5/6- sleep disorders + dental related pulmonary disease
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
T/F: amount of oxygen consumed by the brain during sleep is the same as in the awake state
true
4 stages of sleep
NREM1
NREM2
NREM3: slow wave brain activity
REM: skeletal muscles in hypotonic state
what’s a polysomnogram
sleep study: uses EEG (brain activity), EOG (eye movement), EMG (muscle activty)
3 sleep disorders related to dentistry
insomnia
sleep bruxism
sleep apnea
definition of insomnia
inability to fall asleep or remain asleep at least 3x/week for longer than 1 month
3 types of insomnia
sleep onset: difficulty falling asleep
sleep maintenance: difficulty staying asleep characterized by spontaneous awakenings and difficulty in returning to sleep
terminal: early morning awakenings
4 sleep related breathing disorders (SRBD)
sleep apnea
sleep related hypoventilation disorders
sleep related hypoxemia
snoring
definition of apnea
cessation of breathing for 10 seconds or longer
80-100% in airflow
reduction in thoracoabdominal movement
definition of hypopnea
a 30% decrease in airflow + thoracoabdominal movement
for 10 seconds or longer
what’s needed to confirm an apnea/hypopnea diagnosis
4% drop in oxygen saturation
how is respiratory effort related arousals (RERAs) related to apnea/hypopnea
has 4% oxygen desaturation
how is upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS) different from SRBDs
lacks drop in oxygen levels
criteria of sleep apnea
1 of the following:
pt complains of unintentional sleep
pt awakes w/ breath holding, gasping, or choking
bed partner reports loud snoring, breathing interruptions
polysomnograph records the following:
5+ scorable respiratory even per hr of sleep
evidence of respiratory effort during all or portion of each respiratory even
3 types of sleep apnea
obstructive: cessation of breathing 10+ sec
central: cessation of breathing 10+ sec and no effort to breath
mixed: both
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is usually due to an obstruction where
level of tongue or epiglottis
cause of central sleep apnea
malfunction in the neurological controls for breathing usually at the level of the brainstem
central sleep apnea can also present as which condition
Cheyne-Stokes respiration: pattern of deep/fast breathing followed by gradual decrease in breathing resulting in apnea, more prevalent at high altitudes
3 categories of apnea severity
mild: apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of 5-15
moderate: AHI of 15-30
severe: AHI of >30
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) affects more women or men
men
12 risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
obesity
chronic snoring
male gender, but females have increased risk post menopause
50+ age
family hx
endocrine disorders
neurological disorders
alcohol use, eating near bedtime, smoking
chronic nasal congestion + inability to breathe through nose
increased neck circumference: 17+ in for men, 15.5+ in for women
waist above 40 in for men, 35 in for women
meds that relax the airway
7 anatomical risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
nasal obstruction
enlarged tonsils + adenoids (especially in children)
small nostrils
mandibular retrognathia
macroglossia
scalloping of the tongue
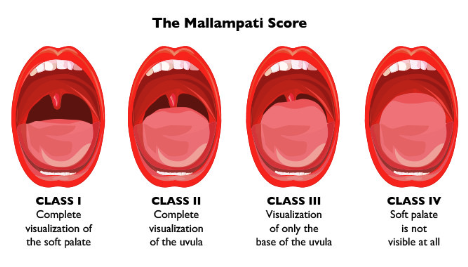
Mallampati score
which anatomical OSA risk factor is used by anesthesiologists to determine intubation difficulty
Mallampati score: class I-IV
6 medical conditions associated w/ obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
CVD: atrial fibrillation, arrhythmias, stroke, CHD, congestive heart failure
HTN
type 2 diabetes
GERD
depression + anxiety
ADHD + ADD in children
3 consequences of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
orofacial pain disorders: myofascial pain, fibromyalgia, headaches
daytime sleepiness → accidents
decreased cognitive function
normal oxygen saturation % for adults + children
adults: 88%+
children: 90%+
gold standard for sleep apnea diagnosis
polysomnograph (PSG) performed in a hospital or a separate sleep testing facility
what does the home sleep test (HST) not measure compared to PSG
doesn’t define REM or NREM (sleep staging) + may not truly determine if the patient is actually asleep
3 management tx for sleep apnea
positive airway pressure (PAP) aka CPAP or BiPAP
oral appliances (OA)
surgery
which PAP is the gold standard
CPAP
oral appliances are recommended for which pts
for mild/moderate sleep apnea + cannot tolerate PAP devices
how oral appliances (OA) work
repositions mandible in an open (vertically) position and then advancing mandible forward to open airway + stabilize it during sleep, prevents tongue + mandible from collapsing backward + compromising airway
when is surgery recommended
severe OSA
PAP resistant
does not respond to OA
what surgery is used to treat OSA
MMA (Maxillomandibular Advancement): surgical advancement of maxilla + mandible
5 pulmonary diseases important to dentists
obstructive lung disease (asthma, emphysema)
upper airway diseases
restrictive lung disease
sleep apnea
tuberculosis
how is lung function measured
pulmonary function tests (PFTs):
spirometry (obstruction)
flow volume loop (upper airway, obstruction, restriction)
lung volume (restriction)
diffusion (gas exchange)
2 types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
emphysema: abnormal + permanent enlargement of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles w/ destruction of their walls
chronic bronchitis: chronic cough for 3 months
signs to look for in COPD diagnosis
pts >40 years old w/
chronic cough
chronic sputum production
progressive dyspnea
history of exposures (>1 pack of cigs x 20 years)
obtain spirometry
obstructive disease (asthma + emphysema) manifests as what in PFTs
increased total lung capacity (TLC) due to hyperinflation of their lungs
T/F: behavioral counseling + pharmacotherapy are used together for greater efficacy when treating smoking cessation
true
asthma usually affects pts of what age
children, most diagnosed by age 7
restrictive pulmonary disease (pulmonary fibrosis) is characterized by what
decreased compliance + decreased TLC on PFTs
how can OSA lead to cardiovascular morbidity
OSA w/ repetitive upper airway obstruction + subsequent catecholamine surges → cardiovascular morbidity
how to differentiate latent vs. active Tb
latent: positive skin test w/ no symptoms + normal x-ray
active: positive/negative skin test w/ symptoms + abnormal x-ray
what’s the diagnosis?
50 year old woman presents with 1 year of increasing dyspnea & productive cough. She smoked 2packs/day for 35 years. On exam she uses accessory respiratory muscles to breathe. Respiratory rate is 24. Chest exam notable for poor air entry, expiratory wheezing, prolonged expiratory phase (I/E 1/5), positive Hoovers sign, and thoraco-abdominal paradox
emphysema
what’s the diagnosis?
35 year old woman presents with 2 months of coughing that was triggered by an upper respiratory infection. She denies smoking, but her parents smoked when she was a child. On exam she is not using accessory respiratory muscles to breathe. Respiratory rate is 20. Chest exam notable for good air entry and scattered expiratory wheezes. Cardiac exam + spirometry are normal.
asthma
What’s the diagnosis?
65 year old woman presents w/ 1 year of increasing dyspnea, fatigue & cough. She has a prior smoking history but quit 20 years ago. On exam her respiratory rate is 30. Chest exam is notable for velcro crackles posteriorly. Extremity exam reveals clubbing. Her O2 saturation by pulse oxymeter is 94% at rest, but drops to 88% with exertion.
pulmonary fibrosis (restrictive disease)