Rates of reaction
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
How are reaction rates measured?
By observing the changes in the quantities of reactants or products over time
What are the equations to calculate the rate of reaction (simple)
rate = quantity reacted or produced / time
rate = change in concentration / change in time
What are the units for rate?
moldm-3s-1
What does changing the concentration of a reaction do to the rate?
change it
Complete the sentence:
The rate of reaction is proportional to the _______________ of a particular ______ raised to a _______
The rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of a particular reactant raised to a power
What is the power of a reactant in the rate equation?
The order of the reactant
What is 0 order?
When the concentration of a reactant has no effect on the rate
What is first order?
When the rate depends on the concentration raised to the power of one
What is second order?
When the rate depends on the concentration of the reactant raised to the power of 2
What does the rate equation show?
The mathematical relationship between the concentrations of the reactants and the reaction rate
What is the rate constant? k
The proportionality constant - the number that mathematically converts between the rate of reaction and the concentration and orders
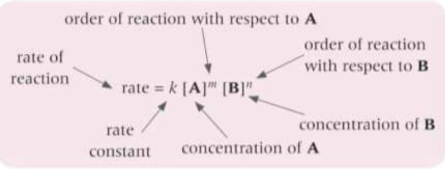
What does the overall order of a reaction do?
Give the overall effect of the concentrations of all reactants on the rate of reaction
overall order = sum of orders with respect to each reactants
How do you rearrange to find k and the units of k?

How are orders of reactions determined?
Experimentally, by monitoring how a physical quantity changes over time
Can orders be found from a chemical equation
no
what is the initial rate?
The instantaneous rate at the beginning of an experiment when t=0
How rate be continuously monitored?
Concentration-time graphs can be plotted from continuous measurement taken during the course of reaction
What are the two methods for continuous monitoring rate of reaction?
Monitoring by gas collection and monitoring by mass loss
If you are not monitoring mass loss or gas collection what can you use to determine the rate of reaction and how?
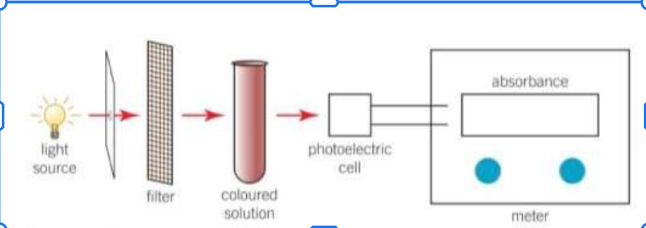
Colour change - can be estimated by eye or monitored in a colorimeter.
In a colorimeter the wavelength of light passing through a coloured solution is controlled using a filter. The amount of light absorbed by a solution is measured
What part of the concentration time graph is the rate of reaction?
The gradient
What is the rule for the order with respect to a reactant being obtained from a concentration time graph?
all other reactant concentrations must remain constant
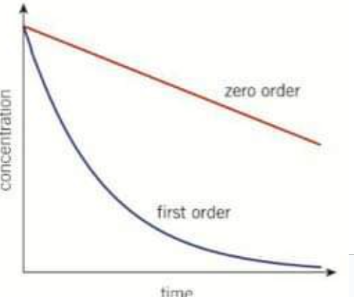
On a concentration time graph what would a 0 order reaction look like?
A straight line with a negative gradient. The reaction rates does not change during the course of the reaction. The value of the gradient is equal to k
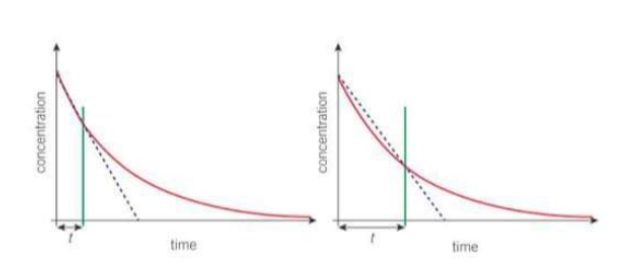
On a concentration time graph what does a first order reaction look like?
A downward curve with a decreasing gradient over time. As the gradient decreases with time, the reaction gradually slows down. In a first order concentration - time graph, the time for the concentration of a reactant to halve is constant - the half-life.
How can you determine the half life of a reactant of a first order reaction
using the rate constant
What does a second order reaction look like on a concentration time graph?
there is a steeper downward curve that tails off more slowly
How can you find the rate of reaction from a concentration time graph?
draw a tangent and work out the gradient
use the equation k = ln2/t1/2
t1/2 = half life
What does a 0 order reaction look like on a rate concentration graph?
produces a horizontal straight line with a 0 gradient
the y intercept gives the rate constant k (because power to the 0 = 1)
the reaction rate does not change with increasing concentration
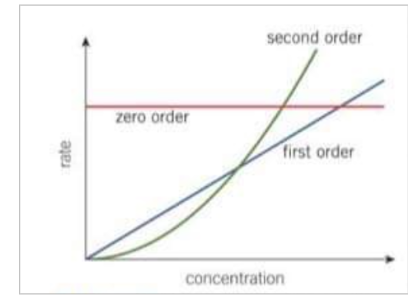
What does a first order reaction look like on a rate-concentration graph?
Produces a straight line graph through the origin
rate is directly proportional to the concentration for a first order reaction
the rate constant can be determined by measuring the gradient of the straight line graph
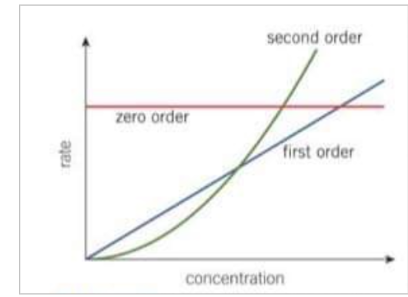
What does a second order reaction look on a rate - concentration graph
produces an upward curve with increasing gradient
the graph is a curve, the rate constant cannot be obtained directly from the graph
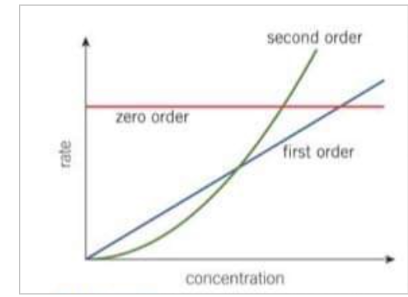
How can you obtain a straight line for a second order reaction - and what is the gradient?
plot rate against concentration squared to
How can you obtain the initial rate of reaction (reaction)
A clock reaction - take a single measurement. The time from the start of an experiment is measured for a visual change to be observed e.g. colour or precipitate
provided there is no significant change in rate during this time, it is assumed the average rate of reaction over time will be the same as the initial rate
What is the initial rate of reaction proportional to?
1/t
What happens in a clock reaction?
You are measuring the average rate during the first part of a reaction. Over time, you can assume that the average rate of reaction is constant and the same as the initial rate
What do you measure during a clock reaction?
You are measuring the average rate of a change in a reactant over time. The shorter the period of time over which an average rate is measured, the less the rate changes over time
How accurate is the initial rate measured during a clock reaction?
it is an approximation but it is still reasonably accurate provided less than 15% of the reaction has taken place
True or false reactions are more likely to take place in a series of steps?
true
True or false it is likely that more than 2 particles collide together at the same time
false
What is the reaction mechanism?
The series of steps that make up an overall reaction
Which reacting species does the rate equation include?
the reacting species involved in the rate determining step
What does the orders in the rate equation mean for the rate determining step?
The order determines the number of species involved in the RDS
How does temperature affect rate (refer to k)
As temp increases, rate increases and the value of k increases. For many reactions, each 10degrees Celsius increase in temp double k and the rate of reaction
How does temperature affect the boltzmann distribution?
shifts it to the right, increasing the proportion of particles that exceed the Ea
How does temp increase rate of reaction (collision)? - relating to: what affects rate of reaction more: Ea or collisions
As temp increases, particles move faster and collide more frequently. With increasing temp, the increases frequency of collisions is comparatively small compared to the increase in the proportion of particles that exceed Ea from the shift in the bolztmann distribution therefore, rate is mainly determined by Ea.
What is arrhenius equation?

How can the arrhenius equation be expressed in a logarithmic form and why?
Is is useful as it enables both Ea and A to be determined graphically - straight line graph

For the log arrhenius equation can k be positive or negative?
it can be both positive or negative
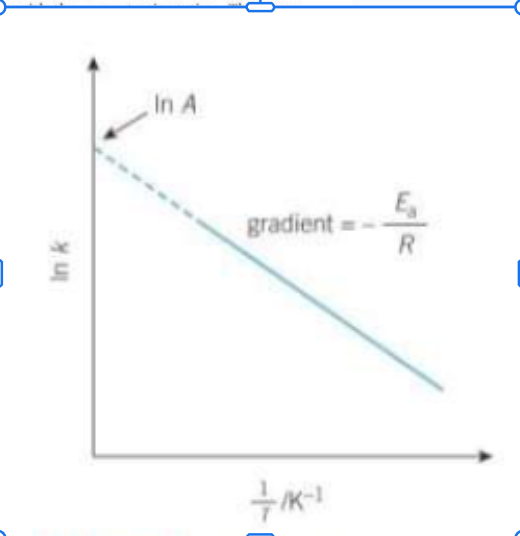
What is the pre-exponential term (frequency factor) A in arrheniuses equation?
it takes into account the frequency of collisions with the correct orientation. This term does increase slightly with temperature as frequency of collisions increases but it is essentially constant over a small temp