forensics 25 master set
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
the accurate chemical name for alcohol found in alcoholic beverages
ethanol
alcohol is produced though the process of
diffusion
the reactants and products involved in the creation of champagne
white grapes + yeast → alcohol + carbon dioxide
which type of alcoholic beverage has the highest concentration of alcohol by volume
distilled spirits
which area of the brain is the first ti be affected noticeably by alcohol that is absorbed into the body
cerebrum
people are considered to be legally impaired in canada if they
have more than 80mg of alcohol per 100mL of blood
the blood alcohol concentration of a person increases when
twenty minutes after drinking alcohol
which country has a higher bac legal limit than canada
swaziland
the countries in which alcohol consumption is not permitted due to religious reasons is
the arab states
cerebrum
causes difficulty hearing and seeing clearly, you don’t exhibit good judgment
cerebellum
makes someone unable to touch their nose w/ closed eyes, and can also cause frequent stumbling and falling
hypothalamus
causes frequent urination where the urine contains a high concentration of water
medulla oblongata
causes a decrease in blood pressure and breathing rate that can lead to unconsciousness
two symptoms of alcohol consumption that may impair one’s ability to drive
poor judgment of situations
may cause them to turn across traffic or lane change w/o enough time to safely do same, putting themselves and those around in danger
jerky or uncoordinated movements
may cause the driver to veer into oncoming traffic or into the ditch
when alcohol is absorbed into the blood and is being transporting through the blood what does it not do?
change chemically in any way
how does the concentration of alcohol in the blood compare w/ the concentration of alcohol in the alveoli?
the alcohol concentration is 2100x greater in the alveoli
individualized physical evidence
is unique and can be directly linked to a specific person and/or source
ex) fingerprints, dna, bullets, bullet casings, dental
impressions
identified physical evidence
shares a common source; it can be grouped into a class of items having similar properties
ex) clothing, shoe prints, blood type
why is physical evidence important?
it can confirm the identity of the suspected individual
which type of physical evidence is more important and why?
individualized evidence since it can be linked directly to a specific individual
visible fingerprints
are easily seen by the human eye
may be left on an object at a crime scene because of blood, perspiration, dirt, or oils on a suspect’s hands
latent fingerprint
are hidden or concealed in some way so they aren’t visible to the naked eye that need to be enhanced in some way to be seen
usually composed of perspiration and/or body oils
physical fingerprints
leave a distinct impression is left upon soft materials like wax, food items, or the caulking around windows and doors
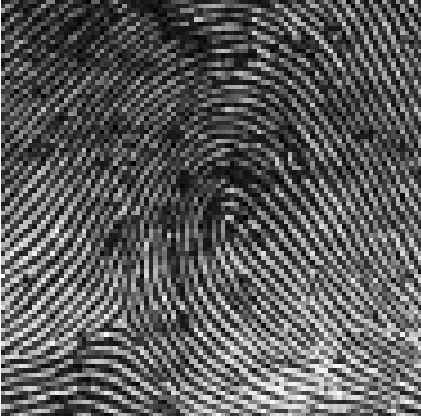

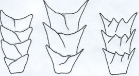
radial loop (left hand)
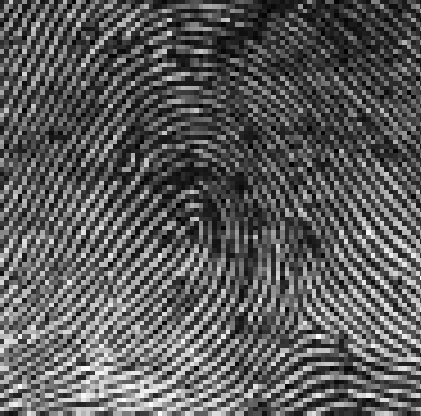

ulnar loop (left hand)

ulnar loop (right hand)

radial loop (right hand)
loop fingerprints
approx 60% of people have this pattern
lines rise, curve, and return
sub-classifications are ulnar loop, radial loop, and double-twinned loop
how to distinguish between a right and left fingerprint loop pattern
you have two bones in your lower arm: the ulna bone, which is lined up w/ the pinky finger, and your radial bone, which is lined up w/ your thumb
the bone that the begins and ends at determines the type of loop
known as a road test
you must know if the print came from the right or left hand

double-twinned loop
whorl fingerprints
approx 34% of people have this pattern
lines form concentric (having a common centre) circles
sub-classifications are plain whorl, central pocket whorl, and accidental whorl

simple plain whorl

central pocket whorl

accidental whorl
arch fingerprint
approx 6% of people have this pattern
lines cross smoothly or upthrust at the centre
sub-classification are plain simple arch and tented arch

plain simple arch

tented arch
how is a fingerprint impression made?
oils and sweat mix → settle on the finger ridges → finger pad comes into contact w/ an object → the mixture leaves a residue or fingerprint impression
how to enhance a latent fingerprint
lifting powder application
iodine fumigation
cyanoacrylate fumigation
lifting powder application
works best on smooth, solid surfaces like glasses, door handles, steering wheels, credit cards, car doors, knife blades, and some knife or gun handles
the powder is usually made of metals like aluminum, tin, iron, or carbon or a combo of homogeneous metals
used a piece of wide, clear, smooth tape
the brush has very soft bristles made of bird feathers, squirrel or camel hair, or fiberglass
could also have a magnet at the end to attract metal'-based lifting powders not sticking to the surface when applied
iodine fumigation
human sweat is a mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl)
fixing solution is used
iodine crystals give off vapors (sublimation) that adsorb physically to the oily substances of a fingerprint
turns the fingerprint dark blue after a reaction
is permanent
cyanoacrylate fumigation
in a sealed chamber, heat and moisture are introduced and the ‘super glue’ will turn from a liquid to a gas
works best on dark surfaces w/ smooth or slightly textured surfaces
needs to be photographed
turns the impression white
advantages of each latent enhancement method`
lifting powder application: useful to identify on hard surfaces
iodine fumigation: extremely easy to see
cyanoacrylate fumigation: is permanent via photograph
disadvantages of each latent fingerprint enhancement method
lifting powder application: inhaling the powder is harmful to the lung tissue
iodine fumigation: developed impressions aren’t permanent
cyanoacrylate fumigation: leaves a white residue on surrounding surfaces that came into contact w/ the fumes
what latent fingerprint enhancement technique was used on cheri jo bates’s car (zodiac killer case)?
lifting powder
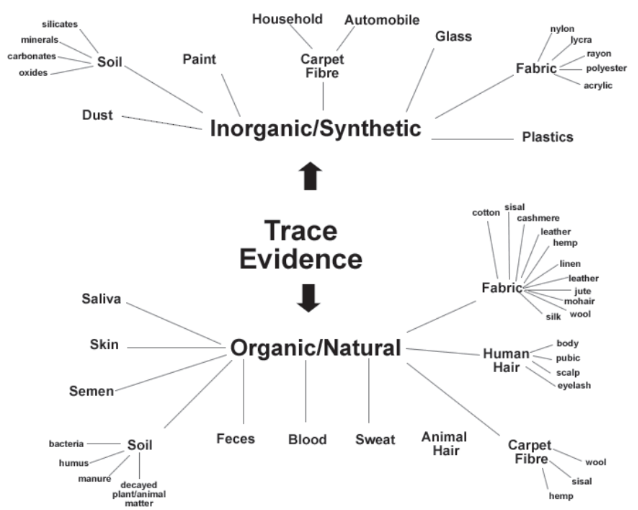
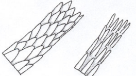
trace evidence
a general term for evidence that cannot be seen clearly by the human eye
is significant and should not be ignored
common examples are human hair, animal hair, carpet fibers, clothing fibers, glass fragments, and paint fragments.
trace evidence diagram
trace evidence collection procedure
securing the Crime Scene and Questioning:
police restrict access to the crime scene
victims, witnesses, and suspects are questioned
no one is allowed in or out until spoken to by the police
prevents disturbance of potential evidence
observations of the Crime Scene:
forensic investigators take photos and videos
crime scene details are documented
evidence is photographed, and observations are noted
trace evidence is lifted using specialized tools
collection of Trace Evidence:
investigators wear protective suits
trace evidence is collected gently to avoid contamination
each piece is labeled with relevant details
double packaging ensures evidence preservation
tools include vacuums, forceps, cotton swabs, and various containers
evidence is stored in lockers, with larger ones for homicide cases.
examples of inorganic or synthetic trace evidence
carpet fiber: household and automobile
paint
dust
soil: silicates, minerals, carbonates, oxides
glass
fabrics: nylon, lycra, rayon, polyester, acryluc
plastics
examples of organic or natural trace evidence
fabric: cotton, sisal, cashmere, leather, hemp, linen, leather, jute, mohair, wool, silk
human hair: body, pubic, scalp, eyelash
carpet fiber: wool, sisal, hemp
animal hair
sweat
blood
feces
soil: bacteria, humus, manure, decayed plant/animal matter
semen
skin
saliva
types of human hair
head hair:
longest body hair; may determine gender
sun-bleached or color-treated hair show little variation in the medulla
roots may be darker
often has cut or split tips
body hair:
short (less than 1 cm), fine, and thin
typically arc-shaped and lighter in color
humans shed these hairs less frequently
eyebrow or eyelash hair:
short (less than 1 cm) and tapered
usually darker than head and body hair.
pubic hair:
dark (brown or black), very curly, stiff
thicker and longer (1-2 cm) than body and eyebrow/eyelash hair

various strands of color-treated hair
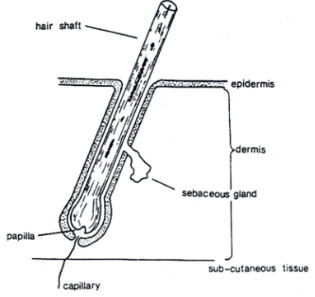
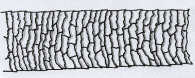
gross anatomy of a hair
parts of a hair
hair root: only part of the hair that requires nutrients and oxygen from a follicle
hair tip:
hair shaft:

rounded (club) root
a root of human hair that fell out naturally
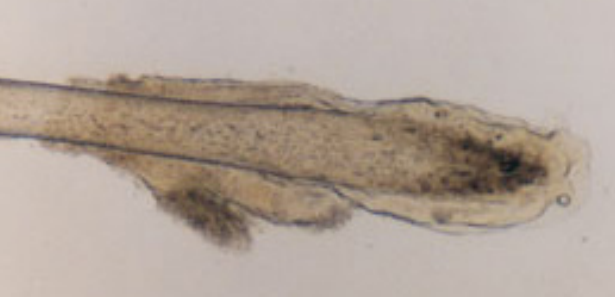
follicle-attached root
a root of hair that was forcibly removed possibly during a violent struggle where the follicle is still attached to the root (the follicle looks like transparent skin)
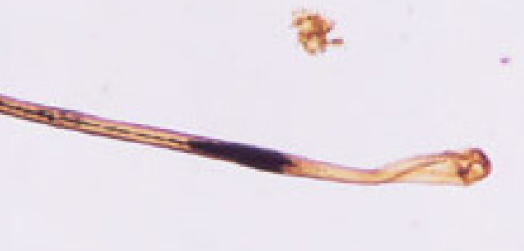
dark band root
likely indicates the hair was shed after the person has died :(

frayed root
likely came from a cat

spade-shaped root
likely came from a dog

wineglass-shaped root
likely came from a deer
the hair tip
can be distinguished from the root since it will never have skin directly attached to it
slightly rounded tip: indicates the individual has not cut their hair in a long period of time (likely more the four weeks since last cut)
linear or straight tip: indicates individual has recently cut their hair
blackened or frayed tip: indicates the individual has come into contact w/ flames or high heat

blackened or frayed tip photograph
the hair shaft
is found in the region between the root and tip
three parts of it are called the cuticle (outermost layer), cortex, and medulla (middle region)
imbricate cuticle
scale pattern found in all human hairs and some animals
coronal cuticle
scale pattern found in the hair of bats and small rodents like mice, rats, and vole
spinous cuticle
scale pattern found in the hair of minks, seals, and cats
unisereal medulla
found in hair from a cat or rabbit
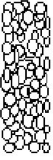
lattice medulla
found only in hair from a deer, elk, or goat

multisereal medulla
found in hair from a rabbit or chinchilla
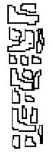
vacuolated medulla
found in hair from a dog, red fox, or cattle

fragmented amorphous medulla
found in human hair of people of hair colors that usually isn’t black

continuous amorphous medulla
found in human hair that is black in color and commonly are of asian decent
what fiber evidence can help prove
occurrence of physical contact:
discovery of a single transferred fiber increases likelihood of physical contact
many fibers found on clothing from suspect, victim, or crime scene strongly suggest contact
each fiber is treated as independent evidence
multiple pieces of evidence refute the argument of no contact between suspect and victim or crime scene
type of contact:
violent physical contact over time often leads to the exchange of numerous fibers among suspect, victim, and crime scene
direct (primary) fiber transer
occurs when a fiber is directly exchanged between fabrics
ex) a suspect's hair on the victim's clothing
indirect (secondary)
happens when a fiber on the suspect is placed on the victim or vice versa
ex) a carpet fiber from a suspect's home is transferred to the suspect's clothing and then to the victim
natural fibers from plants
cotton fibers:
helps in crime investigations because of its variations
vary in length with some being short while others are long
naturally twist in different ways w/ some being tight and others being loose
flax fibers:
since cotton fibers like white cotton and denim are so common, less common natural plant fibers are more help
ex) flax (linen), sisal, jute, and hemp
natural fibers from animals
most common type is from the wool of sheep
coarser or thicker than cotton
can also be more uncommon wool made from camels, alpacas, cashmere, and mohair
fine wool fibers are used for clothing while coarser wool is used in carpet
man-made fibres
are created by machines from natural or synthetic chemicals\
more than 50% of all fibers are this
polyester and nylon are the most common w/ acrylic and rayon being the next most common synthetics
many of those fibers have unique manufacturing-specific textures and shapes
only only produced for a limited time
what does it mean when red blood cells are anucleated?
is an evolutionary trait that allows oxygen to be carried throughout the body only in human
what is the rarest blood type?
blood type ab
identifying one type of blood enzyme or protein in blood evidence is helpful since?
it helps narrow down the list of suspects
phenolphthalein
reacts w/ hydroxide ions
is a colorless acid-base indicator
turns pink in a basic solution
the hemoglobin in blood makes the blood basic
results are immediate
can detect blood concentration w/ a ratio of 1: 5 million
gives a positive result for any type of blood
luminol
is used when investigators suspect the blood evidence has been cleaned up
is attracted to the iron pigment of red blood cells
produces a greenish-blue light when it comes into contact
sensitive w/ the ability to detect blood w/ a ratio of 1: 5 million parts
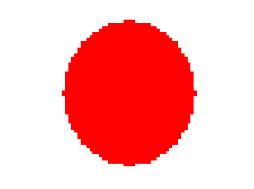
free-falling blood droplets onto glass

free-falling blood droplet onto cement/concrete

partially dried bloodstain smeared from activity

medium-velocity impact blood spatter from something such as being beaten by a blunt object
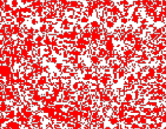
high-velocity impact blood spatter from something such as a gunshot wound
why might an investigator spray a crime scene w/ hydrochloric acid before using luminol?
to speed up the decomposition of the red blood cells
fast blue b test
reacts w/ acid phosphate in the the proteins of the prostate gland’s secretion
turns from blue to a deep purple when it comes into contact
indicates the presence of semen
polygraph test
monitors perspiration, heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate
control question technique (cqt)
aren’t directly related to the criminal case
used in the pre-test interview
important to convince the subject that they just as the relevant questions
used for comparision purposes
relevant/irrelevant technique (i/r)
is a mixture of questions relevant to the crime and irrelevant questions
ex) do you own a handgun? (relevant)
are you forty years old? (irrelevant)
an innocent person will have a similar physiological response to both questions, but a guilty person will react more strongly to the questions relevant to the crime
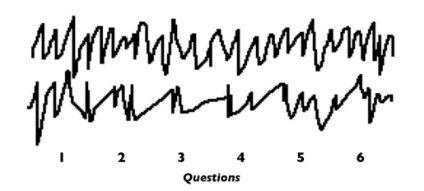
subject was truthful
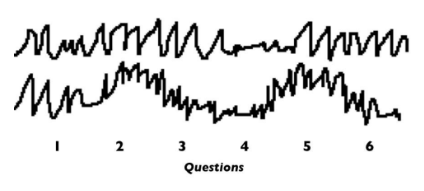
suspect was deceptive (lying or misleading)
letters of a forged document are usually?
larger than normal
for a dna match to be declared, how many unique sections of dna must be found?
five