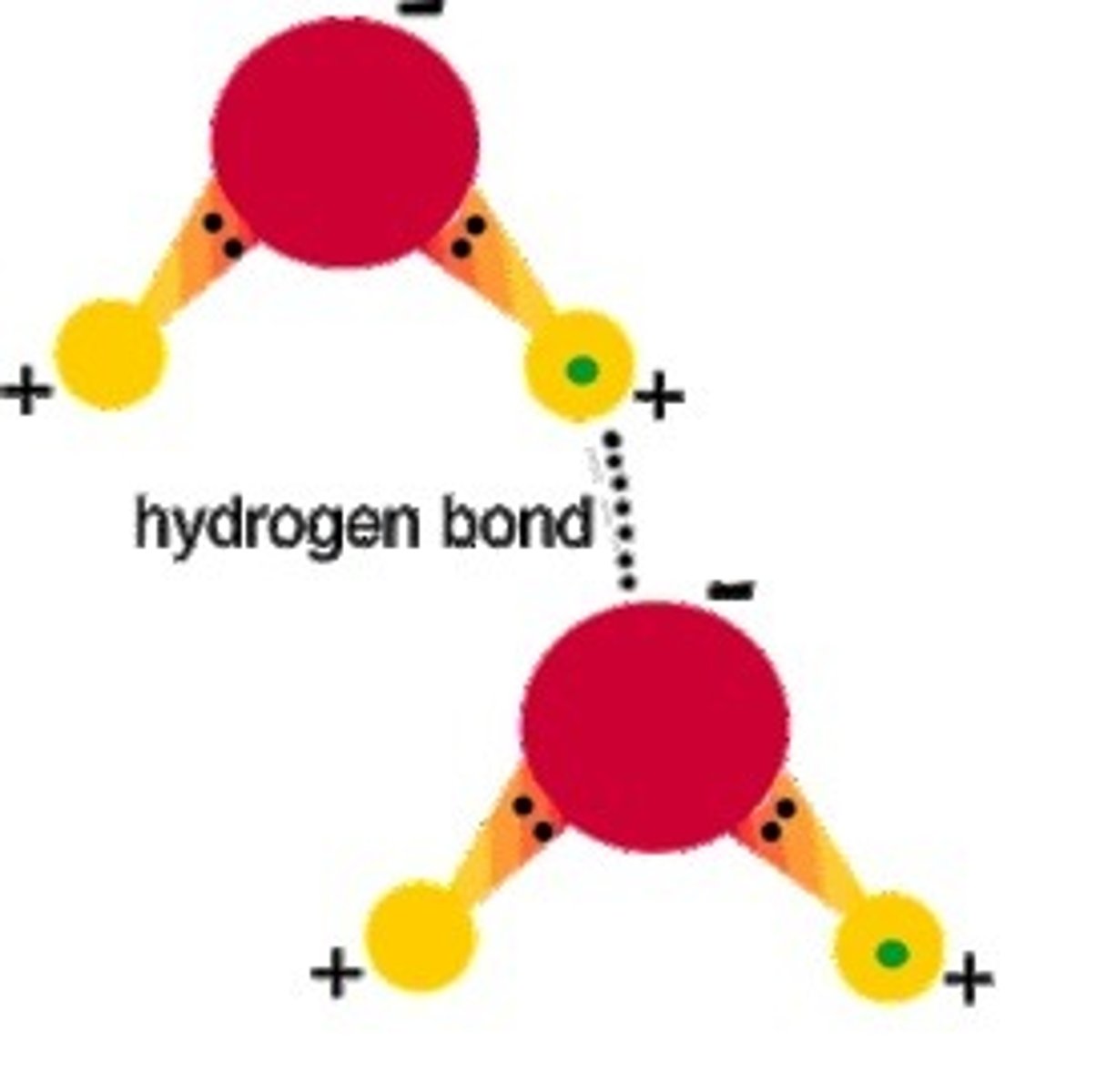
hydrogen bond
a weak, physical, cross-link side bond that is easily broken by water or heat.
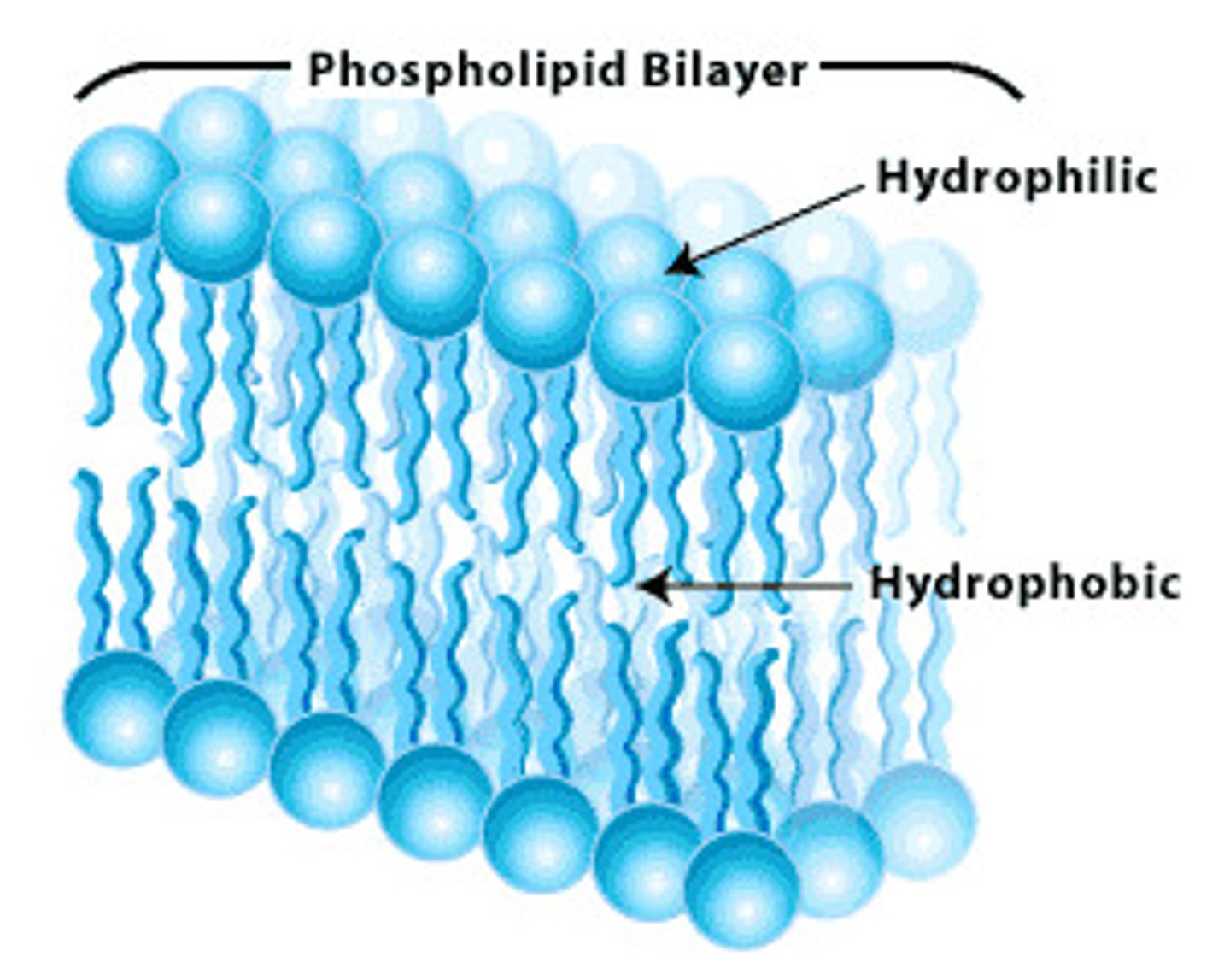
hydrophilic
easily absorbs moisture; in chemistry terms, capable of combining with or attracting water (water-loving).
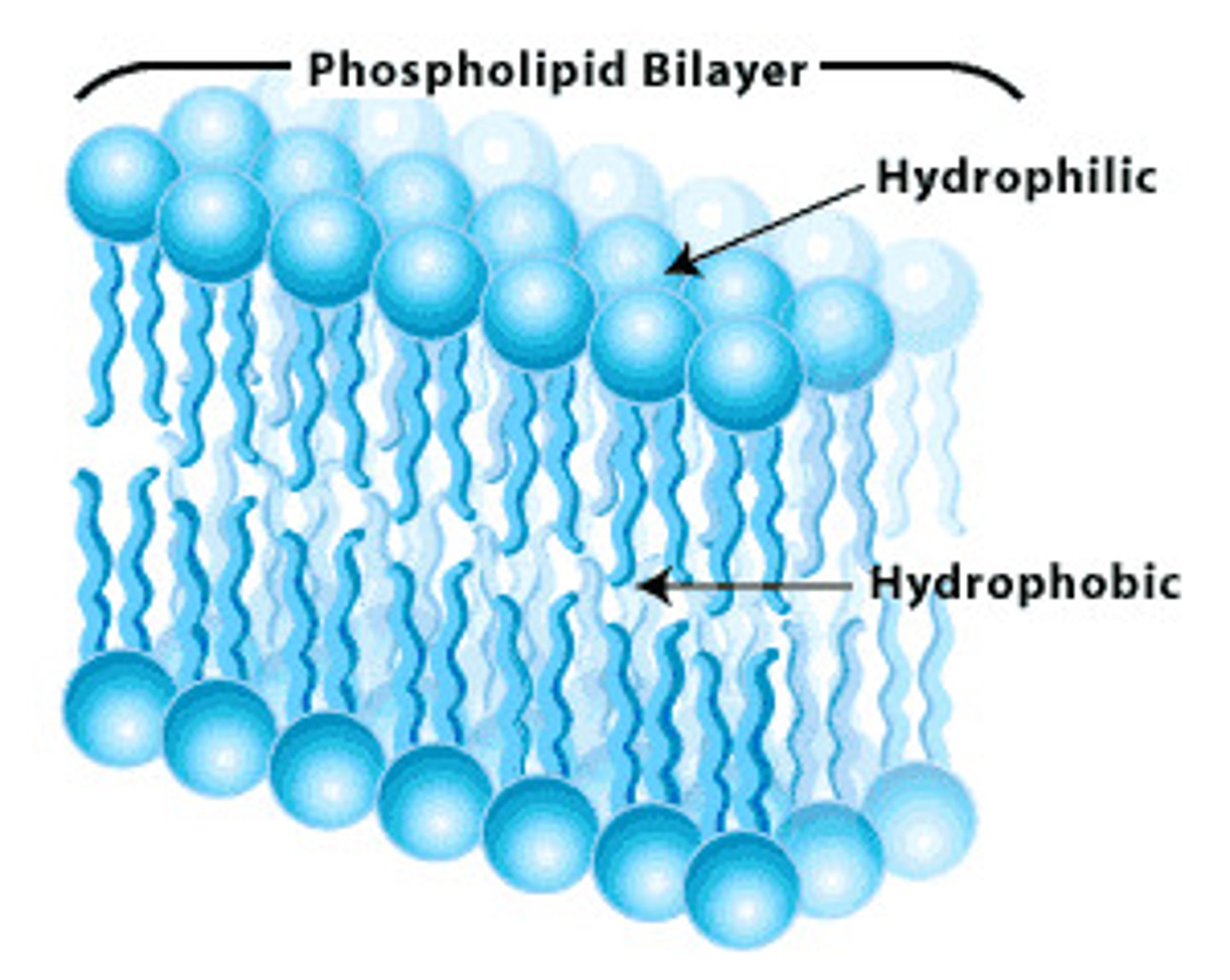
hydrophobic
naturally resistant to being penetrated by moisture.
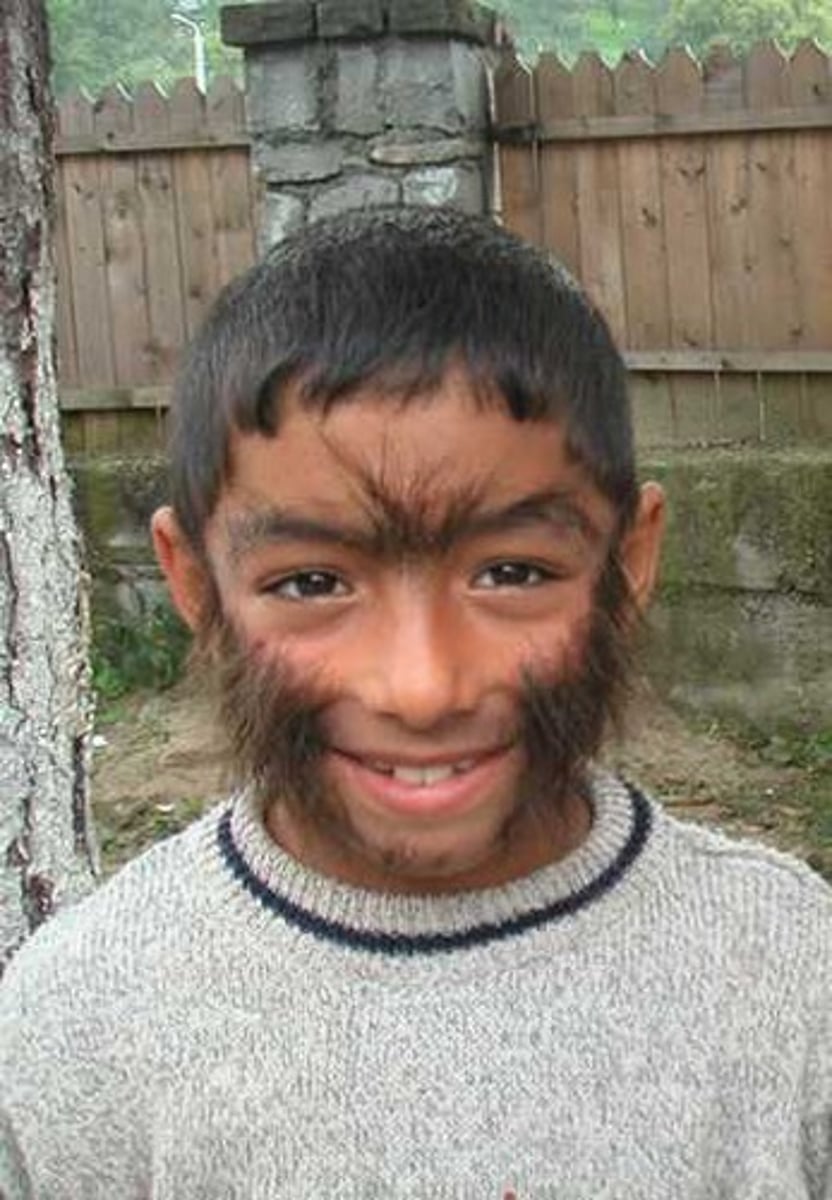
hypertrichosis
(hirsuties) condition of abnormal growth of hair, characterized by the growth of terminal hair in areas of the body that normally grow only vellus hair.

keratin
a fibrous protein that grows from cells originating within the hair follicle.
keratinization
process by which newly formed cells in the hair bulb mature, fill with keratin, move upward, lose their nucleus, and die.
lanthionine bonds
the bonds created when disulfide bonds are broken by hydroxide chemical hair relaxers after the relaxer is rinsed from the hair.
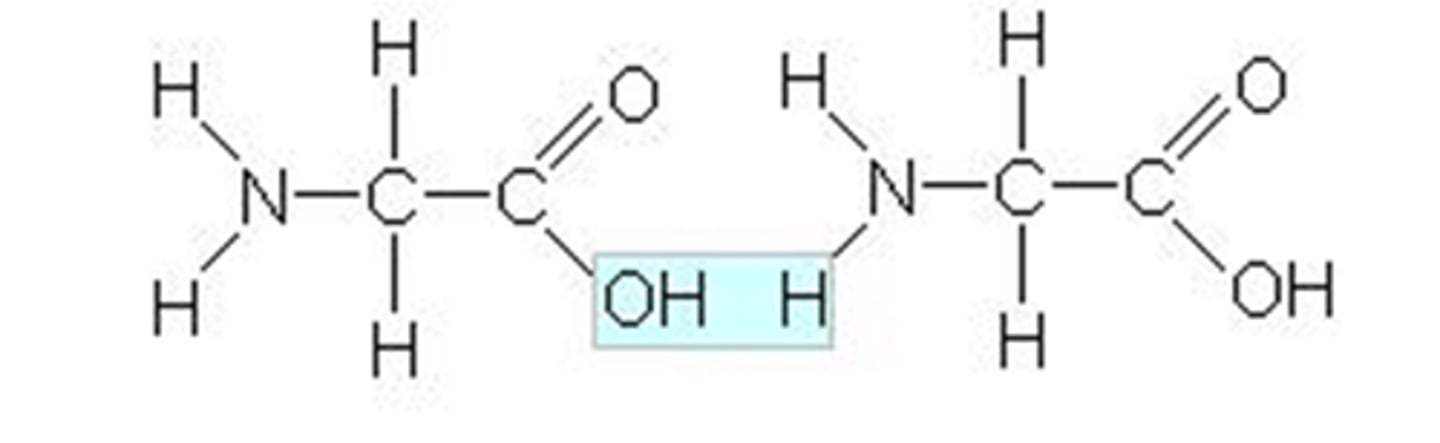
malassezia
naturally occurring fungus that is present on all human skin, but is responsible for dandruff when it grows out of control.
medulla
innermost layer of the hair that is composed of round cells; often absent in fine and naturally blond hair.
melanin
the tiny grains of pigment in the cortex that gives natural color to the hair
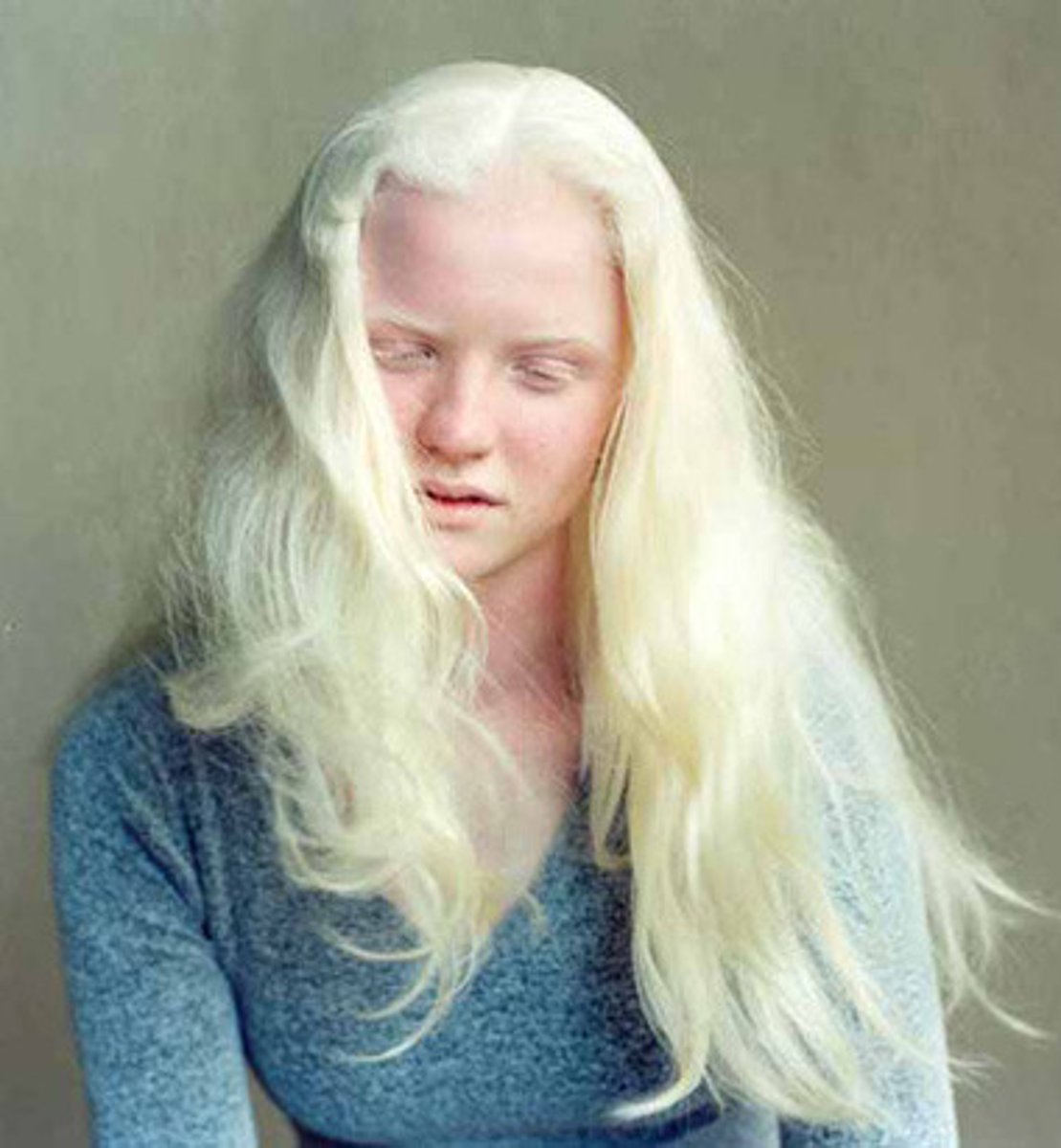

monilethrix
technical term for beaded hair.
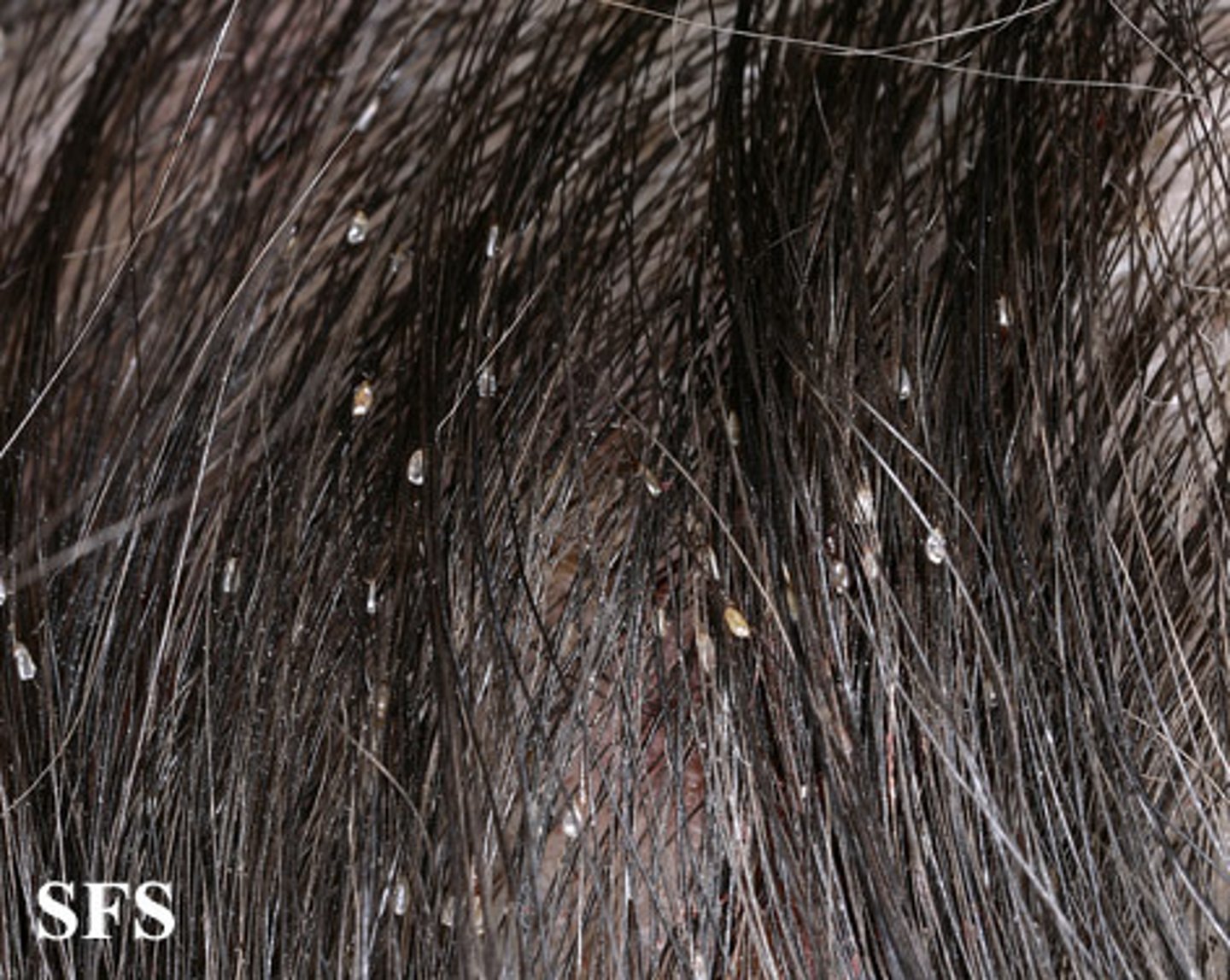
pediculosis capitis
infestation of the hair and scalp with head lice.
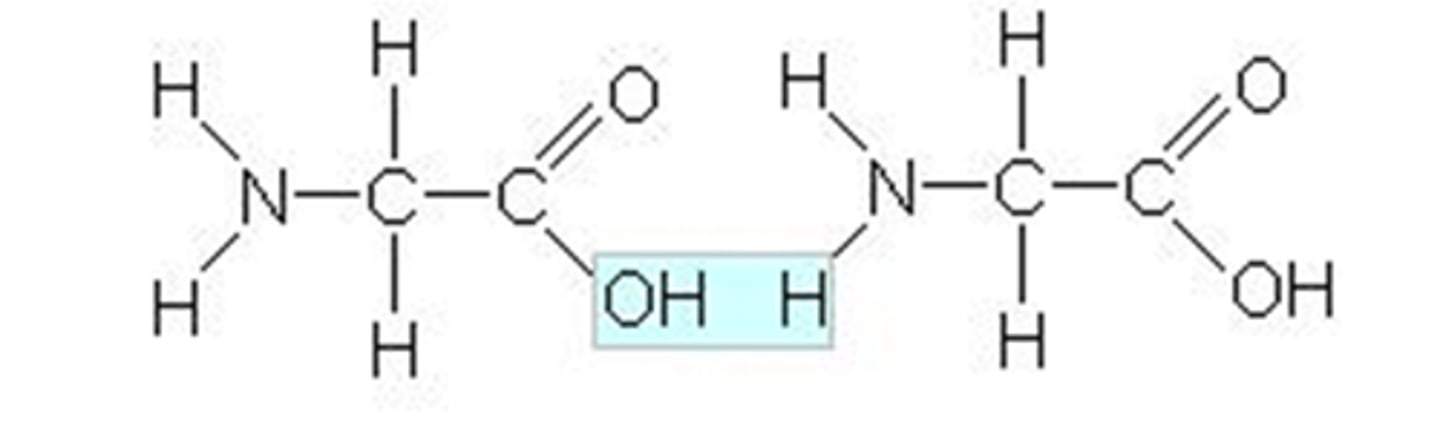
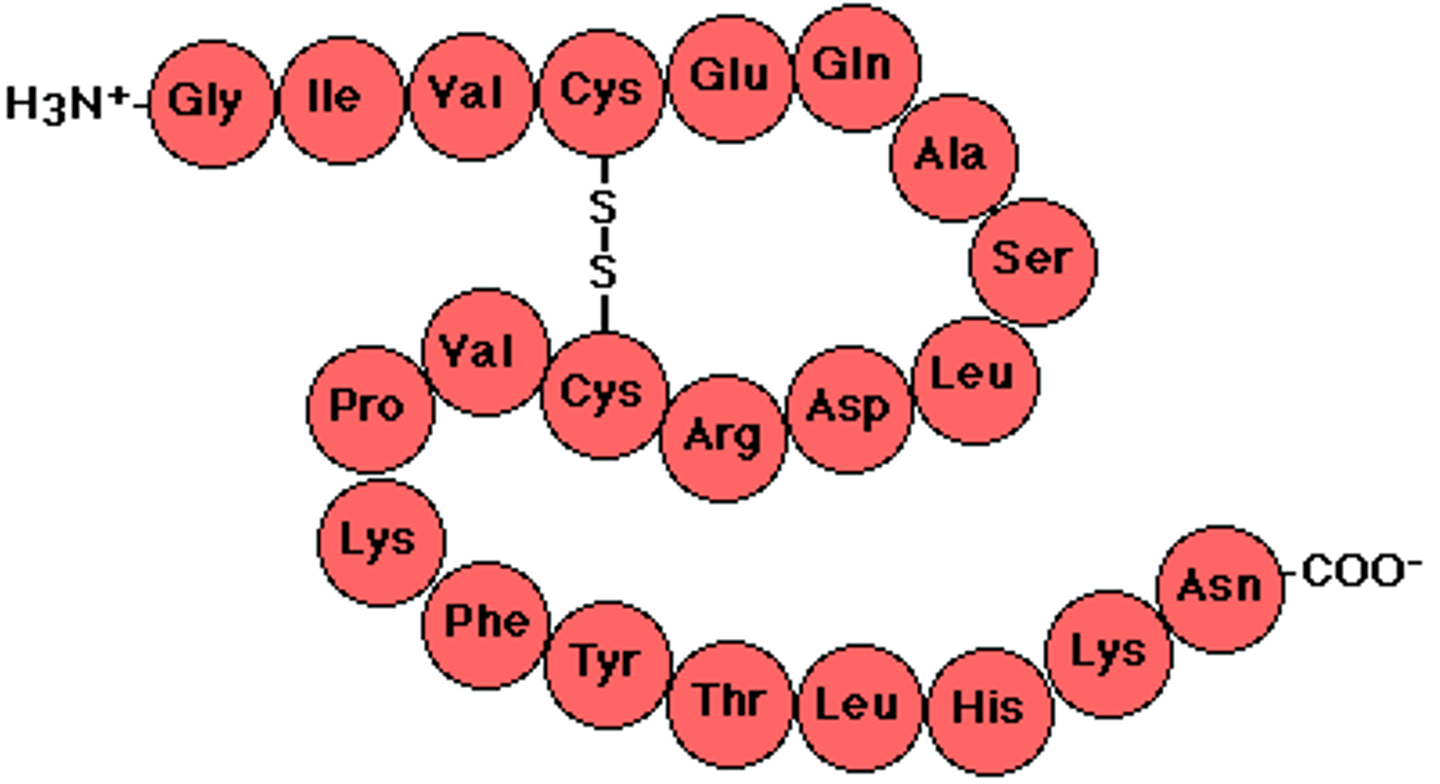
peptide bond
(end bond) chemical bond that joins amino acids to each other, end to end, to form a polypeptide chain.
pheomelanin
the lighter pigment that provides natural colors ranging from red to ginger to yellow and blond tones.
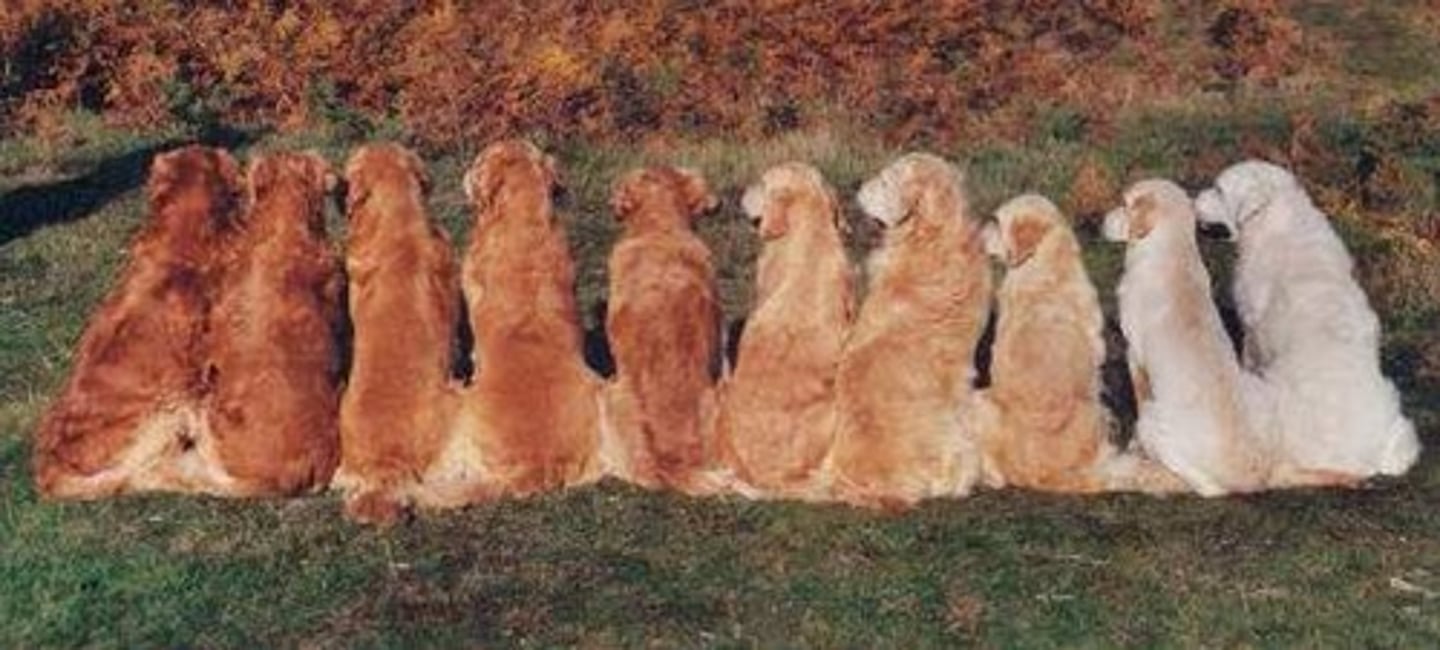

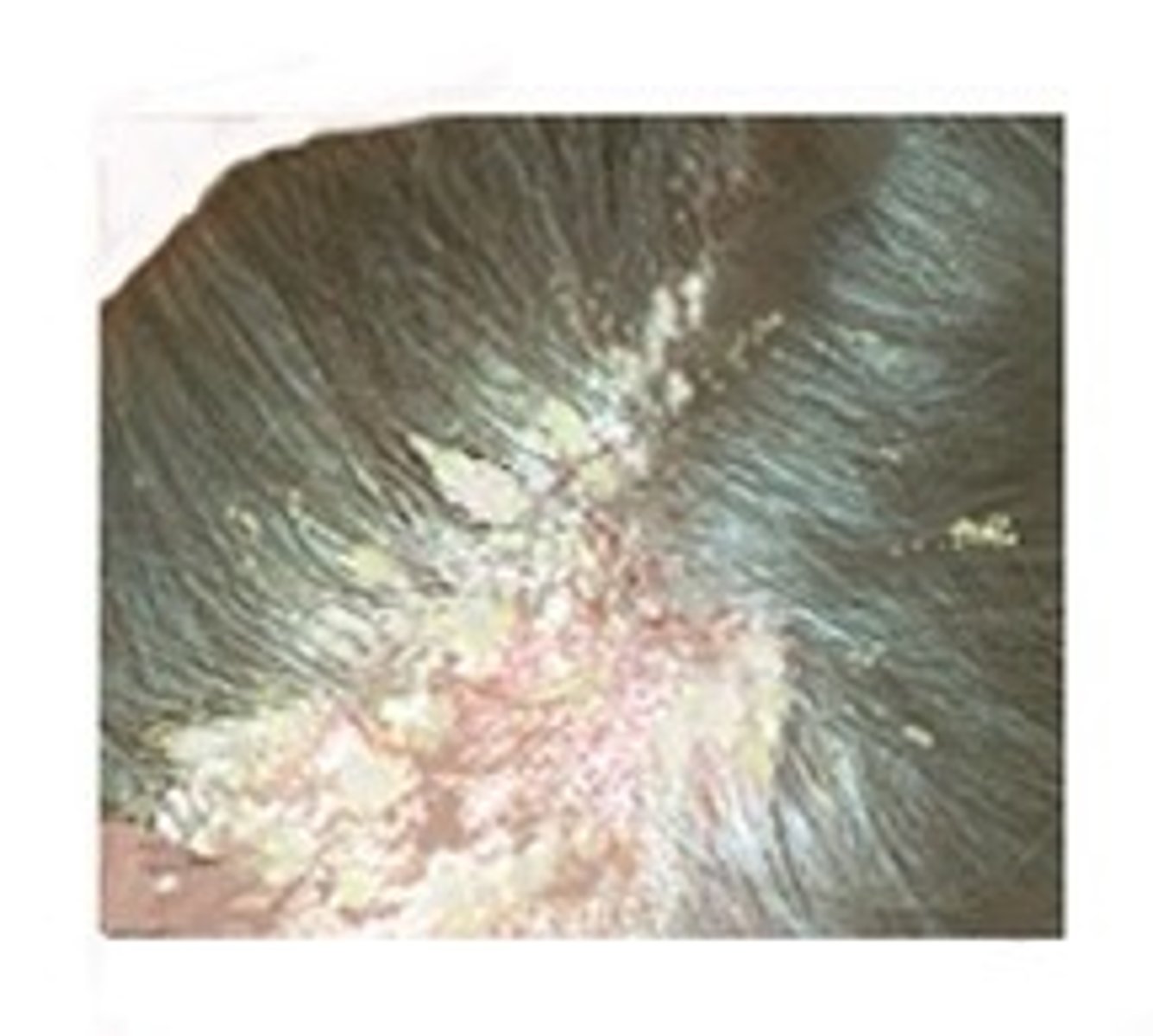
pityriasis
technical term for dandruff; characterized by excessive production and accumulation of skin cells.
pityriasis capitis simplex
technical term for classic dandruff; characterized by excessive production and accumulation of skin cells.
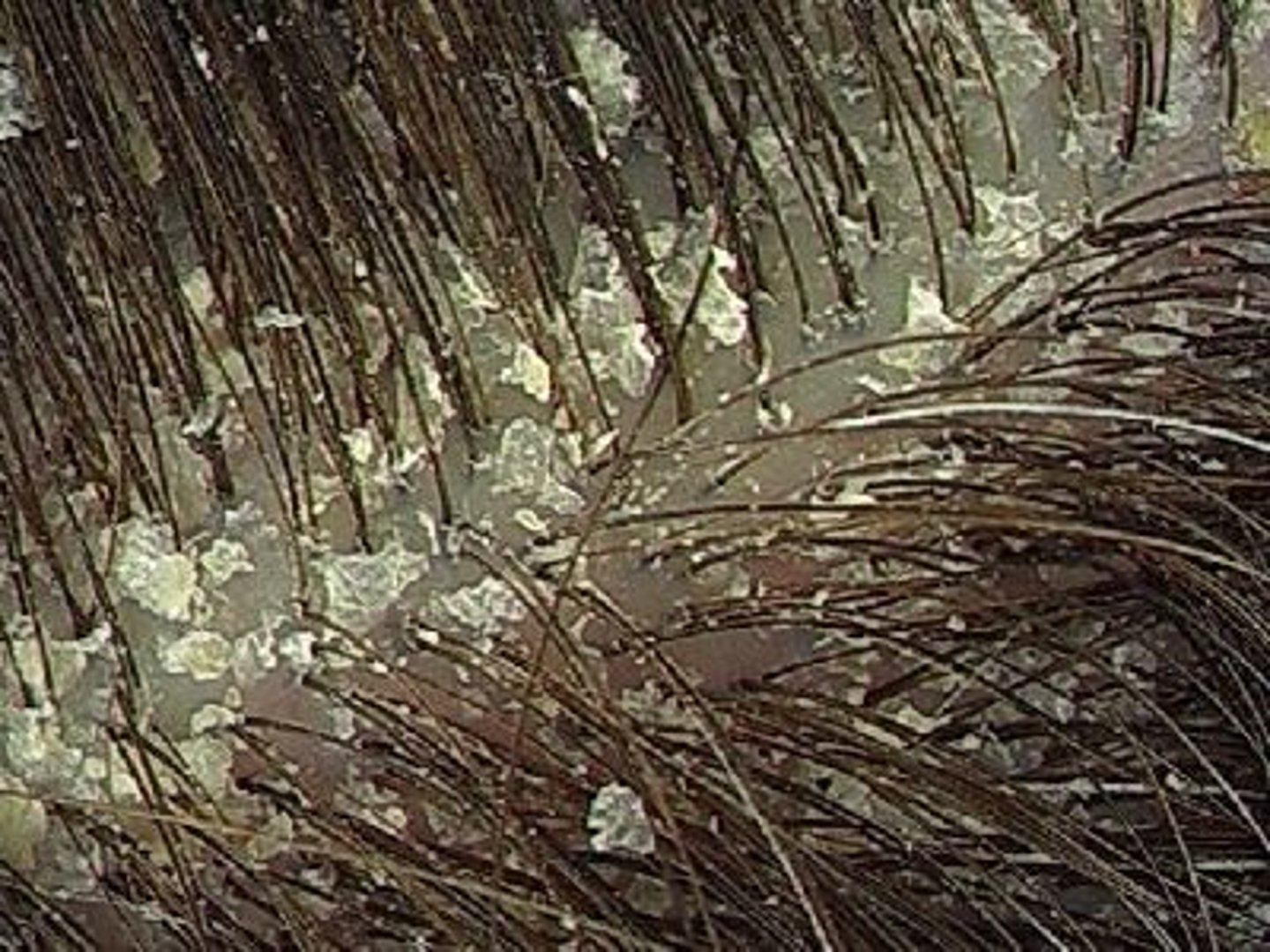

pityriasis steatoides
severe case of dandruff characterized by an accumulation of greasy or waxy scales mixed wth sebum, that stick to the scalp in crusts.
polypeptide chain
a long chain of amino acids liked by peptide bonds.
postpartum alopecia
temporary hair loss experienced at the conclusion of a pregnancy.

proteins
long, coiled complex polypeptides made of amino acids.
ringed hair
variety of canities characterized by alternating bands of gray and pigmented hair throughout the length of the hair strand. M: cats
salt bond
a weak, physical, cross-link side bond between adjacent polypeptide chains.
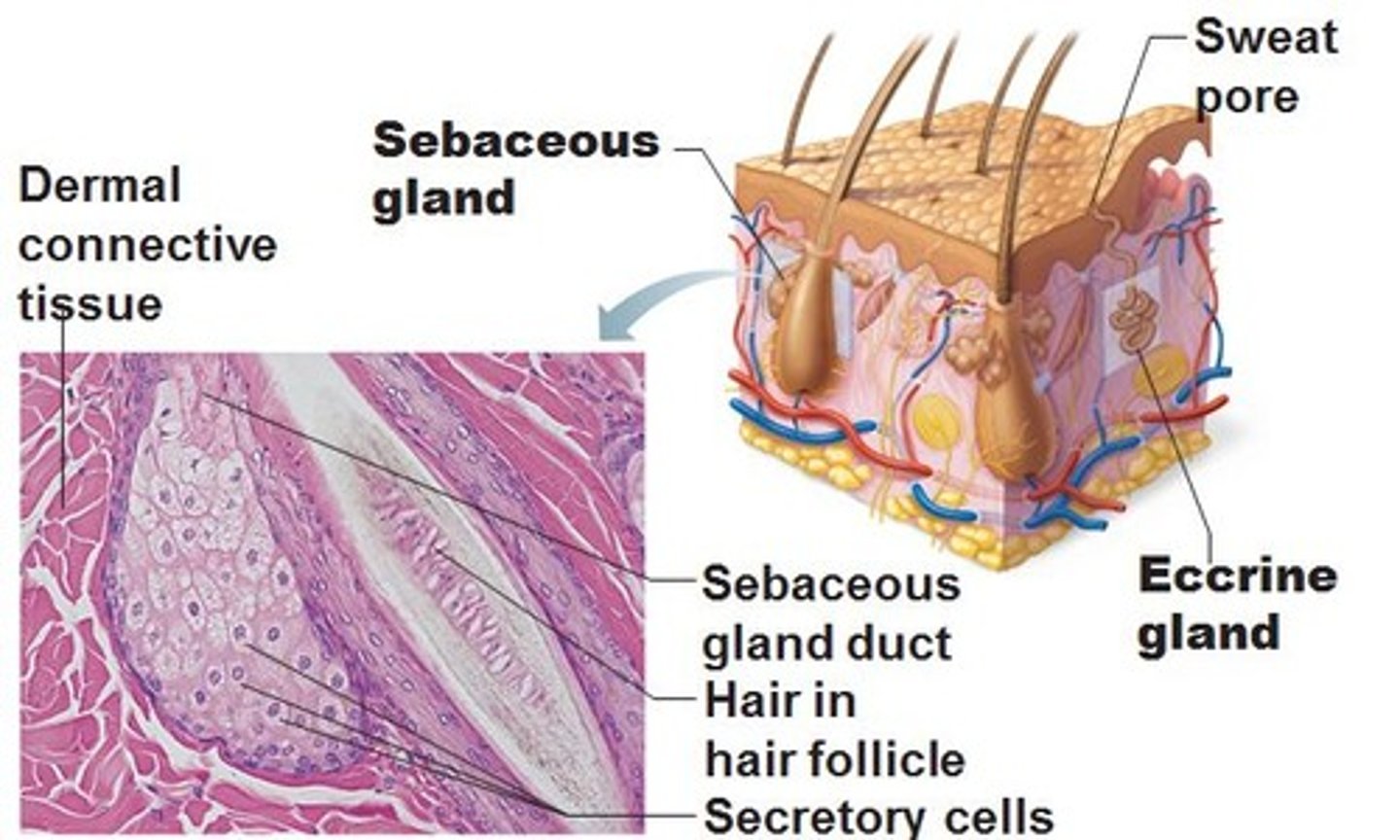
sebum
a fatty or oily substance secreted by the sebaceous glands that lubricates the skin.
sebaceous glands
oil glands in the skin that are connected to the hair follicles.
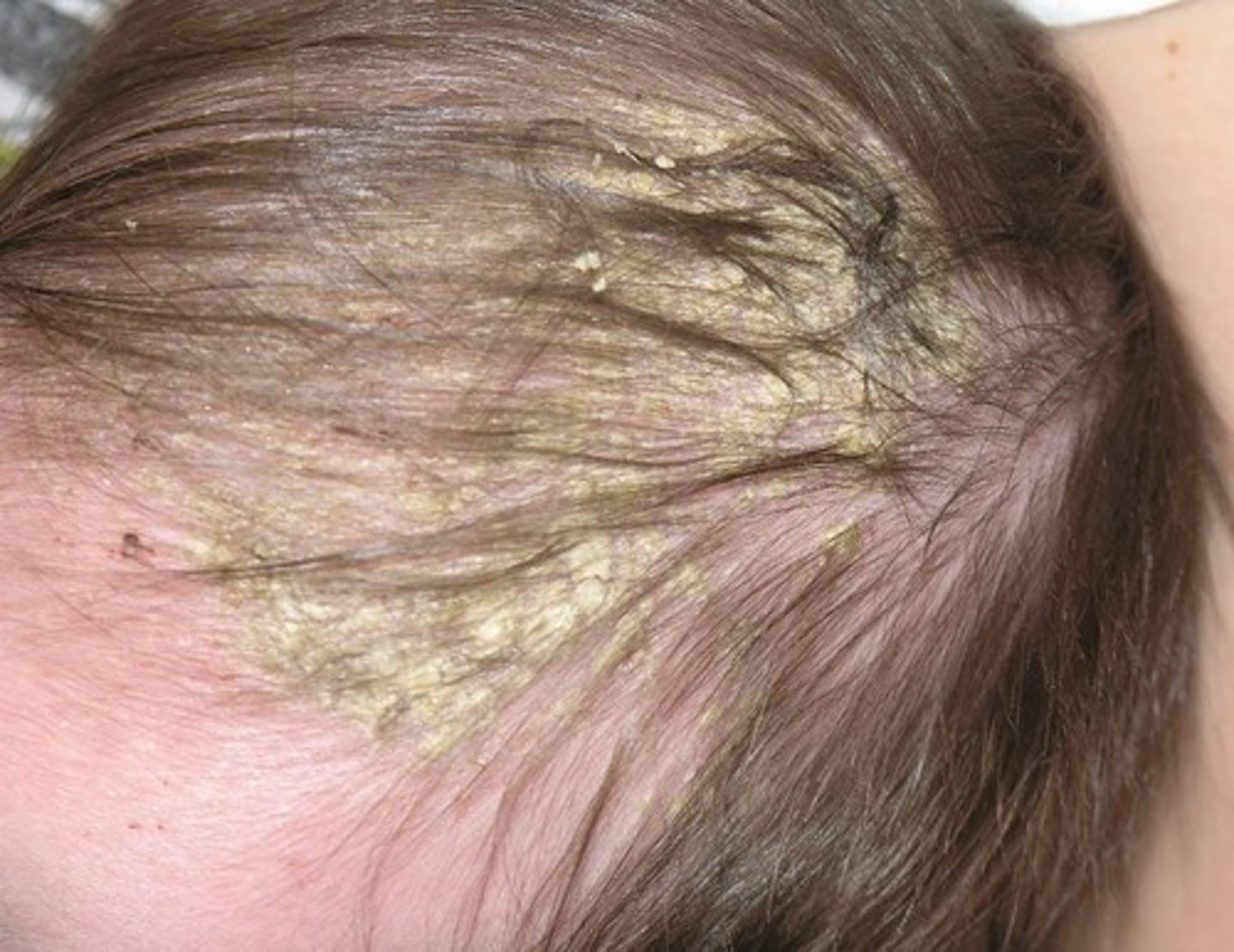
scatula
dry, sulfur-yellow, cup-like crusts on the scalp in tinea favosa or tinea favus. M
side bonds
bonds that cross-link the polypeptide chains together and are responsible for the extreme strength and elasticity of human hair.
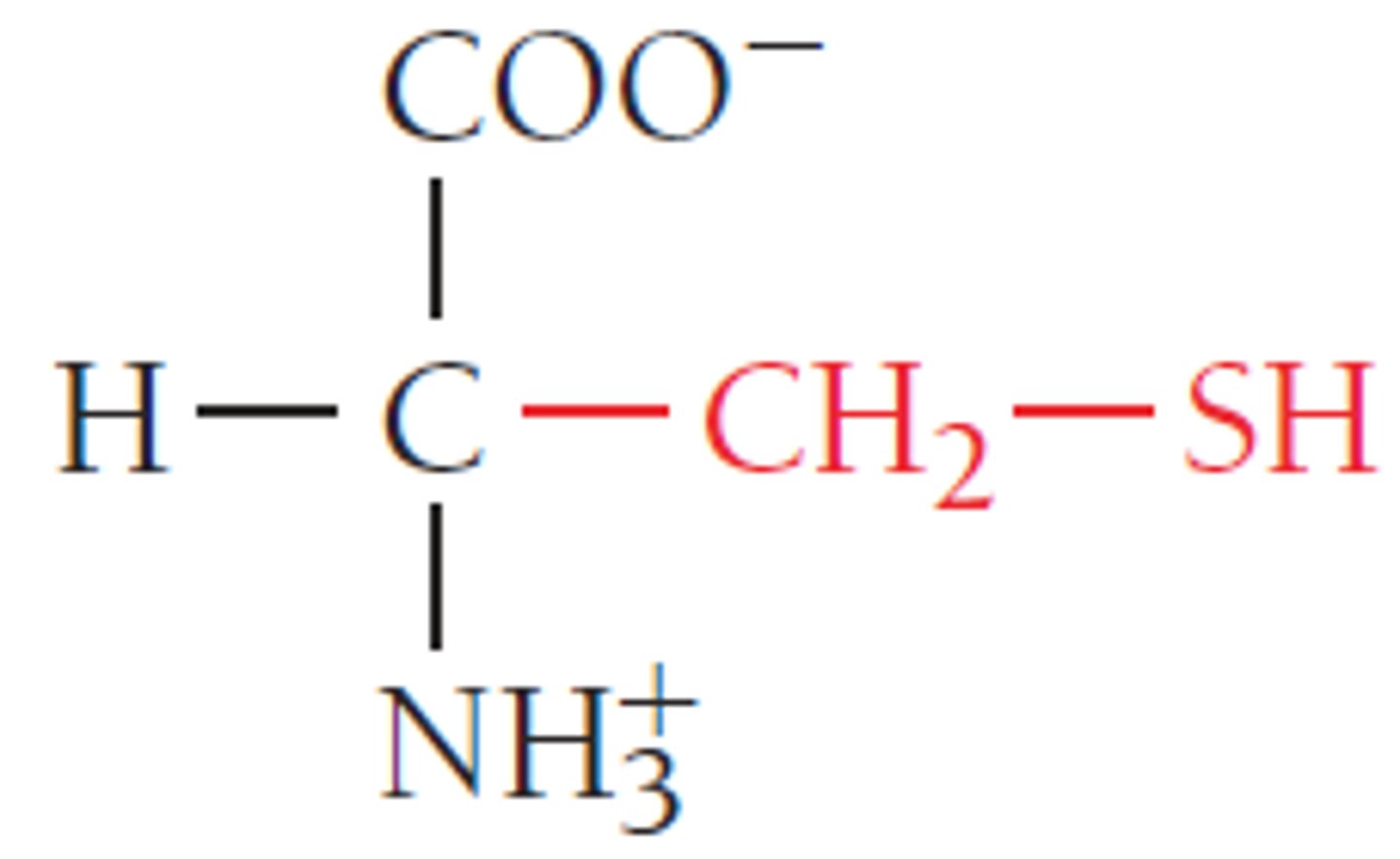
telogen phase
(resting phase) the final phase in the hair cycle that lasts until the fully grown hair is shed.
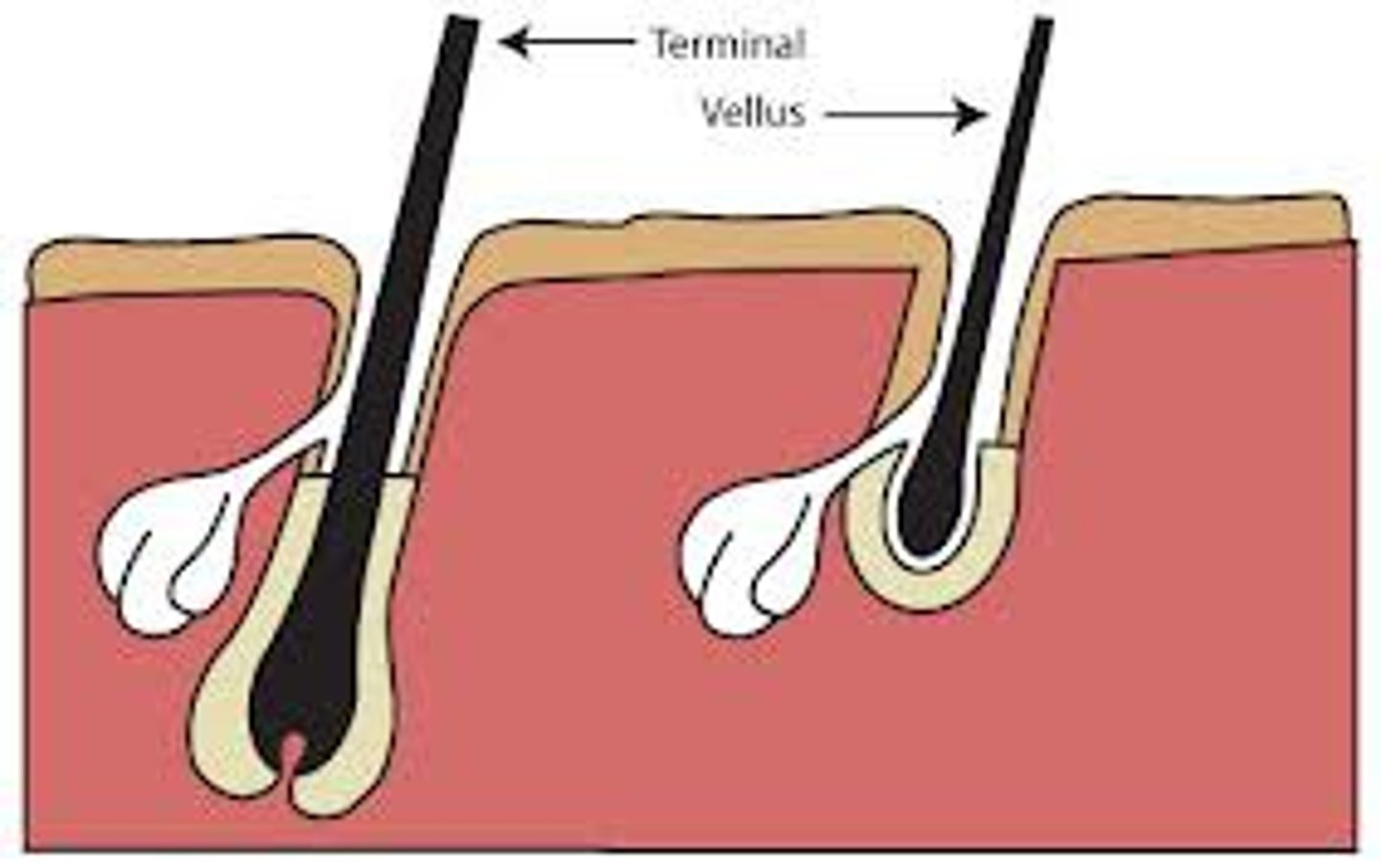
terminal hair
long,coarse, pigmented hair found on the scalp, legs, arms, and bodies of males and females.
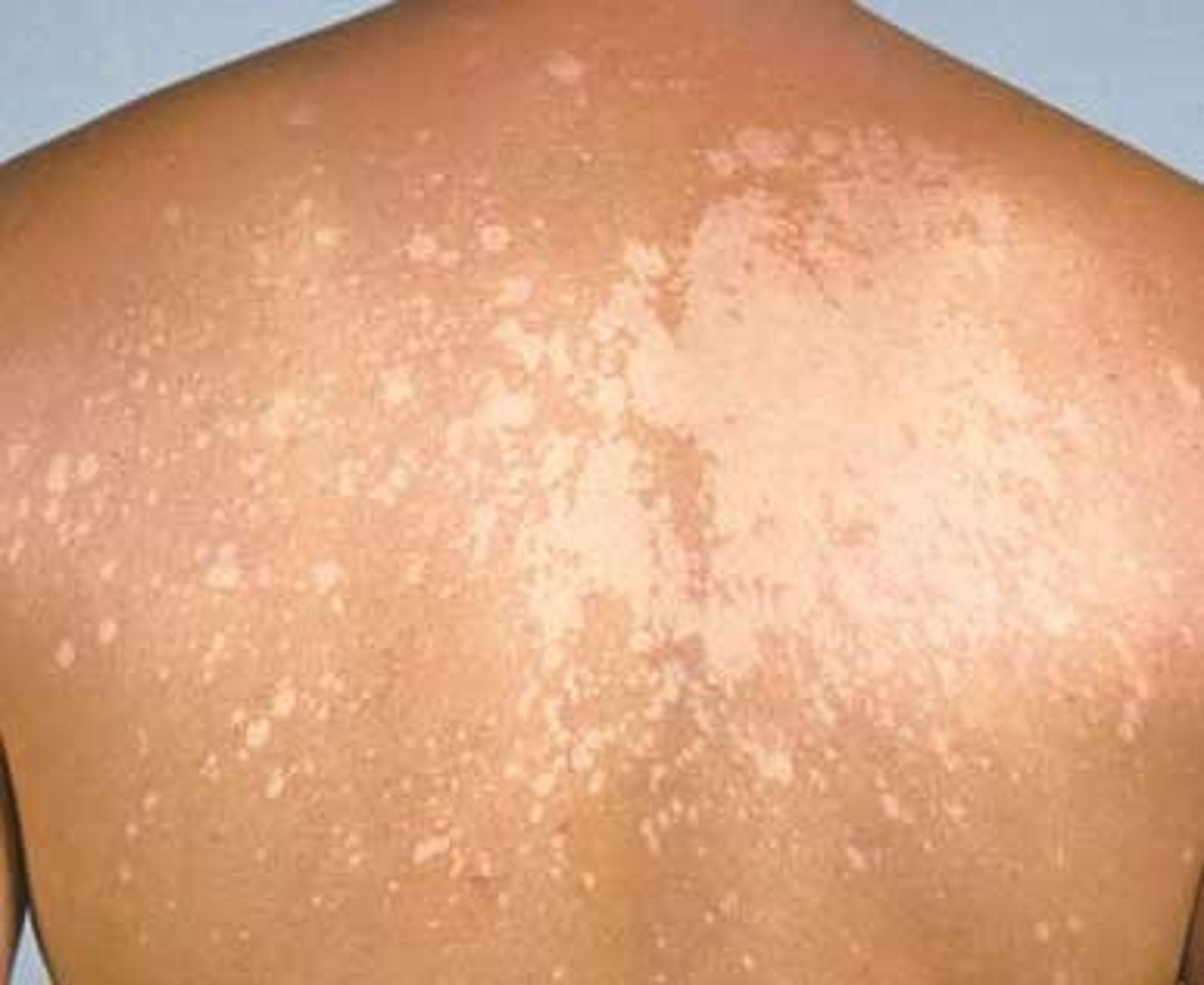
tinea
technical term for ringworm, a contagious condition caused by fungal infection and not a parasite; characterized by itiching, scales, and sometimes, painful lesions.
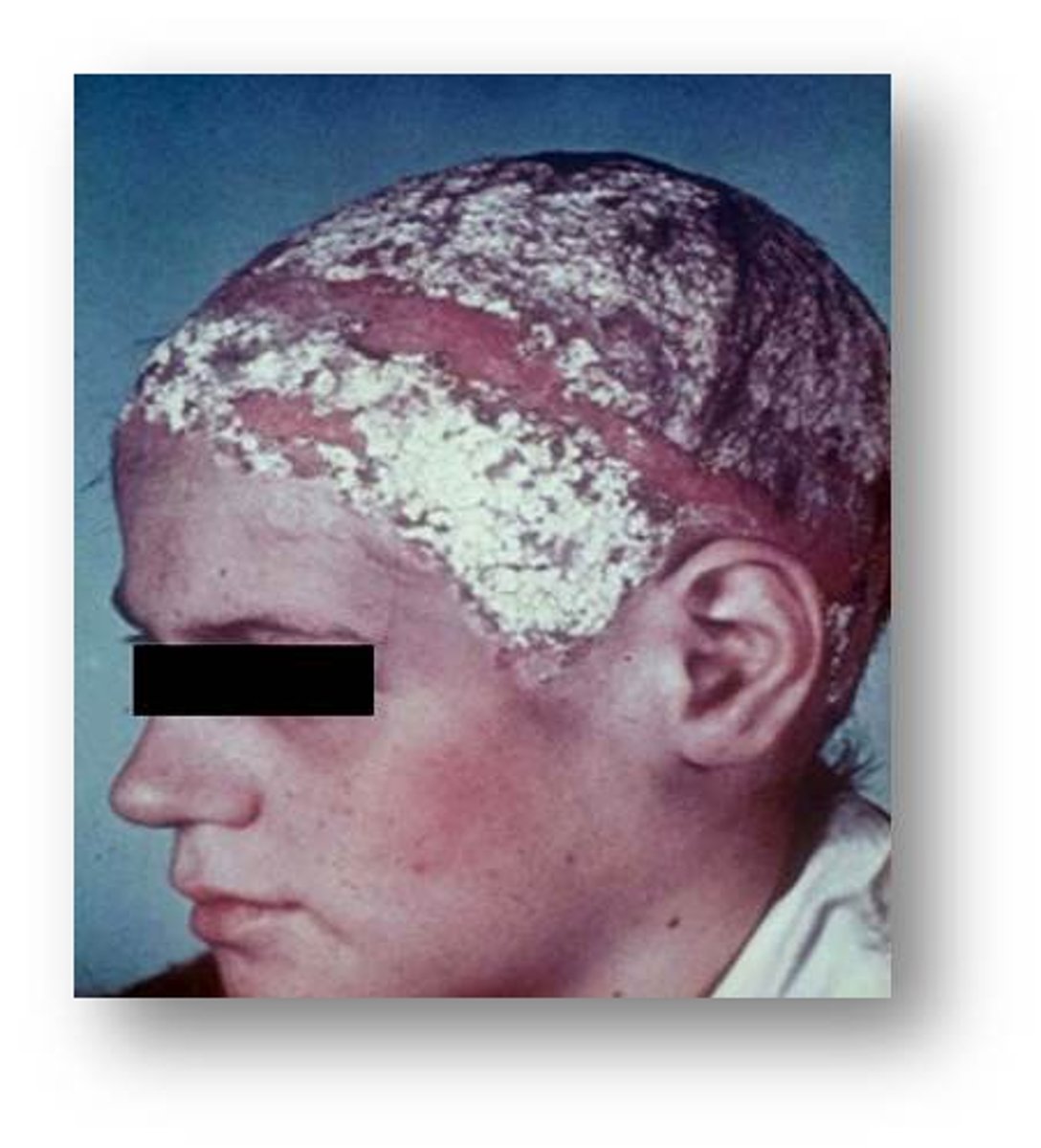
tinea favosa
(tinea favus) fungal infection characterized by dry, sulfur-yellow, cup-like crusts on the scalp called scutula.
trichology
scientific study of hair and its diseases and care.
trichoptilosis
technical term for split ends
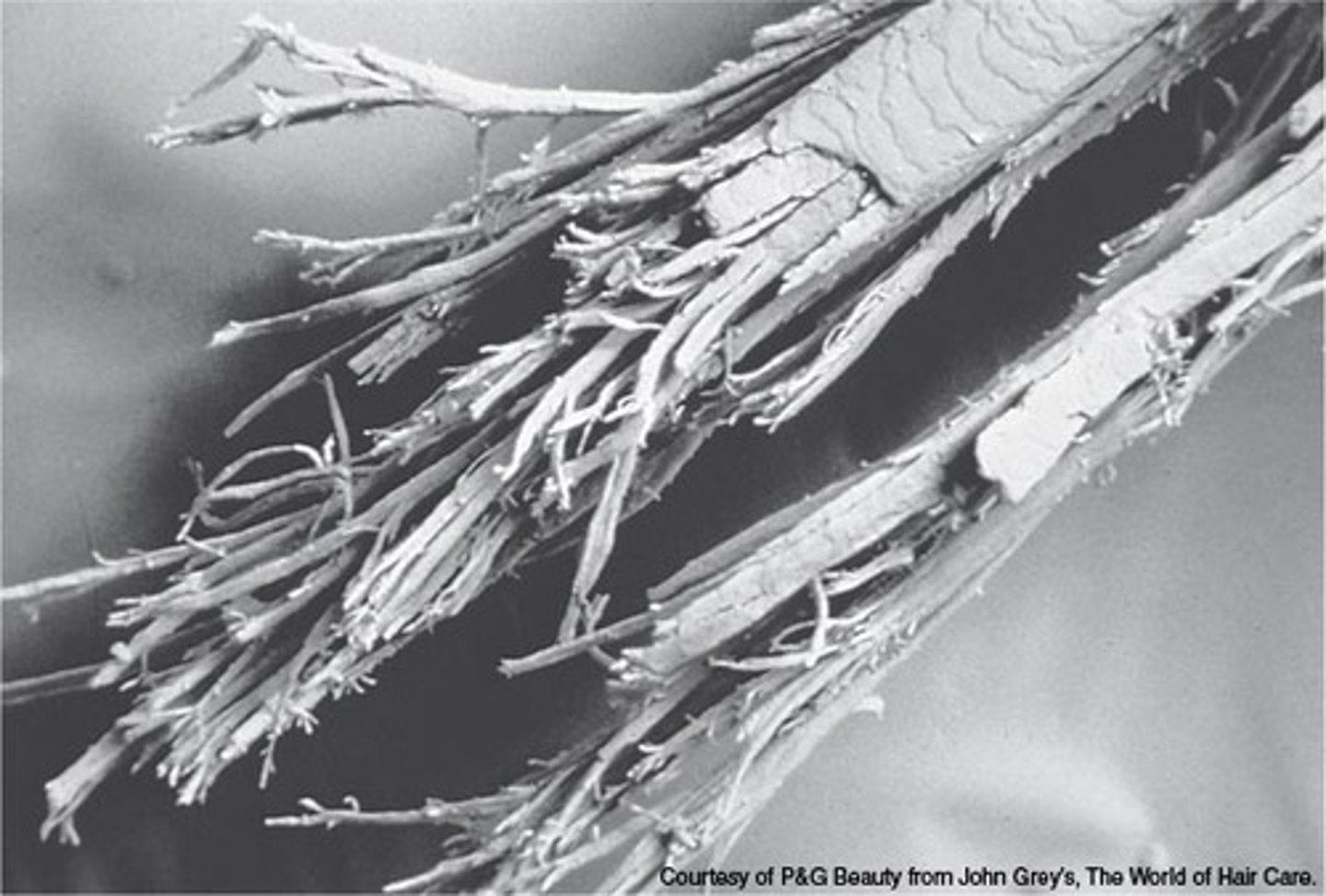
trichorrhexis nodosa
technical term for knotted hair; it is characterized by brittleness and the formation of nodular swellings along the hair shaft.
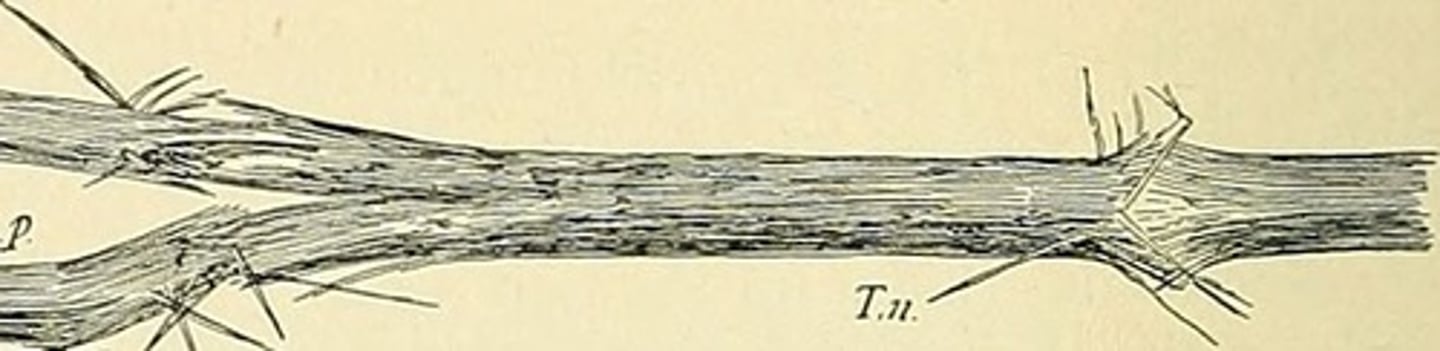
vellus hair
(lanugo hair) short, fine, unpigmented downy hair that appears on the body, with the exception of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.

Scabies
A contagious skin disease caused by the itch mite, which burrows under the skin.
Tinea Capitis
Ringworm of the scalp.
Whorl
Hair that forms in a circular pattern on the crown of the head.
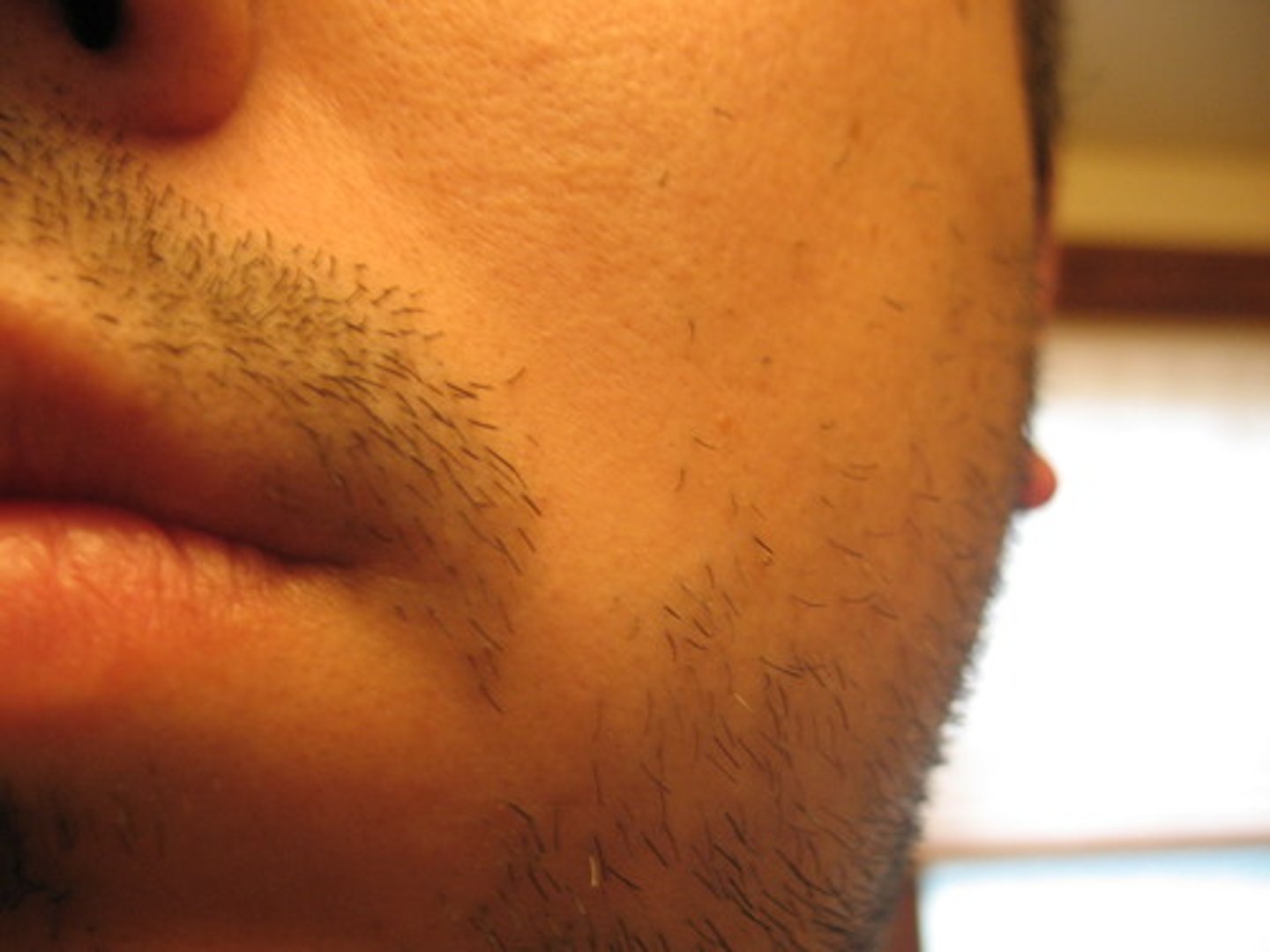
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
The medical term for an ingrown hair.
Folliculitis
An infection of the hair follicles frequently caused by staphylococcus or other bacteria.