BCH4024 Lectures 1 & 2
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
basic principles of organic chemistry
elements of biochemistry, atomic structure and bonding, delocalization of electrons, functional groups, thermodynamics and kinetics, isomerism, and reactions and applications with carbonyl groups
elements in the body
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium, phosphorous. also sodium, magnesium, potassium, sulfur, chloride.
interaction strengths
covalent > salt bridge (H bond + electrostatic) > ionic (electrostatic) > H > pi stacking ~ dipole ~ H phobic ~ VDW/LDF.
acylphosphate
O=-O-PO3
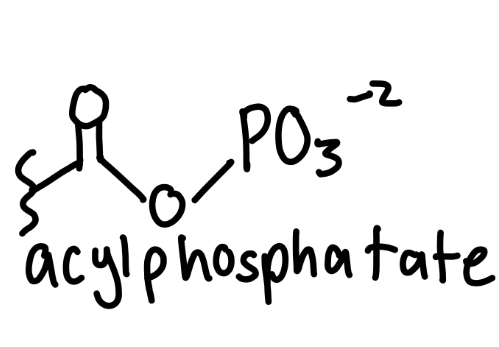
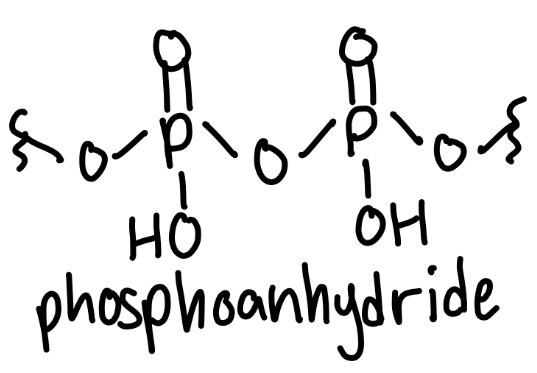
phosphoanhydride
2 phosphates
disulfide
-S-S-
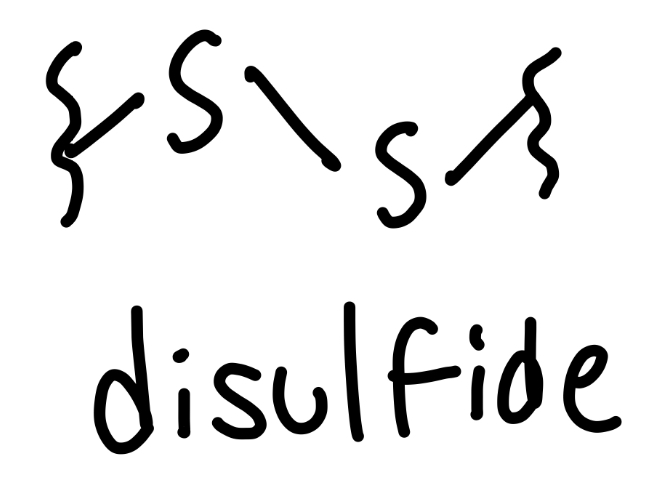
gibbs free energy formula
ΔG = ΔH-TΔS
ΔG = Gibbs free energy, ΔH= enthalpy, T = temperature in Kelvin, and ΔS = entropy.
**Gators Hate The Seminoles**
ΔG’ = -RTlnK
ΔG = ΔG’ + RTln([C][D]/[A][B])
cell limit is set by
rate of transport and O2 need
subunits of a cell are held by ___ bond
covalent
guanidium
NH-(=NH2+)-NH2

immidazol
cyclo
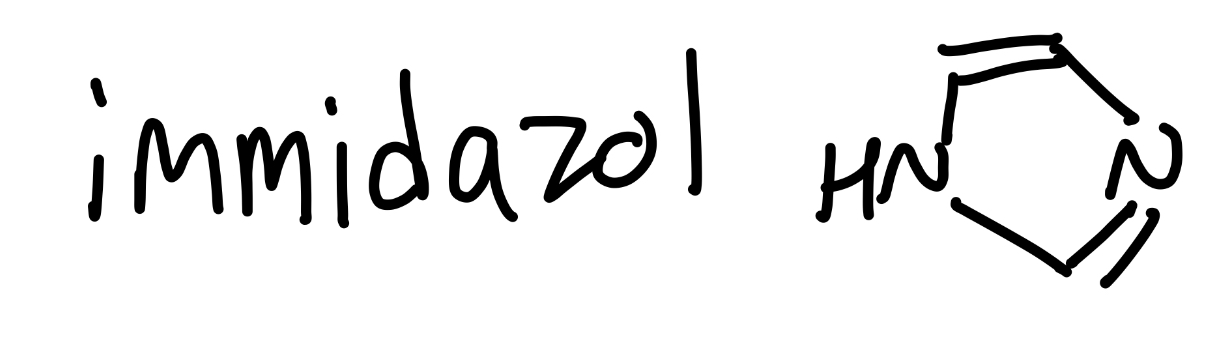
sulfhydryl
-SH
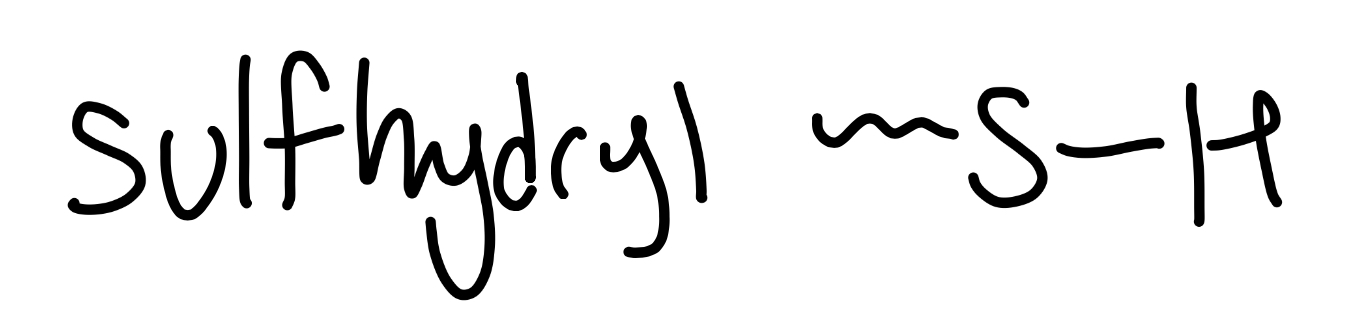
thioester
O=-S

phosphoryl
phosphate -
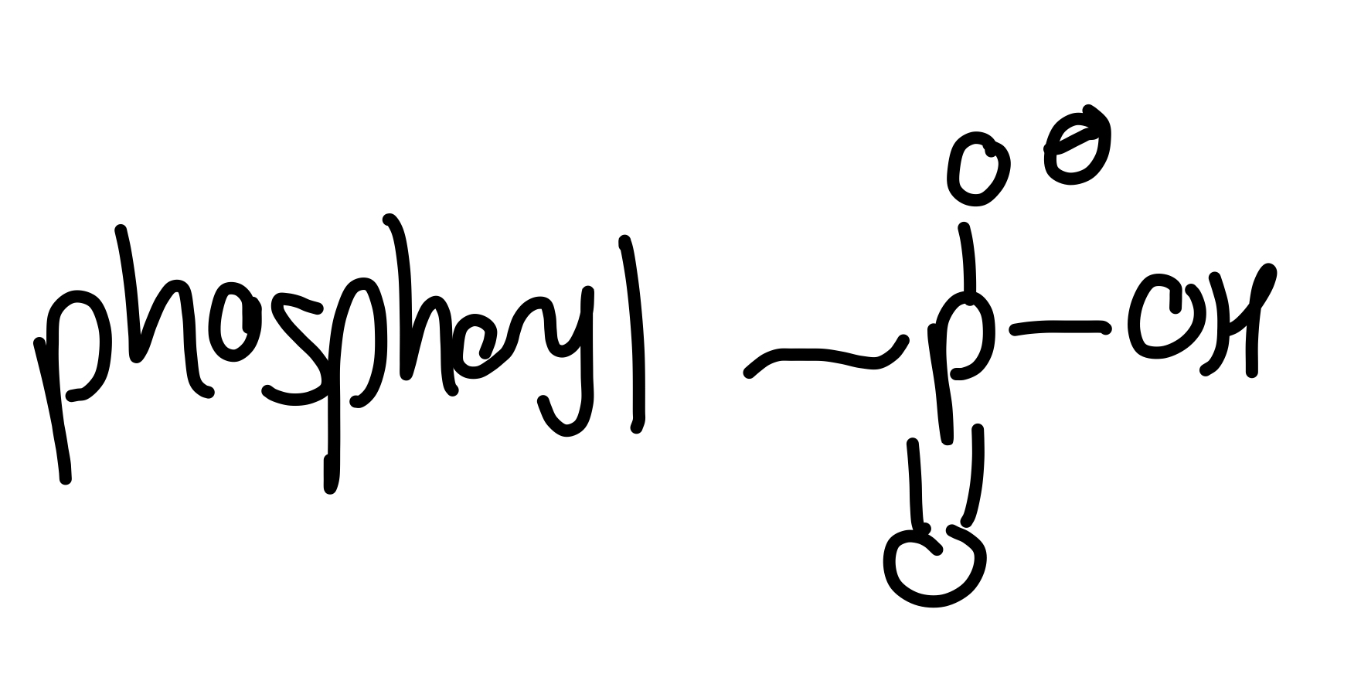
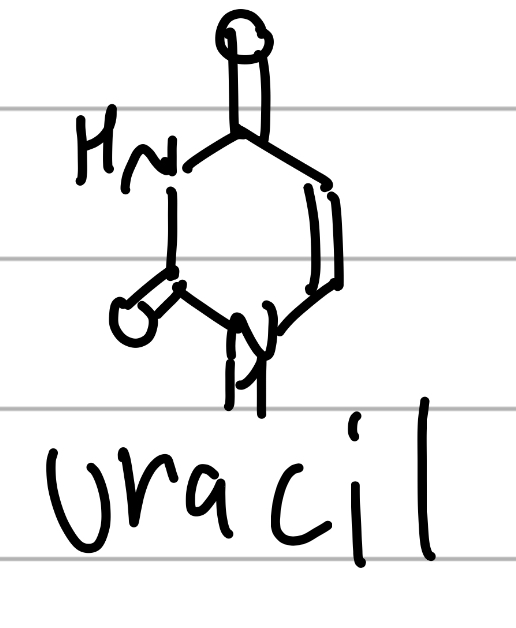
uracil
ketone surrounded by NH, conjugated;
component of NAs
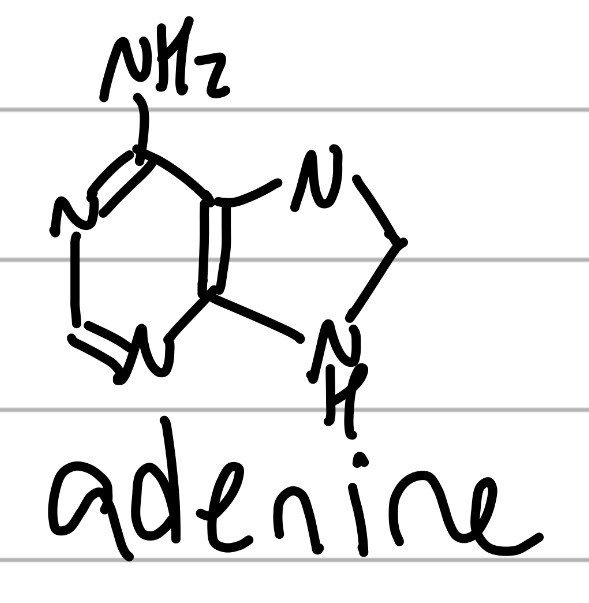
adenine
5 N, 2 cyclo 1 conjugated;
component of NAs
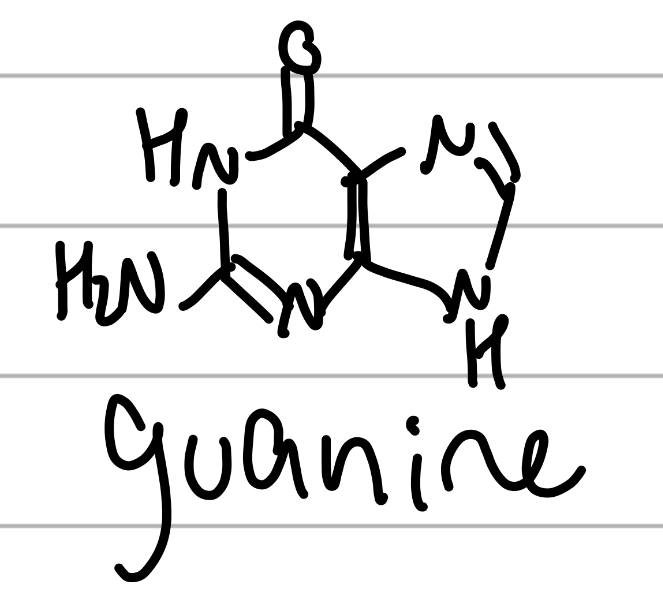
guanine
same as adenine, but replace NH2 w carbonyl and add NH2;
component of NAs
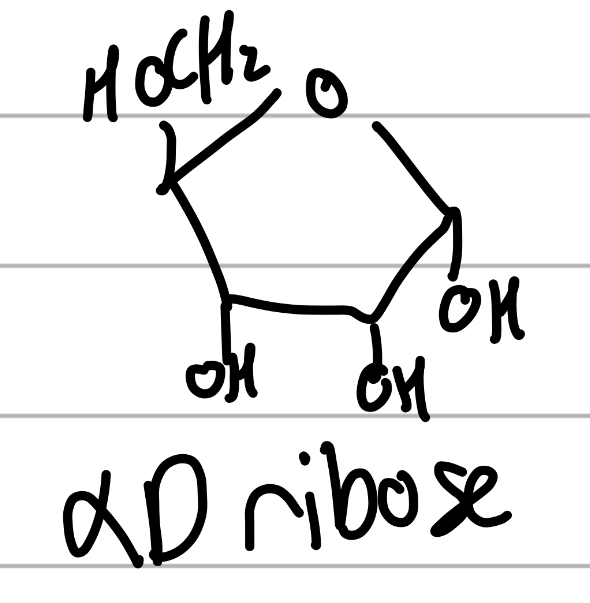
alpha D ribose
has extra OH in between other OHs;
5C sugar
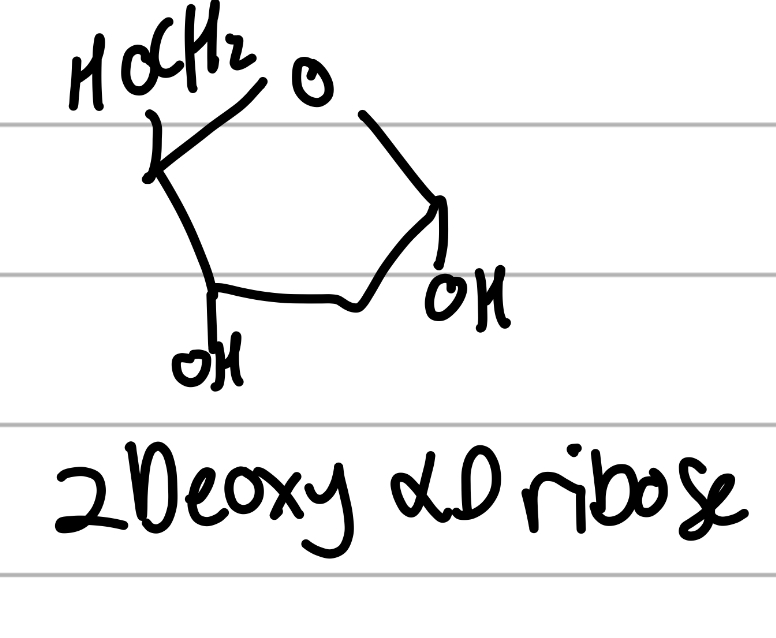
2 deoxy alpha D ribose
has 2 main OHs and one other;
5C sugar
palmitate
COO- and a 15C chain;
component of lipids

glycerol
3C 3OH, achiral;
component of lipids
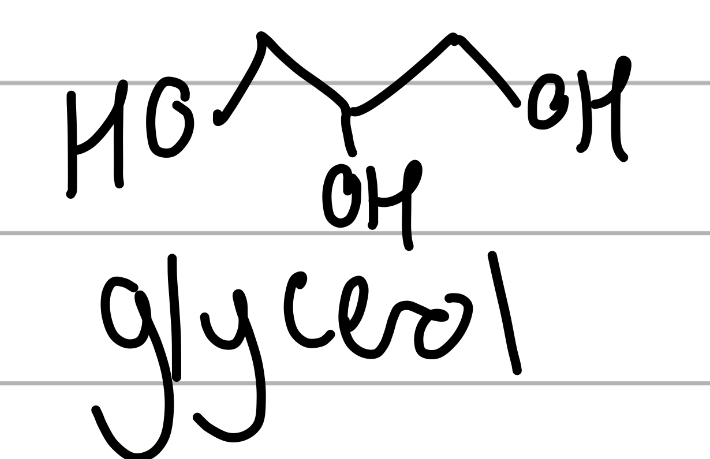
choline
Me3-N+ CH2CH2OH;
component of lipids

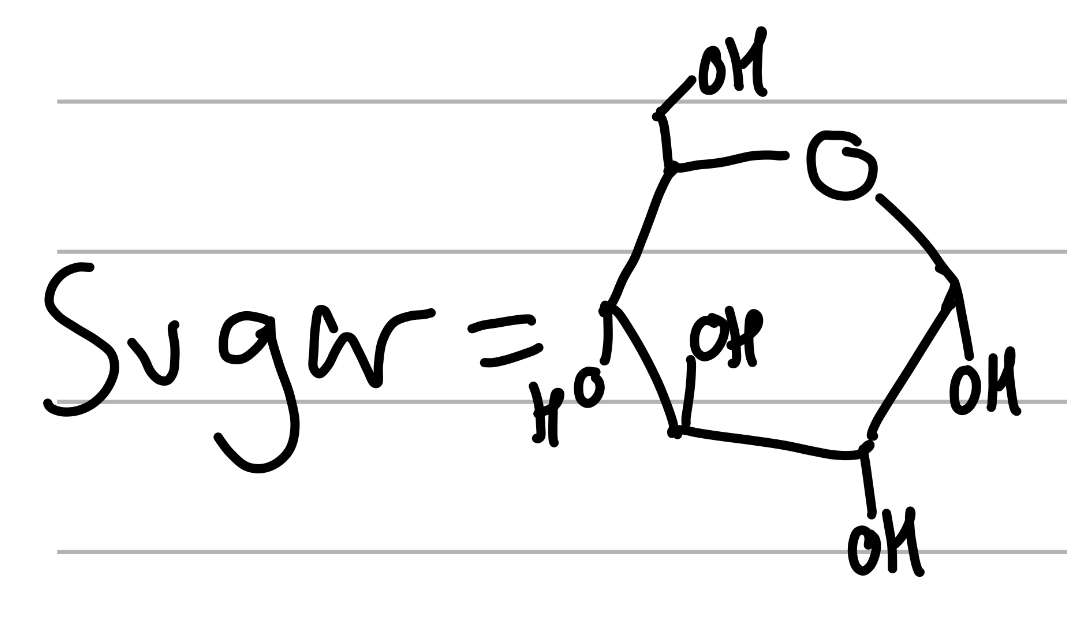
alpha D glucose
4 main trans OHs, ether and MeOH next door ;
parent sugar
native conformation
precise 3D protein, functional
amphipathic
H philic & phobic
long chain fatty acids
H phobic alkyl chains surrounded by water
free energy for dissolving np in water is ___
unfavorable, bc clustering ↓ SA which ↓ needed water
H+ hopping
water molecules ionize and deionize bc of high ionic mobility and conductivity.
pH =
log(1/H+) = -log(H+)
pKA + log(A-/HA)
K =
[(H3O+)(A-)]/[(HA)(H2O)]
or
[(H+)(A-)]/(HA)
pKA =
log(1/Ka) = -logKa
pepsin
digestive enzyme, gastric acid, pH 1.5
trypsin
digestive enzyme, small intestine, lumen pH
alkaline phosphatase
hydrolytic bone tissue enzyme
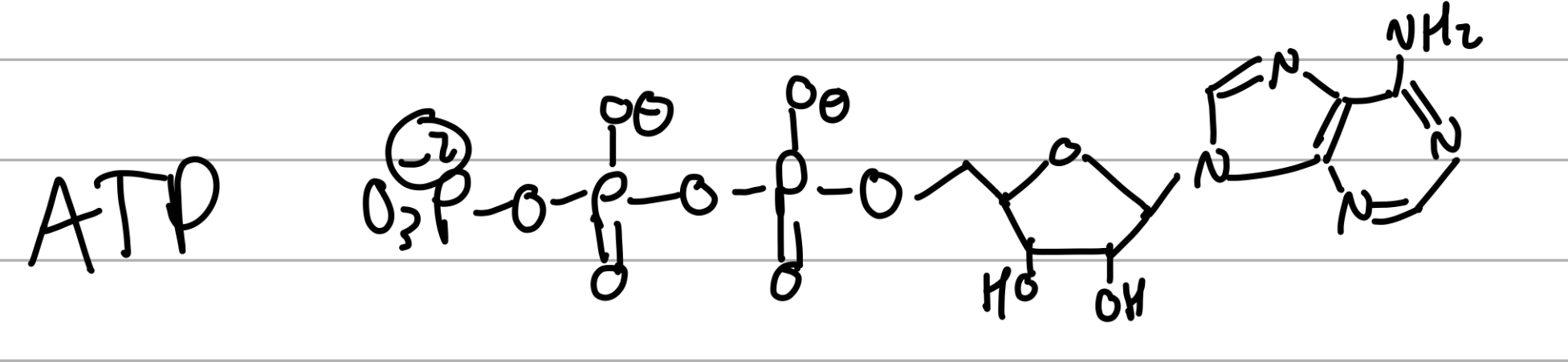
ATP
last PO3 is removed into ADP
subunits are held together by ____ bonds, whereas macromolecules are held by _____ bonds
covalent, weaker (ionic, VDW, Hphobic)
how many H bonds can a water molecule have
ice 4 but liquid 3.4
what causes flickering
H bonds have short lifetime and fail and rejoin
CORN Law
cLockwise (L), counter
ampholyte
both basic and acidic groups, exist as zwitterions
zwitterion
a molecule or ion having separate positively and negatively charged groups at neutral pH
isoelectric point
pI = (pK1+pK2)/2 = pKa1 + log(HA/HAH+) = pKa2 + log(HA/HAH+)
2pI = pKa1 + pKa2 + log(A-/HAH+)
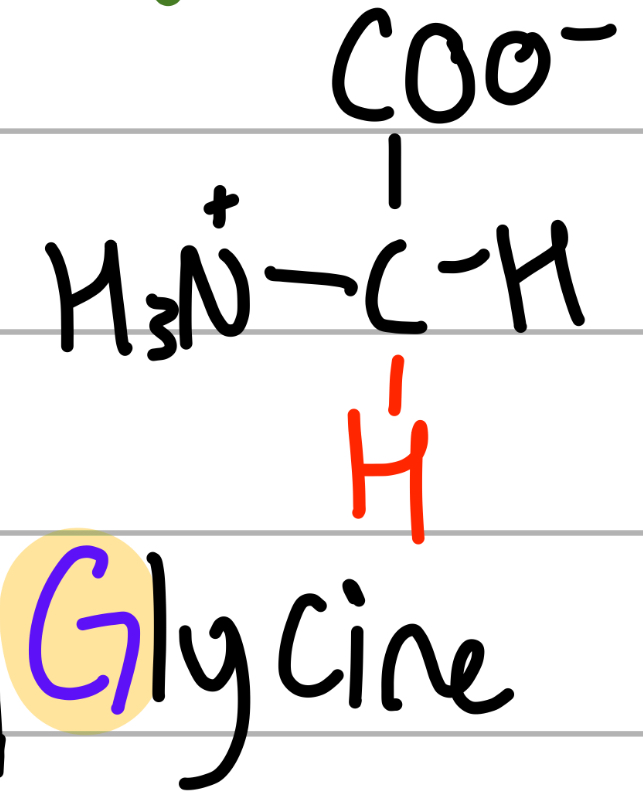
glycine
-H;
G = ?;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
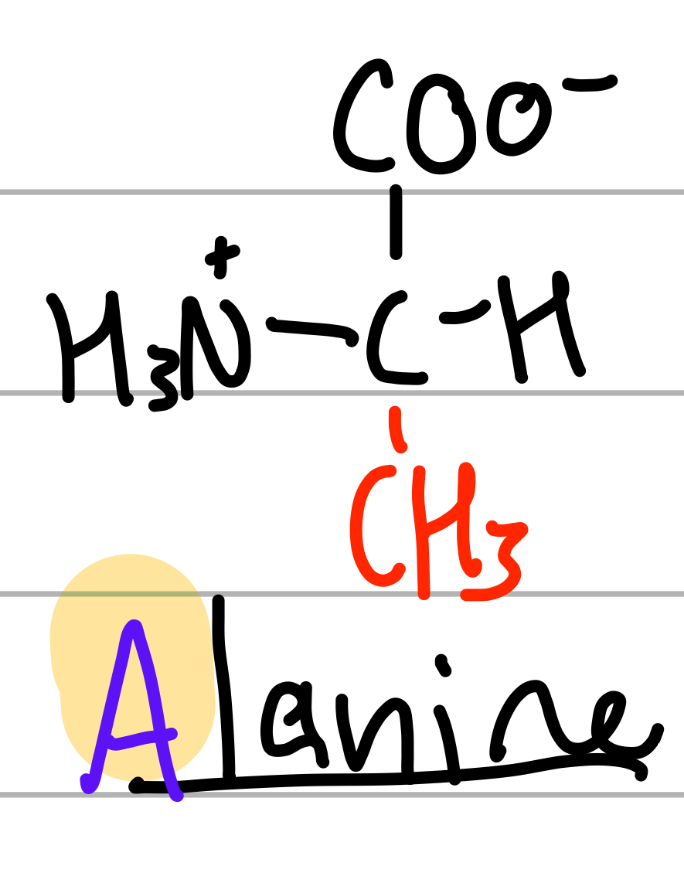
alanine
-CH3;
A = first in alphabet of the As;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
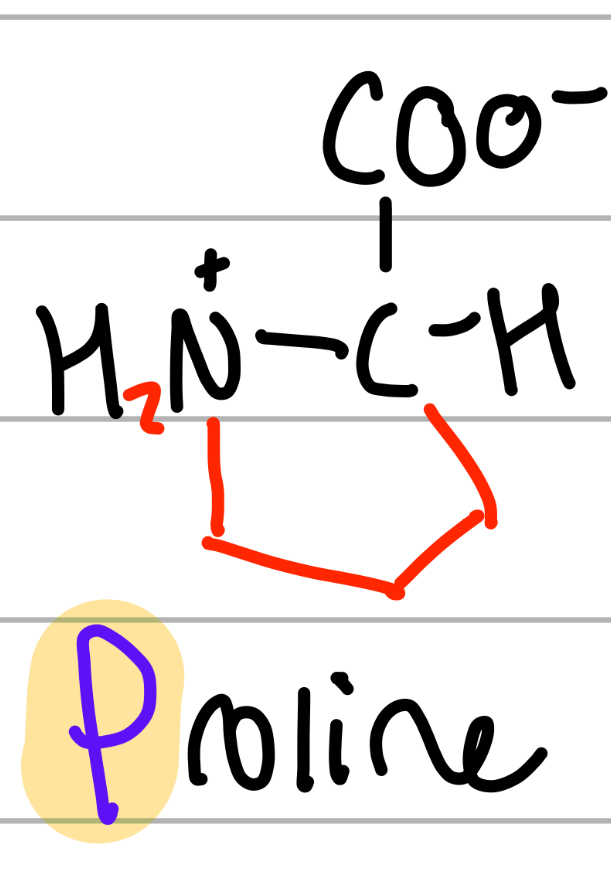
proline
cyclo NH2CH2CH2CH2;
P = P shaped cause cyclo;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
valine
-CH(CH3)2;
V = only V;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic

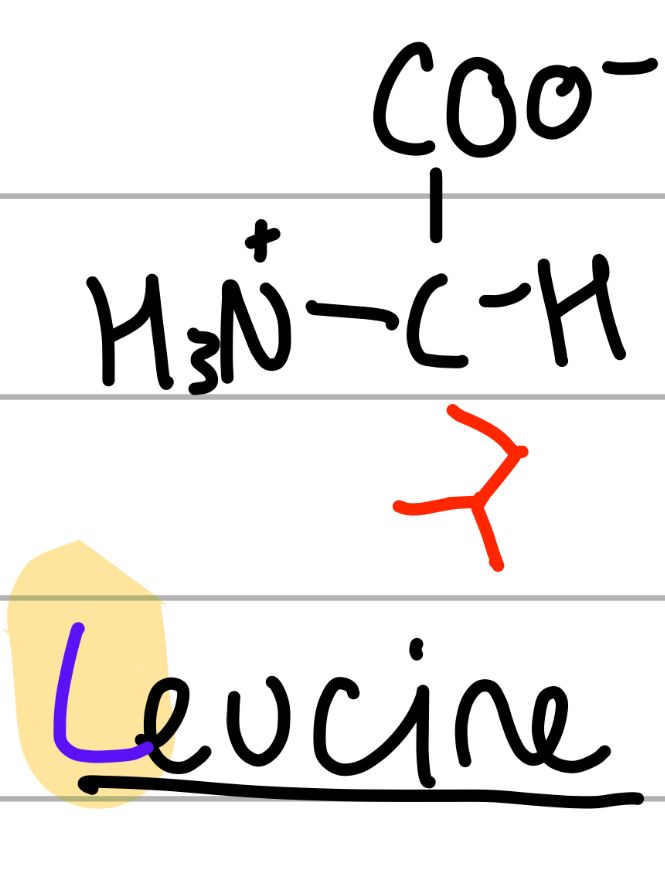
leucine
CH2CH(CH3)2;
L = alphabetically first of the Ls
leuc = 4C;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
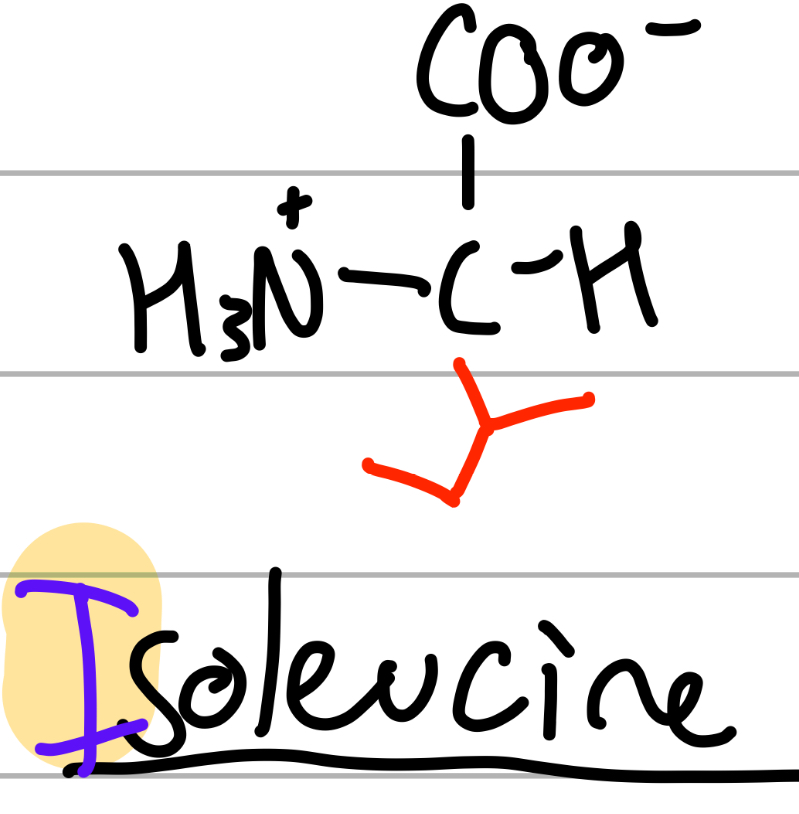
isoleucine
CH(CH3)(CH2CH3);
I = only I
leuc = 4C, iso = split;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
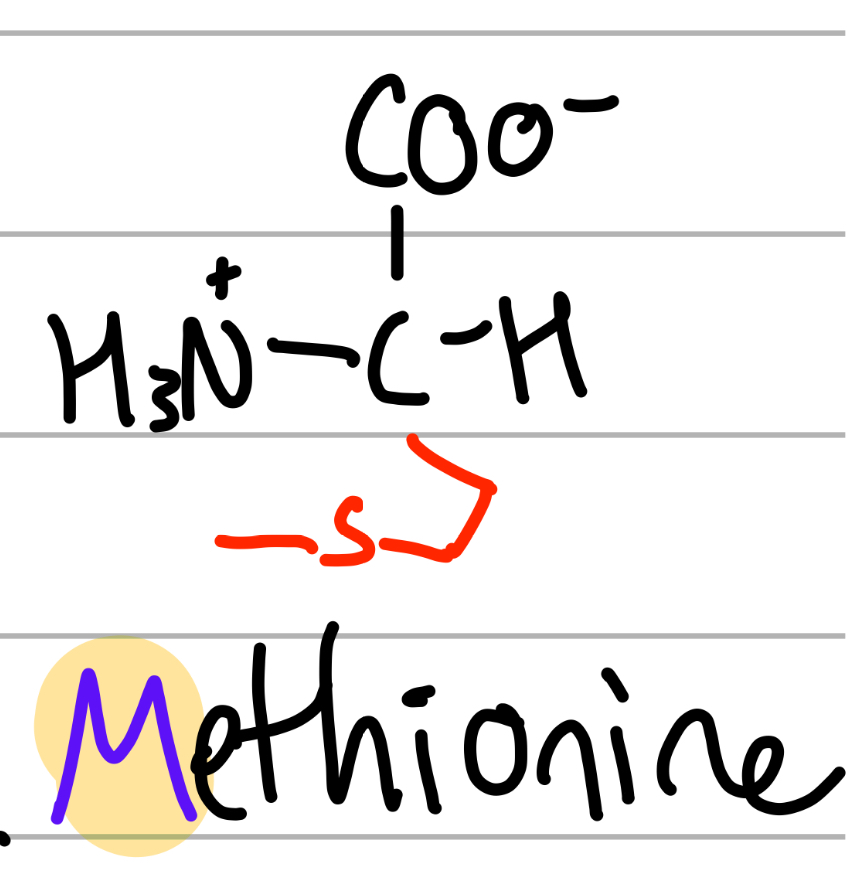
methionine
-CH2CH2SCH3;
M = only M;
Me = CH3, Thio = S;
np, Hphobic, aliphatic
phenylalanine
-CH2Ph;
F = fenyl;
polar, uncharged, Hphobic

tyrosine
-CH2-PhOH;
Y = tYrosine, alphabetically after tryptophan;
polar, uncharged, Hphobic but can form H bonds
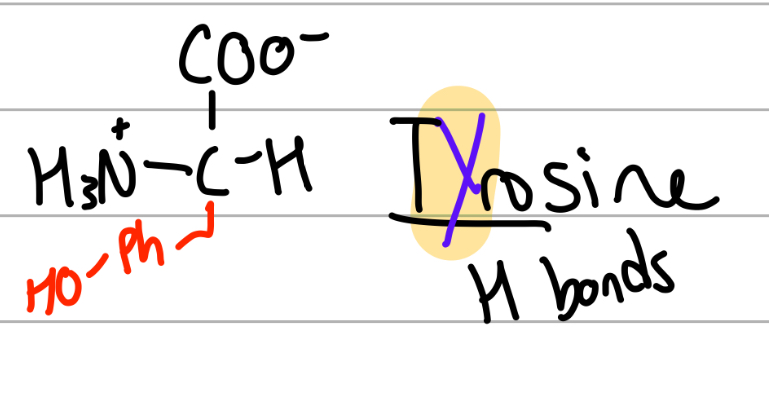
tryptophan
-CH2 cyclo =C-N-C=Ph;
W = twyptophan, W before Y in alphabet,
polar, uncharged, Hphobic

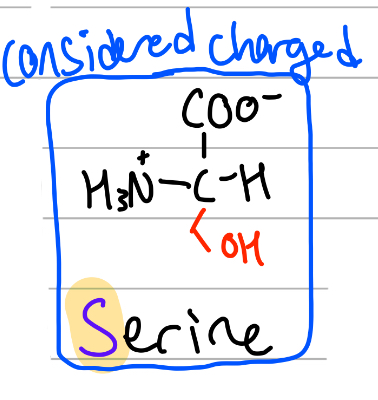
serine
-CH2OH;
S = only S;
polar, uncharged, Hphilic
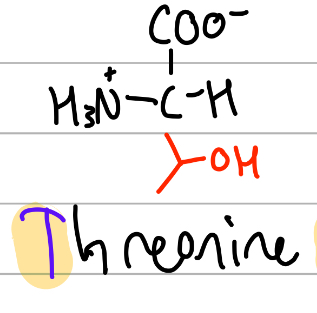
threonine
CH-(OH)(CH3);
T = alphabetically first T, THREE (CH3) O (OH);
polar, uncharged, Hphilic
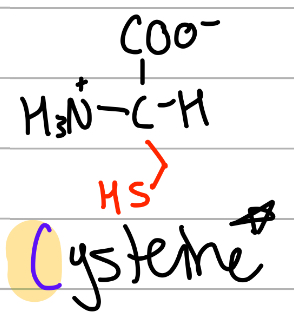
cysteine
-CH2SH;
C = only C, CyStine;
polar, uncharged, Hphilic
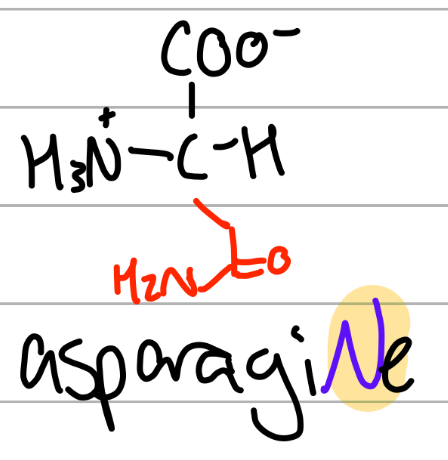
asparagine
-CH2C(=O)NH2;
N = asparagiNe, amide of aspartate
Asn = cant be asp cause aspartate;
polar, uncharged, Hphilic
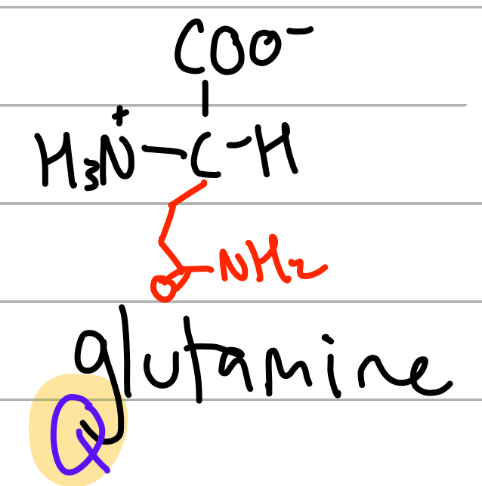
glutamine
-CH2CH2C(=O)NH2;
Q = Qtamine, amide of glutamate
Gln = Glu but with an n;
polar, uncharged, Hphilic
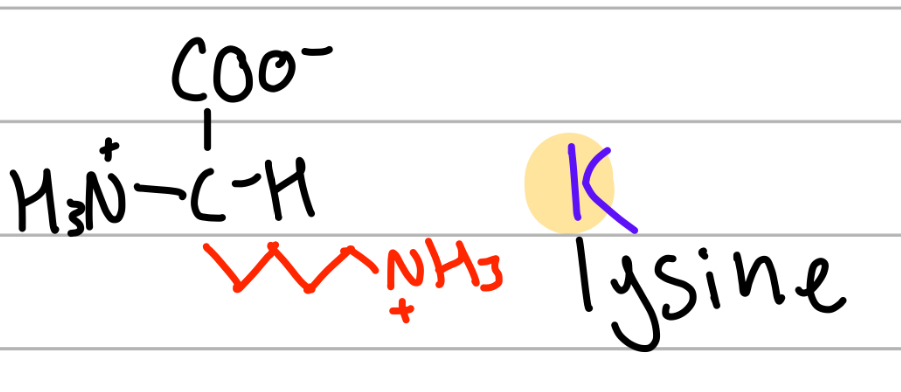
lysine
-4CH2 NH3+;
K = next to L, Leuc = lys = 4, 4CH2;
positive charge, Hphilic
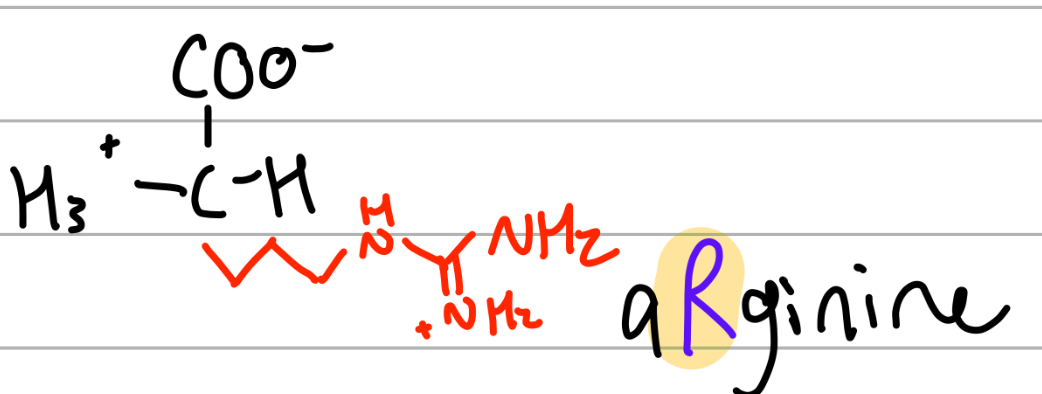
arginine
-3Ch2NHC(=NH2+)NH2;
R = aRginine, pirates go arrgg;
positive charge, Hphilic
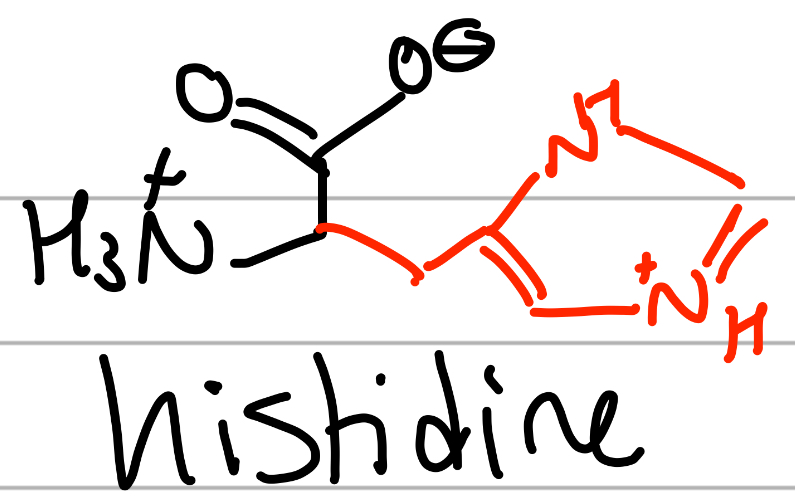
histidine
-CH2(NHCH=NCH=C) loop;
H = only H;
positive charge, Hphilic, ionizable side chain with neutral pKa
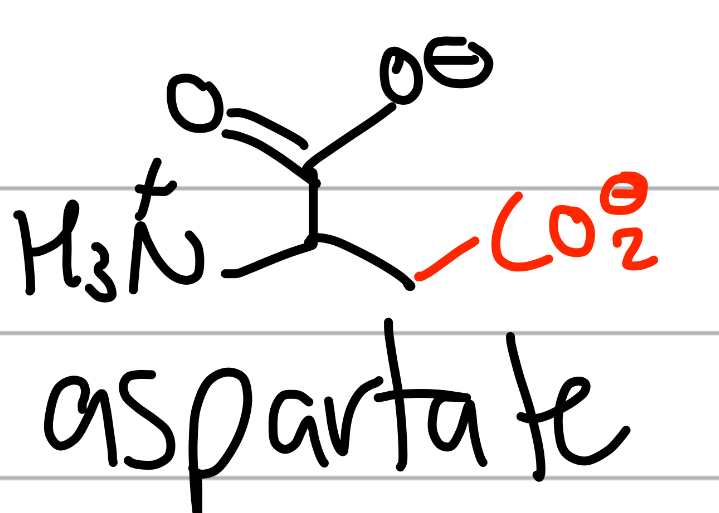
aspartate
-CH3CO(O-);
D = asparDate, you ASk for a Date;
negative charged second carbonyl
glutamate
-CH2CH2CO(O-);
E= gluEtamate ,Glu;
negative charged second carbonyl

what letter don’t have amino acids?
B J O U X Z
labeling C
COO- goes first, alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon
cysteines can ___
oxidize into cystine with a disulfide bond
what two aas are mostly not in plant proteins?
lysine and tryptophan