UNIT 1 REVIEW HSB4U
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Define Anthropology
Anthropology is the study of human nature, human society, human past and culture
Define Psychology
The study of mind and behavior
Define Sociology
The study of how society and group of humans interact with one another
Explain the similarities and differences between anthropology, psychology, and sociology
Similarity
- Study of the human mind
- How the human brain thinks and behaves
Difference
- Anthropology focuses on culture and human evolution
- Psychology focuses on how the human brain thinks and how the human behaves
- Sociology focuses on how the society interacts with one another and how they behave
Questions asked by anthropologists
How do different cultures shape the way people live?
How have humans changed over time?
How does language connect to culture?
Questions asked by psychologist
How do our thoughts and feelings affect our behavior?
How do people learn new behaviors?
What causes mental health problems, and how can they be treated?
Questions asked by sociologist
How do different social groups influence people's behavior? How does society change over time?
What causes inequality in society, and how can it be reduced?
What do anthropologists study?
Cultures: Customs and traditions
Society: Group organizations
Languages: Communication
Physical traits: Human evolution
History: Past human life
Three major schools of thought in anthropology
Functionalism, Structuralism, Cultural Materialism
Explain functionalism
Studies social problems and how institutions address them
Explain structuralism
Studies what makes cultures different and unique. Structural anthropology aims to find the unspoken rules people follow but can't explain.
Explain cultural materialism
Cultural materialism studies how technology and economy shapes society.
Describe the difference between knowledge and intuition
Knowledge is learned information; intuition is a gut feeling or instinct without any knowledge.
What do psychologists study?
The study of how and why humans act on an individual basis. The thinking behind the human brain.
The three major schools of thought in psychology
Psychoanalysis, behaviorism, learning theory
Explain psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud (1865-1939) - a process to uncover a patient's unconscious thoughts by encouraging them to discuss their background, feelings and experiences with a trained psychologist.
Explain behaviorism
John Watson (1878-1958) - believes that our actions are shaped by our environment. Change the environment, and behavior will change as well.
Explain the learning theory
Pavlov, Skinner, and Bandura believe behavior is mostly learned, especially in childhood.
Explain the difference between clinical psychology and experimental psychology
Clinical Psychology
- Programs and treatments specifically made for individuals who suffer from mental illnesses and disorders.
Experimental Psychology
- Study how individuals act in different situations to understand human behavior and its causes.
Describe what sociologists study
Study societies, groups, and how people interact with one another. Looks at culture , relationships, and social issues
Describe the five major schools of thought in sociology with reference to their approaches
Structural Functionalism: Looks at how all parts of society (like family, schools, and government) work together to keep things running smoothly.
Neo-Marxism: Focuses on the struggles between rich and poor people, and how this creates inequality in society.
Symbolic Interactionism: Studies how people use symbols, language, and actions to make sense of the world.
Feminist Theory: Examines how women are mistreated in society and how gender roles affect both men and women.
Inclusionism: Focuses on including everyone's perspectives, especially those from marginalized groups, to better understand society.
Explain primary and secondary groups
Primary groups
- More connected to you (ex. family members)
Secondary groups
- Not too connected with you (ex. classmates or teachers)
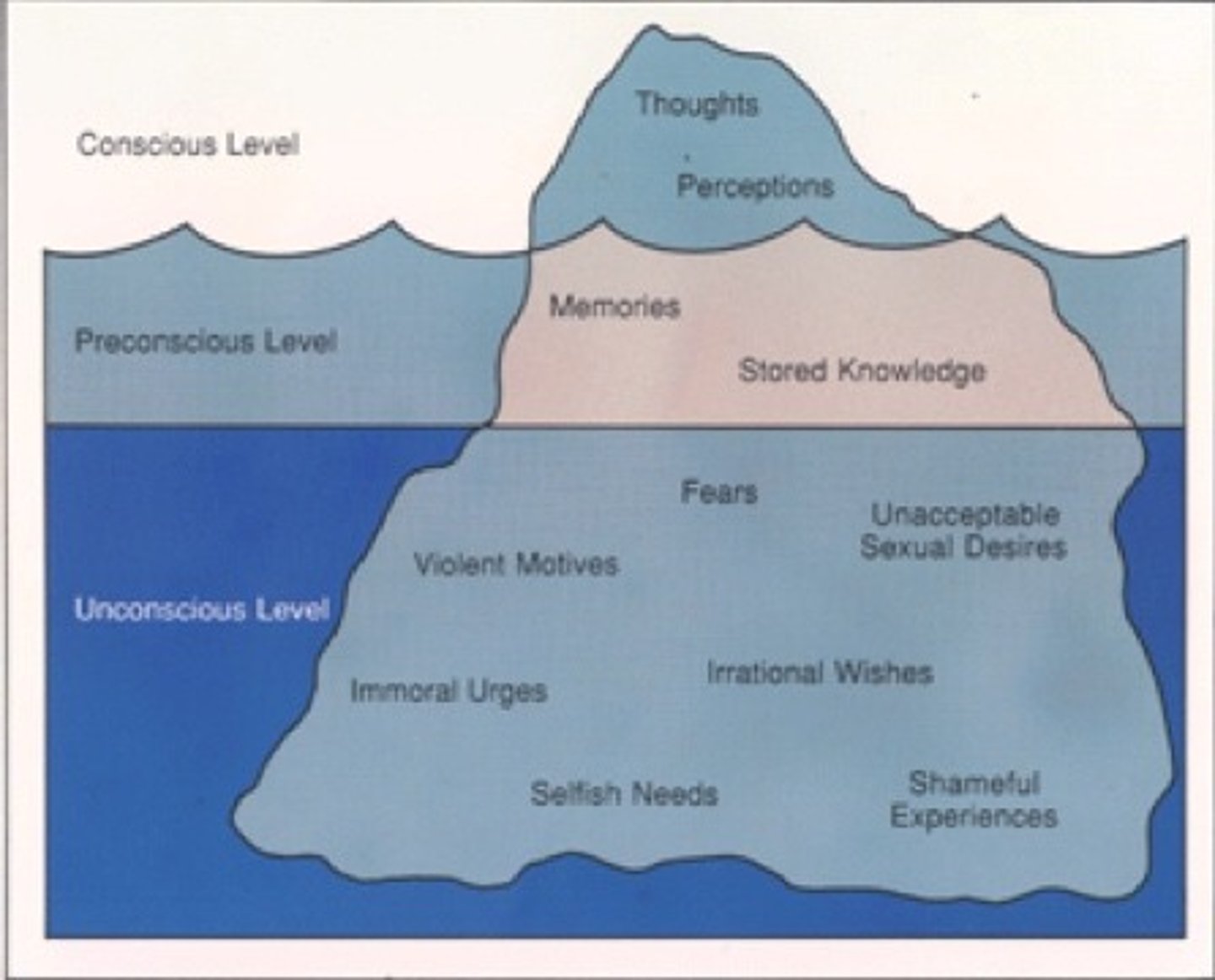
Freud's Iceberg Model
Conscious: Thoughts and awareness
Preconscious: Memories and thoughts easily recalled.
Unconscious: Hidden thoughts and feelings.
Freud's Three Parts of Personality
Id: Wants pleasure now! ("I want cake!") [UNCONSCIOUS]
Ego: Balances wants and reality. ("A small slice is okay.") [CONSCIOUS DECISION MAKER]
Superego: Follows rules. ("Cake is unhealthy, I won't eat it.") [UNCONSCIOUS]
![<p>Id: Wants pleasure now! ("I want cake!") [UNCONSCIOUS]</p><p>Ego: Balances wants and reality. ("A small slice is okay.") [CONSCIOUS DECISION MAKER]</p><p>Superego: Follows rules. ("Cake is unhealthy, I won't eat it.") [UNCONSCIOUS]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/be6d2f8f-6750-4a3d-82a2-73b5df0bb967.jpg)
What is positive and negative reinforcement?
Positive Reinforcement: Reward for good behavior (e.g., getting candy for good grades).
Negative Reinforcement: Removing something bad to encourage behavior (e.g., no homework for good class participation).
What is positive and negative punishment?
Positive Punishment: Adding something unpleasant (e.g., getting a fine for speeding).
Negative Punishment: Taking away something pleasant (e.g., losing phone privileges for bad behavior).
Pyramid of cultural materialism
Infrastructure (Base): Economy, technology, environment.
Structure (Middle): Social and political systems.
Superstructure (Top): Culture, beliefs, values.
Learning Theory & Bandura's Bobo Doll Experiment
Kids watched an adult act aggressively toward a Bobo doll. Those who saw aggression were more likely to copy it. This supports Learning Theory, which says behavior is shaped by watching and modeling others.
Examples of institutions
Schools, Government, Religion
Four Perspectives of Feminist Theory
Liberal Feminism: Equal rights and opportunities.
Radical Feminism: Patriarchy causes oppression.
Marxistinism Feminism: Capitalism creates gender inequality.
Intersectional Feminism: Oppression comes from race, class, and gender.