NURS 354 Key Review (Amalie!!!)
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
T/F: birth is viewed as a normal life event rather than a medical procedure
TRUE
Still birth
fetal death after 20 week gestation in the womb
What are the top 5 causes of pregnancy-related deaths?
post partum hemorrhage
post partum infection
preeclampsia/eclampsia
cardiovascular disease
abortion complications
Barriers to healthcare for women
finances, transportation, language/culture, low health literacy
# 1 cause infant mortality
congenital anomaly
# 1 cause maternal mortality
cardiovascular disease
Primary Prevention
preventing disease before it occurs
(folic acid to decrease neural tube defects)
Secondary Prevention
early identification of those who have developed a disease- shortening duration/ reduce severity (pap smears, mammograms, etc.)
Tertiary prevention
treating those who have developed a disease- reduce progression and restore maximum health potential (chronic effects of STIs)
Complementary Medicine (integrative medicine)
a combination of mainstream/conventional medical therapy and CAM therapy
ie. aromatherapy with NSAIDs for pain relief
What is the most common form of CAM?
prayer!
What is an example of CAM used in pregnancy?
ginger lolipops
seabands
acupuncture/pressure
vitamin B6
When is differentiation of external genitalia complete?
12th week gestation
(ovaries-10 wk, testes 7-8w gestation)
Normal vaginal pH
4-5
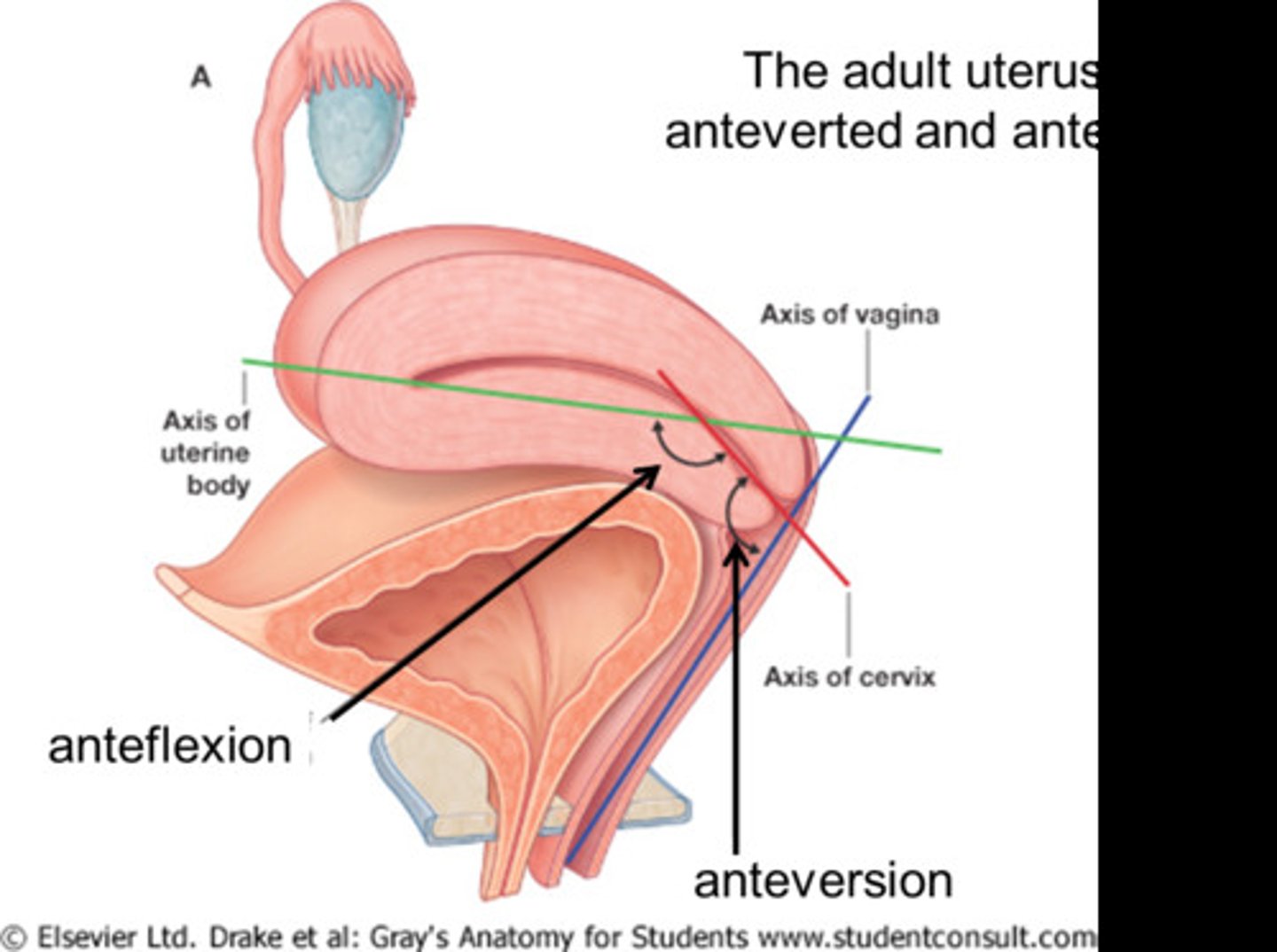
Anteverted
tilted forward uterus (only cervix is anchored)
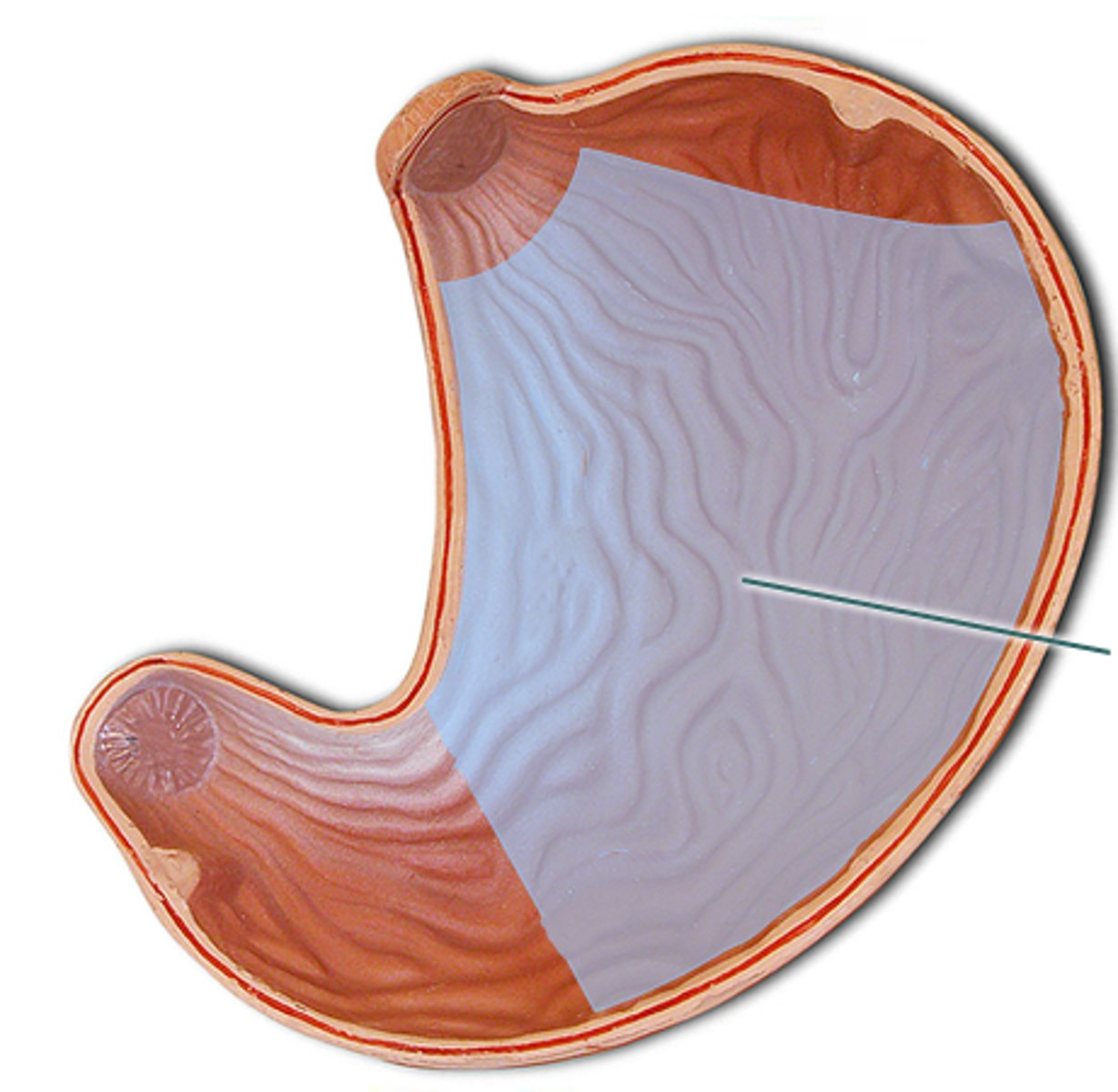
Isthmus
divides uterus into 2 unequal parts
Corpus
body of uterus
(3- layers- perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium)
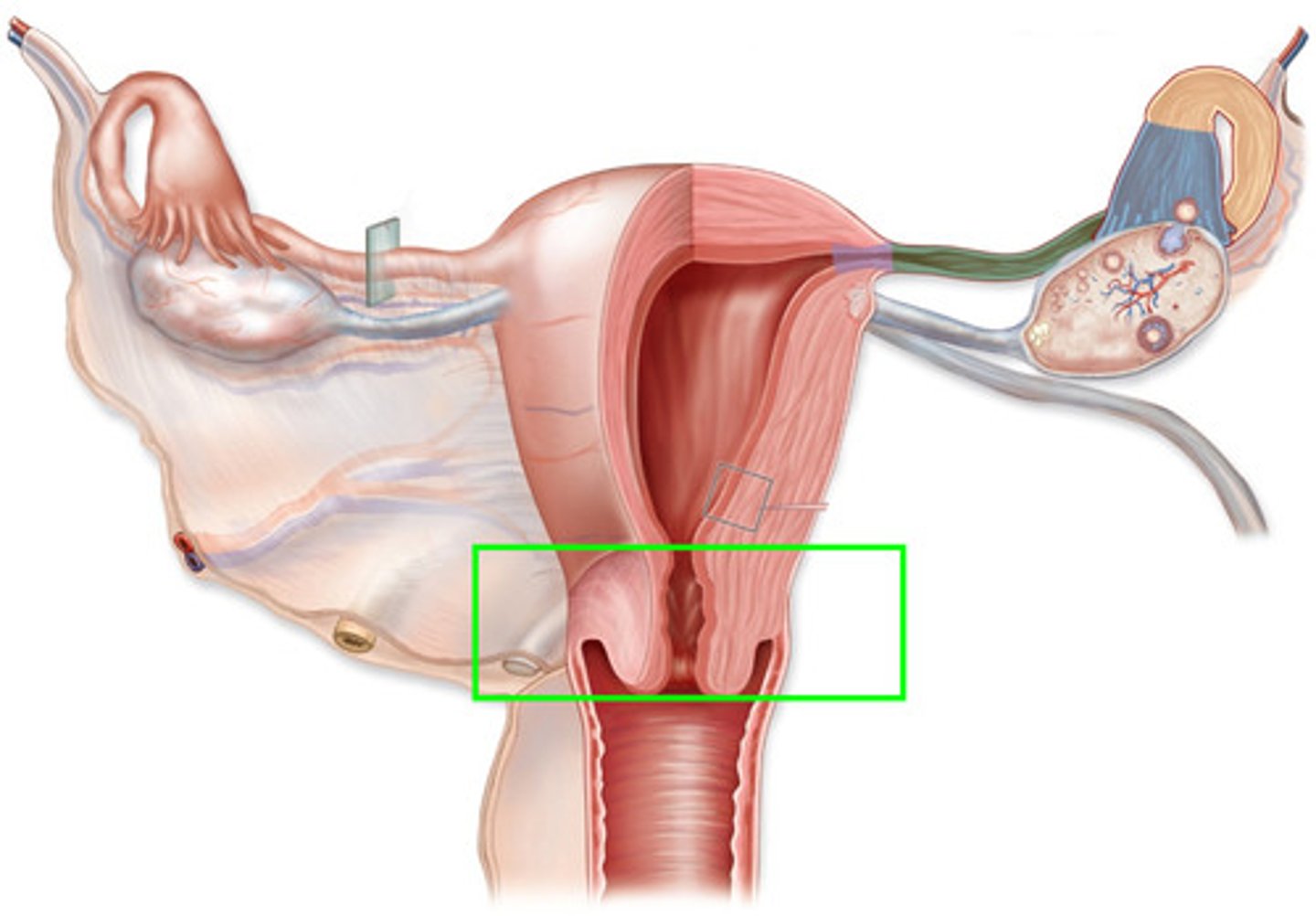
Cervix
lower 1/3 of uterus, opens into vagina
Fundus
uppermost or top portion of uterus
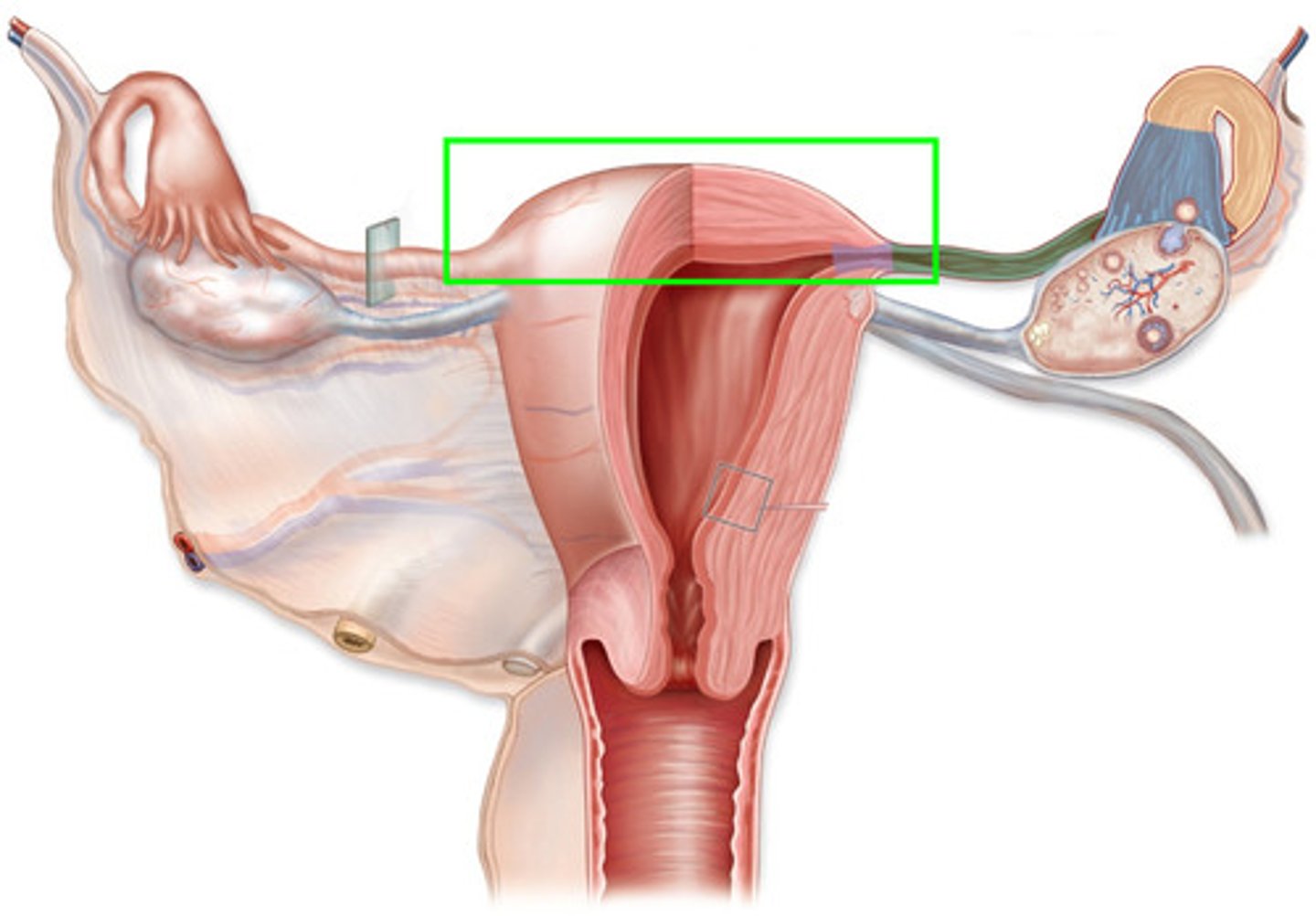
Carnua
narrowed area where fallopian tubes enter the uterus
Uterine contractions are responsible for?
cervical dilation (major force of passage for baby through pelvis and vagina)
T/F: cervical mucous is alkaline
true! (protects sperm from acidic vaginal secretions)
Why does cervical mucous thin at ovulation?
for sperm to enter
Fallopian tube
infudibulum, ampulla, isthmus
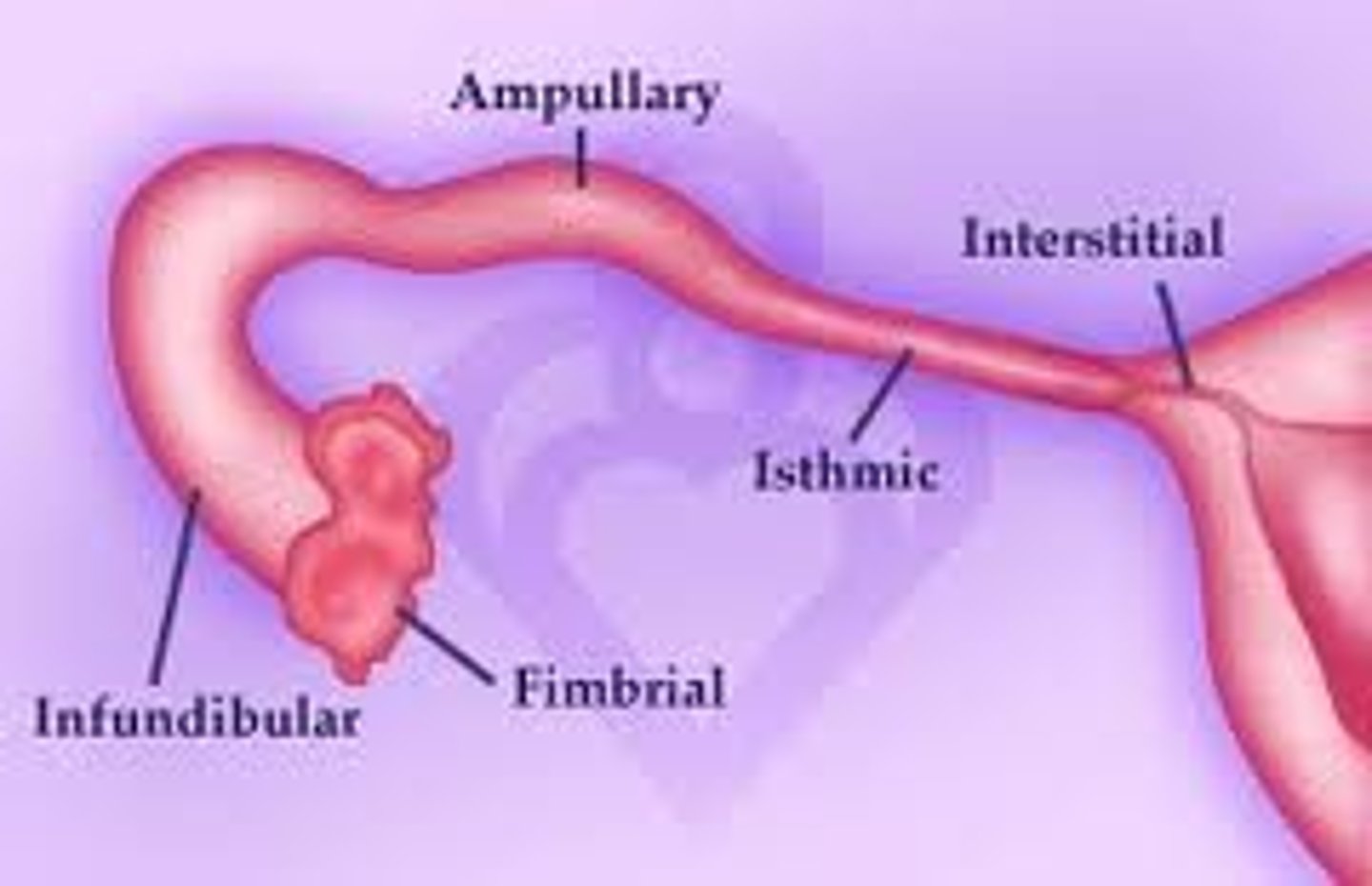
T/f: ovaries are attached to the fallopian tube
FALSE (supported by ligaments)
What is the typical lifespan of the egg?
6-24 hours
Follicular Phase (1-ovarian cycle)
begins on day 1 of menstrual cycle, continues until ovulation (day 14)
FSH is released
follicle maturation in ovary and release of mature egg
menstrual cycles vary due to variations in length of this phase
Ovulation Phase (2-ovarian cycle)
release of mature egg
triggered by LH surge
estrogen decreases
egg lives 6-24 hours
spinnbarkheit
mittelschmerz
increased discharge, mid-cycle spotting
increased temperature
Luteal Phase (3-ovarian cycle)
release of LH (days 15-28)
begins when egg leaves follicle
corpus luteum develops and secretes increased amounts of progesterone (causes 0.5-1 F temp increase)
fertilized ovum secretes hCG
unfertilized ovum causes corpus luteum degeneration, estrogen/progesterone fall, endometrial lining shedding
Menstrual Phase (1-uterine cycle)
spiral arteries rupture
estrogen/progesterone levels fall
endometrial lining sloughs
menstrual bleeding occurs
Proliferative Phase (2-uterine cycle)
estrogen levels begin to rise
endometrium thickens
cervical mucous thin, clear, watery, more alkaline for sperm
begins near day 5 of menstrual cycle
ends at ovulation
Secretory Phase (3-uterine cycle)
begins at ovulation
ends approx. 3 days before onset of next cycle
progesterone increases
endometrium thickens, vascularity increases
Ischemic Phase (4-uterine cycle)
occurs 3 days prior to onset of menstrual flow
sharp drop in estrogen and progesterone levels
endometrial vessels spasm
basal layer becomes ischemic
Spinnbarkheit
thin, stretchy slippery mucous produced by cervix at ovulation
What does the ovum secrete that is necessary to maintain the corpus luteum?
Hcg
What is the most important factor in determining age of menarche?
genetics
GnRH
induces release of FSH and LH for ovulation
FSH
ovarian follicle maturation
LH
necessary for final follicle maturation
surge occurs in the hours prior to ovulation
responsible for increased progesterone from the follicle
What causes the uterus to increase in size and weight?
estrogen
Progesterone
calming affect on uterus, maintains pregnancy
high levels necessary for implantation to occur
maintains endometrium
smooth muscle relaxant (inhibits contractions)
stimulate maternal metabolism/breast development
provides nourishment for early conceptus
Pathogenesis of menstrual cramps
prostaglandin F2a (powerful myometrial stimulant/vasoconstrictor)
Tx of choice- NSAIDs
Primary Amenorrhea
no menses by age 15 AND absence of growth and development of secondary sex characteristics
OR
no menses by age 16 with NORMAL growth/development of secondary sex characteristics
Tx: estrogen replacement therapy
Secondary Amenorrhea
absence of menses for 3 cycles
OR
irregular menses for 6 months in women who have previously menstruated regularly
Tx: oral contraceptives
T/f: there is increased evidence in the correlation between decreased menstrual irregulatiry and development of osteoporosis/hip fractures later in life
TRUE
What is the leading cause of absenteeism from work/school?
dysmenorrhea
When does PMS/PMDD occur?
luteal phase!
Tx of PMS/PMDD
vitamin/mineral supplements (VitB, Ca, Mg)
NSAIDs
spironolactone
various herbal supplements
diet
lifestyle
What are the 2 most common symptoms of endometriosis?
infertility and pelvic pain
Definitive diagnosis of endometriosis
laparoscopy
What is gold standard treatment of endometriosis?
laparoscopic lesion excision
What is the most important indicator of male infertility?
semen analysis
What is gold standard assessment of tubal patency?
hysterosalpingography (HSG)
*fallopian tube obstruction one of most common causes of female factor infertility
Shoot in dye!!
How to improve fertility
normal vaginal pH
promote sperm retention during/after intercourse
promote adequate nutrition/stress reduction
promote patient education to maximize fertilization (time of ovulation/intercourse)
Fertile period total days
6 days- 3 days prior and 3 days after ovulation
Cervical Mucous Method
characteristics near and at ovulation
estrogen dominant (promote sperm survival)
spinnbarkheit
After ovulation, cervical mucous is dominant in what hormone?
progesterone (thick/sticky)
Basal Body Temperature (BBT) method
take and record temp upon awakening each morning
pre-ovulation- estrogen, normal BBT
post-ovulation- progesterone, BBT increases
pregnancy= elevated temp remains
not pregnant= temp returns 1-2 days before menses
Sympto-Thermal method
note and record symptoms and temperature
-spinnbarkeit
-cervical position and firmness (soft, high, deep)
-increase BBT
-mittelschmerz
-breast tenderness
Standard days method
abstain/barrier days 8-19 of cycle
*need a regular cycle to use!
2 day method
presence of cervical secretion = fertile
not present = not fertile
Do spermicides have protection against STI/HIV/AIDS?
NO!
Teach with diaphragm/cervical cap to refit
after childbirth, abortion, weight change, surgery
Timing for Contraceptive methods
once day = pill
once week = patch
once month = ring
What does depo-provera (the shot) increase?
bone demineralization and issues with contraception after!
IUD Use requirements
pap smear for cervical CA, routine testing (chlamydia/gonorrhea), MUST schedule during menses
When is the best time for tubal ligation?
postpartum
Medications for Abortion
mifepristone (associated with bleeding) and misoprostol
In women, STI's contribute to?
cervical CA, chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, death
What is a must for STIs?
cultural sensitivity!
teach: value of testing and treatment if indicated
STI Nursing Mangement
prevention is critical
provide: counseling/education
consider: developmental level
teach: sex development, sexual health, condoms if sexually active, treatment follow up plan if diagnosed
Teaching for Condom Use
use latex as mechanical barrier to STI/pregnancy
use new condom with each act
handle with care to prevent damage
ensure it is stored in cool, dry place
check expiration date
open wrapper carefully
do not use if brittle, sticky, or discolored
hold tip when unrolling
ensure adequate lubricant
withdrawal while still erect
STI high risk population
adolescents
Over age 60 STIs
increased risk, decreased immunity/skin integrity, do not see selves as vulnerable, involved in risky behavior, don't see it in HC setting
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC)
NOT an STI- thick, curdy, white vaginal wall
Prevent VVC
cotton underclothes
loose non tight clothing
discontinue OCs
avoid douching, vaginal powders, sprays
encourage glycemic control in DM
yogurt/probiotics
Bacterial Vaginosis
most common cause vaginal discharge, watery, grey/white odorous (whiff test- fishy)
increased pH > 4.5
Trich
most curable nonviral STI
70% asymptomatic
yellow/green odorous, vulvar itching
whiff-test: fishy
pH > 4.5 (normal 3.8-4.2)
Chlamydia
leading cause blindness in world (often asymptomatic)
burning/frequent urination, abdominal pain, bleeding easy, micropurulent pain
PID and infertility untreated
**screen: ALL sex-active under 25 (AT RISK), pregnant women first prenatal visit, and 3rd trimester
Chlamydia Newborn w/o Prophylaxis
ophthalmia neonatorum
chlamydial conjunctivitis
chlamydia PNA
Gonorrhea
asymptomatic 70%
abdominal pain, pelvic pain, urination pain, abnormal vaginal discharge
PID and infertility left untreated + disseminated gonococcal infection (brain, liver, joints, heart)
*Screen same as chlamydia
Gonorrhea Newborn w/o Prophylaxis
ophthalmia neonatorum
blindness
pharyngeal infections
PID
pain sharp lower abdominal
fever > 101
flu-like s/sx
vaginal discharge mucopruluent
cervical motion tenderness
PID Diagnostic
chandelier sign (cervical/uterine tenderness with movement)
Genital Herpes
80% asymptomatic
treatable NOT curable
primary after initial exposure
secondary triggered by stress
tingling, itching, pain, usually les severe
Herpes Neonatal Risks
low birth weight
congenital cataracts
neurological damage
tx: acyclovir
Syphillis
curable (VDRL + RDR) or (FTA-ABS & TP-PA)
**screen all pregnant women first prenatal vist and 3rd trimester
c section IF lesions present
neonatal: IUGR, LBW, systems failure
HPV
cause all cervical cancer, treatable NOT curable (focus on prevention)
may be asymptomatic
grayish pink wart, cauliflower vulva,
perineum, vagina, anus
gardasil 9 vaccine- ages 9-26 3 doses over 6 months
Hep B
fever, fatigue, nausea, anorexia
transmission body fluids NOT food/water, etc.
*screen at first prenatal visit
3 vaccines over 6 months for newborn
HIV
transmission blood, intercourse, pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding
most maternal-fetal transfer occurs in 3rd trimester or at delivery
delivery: C-section between 37-39 weeks
Mastitis
primarily lactating women (2d-2wk postpartum)
flu-like, red warm breast, upper outer breast common, usually unilateral
risk: milk stasis, nipple trauma
cause: staph aurues
complete emptying, continue feeding, ABX
Engorgement
bilateral, postpartal distension
warm compress, massage, anti-inflammatory, cabbage leaf (bottle feeding)
PCOS
most common endocrine disorder of reproductive age, most common cause treatable infertility
hyperandrogenemia, hyperinsulinemia
When should you screen for intimate partner violence?
at every prenatal visit!
When is gender determined?
fertilization
Where does fertilization occur?
ampulla
Nagele's Rule (Due Date)
first day LMP, subtract 3 months, add 7 days
Term Pregnancy
40 weeks, 280 days
Fertilization Age
two weeks less, 38 weeks, 266 days
Pre-embryonic Stage
day 1 (conception)- day 14
cleavage and morula
blastocyst - embryo
trophoblast - chorion
amnion (thin)- aminotic fluid
chorion (thick)- placenta
^^ make up embryonic membrane