PollEv Block 3
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
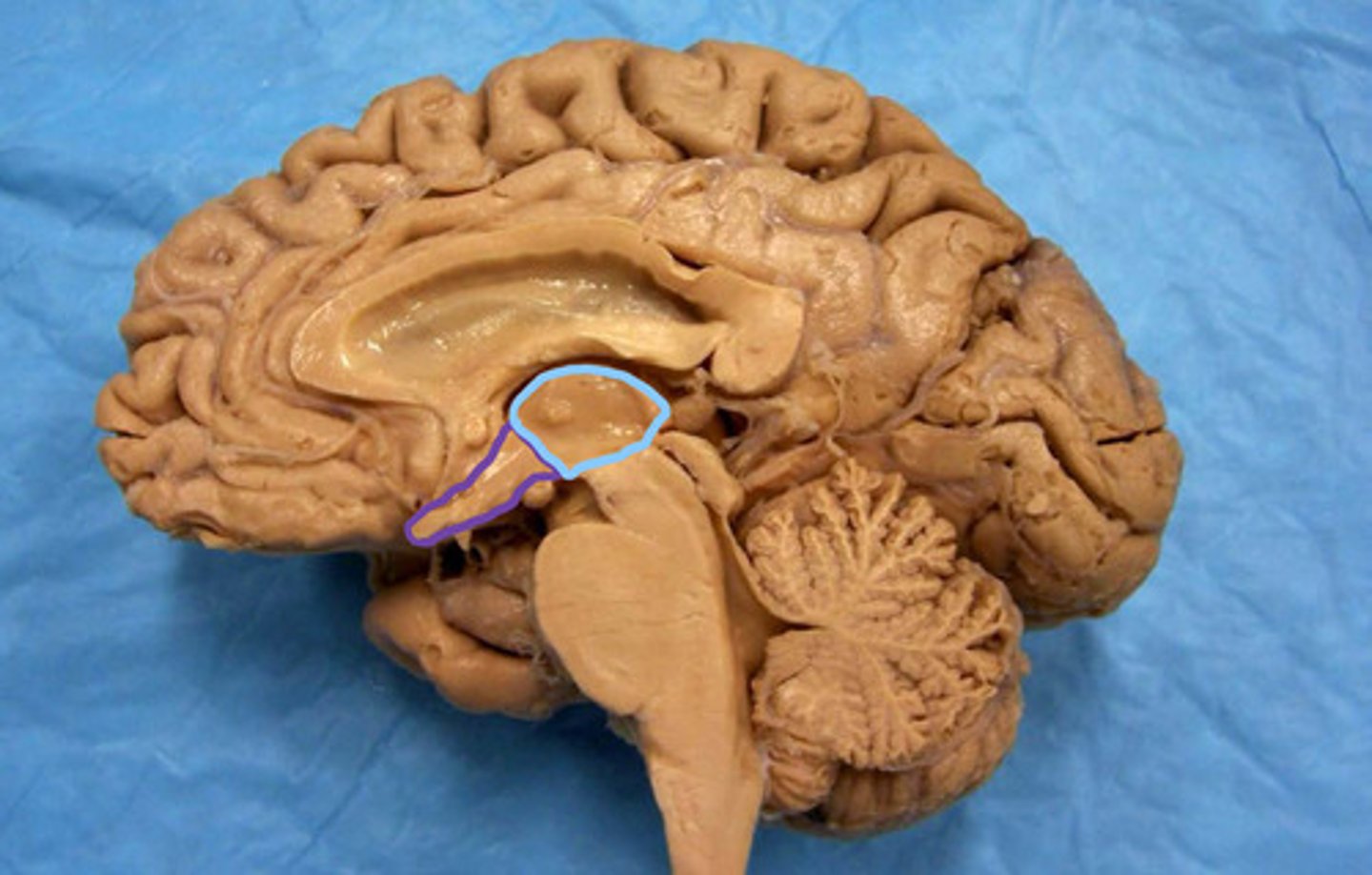
blue - thalamus
purple - hypothalamus
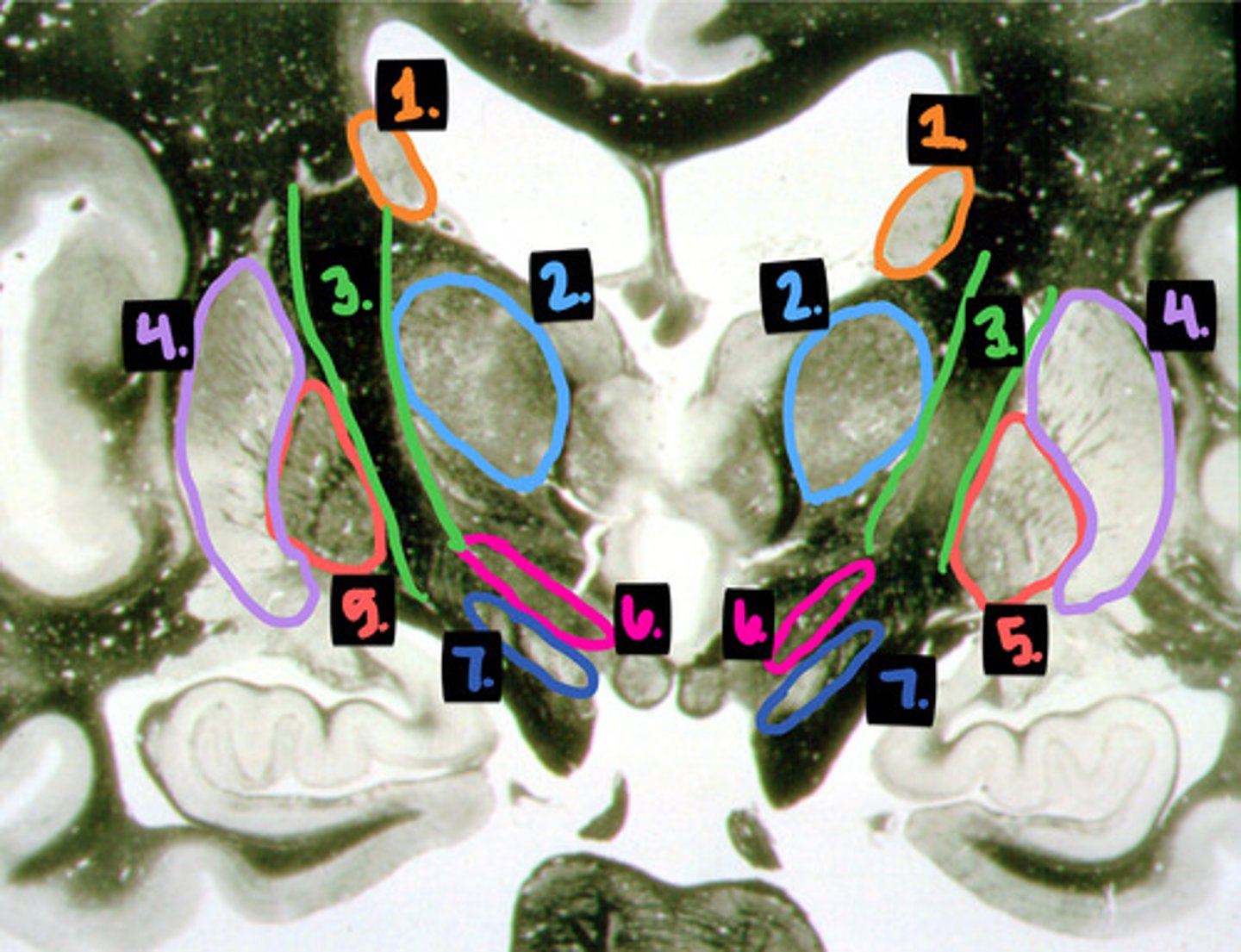
identify the structures
thalamus
identify the structure
hearing (part of the auditory pathway)
what is the function of the medial geniculate nucleus?
vision (part of the visual pathway)
what is the function of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
contralateral somatosensation from the body
what is the function of the ventral posterolateral nucleus?
contralateral somatosensation from the face
what is the function of the ventral posteromedial nucleus?
motor control
what is the function of the ventral anterior/lateral nuclei?
limbic system
what is the function of the anterior and lateral dorsal nuclei?
interpreting and learning written symbols
what is the function of the pulvinar and lateral posterior nuclei?
emotions, moods, feelings, personality
what is the function of the dorsal nucleus?
activates parasympathetic pathway
what is the function of the anterior and medial area of the hypothalamus?
activates the sympathetic pathway
what is the function of the posterior and lateral areas of the hypothalamus?
heat dissipation center and sleep cycle
what is the function of the anterior hypothalamus?
heat conservation center
what is the function of the posterior hypothalamus
satiety center
what is the function of the ventromedial nucleus
feeding center
what is the function of the lateral hypothalamic area
wake cycle
what is the function of the posterior hypothalamus and mammillary bodies?
circadian rhythm (24 hour clock)
what is the function of the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
water balance and hormone synthesis OXY and ADH
what is the function of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei?
hormone regulation for pituitary function
what is the function of the median eminence?
release of reproduction hormones LH and FSH
what is the function of the preoptic nucleus?
contralateral hemiballism
A lesion to the subthalamic nucleus will result in?
pineal gland
What structure converts serotonin to melatonin?
posterior limb of the internal capsule
Which structure contains all 3 body pathways: voluntary motor pathway, posterior column/medial lemnicus, anterolateral system?
posterior limb of the internal capsule
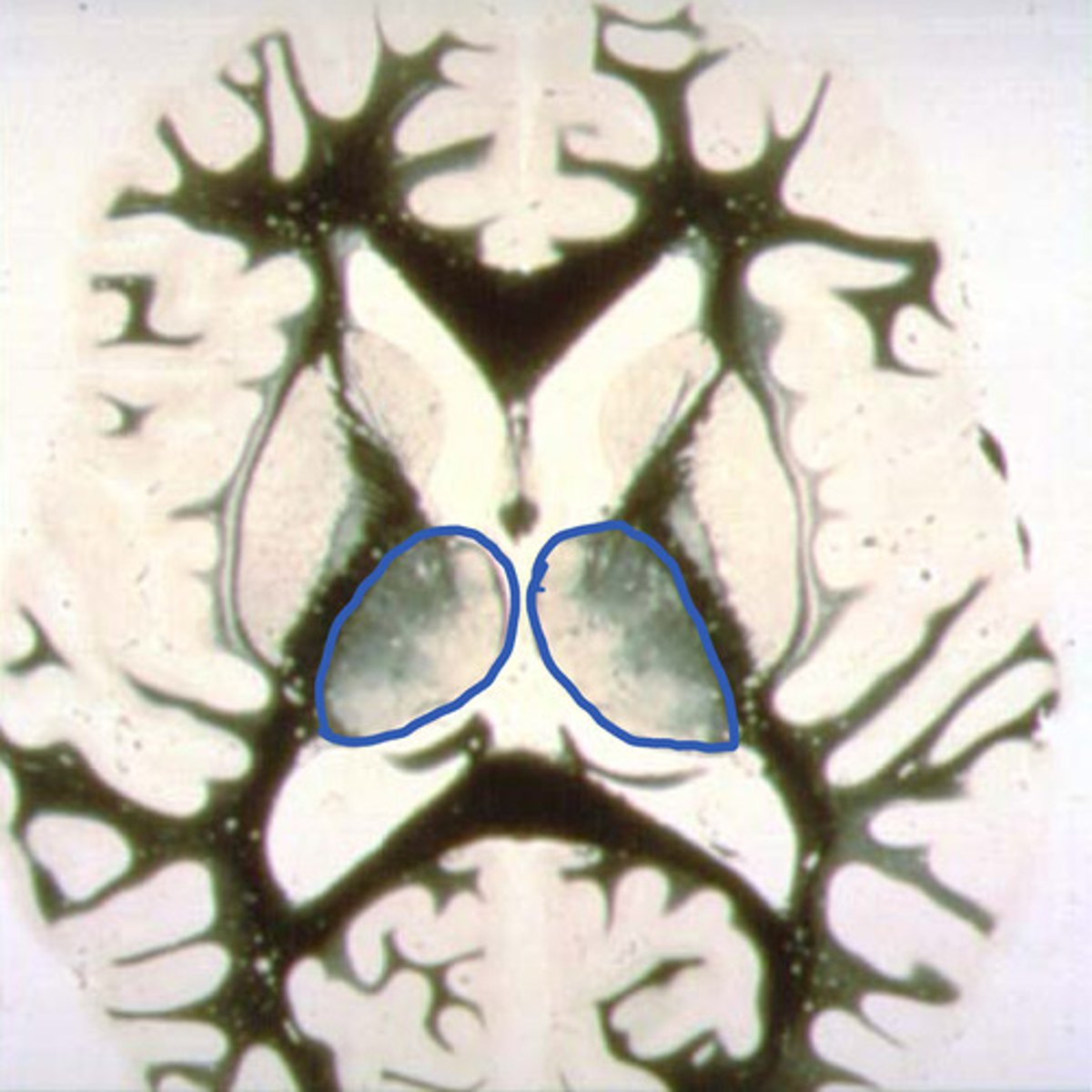
identify the structure
Caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus
corpus striatum consists of what parts?
5
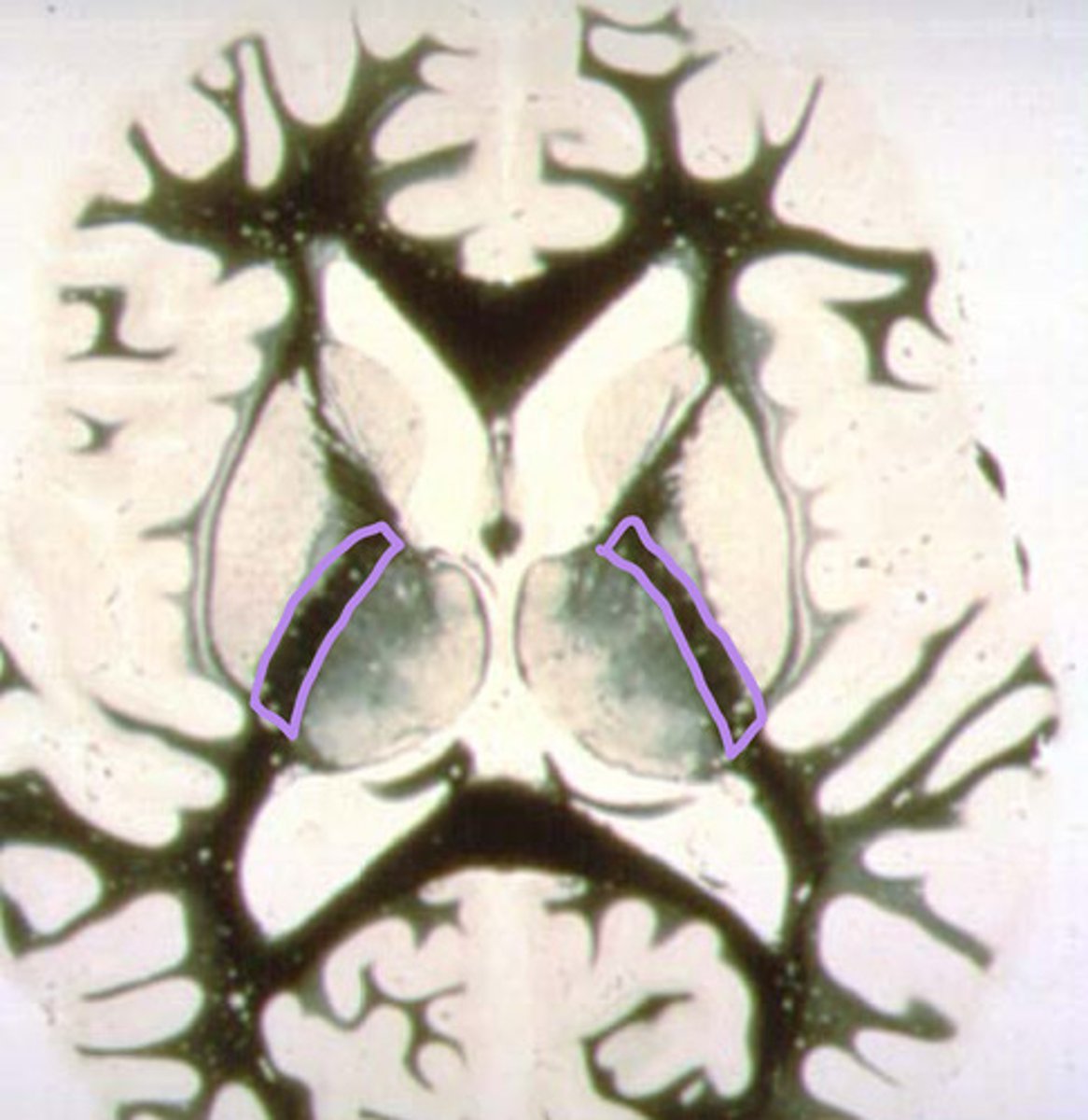
which is the globus pallidus?
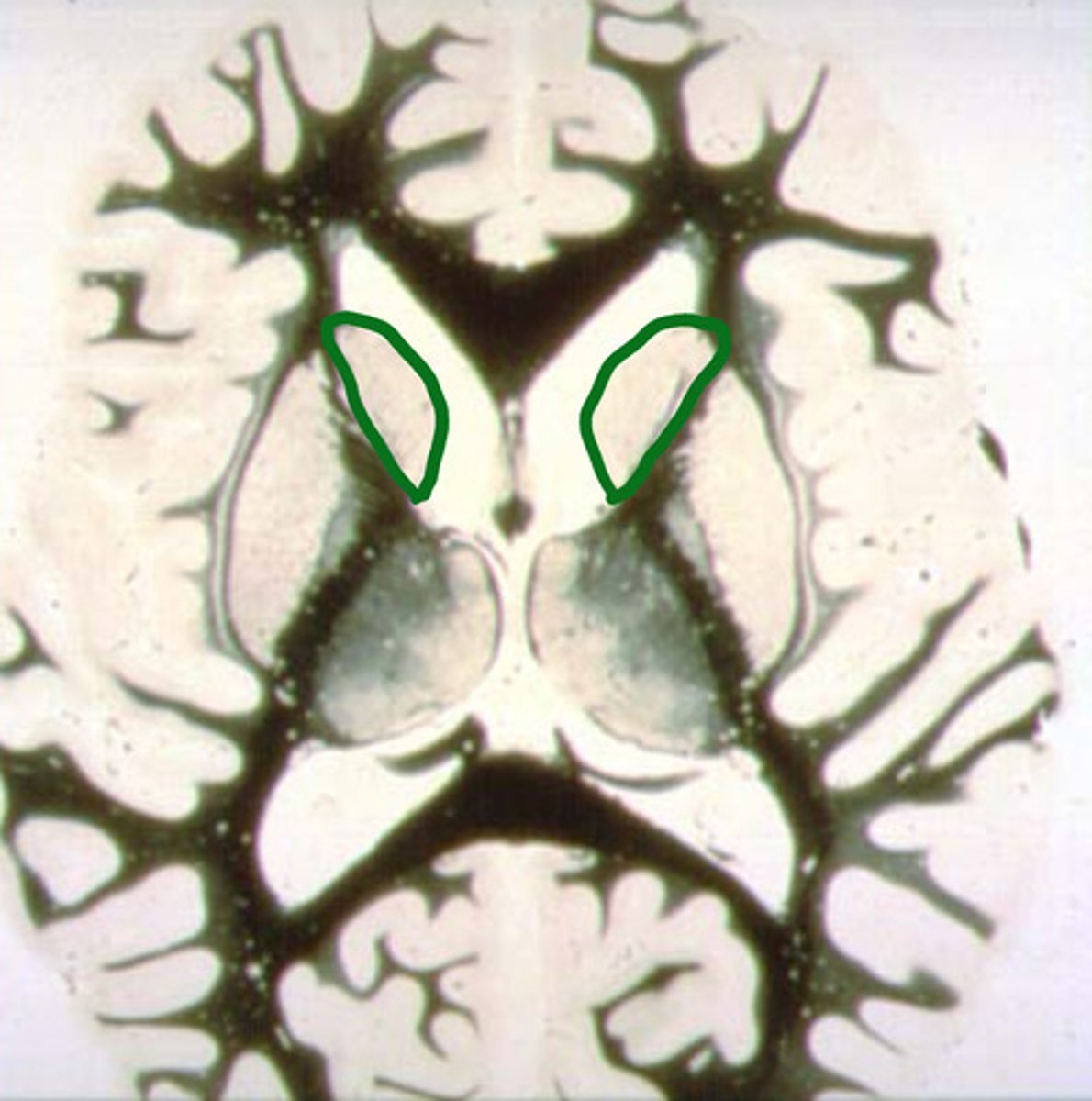
head of the caudate nucleus
identify the structure
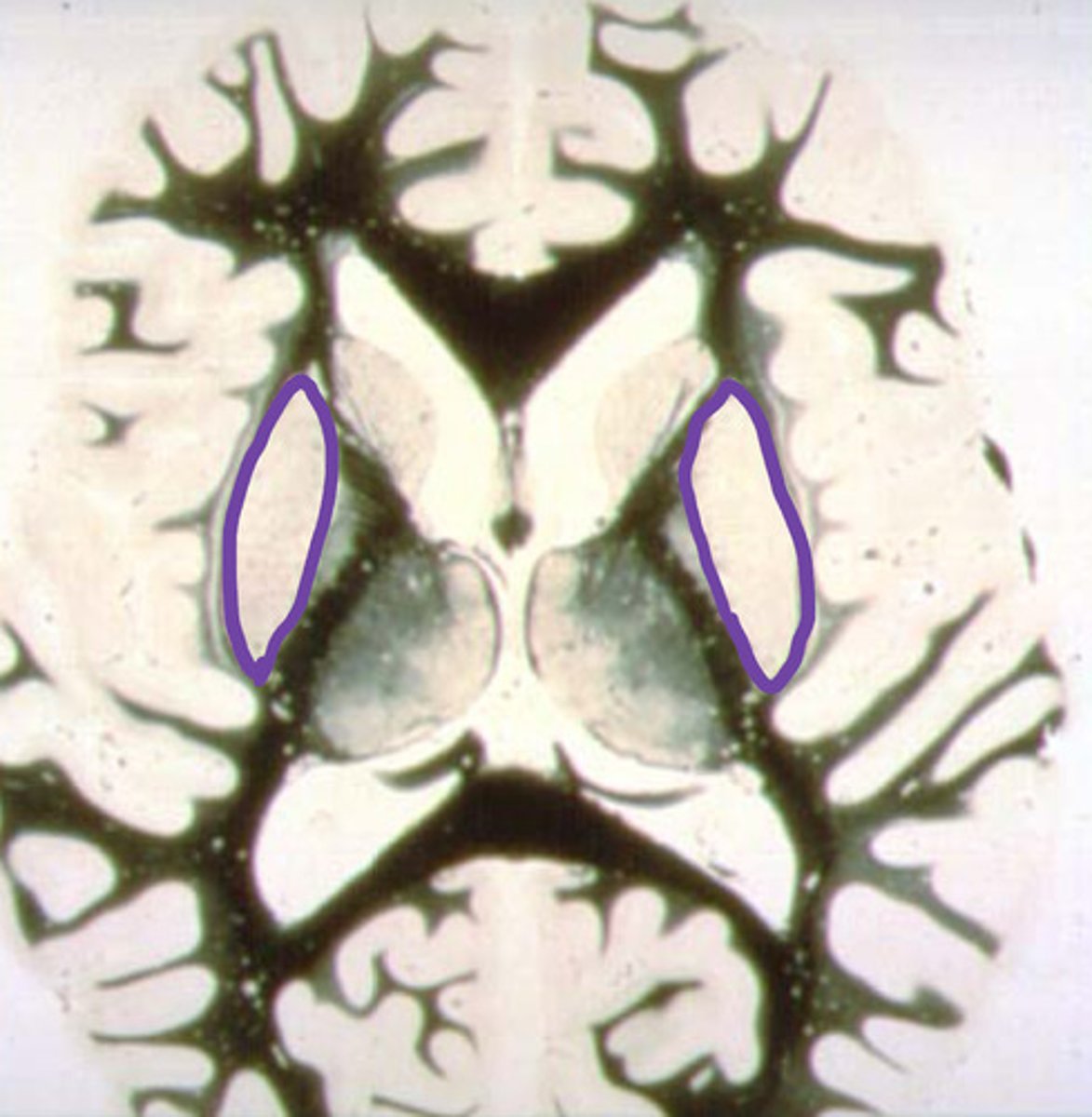
putamen
identify the structure
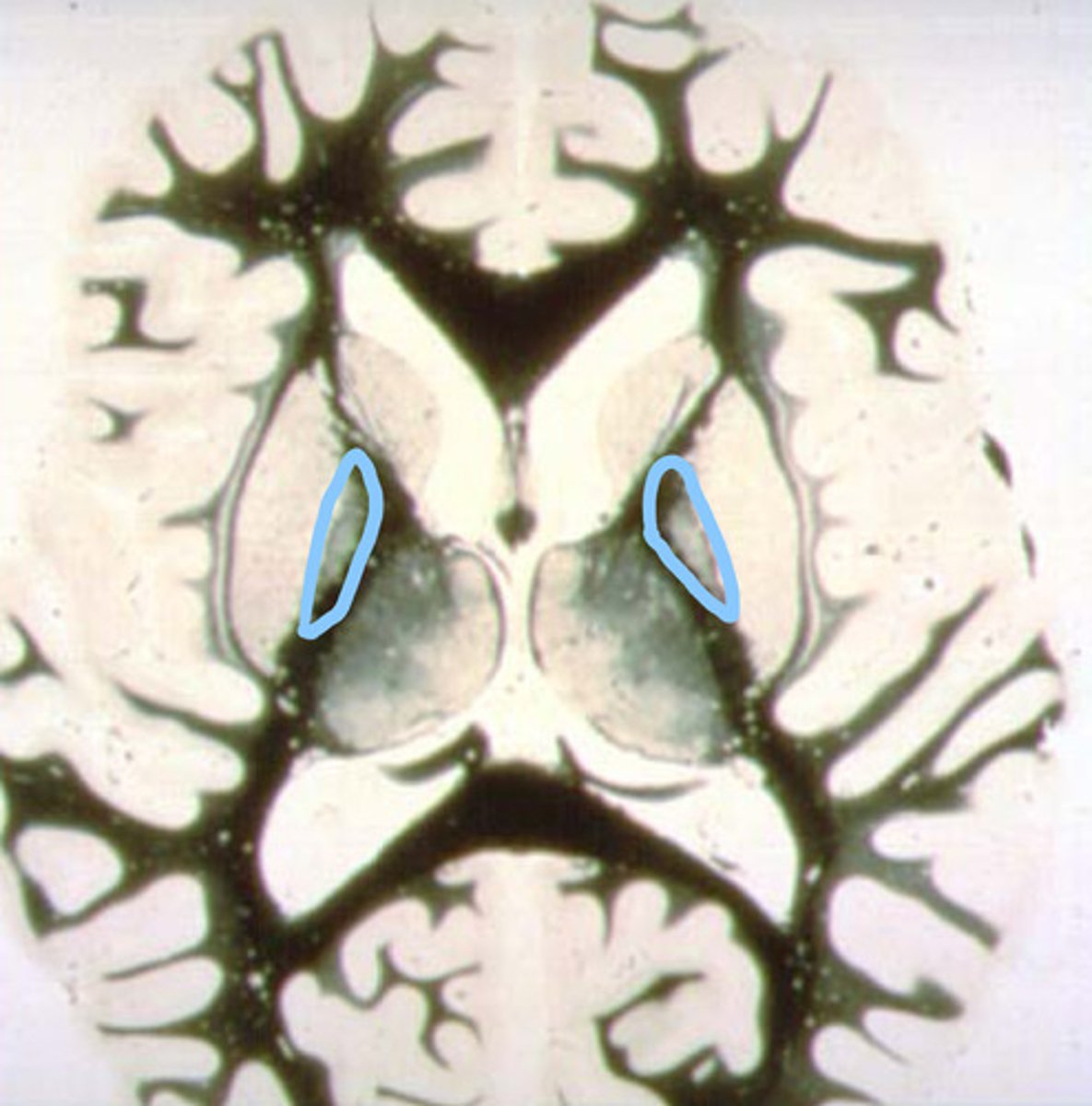
globus pallidus
identify the structure
TRUE
T/F Activation of the basal nuclei direct pathway caused increased motor cortex activity and increased movement.
athetoid movements
a hyperkinetic movements that has slow, writhing, snake-like movements is called?
contralateral hemabalism
a lesion to the subthalamic nucleus will result in?
striatum
what CNS structure is initially affect in huntington's disease?
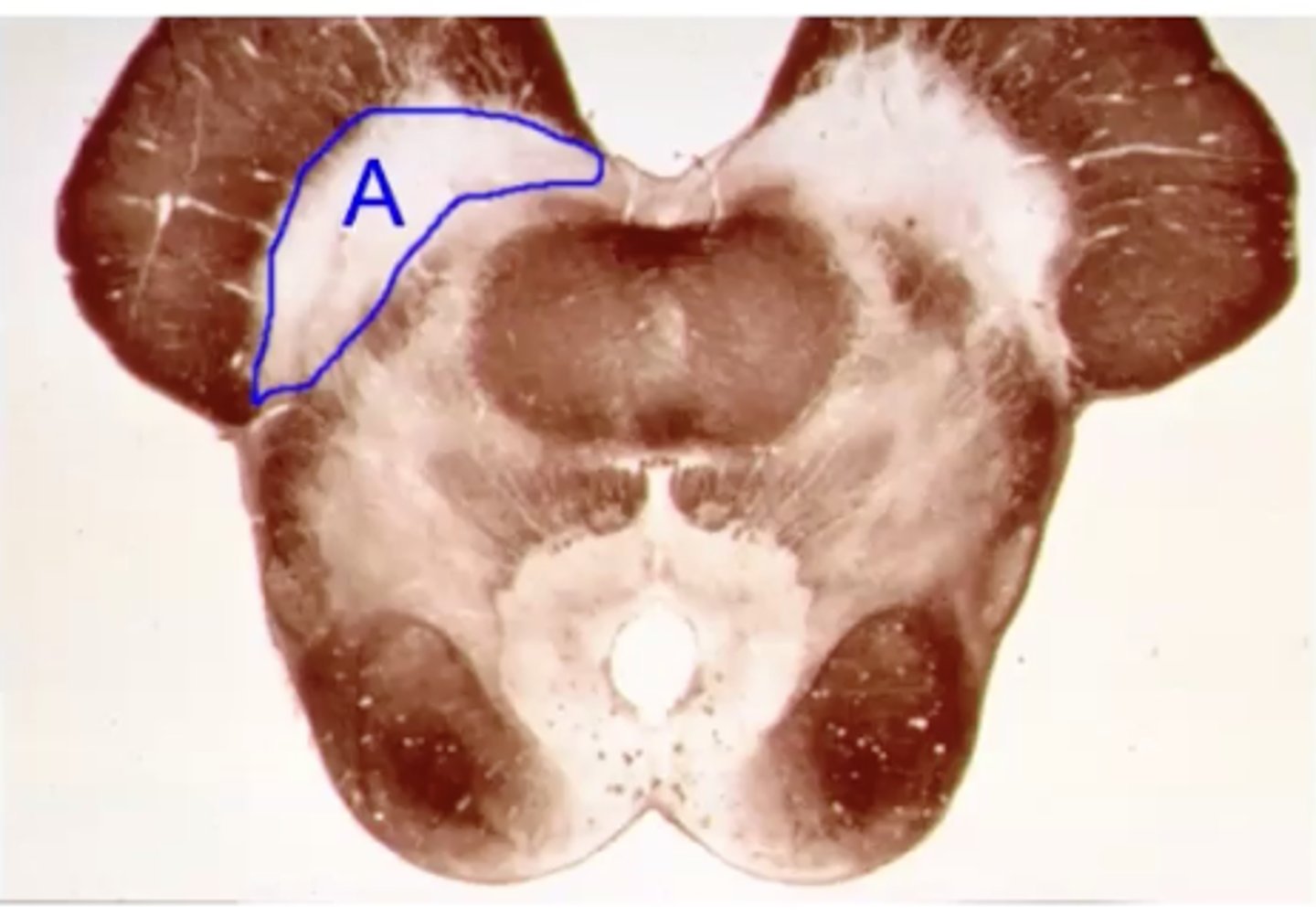
parkinsons
name the clinical condition when A is lesioned
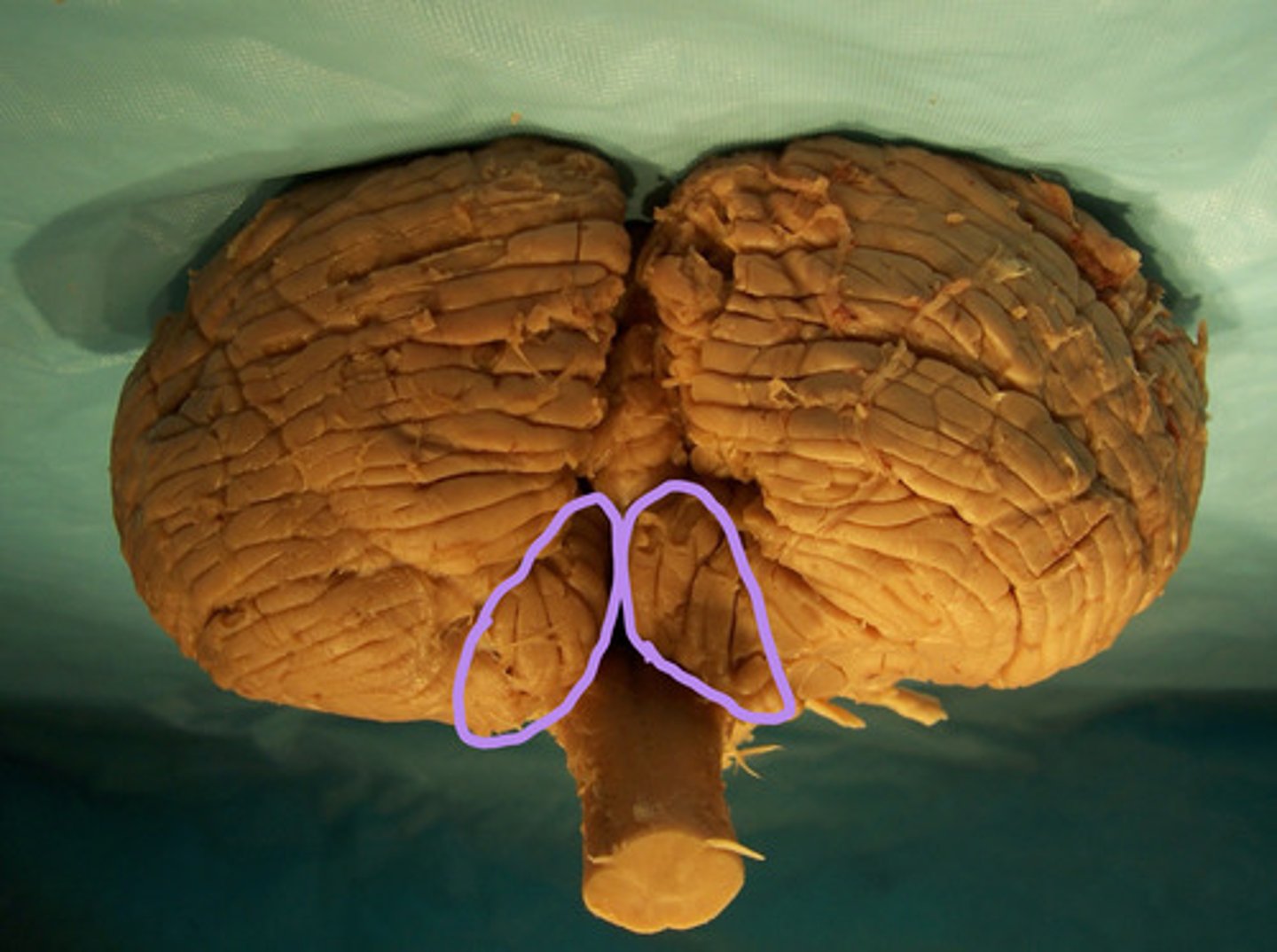
cerebellar tonsils
identify the structure
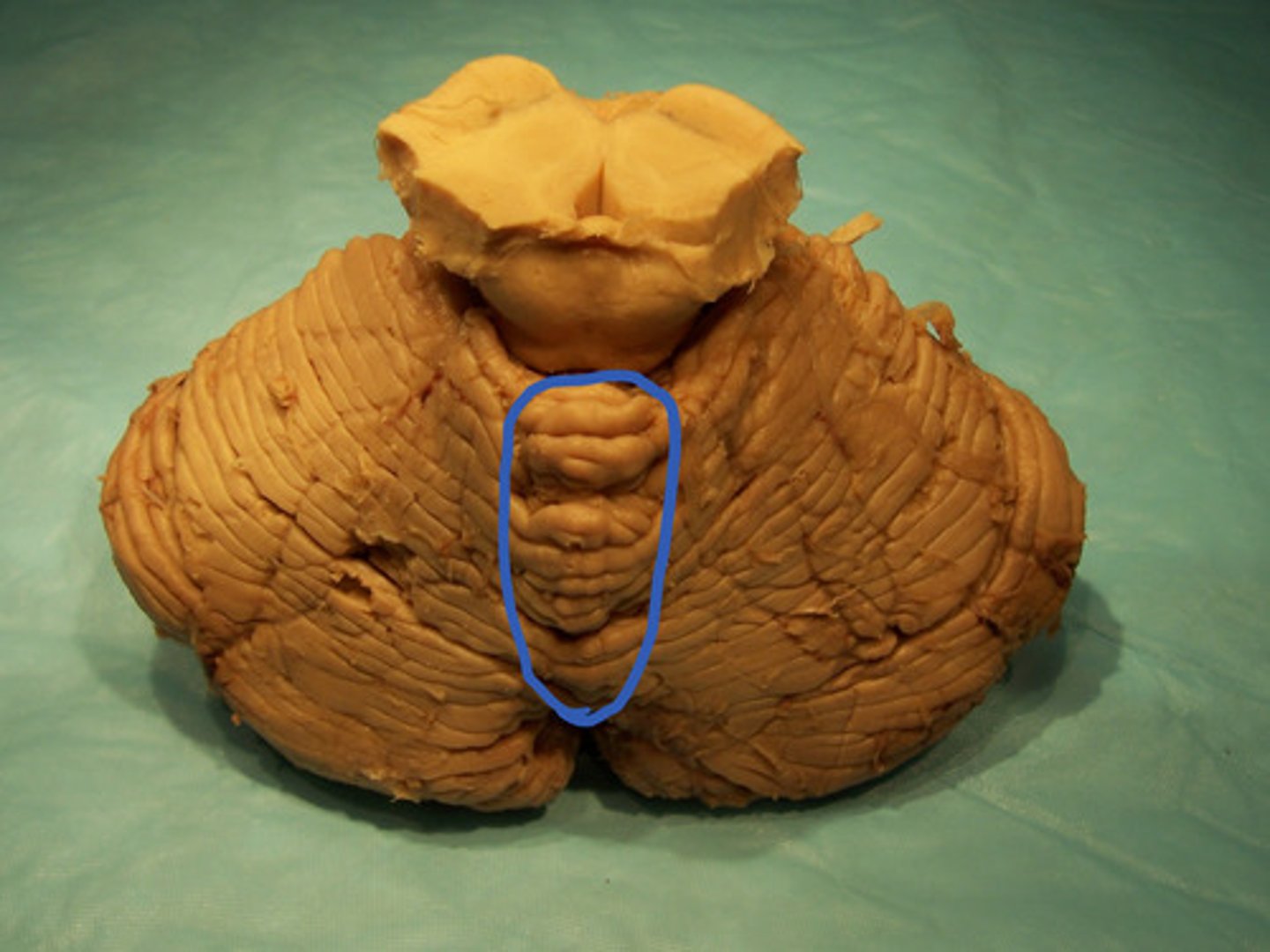
vermis
identify the structure
purkinje cells
Which cerebellar neuron sends inhibitory output to the deep cerebellar nuclei?
vestibulocerebellum
A 59 year old patient presents with trunkal ataxia. Which cerebellar functional zone has been lesioned?
pontocerebellum
A patient presents with hand ataxia. Which cerebellar functional zone has been lesioned?
spinocerebellum
A patient presents with limb ataxia. Which cerebellar functional zone has been lesioned?
Jerky, inaccurate movements
define ataxia
Decreased muscle tone and deep tendon reflexes
define hypotonia
Deterioration and decomposition of coordinated movement
define dyssynergia
Past pointing by over or under shooting the target
define dysmetria
Awkward performance of rapidly alternating movements
define dysdiadochokinesia
TRUE
T/F an intention tremor is caused by a cerebellar lesion?
superior cerebellar artery
which artery supplies the superior surface of the cerebellum?
TRUE
T/F Gamma motor neurons innervate intrafusal muscle fibers to maintain muscle tone
reticulospinal tracts and vestibulospinal tracts
which motor neuronal pathways excite the antigravity muscles?
rubrospinal tracts
which motor pathway activates the flexors of the upper extremity?
A Sensorimotor integration
the lateral premotor cortex is involved in?
A Sensorimotor integration
B Fine control of individual muscle movement
C Initiating and coordinating internally generated movements
D None of the above
(A) Above the red nucleus
A patient with decorticate rigidity has a lesion located:
(A) Above the red nucleus
(B) Below the red nucleus
(B) Below the red nucleus
A patient with decerebrate rigidity has a lesion located:
(A) Above the red nucleus
(B) Below the red nucleus
corticobulbar tracts on the right side
Your 65 year old patient is unable to close their mouth or smile on the left side of their face. They are able to raise their eyebrows and close their eyelids bilaterally. What structure has been lesioned?
corticobulbar tracts on the left side
Your 23 year old patient's tongue deviates to the right when protruded. You inspect the surface of the tongue and note that there is NO atrophy of the tongue muscles. What structure has been damaged?
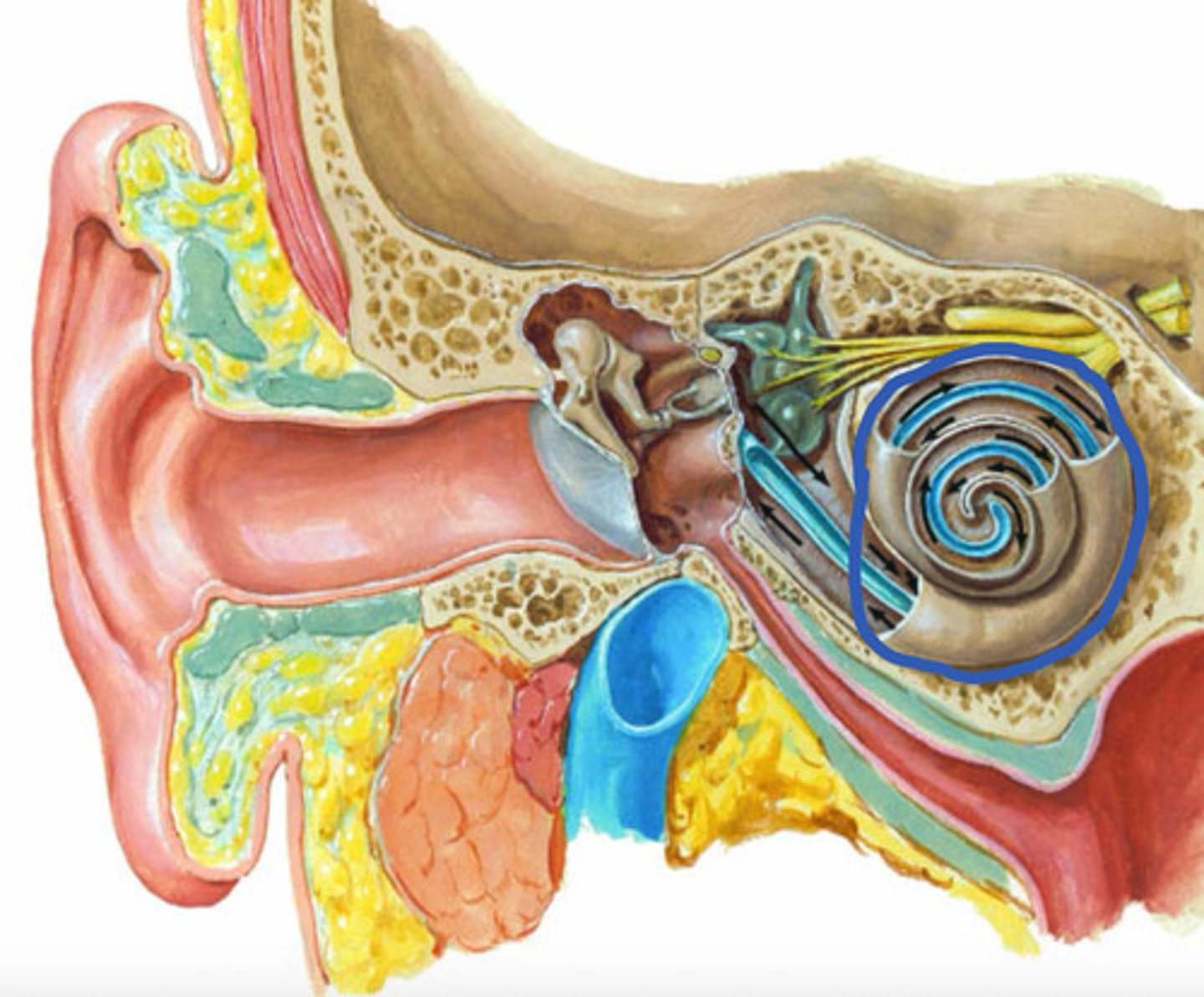
cochlea
label the structure
semicircular canals
label the structure
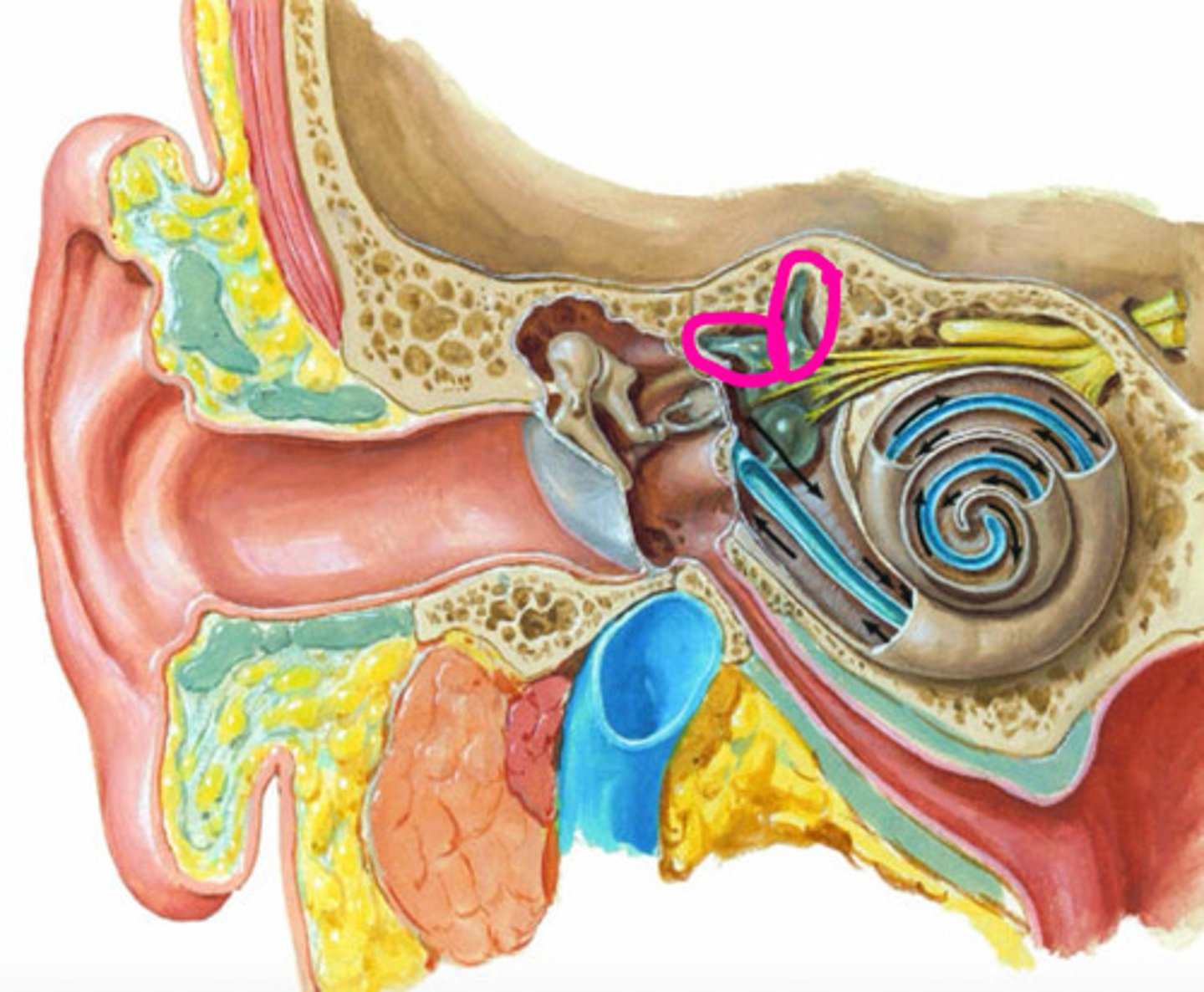
CNVIII
Which cranial nerve is attached to the hair cells in the cochlea and semicircular canals?
TRUE
T/F The endolymph fluid contains a high concentration of K+ in the vestibular and auditory systems
E All of the above
Hair cells are located:
A At the base of each semicircular canal
B Utricle
C saccule
D Cochlear duct (scala media)
E All of the above
TRUE
T/F When hair cells stereocilia bend from short to the tall kinocilium, K+ enters the cell and the cell is depolarized.
TRUE
T/F The utricle and saccule hair cells detect linear acceleration
TRUE
T/F The semicircular canals hair cells detect head rotation.
lateral vestibulospinal tract
Which tract activates the antigravity muscles?
TRUE
T/F In the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR), the fast eye movement in the direction of the head turn is called nystagmus.
B the left side
In the caloric vestibular test, cold water poured into the right ear will cause nystagmus to:
A the right side
B the left side
C both sides
D neither side
TRUE
T/F A head turn to the left, causes nystagmus to the left.
A left side
In the vestibular rotatory test, a spin to the right will result in nystagmus to the
A left side
B right side
C neither side
E All of the above
Vestibular signs and symptoms include:
A Spontaneous nystagmus
B Decreased antigravity muscle reflexes
C Motion sickness
D Vertigo
E All of the above
TRUE
T/F High frequency sound waves are received at the base of the cochlea whereas low frequency sound waves are received at the apex of the cochlea.
timing of sounds
match ventral cochlear nuclei to its function

vertical sound location
match dorsal cochlear nuclei to its function

first place to compare input from both ears, analyzes to help locate the sound source
match superior olivary nuclei to its function

integrates function from all brainstem nuclei
match inferior colliculi to its function

1. optic nerve
2. optic chiasm
3. optic tract
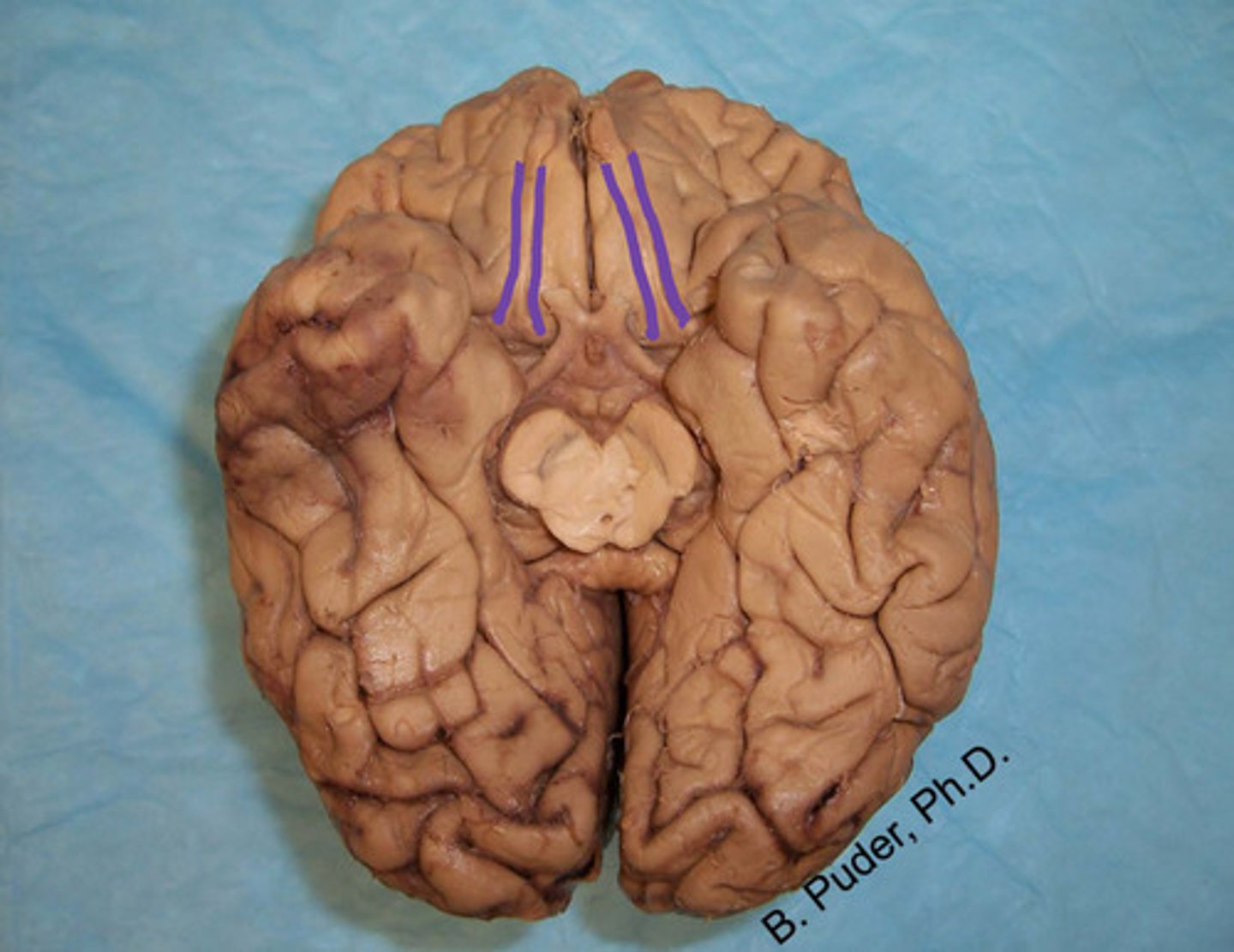
label
calcarine fissure
what is highlighted?
TRUE
T/F Vestibular schwannoma is an example of a sensorineural lesion.
TRUE
T/F Rinne's test will determine if your patient has a conductive hearing loss.
bipolar cell
The 1st neuron in the visual pathway is the?
2 - optic chiasm
which area will cause bitemporal hemianopsia when lesioned?
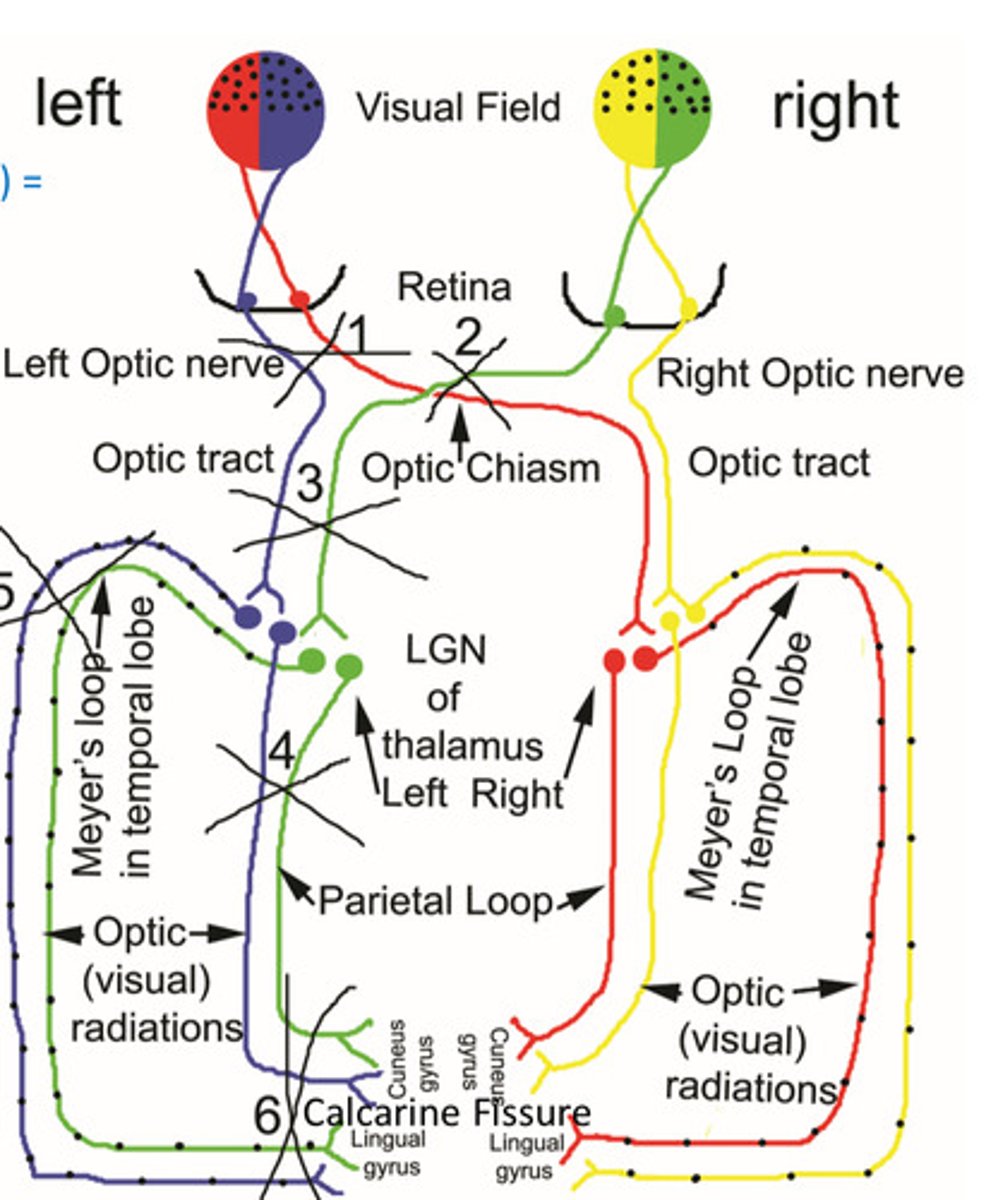
5 - meyer's loop on temporal lobe
which area will cause contralateral homonymous superior quadrantopsia when lesioned?
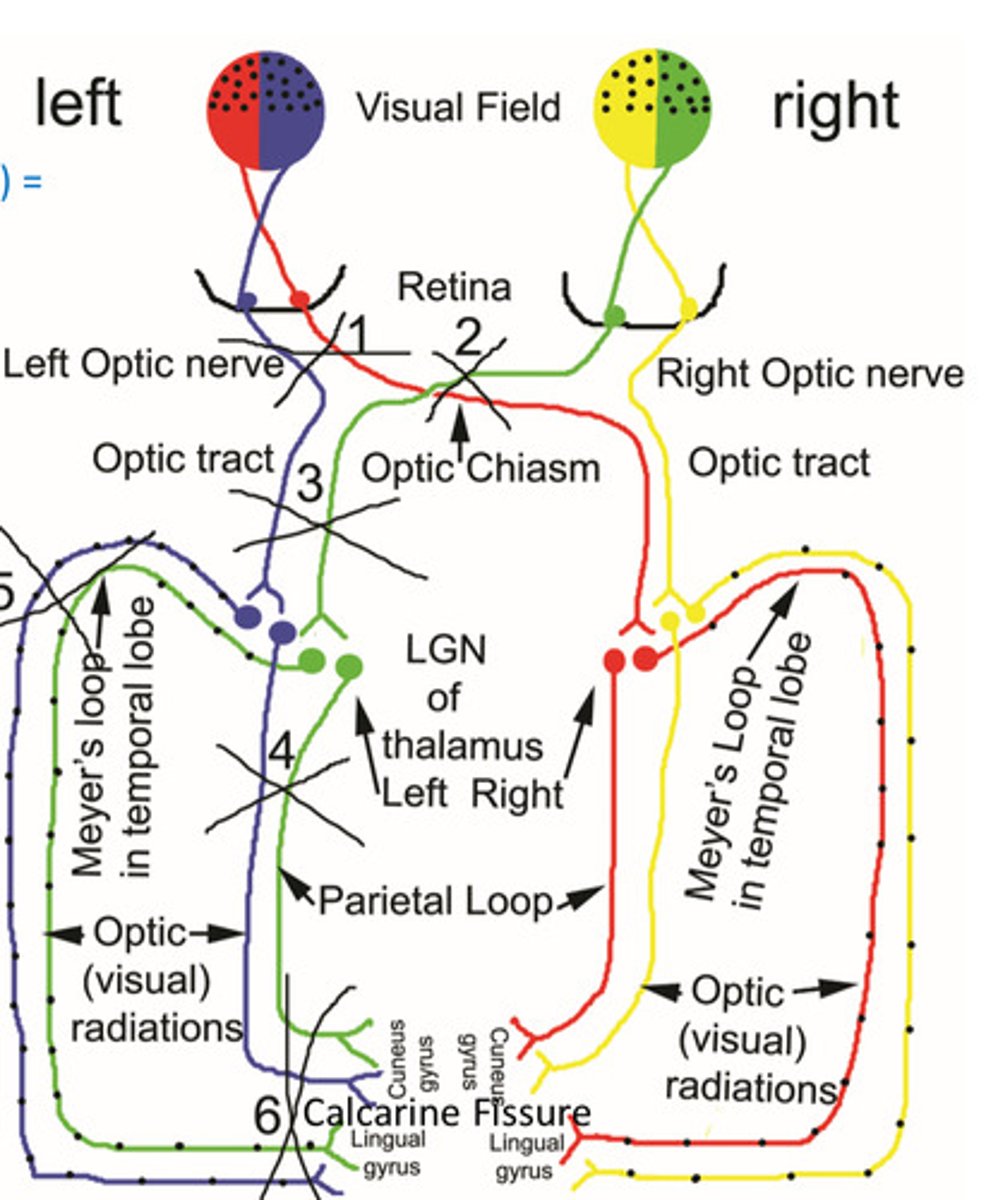
II and III
which two cranial nerves are part of the pupillary light reflex?
sustentacular cell
which cell is the glial-like supporting cell for the olfactory system?
D Ipsilateral ansomia
A lesion to the olfactory nerve or the olfactory bulb and tract will result in:
A Ipsilateral ageusia
B Ipsilateral hemiballism
C Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia
D Ipsilateral ansomia
E None of the above
olfactory tract
label the structure
TRUE
T/F Taste buds regenerate every 10-14 days
- sweet
- salty
- sour
- umami
- bitter
List the 5 basic types of taste
D All of the above
Which of the following are clinical terms describing taste lesions?
A Ageusia
B Hypogeusia
C Dysgeusia
D All of the above
E None of the above
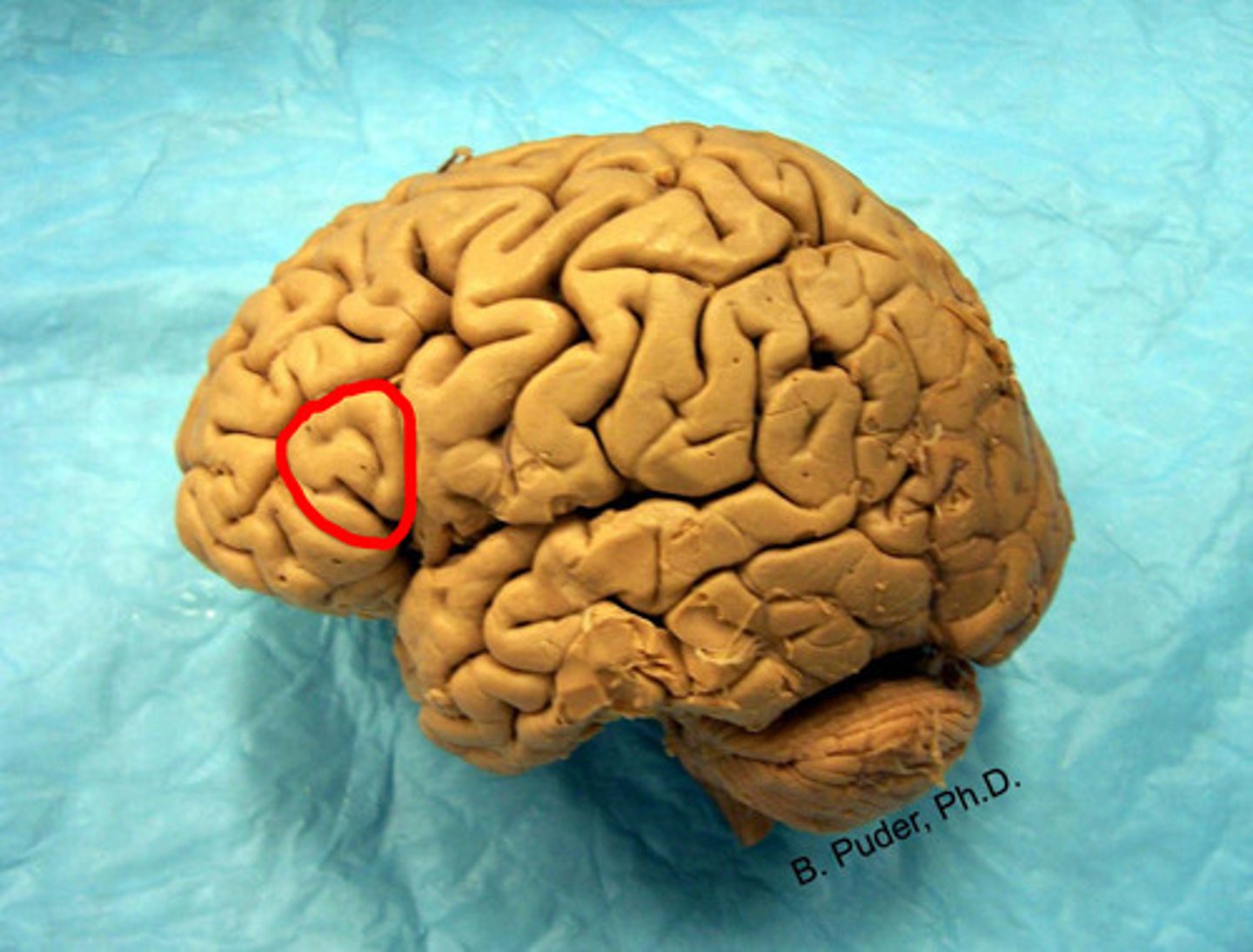
pre-central gyrus
label
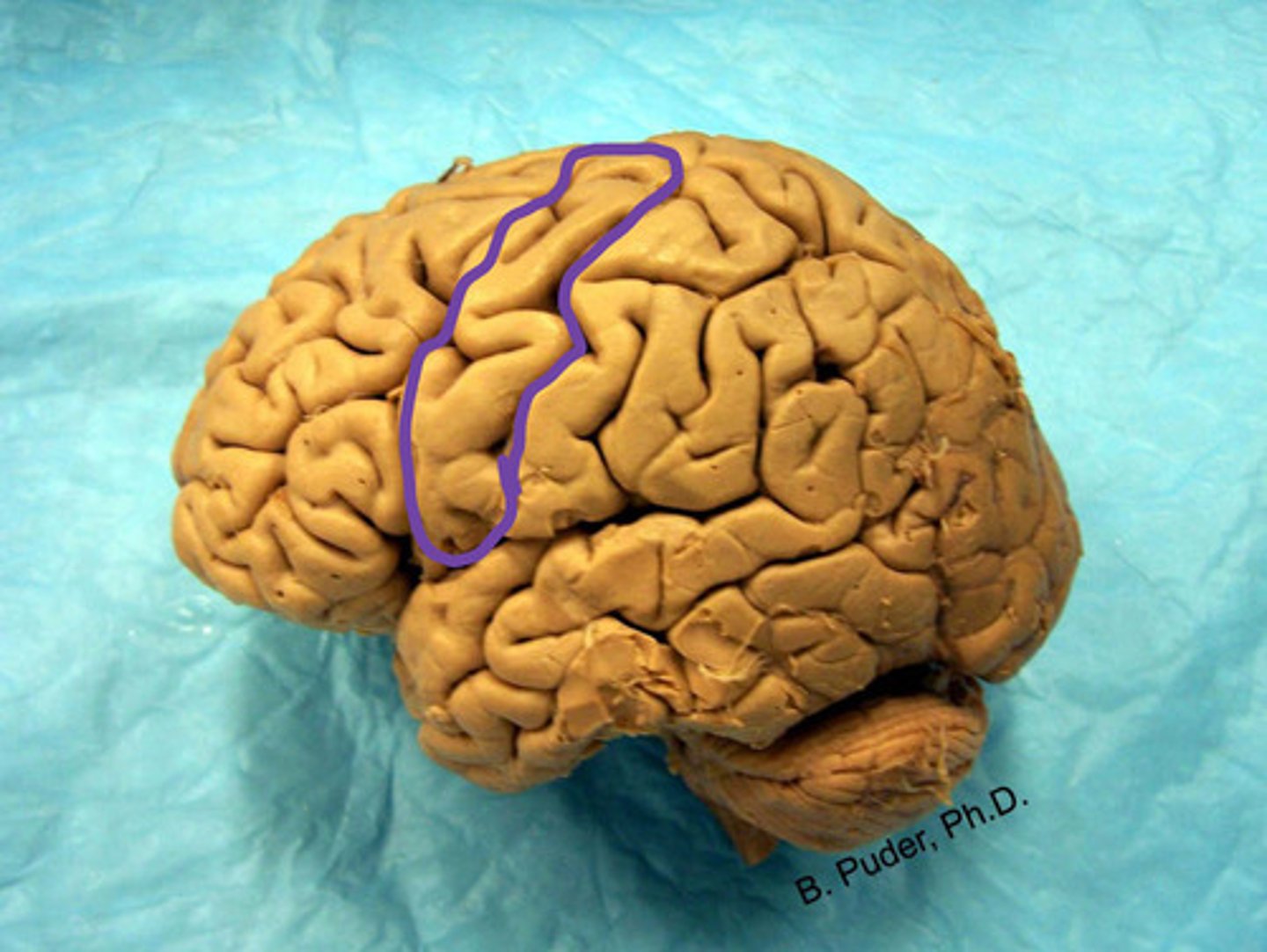
paracentral lobule anterior portion
Which brain area is motor control to the contralateral knee, leg, and foot?
precentral gyrus
Which brain area is motor control to the contralateral from head to hip?
postcentral gyrus
Which brain area is somatosensation control to the contralateral from head to hip?
paracentral lobule posterior portion
Which brain area is somatosensation control to the contralateral from knee to foot?
paracentral lobule
label
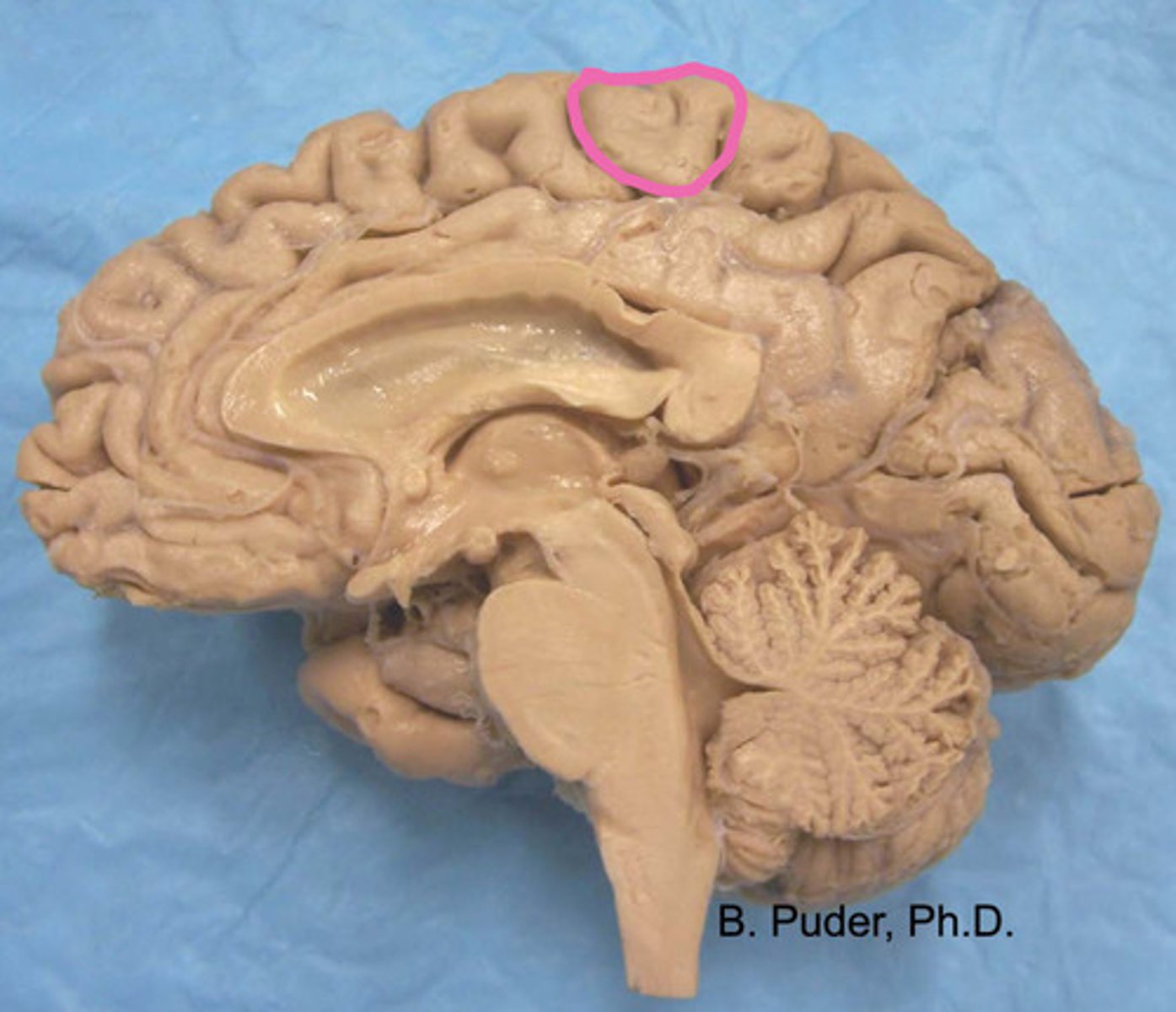
TRUE
T/F Somatosensation from the contralateral head to hip is located in the postcentral gyrus.
broca's motor speech area
label
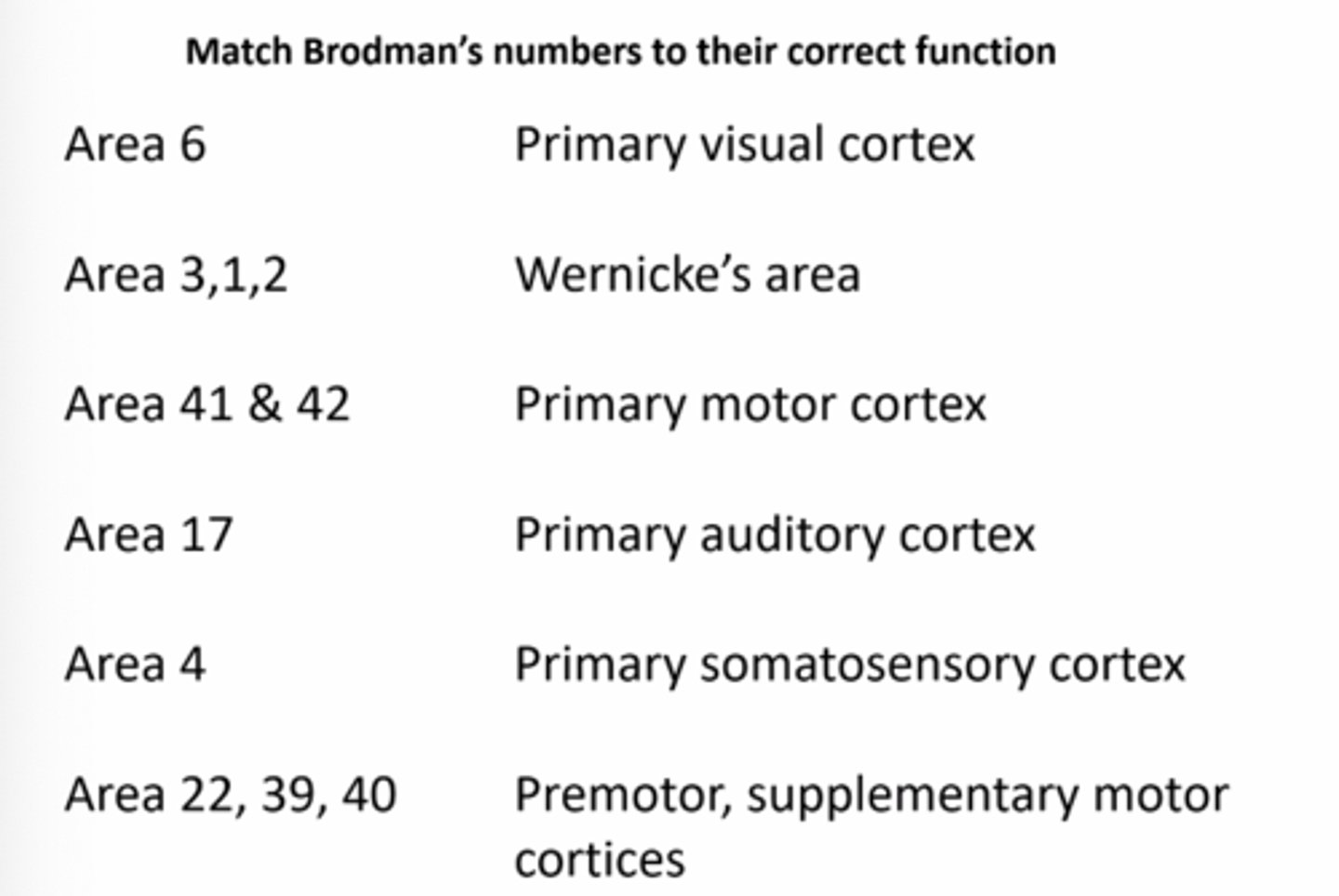
Premotor, supplementary motor cortices
Match Brodman's numbers to their correct function: Area 6
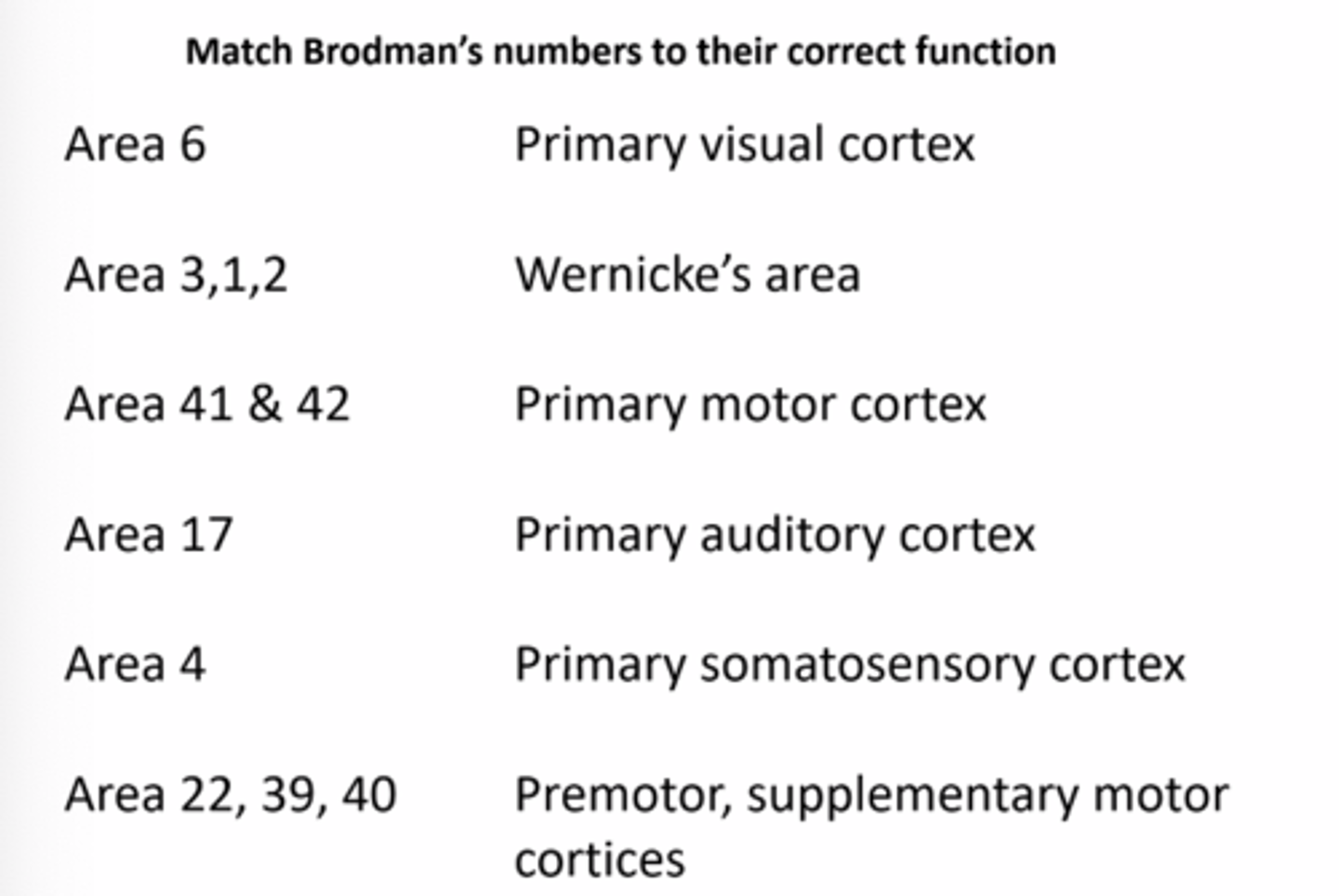
Primary somatosensory cortex
Match Brodman's numbers to their correct function: Area 3,1,2
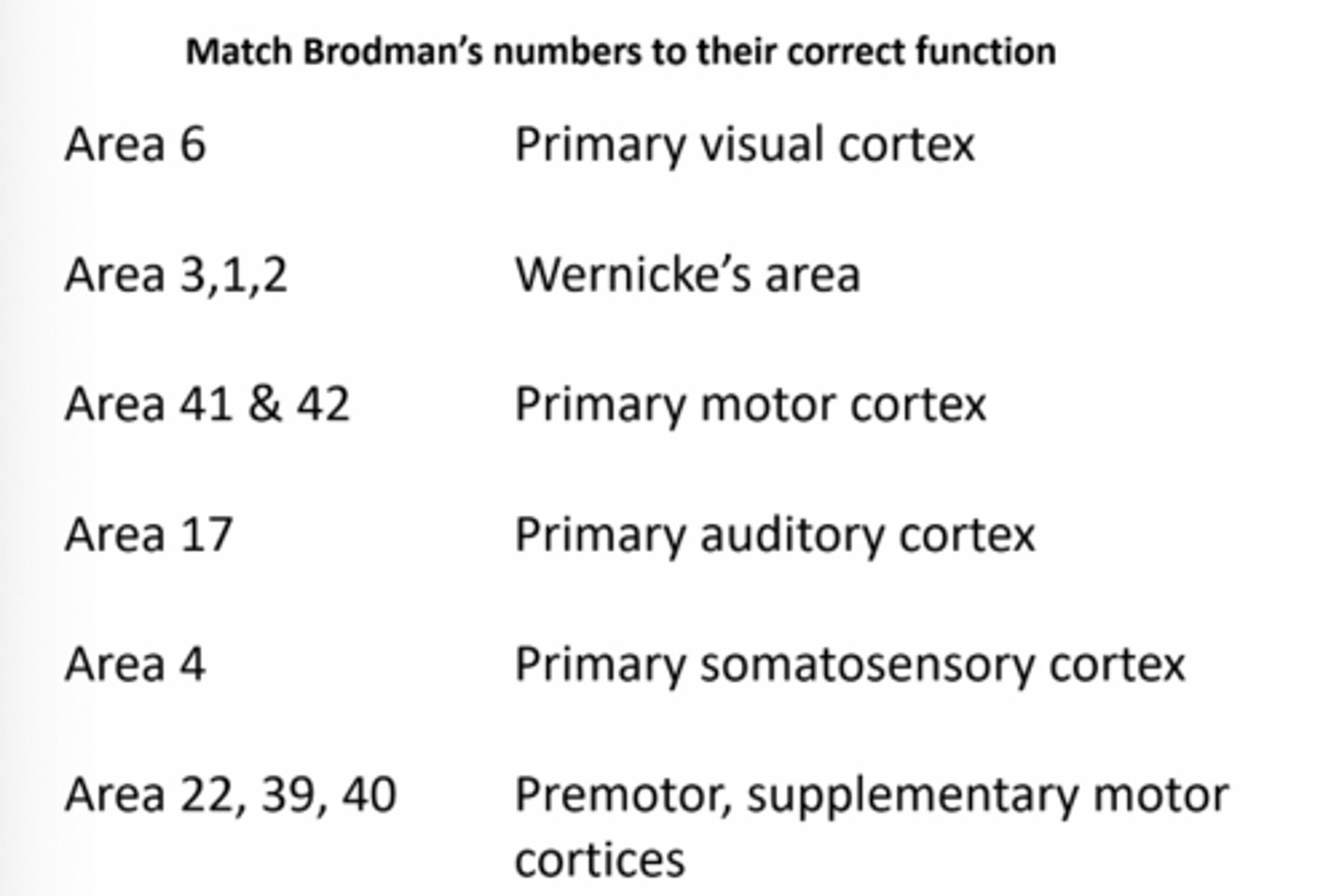
Primary auditory cortex
Match Brodman's numbers to their correct function: Area 41 & 42