Topic VI ELISA and Western Blotting
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
ELISA stands for?
ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY
uses the coupling of ________ and ________ and relies on the ________ and ________ of ________ for ________.
coupling of antigens and antibodies;
relies on the specificity and affinity;
antibodies for antigens
A widely used biochemical assay to detect in a sample the presence of and quantity of proteins, such as hormones and antibodies and bacteria or viruses.
ELISA
the ability to discriminate among diverse proteins
Specificity
the ability to tightly bind to molecules.
Affinity
One can determine how much ________ is present by starting with an ________, or one can determine how much ________ or ________ is present by starting with an ________.
antibody, antigen;
antigen or hormone, antibody
large glycoprotein molecules produced by B-lymphocytes during the humoral immune response to antigens introduced into the body
Antibodies
Other term for the white blood cells that form from the hematopoietic (blood) stem cells in the bone marrow. .
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes include:
B-lymphocytes (B-cells) and Tlymphocytes (T-cells)
Antibodies bind to antigens following the ________-________-________ model. Antigens bind to the ________ ________.
lock-and-key model; receptor sites
What antibodies can also bind to antibodies that can either bind to the receptor site or the tail part?
Secondary antibodies
word interpretations for the name, ELISA
• The antibody is recognized by the second antibody which has an enzyme attached (enzyme-linked)
• Antigen is recognized and binds to a specific antibody (immuno)
• Antigen/antibody of interest is adsorbed on a plastic surface (sorbent)
•Substrate react with the enzyme to produce a product, usually colored (assay)
The ELISA method has been used to detect ________ ________, ________, and ________ through antibodies in the blood serum, just to name a few diseases, or to measure the amount of various other ________ in the blood serum, such as ________, ________, and ________.
to detect hepatitis B, rabies, and HIV;
proteins such as hormones, toxins, and allergens
What detects antibodies in the sample?
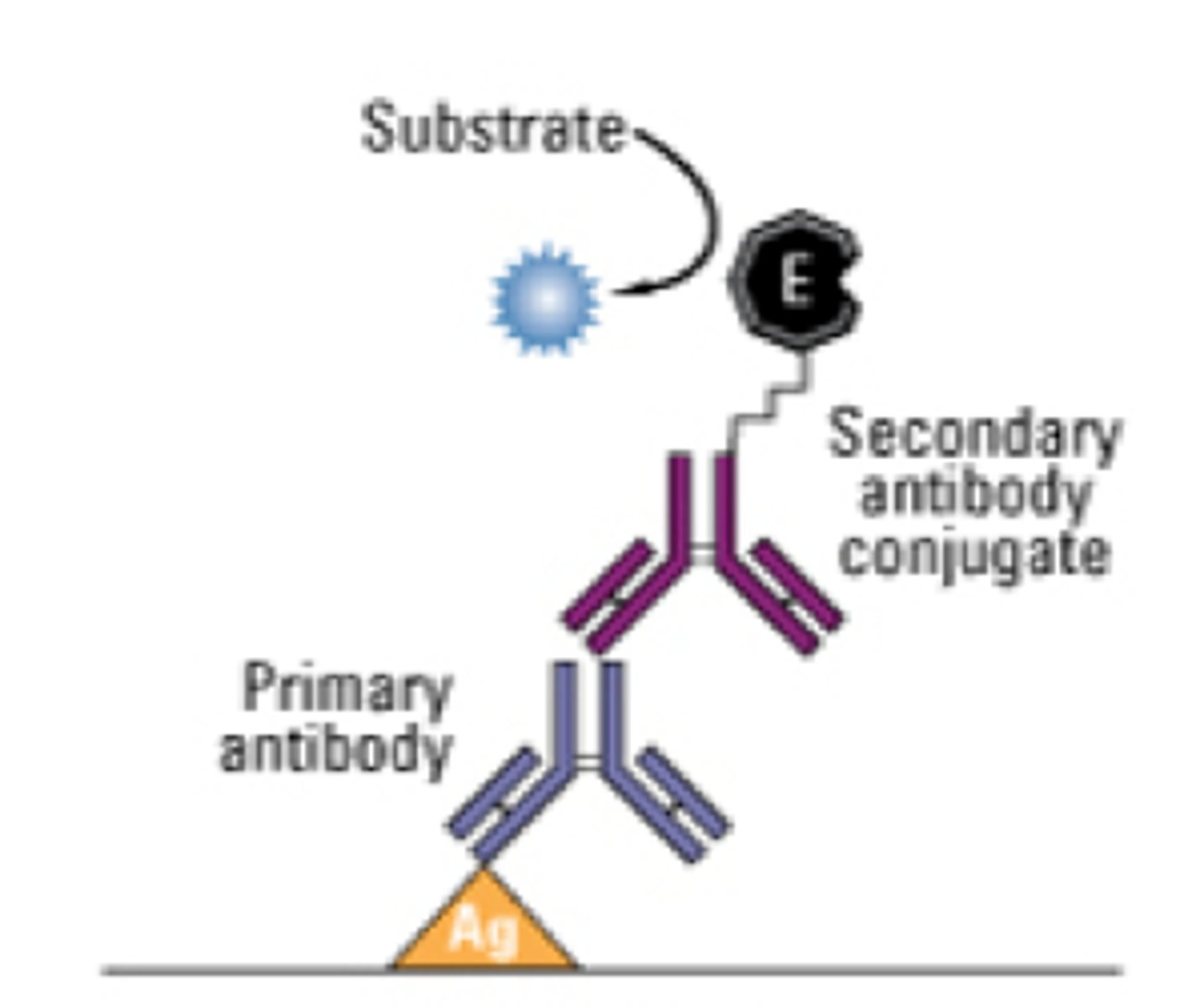
INDIRECT ELISA
Steps of an INDIRECT ELISA test
a) Binding Known Antigen
b) Blocking
c) Washing
d) Adding Test Sample Primary Antibody
e) Washing
f) Adding Enzyme-linked Secondary Antibody
g) Washing
h) Adding Substrate
i) Reading Results
he indirect ELISA method begins with a sample of known antigen being bound to the wells of a microtiter plate.
a) Binding Known Antigen
The other unoccupied sites in each well are then bound by a concentrated solution of non-interacting protein, like casein or bovine serum albumin, to block or prevent other proteins in the test sample from adhering
b) Blocking
Rinse to remove any unbound antigen and non-interacting protein
c) Washing (i)
The test sample of serum containing the primary antibodies is added to each well. Antibodies could be HIV, rabies, or hepatitis B antibodies, for example.
d) Adding Test Sample Primary Antibody
Rinse to remove any antibodies that did not bind to the known antigen
e) Washing (ii)
An enzyme-linked secondary antibody is added next to bind to the test sample antibodies. The enzyme on the secondary antibodies are proteins, such as horse radish peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase.
f) Adding Enzyme-linked Secondary Antibody
Rinse to remove any secondary antibodies that did not bind to the primary antibody.
g) Washing
A substrate is then applied which is converted by the enzyme to give a color or fluorescence or electrochemical signal. In the presence of horse radish peroxidase, TMB turns blue/
h) Adding Substrate
By using a spectrophotometer, spectrofluorometer, or electrochemical device, the results can be read and recorded. The amount of color produced is proportional to the amount of primary antibody bound to the antigen proteins on the bottom of the wells.
i) Reading Results
In ELISA, TMB (3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine) plays the role of a ________ substrate, and is also one of the most ________ substrates for ________.
chromogenic; sensitive; HRP (Horseradish Peroxidase)
chemical name of TMB
(3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine)
When a TMB solution is added to HRP, HRP will ________ hydrogen peroxide and ________ TMB, turning it from ________ to ________.
reduce; oxidize;
colorless to blue-green.
Commonly used to read ELISA results
Spectrophotometers (microplate reader)
Direct ELISA vs Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA has the advantage of signal amplification
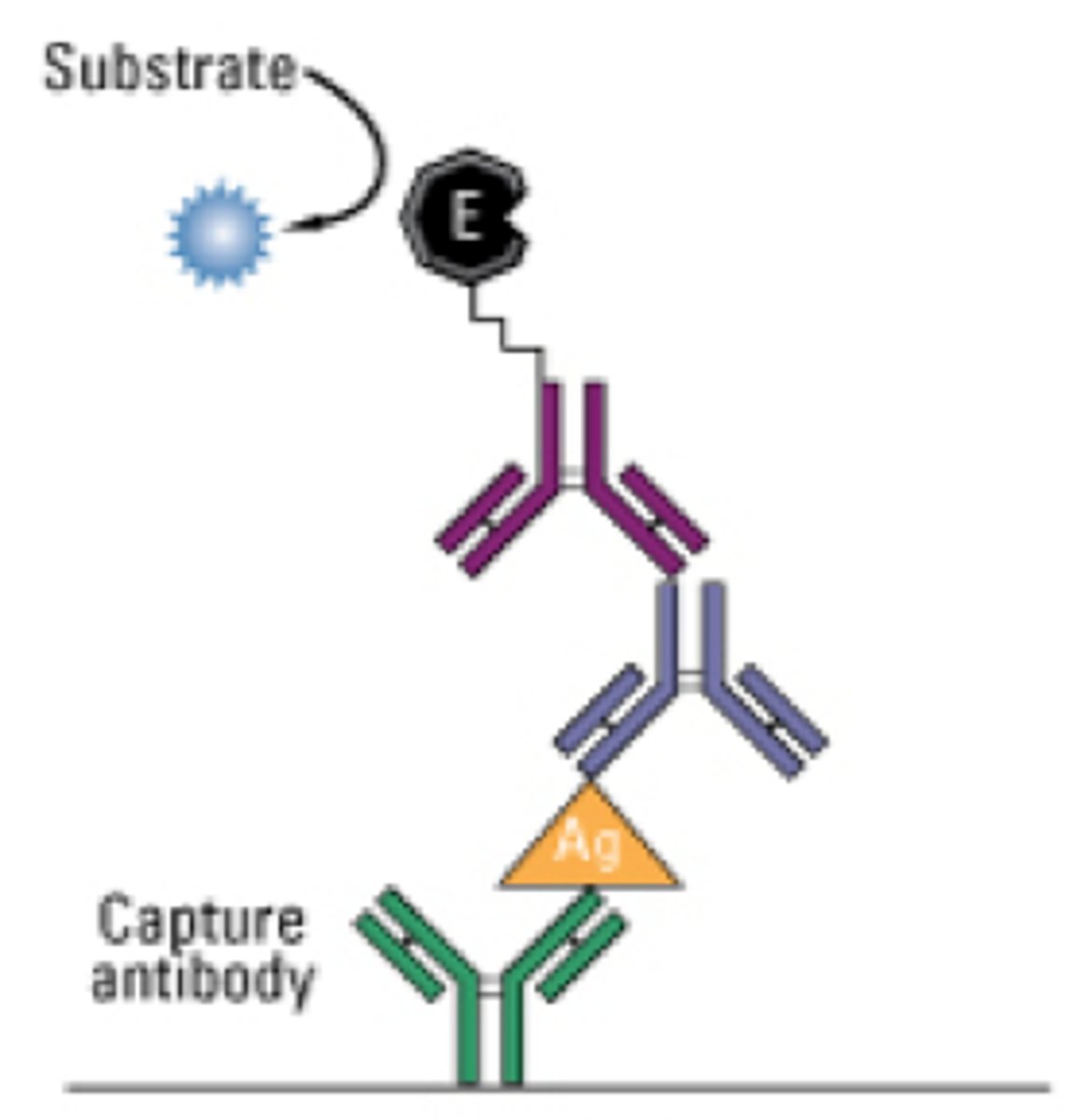
detect antigens in the sample
SANDWICH ELISA
Format Description of SANDWICH ELISA:
• This is the most commonly used format.
• This format requires two antibodies specific for different epitopes of the antigen.
• Highly specific which minimizes false positives
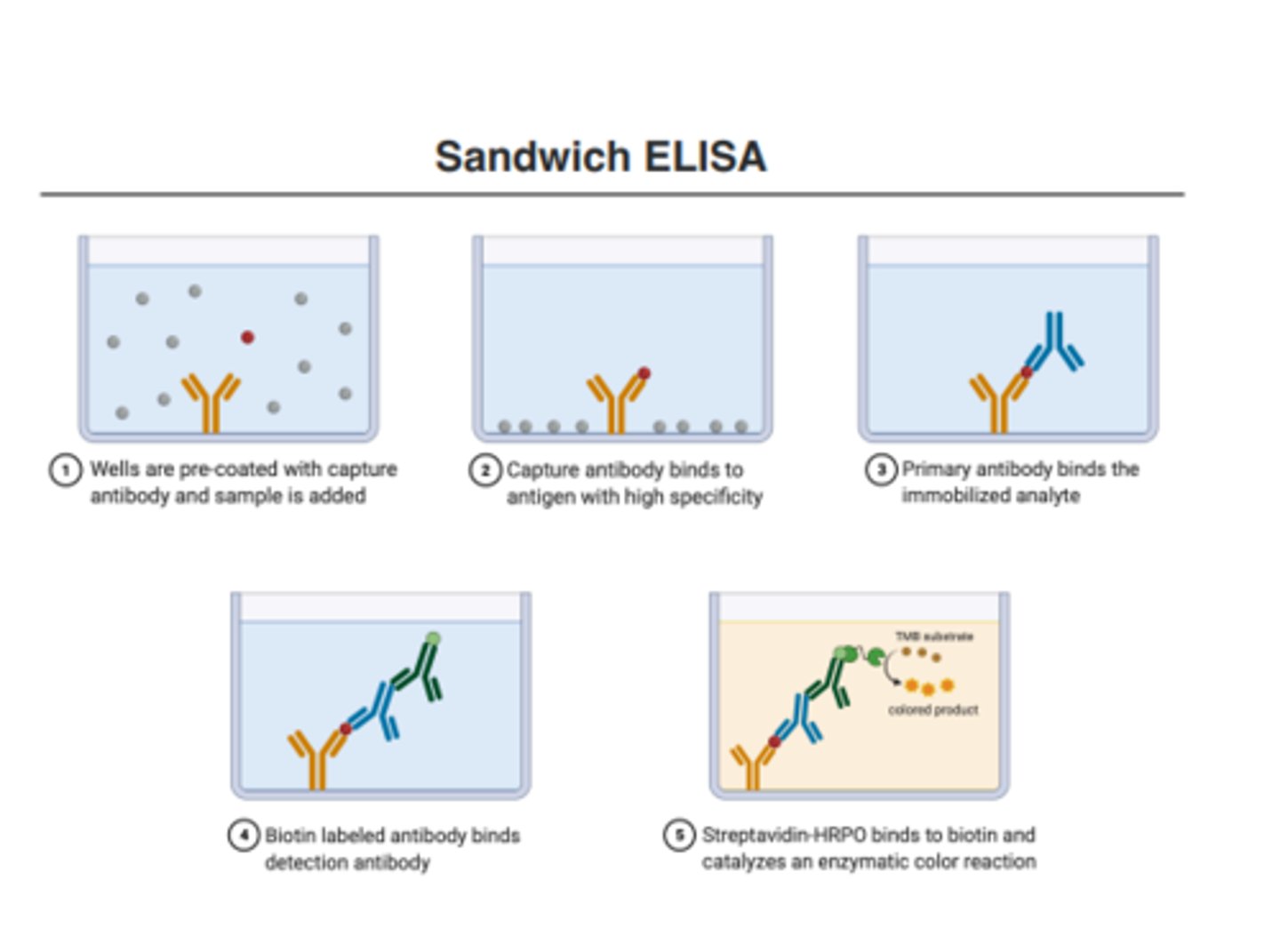
The two antibodies in SANDWICH ELISA are normally referred to as?
matched antibody pairs
it is common for ELISAs to detect antigens at the picogram level in a very specific manner due to the use of antibodies
High sensitivity and specificity
ELISA ADVANTAGES:
1. High sensitivity and specificity
2. High throughput:
3. Easy to perform
4. Quantitative
5. Possibility to test various sample types
High sensitivity and specificity:
it is common for ELISAs to detect antigens at the picogram level in a very specific manner due to the use of antibodies.
High throughput:
commercial ELISA kits are normally available in a 96-well plate format. But the assay can be easily adapted to 384-well plates.
Easy to perform:
protocols are easy to follow and involve little hands-on time.
Quantitative:
It can determine the concentration of antigen in a sample. •
Possibility to test various sample types
Serum, plasma, cellular and tissue extracts, urine, and saliva among others.
ELISA DISADVANTAGES:
1. Temporary readouts
2. Limited antigen information
Temporary readouts:
detection is based on enzyme/substrate reactions and therefore readout must be obtained in a short time span.
Limited antigen information:
information is limited to the amount or presence of the antigen in the sample
ELISA are widely available as?
test kits
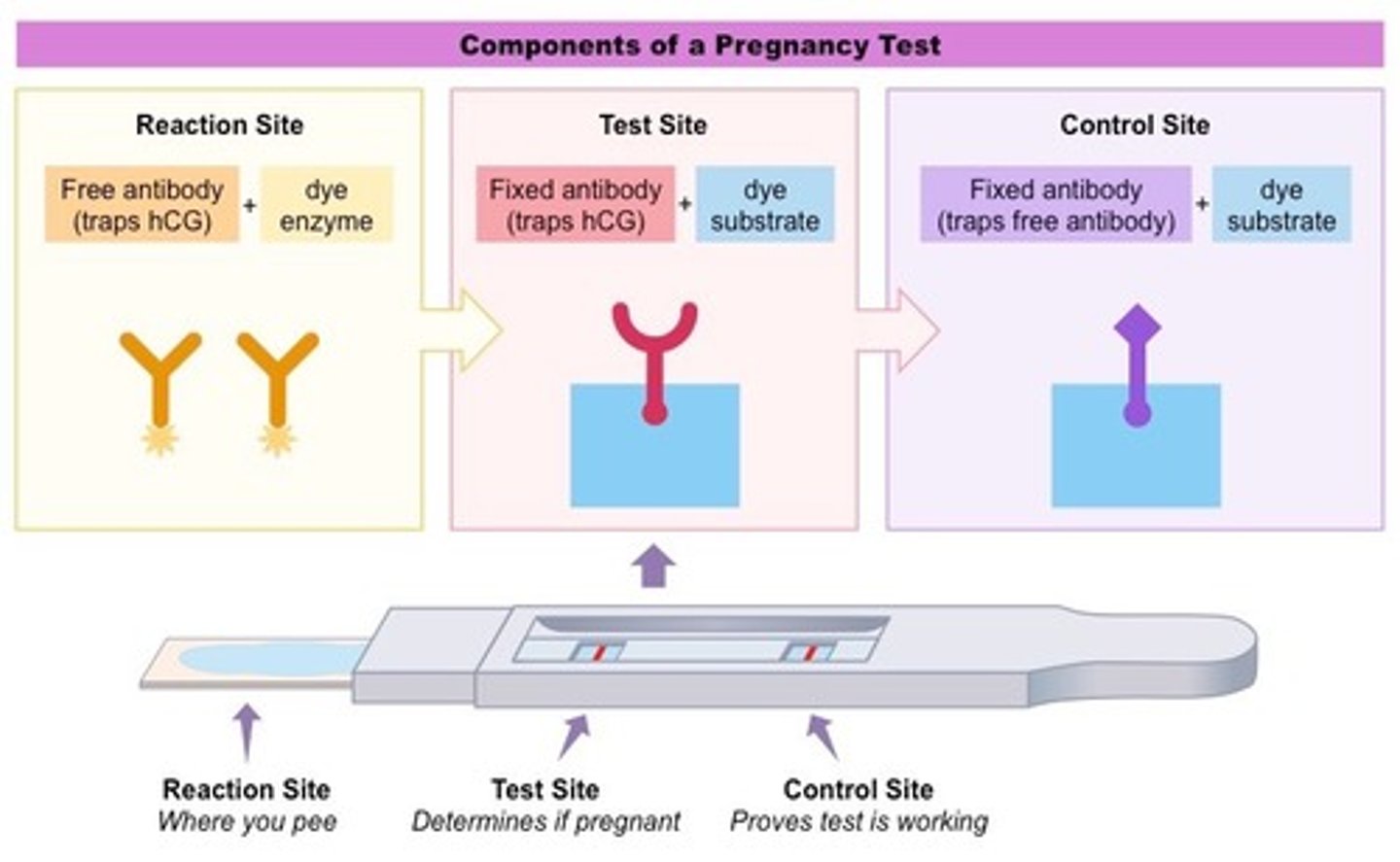
hCG stands for
human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Blots are techniques for transferring ________, ________, and ________ onto a ________ so they can be ________, and often follows the use of a ________ ________.
for DNA, RNA and proteins;
carrier;
separated;
gel electrophoresis.
1. Southern blot?
2. Northern blot?
3. Western blot?
4. Eastern blot?
1. DNA
2. RNA
3. proteins (immunoblot)
4. post-translational proteins
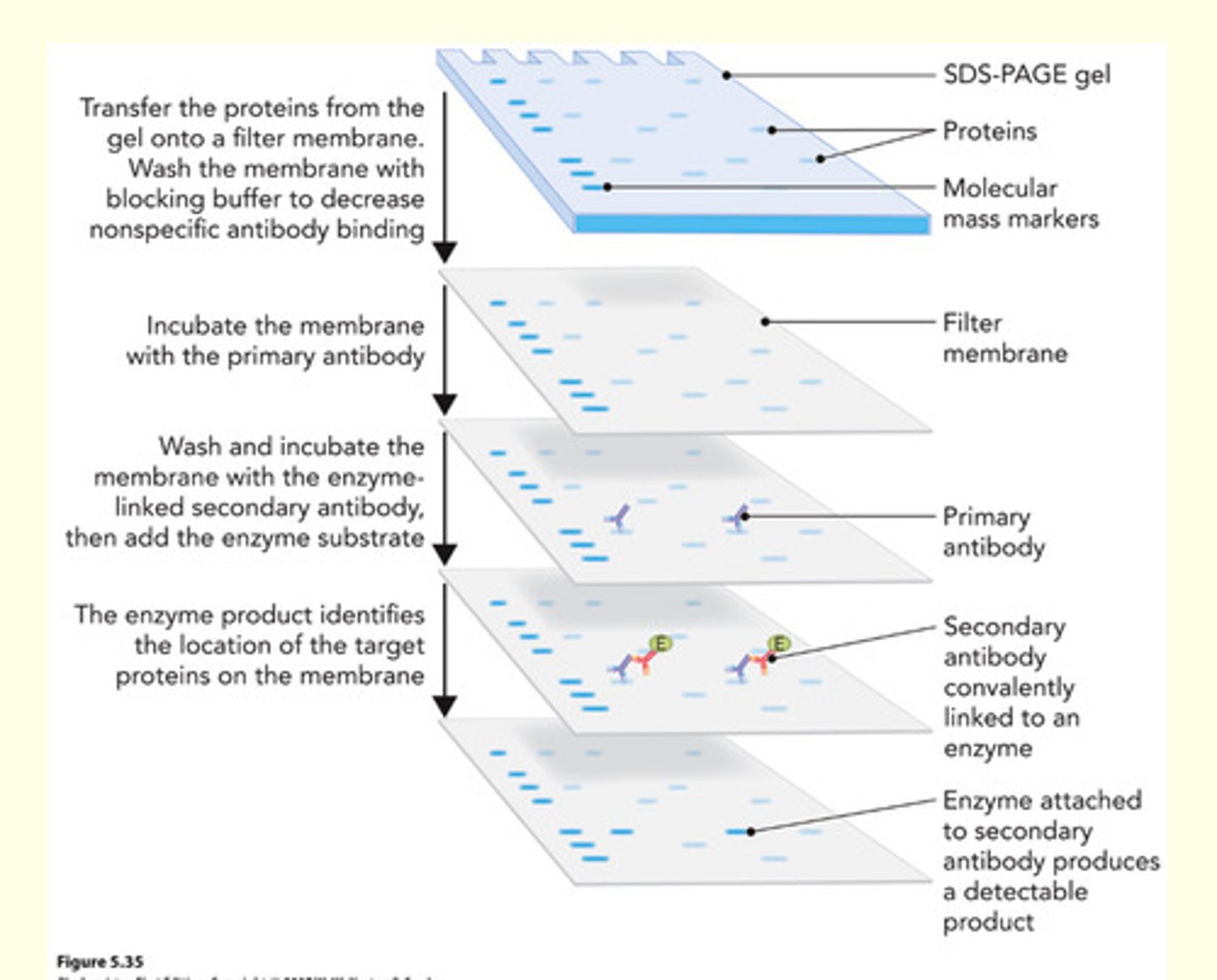
An analytical method that involves the immobilization of proteins on membranes before detection using antibodies.
Protein blotting
What is an electrophoresis method that allows protein separation by mass?
SDS-PAGE
(Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis )
The SDS PAGE technique
is a prerequisite for?
Western blotting
What is a negatively charged detergent used to denature and linearize proteins?
Sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS)
What causes the migration and separation of proteins?
Application of electric field
What is is used to form a gel that provides a matrix of pores through which molecules migrate at different rate?
Polyacrylamide
Common methods for VISUALIZATION OF PROTEIN BANDS:
1. Visualize the band under UV
2. Visualize by staining
a. Coomassie Blue
b. Silver stain
a. What is the most common visualization?
b. What is the most sensitive?
1. Coomassie Blue
2. Silver Stain
In order to make proteins accessible to antibody detection, they are transferred onto a membrane made of nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF)PVDF)
nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF)
In order to make proteins accessible to antibody detection, they are transferred onto a membrane made of?
nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF)
Ways to transfer proteins from a gel to a membrane in Western blotting:
Kamo nay sabot ani
1. Diffusion transfer
2. Electro tansfer
Basics Steps of a Western Blot:
Kamo nay sabot ani
1. SDS-PAGE ->
2. Transfer to a membrane ->
3. Blocking and reaction with antibodies -> 4. Detection of bands