mock 2 paper 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
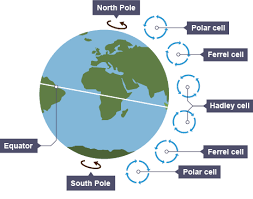
conditions that cause tropical storms and why 1)
low latitude between 5-30 degrees north and south of the Equator
temperatures are higher here than at the Poles so the sea and air are heated more quickly, to higher temperatures, air pressure is low and air rises

conditions that cause tropical storms and why 2)
originate in oceans with temperatures above 26.5 degrees to a depth of 60-70m
provides heat and moisture so warm air rises rapidly

conditions that cause tropical storms and why 3)
between summer and autumn
typically the warmest seasons to encourage warmer air to rise rapidly on account of low pressure

conditions that cause tropical storms and why 4)
low wind shear
wind is constant and doesn’t vary so clouds rise to high altitudes without being torn apart
formation of tropical storms (1)
tropical Storms start between 5º and 30º north and south of the equator, where surface sea temperatures reach at least 26.5ºC, which is about the temperature of a heated swimming pool, and why we don’t get tropical storms in the UK
air is heated above the surface of these warm tropical oceans, the warm air rises rapidly under low-pressure conditions.
formation of tropical storms (2)
the rising air draws up more airing large volumes of moisture from the ocean, causing strong winds.
the Coriolis effect (spinning movement of the Earth) causes the air to spin upwards around a calm central eye of the storm
formation of tropical storms (3)
as the air rises, it cools and condenses to form large, towering cumulonimbus clouds, which generate torrential rainfall, heat is given off when the air cools and powers the tropical storm.
cool air sinks into the eye therefore, there is no cloud, so it is drier, clear and much calmer
formation of tropical storms (4)
the tropical storm travels across the ocean by the prevailing wind
when the tropical storm meets land, it is no longer fuelled by the source of the moisture and heat from the ocean, so it loses power and weakens
structure of a tropical storm
the central part of the tropical storm is known as the eye, usually between 30-50km across, it is an area of calm, with light winds and no rain and contains descending air
large cumulonimbus clouds surround the eye and are caused by moist air condensing as it rises, wind speeds average 160km per hour around the eye
structure of a tropical storm; weather system
generates heat which powers the storm, causing wind speeds to increase causing the tropical storm to sustain itself, tropical storms rely on plenty of warm, moist air from the sea – this is why they die out over land.
why do tropical cyclone spin?
the rotation of tropical cyclones is a defining feature, giving them their distinctive spiral shape, the strong winds within these storms are driven by air moving from high to low-pressure areas, in the case of tropical cyclones, this movement is influenced by the Coriolis effect
the Earth’s rotation causes these winds to be deflected into a spin, resulting in all tropical cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere rotating counter clockwise and those in the Southern Hemisphere rotating clockwise
primary effects of tropical storms
people are injured or killed by debris being blown around, electric supplies are cut off due to power lines being destroyed, sewage is released due to flooding contaminating water supplies, drowning
secondary effects of tropical storms
road and rail networks can be blocked by debris making it difficult to provide support and aid for people affected, unemployment is caused by businesses being damaged, if crops are destroyed/livestock is killed there can be shortage in food, lack of clean water and sanitation may cause water borne disease in people
immediate responses of tropical storms
temporary shelters are set up for people made homeless by the storm, rescue people trapped and provide medical support for injured people, digital maps are updated immediately after the storm using satellite photographs to support emergency services on the ground
long term responses of tropical storms
improving building regulations so that properties are constructed to withstand the impacts of tropical storms better, offer incentives such as tax breaks to encourage economic recovery, providing grants and aid to people to help rebuild their homes, repairing transport infrastructure
plate boundary
point where two or more plates meet, where earthquakes, volcanoes and fold mountains form
constructive plate boundary
occurs when two plates move away from eachother
landforms: ocean ridge and volcanic islands
destructive plate boundary
occurs when an oceanic plate subducts a continental plate
landforms: fold mountains and oceanic trenches
example: pacific plate and the Eurasian plate
conservative plate boundary
occurs when two plates slide past each other
example: north American plate and the pacific plate
collision plate boundary
occur when two continental plates move towards eachother
landforms: fold mountains
example: Australian and the Eurasian plate
how is technology used to monitor and predict earthquakes: radon gas detection
radon gas detect is used to measure radon gas, which can escape through cracks in the surface of the Earth
how is technology used to monitor and predict earthquakes: seisometers
seismometers are used to measure foreshocks, the location of earthquakes and their times are mapped to look for patterns, and from the results, predictions are made about when and where the next earthquake might occur
how is animal behaviour used to monitor and predict earthquakes
animal behaviour is also monitored as they are thought to act strangely when an earthquake is about to happen
protection against risk of earthquakes
poorly constructed buildings tend to collapse much more quickly than those that have been reinforced
the construction of buildings and roads that are more resistant to the impact of earthquakes is typical, mainly in high-income countries (HICs) such as Japan
this is because they are wealthy enough to be able to afford this type of construction
protection against risk of earthquakes: mitigation
constructing buildings that withstand earthquakes is known as mitigation, although these buildings help reduce injury and death, they may need to be repaired following a significant earthquake
protection against risk of earthquakes: building construction
constructing buildings to withstand the impact of earthquakes includes using seismic isolators, cross bracing, shear walls and counterweights
seismic or base isolators are shock absorbers in the foundations of buildings that absorb the tremors
protection against risk of earthquakes: cross bracing, shear walls and counterweights
cross bracing involves reinforcing walls using two steel beams crisscrossing from corner to corner to brace the wall
shear walls are concrete walls with steel bars to reduce rocking movements
counterweights are rolling weights on the roof that help counteract the energy waves
planning against risk of earthquakes
in some countries, people are encouraged to fasten down furniture so they are less likely to fall over
preparing emergency aid supplies and organising how they will be distributed helps in the aftermath of a tectonic hazard.
planning against risk of earthquakes (example)
earthquake drills happen in Japan on the 1st of September every year, this helps train people how to respond when an earthquake occurs
if residents know how to turn off gas, electricity, and water supplies, this helps reduce the risk of secondary effects such as fires.
there has been a significant increase in global temperatures, why is this?
mainly attributed to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by fossil fuels, commonly known as climate change
climate change: what have we learnt from thermometer readings?
future temperature increases will depend on natural changes in climate and the volume of greenhouse gases being released into the atmosphere
average global temperatures will continue to rise if greenhouse emissions continue at their current rate. though some regions, such as the Arctic, will warm at a faster rate than others
climate change: ice cores
scientists use ice cores to identify temperature changes
falling snow traps air into the ice, when ice cores are taken, changes in the atmospheric concentration of gases when the snow falls are revealed
this data can is used to calculate the temperatures at the time. Scientists have used ice cores to identify the temperature of every year for the last 400,000 years
ice core studies identify clear evidence of a rapid increase in temperature over the previous few decades
climate change: early spring
there is evidence of season shift over recent years, with spring arriving earlier and winters being less severe, it can negatively impact nesting and migration patterns of birds and mammals
hard engineering coastal management
involves building artificial structures that control natural processes, tend to be expensive, last only a short time, and are visually unattractive and unsustainable
they often increase erosion in other places further down the coast.
groynes
groynes are wooden barriers constructed at right angles to the beach to retain the material, the beach material, including sand and pebbles, is trapped between groynes and cannot be transported away by longshore drift, they encourage a wide beach that helps absorb energy from waves, reducing the rate of cliff erosion
advantages and disadvantages of groynes
advantages (social): groynes act as wind-breaks for people on the beach, groynes do not affect access to the beach
advantages (economic): at around £5000 each, they are relatively cheap, and if well maintained, they can last 40 years, they are much cheaper to repair than other hard engineering solutions, a wide, sandy beach attracts tourists, which benefits the local economy
disadvantages (environmental): groynes do not look attractive
disadvantages (social): groynes act as a barrier which impedes people walking along a beach, the beach on the downdrift side of the groyne can be much lower than the up-drift side which can make them very dangerous, particularly for young children
seawalls
usually built along the front of cliffs to protect settlements or other areas of high economic importance, they are often recurved, which means waves are reflected back on themselves
this can cause the erosion of material at the base of the seawall.
advantages and disadvantages of seawalls
advantages (social): a sea wall gives people a sense of safety and security, sea walls often have promenades on top of them, which are popular with tourists
advantages (economic): sea walls have a long lifespan and provide excellent defence where wave energy is large
advantages (environmental): sea walls do not impede the movement of sediment along the coast by longshore drift
disadvantages (social): sea walls can affect access to the beach, coastal flooding can occur when waves overtop (break over) the sea wall
disadvantages (economic): sea walls are costly to construct and maintain, the UK Government is investing £30m in a new sea wall in Dawlish, Devon, to protect the mainline railway after it collapsed during storms on 4 February 2014, reflected waves scour the beach and can cause foundations to be undermined
disadvantages (environmental): recurved sea walls can increase the erosion of beach material, sea walls do not look attractive, destroy habitats and affect the coastal system and reduce the input of sediment
cliffs and wave-cut platforms
where cliffs are made from more resistant rock, wave-cut platforms are often formed
a wave-cut platform is a wide, gently sloping surface found at the cliff’s base and extends into the sea
wave cut platform formation (1)
the sea attacks a weakness in the base of the cliff e.g this could be a joint in chalk.
a wave-cut notch is created by erosional processes such as hydraulic action and abrasion
wave cut platform formation (2)
as the notch becomes larger, the cliff becomes unstable and collapses as a result of gravity
the cliff retreats inland and material from the collapsed cliff face is eroded and transported away, leaving a wave-cut platform
the process repeats over time
headlands
cliff that sticks out into the sea and is surrounded by water on three sides, formed from hard rock, that is more resistant to erosion, such as limestone, chalk and granite
where do headlands form headlands
form along discordant coastlines where bands of soft and hard rock outcrop at a right angle to the coastline
due to the different nature of rock erosion occurs at different rates, less resistant rock erodes more rapidly than more resistant rock
headlands and bays
the bands of soft rock, such as sand and clay, erode more quickly than those of more resistant rock, such as chalk
this leaves a section of land jutting out into the sea called a headland
the areas where the soft rock has eroded away, next to the headland, are called bays.
sandy beaches are often found the sheltered bays where waves lose energy, and their capacity to transport material decreases resulting in material being deposited
difference between discordant and concordant coastlines
concordant coastline is where the same rock runs along the length of the coast and tends to have fewer bays and headlands
discordant coastlines are where geology alternates between strata of soft and hard rock
formation of a headland
waves attack a weakness in the headland, a cave is formed, eventually the cave erodes through the headland to form an arch, the roof of the arch collapses leaving a column of rock called a stack, the base of the stack is then eroded which causes it to collapse leaving a stump
coastal deposition
when the sea drops or deposits material, this includes sand, sediment, and shingle, resulting in landforms of coastal deposition
beach
area between the lowest spring tide level and the point reached by the storm waves in the highest tides
every beach is different but usually made up of material deposited on a wave-cut platform
beaches are formed from sand, sand and shingle or pebbles, they can also be formed from mud and silt
sandy beach
usually forms in sheltered bays, where low-energy, constructive waves transport material onto the shore
the swash is stronger than the backwash, so the material is moved up the beach
exposed beaches
sometimes have a large fetch, the plunging nature of destructive waves, along with their stronger backwash, means that pebbles are not moved far up the beach, which makes the beach profile steep
storm beach
may form when wild, stormy weather and waves hurl boulders and large pebbles to the back of a beach
beach profile
shows the gradient of a beach from the back of the beach to the sea, a sandy beach generally has a gentler profile compared to a pebble beach with a steep, stepped profile
sea defences
also affect the profile of a beach, where there are defences such as groynes, where the material is trapped, a beach tends to have a steeper profile
ridges and runnels
common on wide sandy beaches with a large tidal range
ridges are areas of the beach that are raised, the dips are water-filled troughs called runnels, the cross-section is similar to that of hills and valleys but at a much smaller scale
impact of flooding on humans
floodwater is often contaminated with sewage, which can lead to illness and affect clean drinking water
transport networks can be affected, such as flood damage to bridges, railways and roads
people may have to move out of their properties until flood damage is repaired
impact of flooding on environment
river banks and natural levées can be eliminated as rivers reach bankfull capacity
plants that survive the initial flood may die due to being inundated with water
contaminated floodwater can pollute rivers and habitats
flood plain
large area of flat land on either side of the river that experiences or has experienced flooding
levees
naturally raised riverbanks found along the sides of the river channel that has experienced flooding
how is a floodplain formed (1)
form due to erosion and deposition, erosion removes any interlocking spurs, creating a wide, flat area on either side of the river
during a flood, the material being carried by the river is deposited
how is a floodplain formed (2)
over time, the height of the floodplain increases as the material is deposited on either side of the river
the floodplain is often a wide, flat area caused by meanders shifting along the valley
how are levees formed (1)
when a river floods friction with the floodplain leads to a rapid decrease in the velocity of the river and therefore its capacity to transport material
larger material is deposited closest to the river bank
how are levees formed (2)
this often leads to large, raised mounds being formed
smaller material is deposited further away and leads to the formation of gently sloping sides of the levees
why are floodplains often very fertile
it’s made up of alluvium which is deposited silt from a river flood
characteristics of a flood plain
a large area of flat land either side of a river
layers of alluvium cover the flood plain
a river bluff along the edge of a flood plain
meander scars
levees
rich, fertile soil
reeds and marsh plants
characteristics of a levee
raised river banks
consist of gravel, stones and small sediment
steep on the channel side, gentle sloping on the land side
relatively flat top covered in grass
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) introduction
climate change poses a serious threats people and the planet, so it is essential that strategies are in place to manage it, these strategies fall under two categories: mitigation, which tackles root causes and adaptation which deals with the effects. both play a crucial role in tackling climate change in the short and long term
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) what is mitigation?
means to prevent or reduce the effects of something happening
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) mitigation examples
using renewable energy such as wind, solar or tidal energy can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas, therefore, this will reduce carbon dioxide emissions
carbon capture involves removing greenhouse gases from waste gas from power stations and other direct sources then storing it underground in old coal mines or gas field, this reduces atmospheric emissions.
afforestation through planting trees means carbon dioxide will be absorbed from the atmosphere during photosynthesis
International agreements between countries to pledge to reduce the amount of greenhouses gas emissions, the Kyoto Protocol became international law in 2005 and the countries that signed up agreed to reduce carbon emissions by 5%
this ended in 2012, and its impact has been negligible, The US refused to sign up, and large developing countries such as India and China were not required to make reductions
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) what is adaptation?
responding climate change by reducing its adverse effects
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) adaptation examples
agriculture as farmers will no longer grow some crops, so they will need to adapt and grow crops that suit the changing climate, an example of this is that oranges and grapes could soon become common in the UK
due to water shortages in some areas, water transfer schemes will be developed that will be transferred from water surplus areas to water deficit
reducing the risk from sea-level rise – sea defences may be constructed to protect areas at risk of erosion by sea-level rise
strategies to manage climate change (9 marker) conclusion
in conclusion, I agree that both mitigation and adaptation are essential in managing climate change, while mitigation tackles the root causes and is key to long term prevention, adaptation is crucial for coping with the effects already being felt
a combination of both is needed to effectively address the global challenge of climate change
revetments
traditionally, these have been wooden slatted barriers constructed towards the rear of beaches to protect the base of cliffs, waves breaking against the revetments dissipate energy
concrete revetments have recently been used in places such as Hornsea
advantages of revetments
social: revetments do not impede people from walking along a beach
economic: cheaper and less intrusive than a seal wall
environmental: less beach material is eroded compared to a sea well
disadvantages of revetments
social: revetments can impede access to the beach
economic: a short lifespan mainly when constructed from wood and unsuitable where wave energy is high
environmental: revetments do not look attractive, destroy habitats and affect the coastal system and reduce the input of sediment
rock armour
barrier of large boulders placed before a cliff or sea wall to absorb wave energy and reduce backwash by encouraging percolation
advantages of rock armour
social: does not impede access along the beach unless it is used as a gabion
economic: cheaper than constructing a sea wall, quick and easy to construct. It can be built in weeks rather than months, reducing the economic impact of its installation, if it is well maintained, it will last for years, it is versatile because it can be placed before a sea wall, extending its life span, it can also stabilise slopes on dunes
environmental: rock armour does not impede sediment movement along the coast by longshore drift
disadvantage of rock armour
social: access to the beach is difficult as beach access is limited
economic: cost increase when the rock is imported
environmental: rock armour looks unattractive and has to be quarried which can cause environmental damage
gabions
wire mesh cages filled with pebbles or rocks, they are placed at the back of sandy beaches. As water enters the cages, wave energy is absorbed and dissipated.
advantages of gabions
social: does not impede access along the beach
economic: cheap and easy to construct, structure is quick to build and cheap to maintain, good value as they last between 20-25 years
environmental: does not impede sediment movement along the coast by longshore drift, they blend in better than most other hard engineering solutions, this is especially the case when sand is blown over them or when they are covered by vegetation.
disadvantages of gabions
social: access to the beach is difficult as people may have to climb over the rock armour or make detours, in a damaged state, gabions are very dangerous
economic: gabions are restricted to sandy beaches as material thrown at them on shingle beaches would quickly degrade them
environmental: damaged gabions are unsightly and dangerous to sea birds
breakwater
large concrete blocks and boulders located offshore to change the direction of waves and reduce longshore drift, they also help absorb wave energy
advantages of break water
beaches retain a natural appearance
disadvantages of breakwater
dfficult to maintain, unattractive, does not protect the cliffs directly and does not stop beach material from being eroded.
what causes climate change
the atmosphere traps some of the heat reflected from the Earth’s surface, this natural process is known as the greenhouse effect and without this natural process, temperatures would be much colder on Earth
for example, without naturally occurring greenhouse gases, Earth’s average temperature would be near -18°C instead of the much warmer 15°C
how does the greenhouse effect work
the greenhouse effect works by the atmosphere allowing heat from the Sun (short-wave infrared radiation) to pass through to heat the Earth’s surface
the surface of the heat then gives off heat as longwave radiation. Some of this heat is trapped by natural greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide, radiating the heat back towards Earth, heating the Earth
how do human factors enhance the greenhouse effect
human activities increase the volume of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere leading to the enhanced greenhouse effect because increased greenhouse gases trap more of the infrared heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, average global temperature increases due to this
how do human factors enhance the greenhouse effect: deforestation
trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, when trees are cut down, less carbon dioxide will be absorbed, leading to increased concentrations in the atmosphere.
how do human factors enhance the greenhouse effect: burning fossil fuels
when coal, oil and gas are burned, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere
how do human factors enhance the greenhouse effect: agriculture
increased pastoral (animal) farming leads to more methane being released into the atmosphere
agricultural practices lead to releasing nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere
how do human factors enhance the greenhouse effect: dumping waste in a landfill
as waste decomposes it releases methane
how do natural factors enhance the greenhouse effects: orbital changes
Milankovitch cycles are variations in the tilt/orbit of the Earth around the Sun, causing natural warming and cooling periods
how do natural factors enhance the greenhouse effects: volcanic eruptions
carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere during eruptions
how do natural factors enhance the greenhouse effects: solar output
the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun fluctuates. High levels of radiation lead to an increase in Earth’s temperatures