Exam 1 Class Review
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Relative Abundance
estimated abundances of the chemical elements in the Solar System
Most common elements in the Universe
Hydrogen then Helium
Most common elements on Earth
Iron → Oxygen → Silicon
2 General trends in elements
An alternation of abundance in elements as they have even or odd atomic numbers
a general decrease in abundance, as elements become heavier
What is an atom?
A fundamental piece of matter
An atom is made of 3 subatomic particles
protons
neutrons
electrons
Labels for characteristics of elements
Z = Protons
N = Neutrons
e = electrons
A = Atomic Mass = Z + N

Binding Energy (BE)
energy that would be required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its components
Binding Energy (BE) Formula
= ∆Mc2 = (Mcomponents - Matom) * c2 * 1 amu conversion
[Answer in Joules = 1 kg m2/s2]
Formula for mass of an atom
= (#protons * mprotons) + (#neutrons * mneutrons)
Elemental Isotopes
same element (same number of protons), but different number of neutrons
Two types of isotopes
Radioisotopes (have a half-life and will decay)
Stable isotopes
Types of Plate Boundaries
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
How do we know the temperature of pure hydrothermal fluid?
End-member Mixing Model
Minerals
naturally occurring, solid crystalline substance
generally inorganic, with a specific chemical composition
Rock
an aggregate of one or more minerals
a body of undifferentiated mineral matter
Types of Rock
Igneous
Metamorphic
Sedimentary
Types of weathering
congruent dissolution
incongruent dissolution
Congruent Dissolution
minerals dissolve completely into their constituent ions
Incongruent Dissolution
minerals partially dissolve and leave behind a residual solid weathering product
Atmospheric Circulation Cells
Hadley
Ferrel
Polar
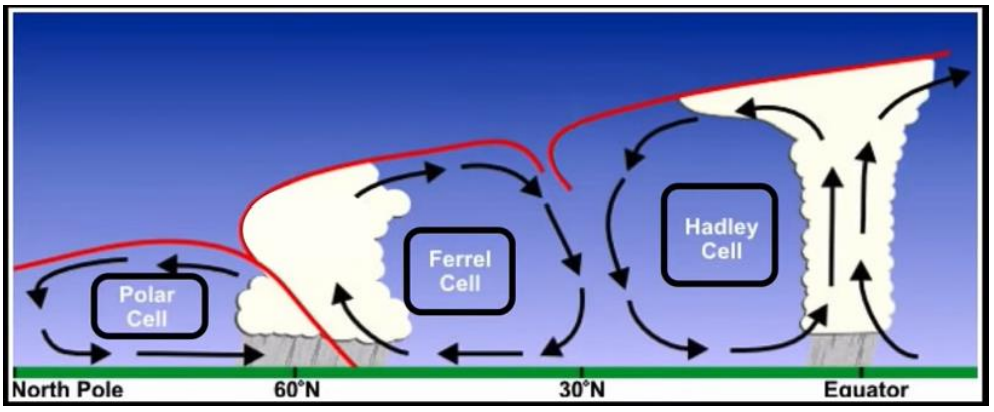
Hadley Cell
closest to equator
covers tropical and sub-tropical climates
Ferrel Cell
mid-latitude
Polar Cell
highest latitudes
Where do storms form in relation to cells?
where hot air rises (making sinking air dry)
(at the equator & higher latitudes of ferrel cells)
Development of Hurricanes requires
sea surface temperature > 26°C
Coriolis force
Types of Hurricanes in order of strength
Tropical Cyclone (lowest strength)
Tropical Depressions
Tropical Storms
Hurricane (highest strength)
How close to the equator can a hurricane form?
must be at least 5° away due to lack of Coriolis force at equator
Ozone absorbs
light in the higher energy ultraviolet range almost totally using oxygen molecules
CFC Compounds
anthropogenic
depletes ozone layer
Greenhouse Gases
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
CCL2F (a CFC)
Which greenhouse gas contributes the most to GH effect?
CO2 because it stays in the atmosphere for so long
Why is methane so dangerous despite a relatively low residence time?
it is more potent than CO2 and can trap more heat
second largest contributor to GH effect
Wien’s Displacement Law
the peak wavelength of blackbody radiation is inversely proportional to temperature
hotter objects have smaller wavelength and vice versa
What does Wien’s Displacement law have to do with climate change?
high intensity, short wave radiation from the sun penetrates the atmosphere to get to Earth’s surface, some of which is absorbed
some of that radiation is re-emitted as lower intensity, long wave radiation, which can then be absorbed/reflected by GHG’s
GHG’s cause some of that radiation to be reflected back towards Earth, warming the planet
C3 Pathway
does not have photosynthetic adaptations to reduce photorespiration
(rubisco is directly in charge of selecting CO2, however it also has a high affinity for oxygen)
C4 Pathway
light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle are physically separated
PEP carboxylase, which has no affinity for O2, is responsible for CO2 uptake
What is the problem with having rubisco responsible for CO2 uptake in C3 plants?
rubisco has an affinity for O2
the more it uptakes O2 instead of CO2, the longer the stomata have to stay open
this leads to more transpiration
Climate Change for C3: Trend for Temperature Increase
will not be able to increase in productivity past a certain temperature due to the fact that it keeps its stomata open for so long and would lose even more water with temp increase
Climate Change for C4: Trend for Temperature Increase
will be able to increase productivity with higher temperatures up to the point of extreme temperatures, still higher, since it has reactions separated
Climate Change for C3: Trend with CO2 increase
rubisco becomes less likely to grab O2 with more CO2 in the air, productivity will increase
Climate Change for C4: Trend with CO2 increase
already had good control over selection of CO2, so it won’t increase in productivity nearly as much
Gross Primary Production (GPP)
total amount of carbon fixation by plants
Net Primary Production (NPP)
= GPP - Rp
Rp: plant respiration
Net Ecosystem Production (NEP)
accounts for heterotrophic respiration
= NPP - (Rh + Rd)
= GPP - (Rp + Rh + Rd)
p: plants
h: herbivores
d: decomposers