Repro Exam 2: Estrous Cycle
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the follicular phase?
Stage of the estrous cycle where ovarian follicles grow, estrogen levels increase, and the female becomes receptive to mating, culminating in ovulation, which is the release of the egg
What is the luteal phase?
The second stage of the animal reproductive cycle, beginning after ovulation with the formation of the corpus luteum (CL) from the ruptured follicle
What is atresia?
A normal degenerative process where the majority of ovarian follicles undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis), rather than reaching maturity for ovulation
What is follicle recruitment, selection, and dominance?
- Recruitment- small follicles recruited into gonadotropin sensitive pool; produce smallest amount of estradiol
- Selection- ovulatory follicles emerge and either become atretic or develop further; produce moderate amounts of estradiol
- Dominance- dominant follicle that will ovulate; produce large amounts of estradiol
What is metestrus?
Phase from ovulation until mature CL with maximum progesterone
What is diestrus?
Mature CL produces maximum progesterone keeping the follicles from ovulating
What is proestrus?
From when progesterone starts to decline until you can see behavioral estrus
What is estrus?
(heat)- noun; period when female is receptive to copulation with the male
“The cow is displaying estrus”
Phases of estrus acronym
My Dog Plays Everyday
Estrus vs estrous
Estrus is a noun: “The cow is displaying estrus”
Estrous is an adjective: “The length of the estrous cycle in the pig is 21 days”
Anestrus vs anestrous
- Anestrus- noun; without cyclcity, ovaries are relatively inactive, neither ovulatory follicles or corpora lutea are present
- Anestrous- adjective; describes something related to the anestrus period
What is polyestrus?
Uniform distribution of estrous cycles throughout the year (cow and pig)
What does it mean to be seasonally polyestrus?
“Clusters” of estrous cycles that occur during certain seasons of the year (ewe and mare)
What is monoestrus?
Only one cycle per year
2-cell, 2 gonadotropin model of estradiol synthesis
*Follicles make estradiol!*
- Theca interna- has LHr receptor, Cholesterol (precursor for formation of steroids) → pregnenolone → progesterone → and then 17a hydroxylate makes androstenedione (testosterone) to be transferred to granulosa cell through basement membrane
- Granulosa- has FSHr receptor and LHr receptor, androstenedione is transformed into estradiol by P450 aromatase
What is the biochemical structure of cholesterol?

What is the biochemical structure of progesterone?

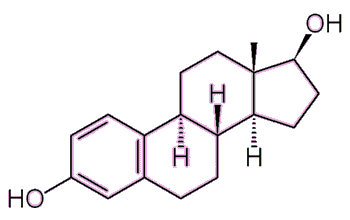
What is the biochemical structure of estradiol?
What are the characteristics of a follicular wave?
- Cohort (small group) of follicles recruited initially
- Some will continue to develop, others will undergo atresia
- Dominant follicle is selected for continued growth to pre-ovulatory size
- If that follicle achieves dominance near time of luteolysis, it will ovulate
How do the ovarian structures and the hypothalamus/pituitary communicate with each other to cause recruitment, selection, and dominance?
- The hypothalamus releases GnRH, which stimulates the pituitary to release FSH and LH, prompting the ovaries to grow follicles
- As estrogen levels rise from the follicles, they signal the hypothalamus and pituitary, influencing the release of these hormones to guide the recruitment of multiple follicles, the selection of one dominant follicle through LH receptor acquisition and estrogen production, and finally, ovulation
At time of recruitment, follicles are already at tertiary stage: true or false
True
What is the relationship/timing of the rise in FSH, growth of a follicular wave, and rise in estradiol?
- A rise in FSH in the early follicular phase initiates the growth of a follicular wave, and as the dominant follicle in the wave grows, it produces rising levels of estradiol
- In the late follicular phase, high estradiol levels trigger LH surge therefore triggering ovulation
How does LH, FSH, estradiol, and inhibin change with the follicular wave?
FSH initially rises, stimulating multiple follicles to grow, but then decreases as a dominant follicle emerges and secretes increasing estradiol and inhibin, which suppress further FSH
How does LH pulse frequency change during the estrous cycle?
Low and slow during the luteal phase and becoming faster and more frequent during the follicular phase, finishing with a surge of LH right before ovulation
What is the role/function of LH?
In selection, FSH secretion is slowed by inhibin and estradiol and LH secretion increases and eventually surges to cause ovulation
What is the role/function of FSH?
During recruitment, FSH increases prompting follicle growth
What is the role/function of PGF2a (prostaglandin)?
Causing regression of CL (luetolysis)
What is the length of the estrous cycle in the cow, mare, sow, and ewe?
Cow- 21 days
Mare- 21 days
Sow- 21 days
Ewe- 17 days
What is the duration of estrous in the cow, mare, sow, and ewe?
Cow- 15 hrs
Mare- 7 days
Sow- 50 hrs
Ewe- 30 hrs
What is the timing of ovulation in the cow, mare, sow, and ewe?
Cow- 24-32 hrs
Mare- 5 days
Sow- 36-44 hrs
Ewe- 24-30 hrs