Synthesis Reactions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
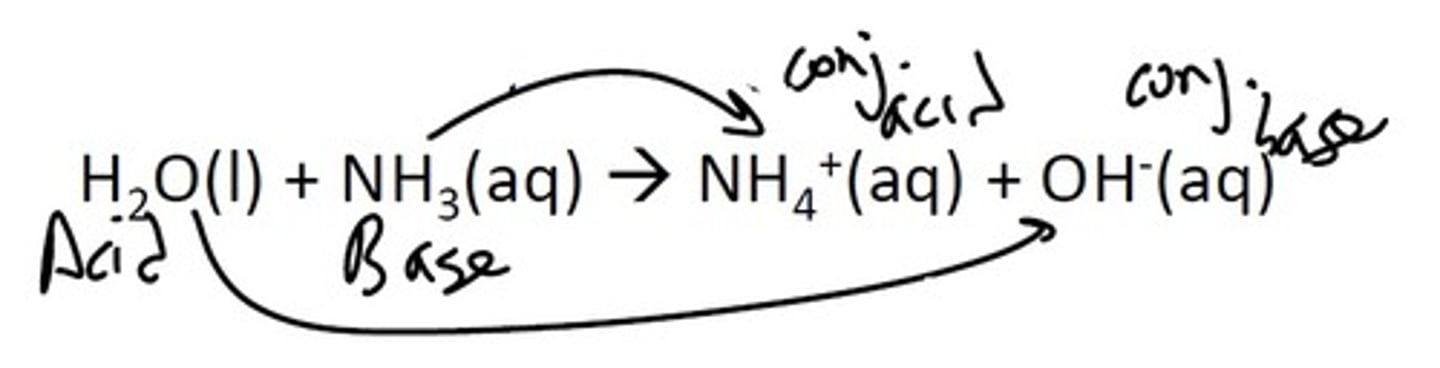
Bronsted-Lowry Acid-base reactions
Bronsted Acid: Proton donor (H+ donor)
Bronsted Base: Proton acceptor (H+ acceptor)
Conjugate Acid- formed from base
Conjugate Base- formed from acid
Weak, Stable base = Strong, Unstable conjugate acid
Weak, Stable Acid = Strong, Unstable conjugate base
Equilibrium favors weak, stable acids AND/OR equilibrium favors most stable conjugate base
Hydration
Alkene Addition Reaction
1. Nucleophilic pi bond attacks an electrophilic atom.
2. Nucleophile attacks electrophilic carbon.
3. Deprotonation
H2SO4, H2O
Follows Markovnikov's Rule
Final Product: C-OH on the MORE substituted carbon. This is a racemic mixture because the OH group can attack from the top or the bottom.
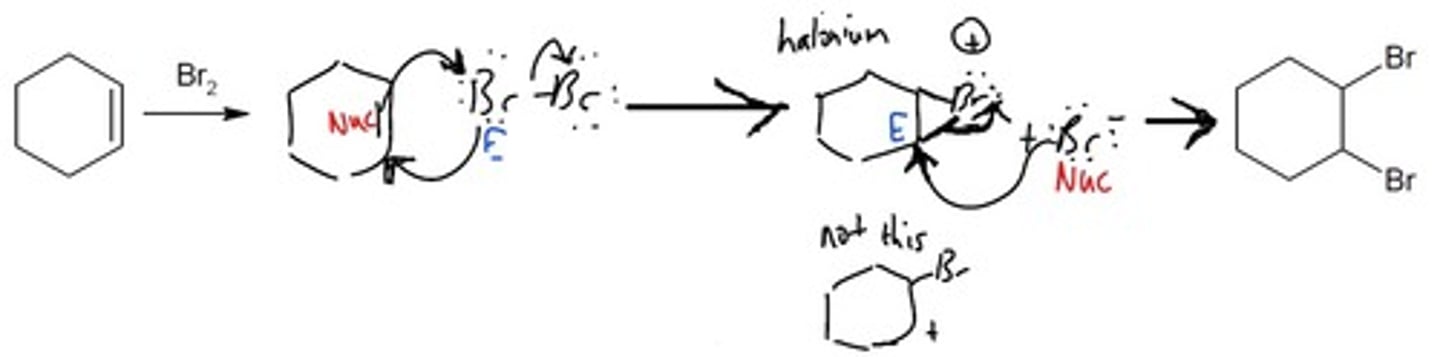
Halogenation
Alkene Addition Reaction
1. Nucleophilic pi bond attacks an electrophilic atom.
2. Halogen donates electron density back
3. Nucleophile attacks electrophilic carbon.
Br2
Creates a halonium ion intermediate
Final Product: A halogen is attached to both carbons.
Halohydrin Formation
Alkene Addition Reaction
1. Nucleophilic pi bond attacks an electrophilic atom.
2. Halogen donates electron density back
3. Nucleophile attacks electrophilic carbon.
4. Deprotonation
Br2, H2O
Creates a halonium ion intermediate and the OH group follows Markovnikov's Rule and attached to the more substituted carbon.
Final Product: OH on the MORE substituted carbon. A halogen is attached to the LEAST substituted carbon.

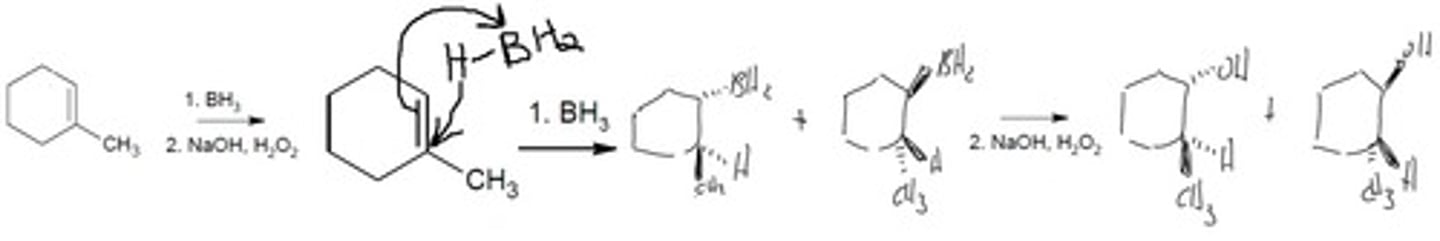
Hydroboration-Oxidation (first step mechanism)
Alkene Addition Reaction
1. BH3 2. NaOH, H2O2
Follows Anti-Markovnikov's Rule. Boron and Hydrogen both form bonds across the alkene at the same time therefore it is a SYN addition
Final Product: BH2 on the LEAST substituted carbon. OH replaces BH2. A halogen is attached to the MORE substituted carbon.
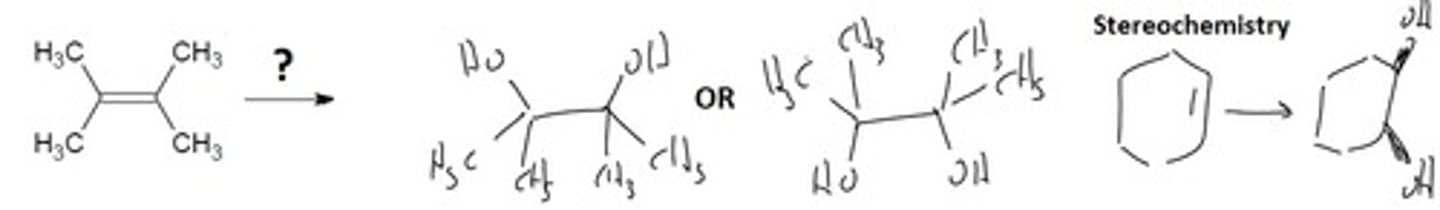
Syn Dihydroxylation (OsO4)
Alkene Addition Reaction
Oxidation Reaction
1. OsO4 2. NaHSO3, H2O
Syn- Same side Diol- 2 alcohol
Addition of two alcohol groups SYN across the double bond
Final Product: 2 OH groups on the same side (either 2 wedges or 2 dashes) of the carbons.
Ozonolysis
Alkene Addition Reaction
Oxidation Reaction
1. O3 2. CH3SCH3 (or Zn, H2O)
Cleavage of an alkene, forming a carbonyl on both sides. Split the double bond down the middle and attach an Oxygen to each end of the double bond.
Final Product: 2 carbonyls
(C=O is a carbonyl)
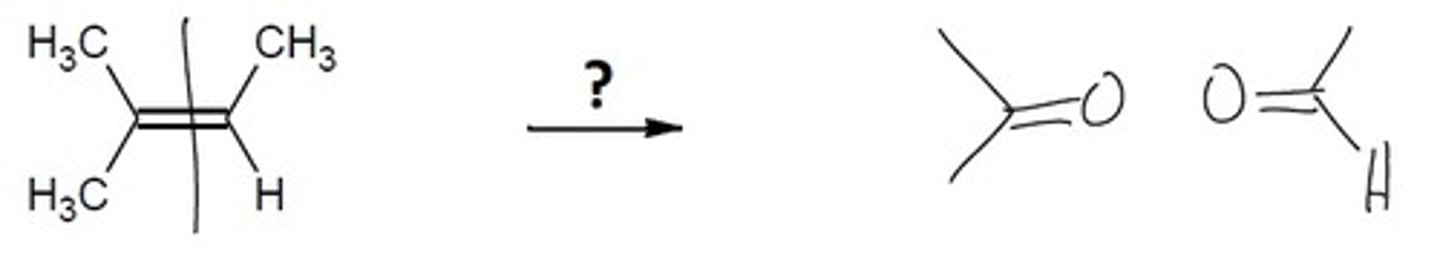
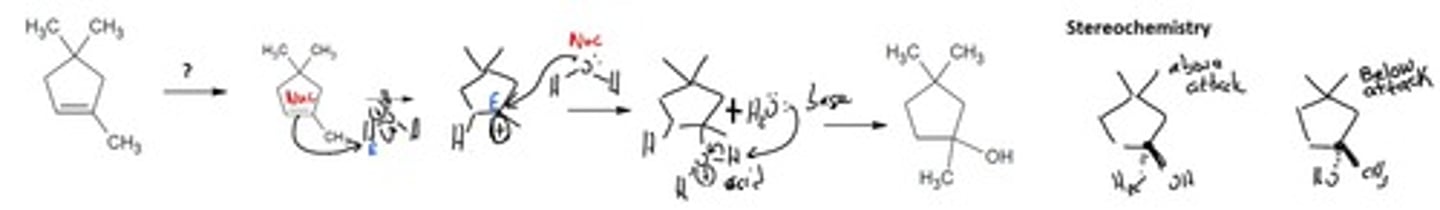
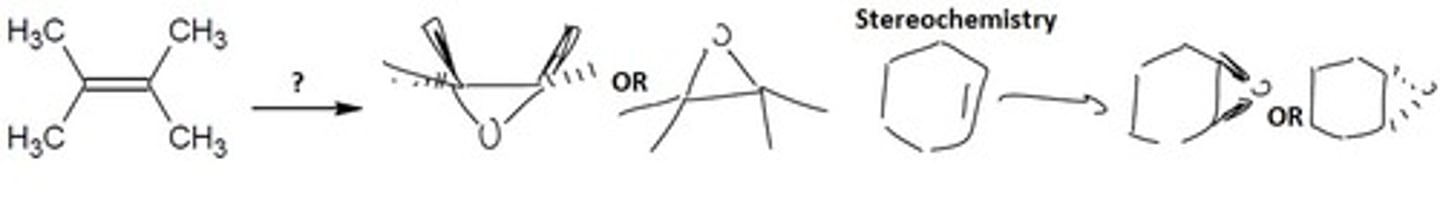
Epoxidation (mCPBA and from the halohydrin)
Alkene Addition Reaction
Oxidation Reaction
mCPBA
Formation of a strained ether called an 'epoxide' from an alkene
Final Product: Has ring strain. Adds 1 oxygen on the same side of the molecule bonded to both carbons.
Hydrogenation Reduction (H2, Pd/C)
Alkene Addition Reaction
Reduction Reaction
H2, Pd/C
SYN addition of Hydrogens across a double bond
Adds 2 Hydrogens on the same side of the molecule bonded to each carbon.
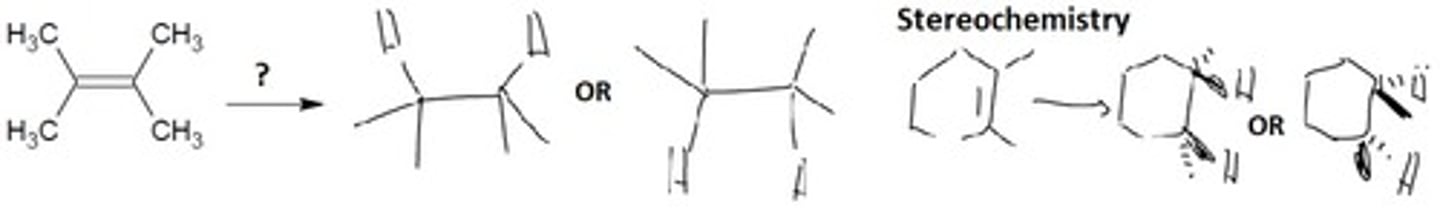
Deprotonation of Alkynes
Alkyne Chemistry
NaNH2
Deprotonates the alkyne
Nucleophile: deprotonated alkyne
Electrophile: alkyl halide
Final Product: A deprotonated alkyne
Note: Equilibrium favors weaker acids with higher pKa values.
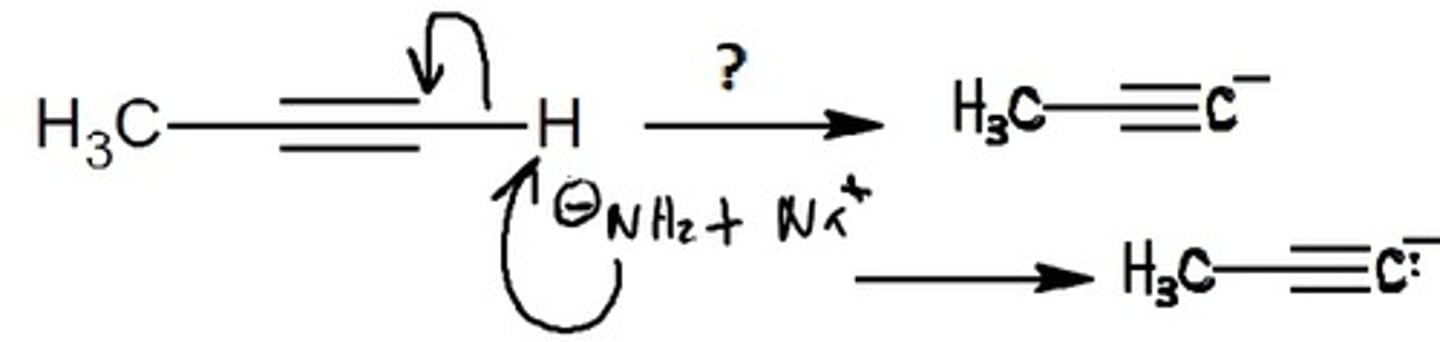
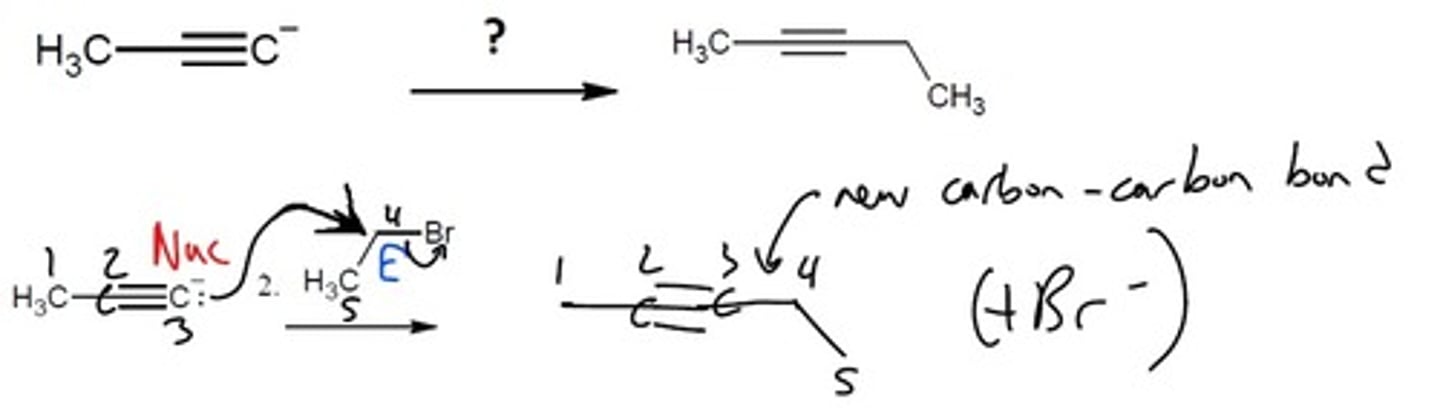
Carbon-Carbon bond formation from acetylide anions
Alkyne Chemistry
BrCH2CH3, halogen-carbon chain
Attacks the electrophile
Nucleophile: deprotonated alkyne
Electrophile: alkyl halide
Final Product: An Alkyne with more newly added carbons
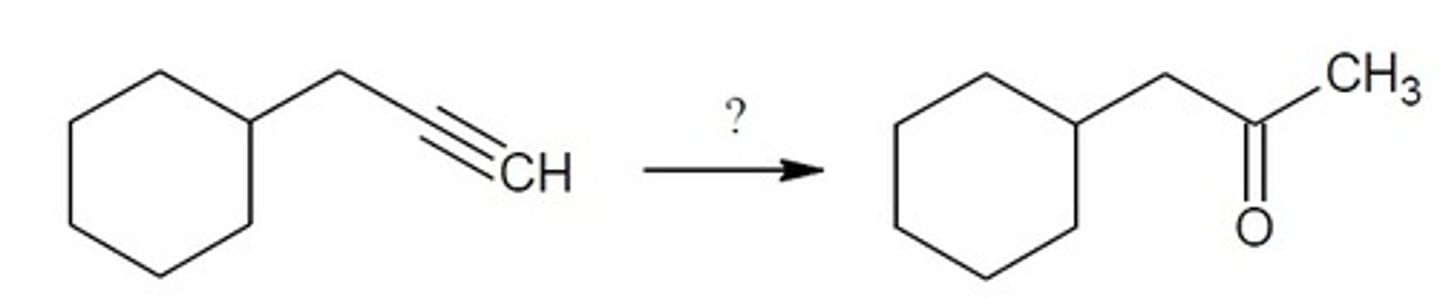
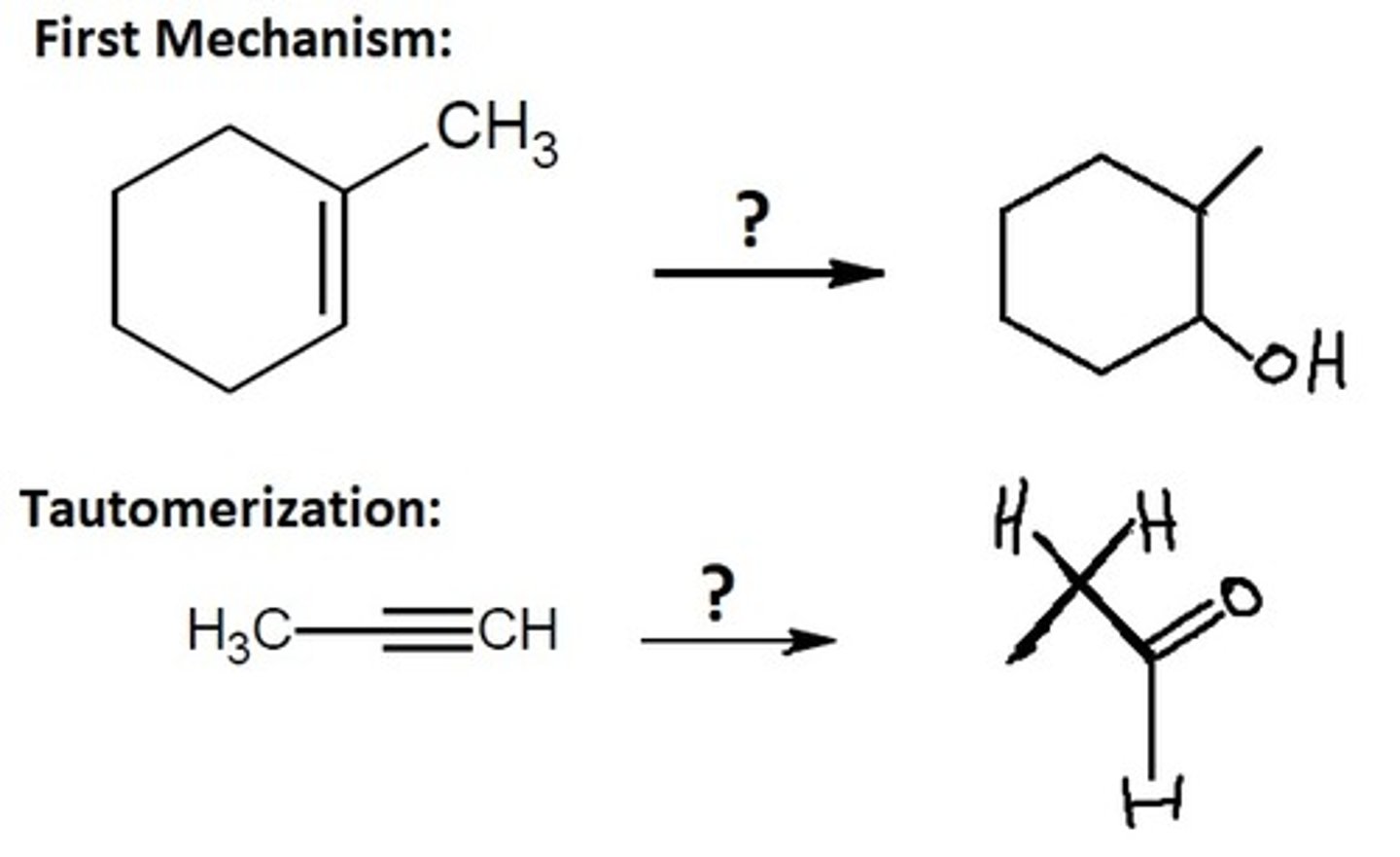
Hydration (tautomerization mechanism)
Alkyne Chemistry
HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
Creates a Markovnikov enol that tautomerizes
Final Product: ketone
(C=O on the MORE substituted carbon)
know the tautomerization mechanism
Hydroboration, Oxidation (tautomerization mechanism)
Alkyne Chemistry
1. BH3 or R2BH (R is sterically bulky) 2. NaOH, H2O2
Creates an Anti-Markovnikov enolate that tautomerizes
Final Product: aldehyde
(C=O on the LESS substituted carbon)
know the tautomerization mechanism
Hydrohalogenation
Alkyne Chemistry
HBr or 2 mol HBr
Creates a Markovnikov product OR a double Markovnikov product
Final Product: reduces an Alkyne to an Alkene with HBr and reduces an Alkene to an Alkane with 2 mol HBr PLUS it adds a halogen
(C-Br on the MORE substituted carbon)

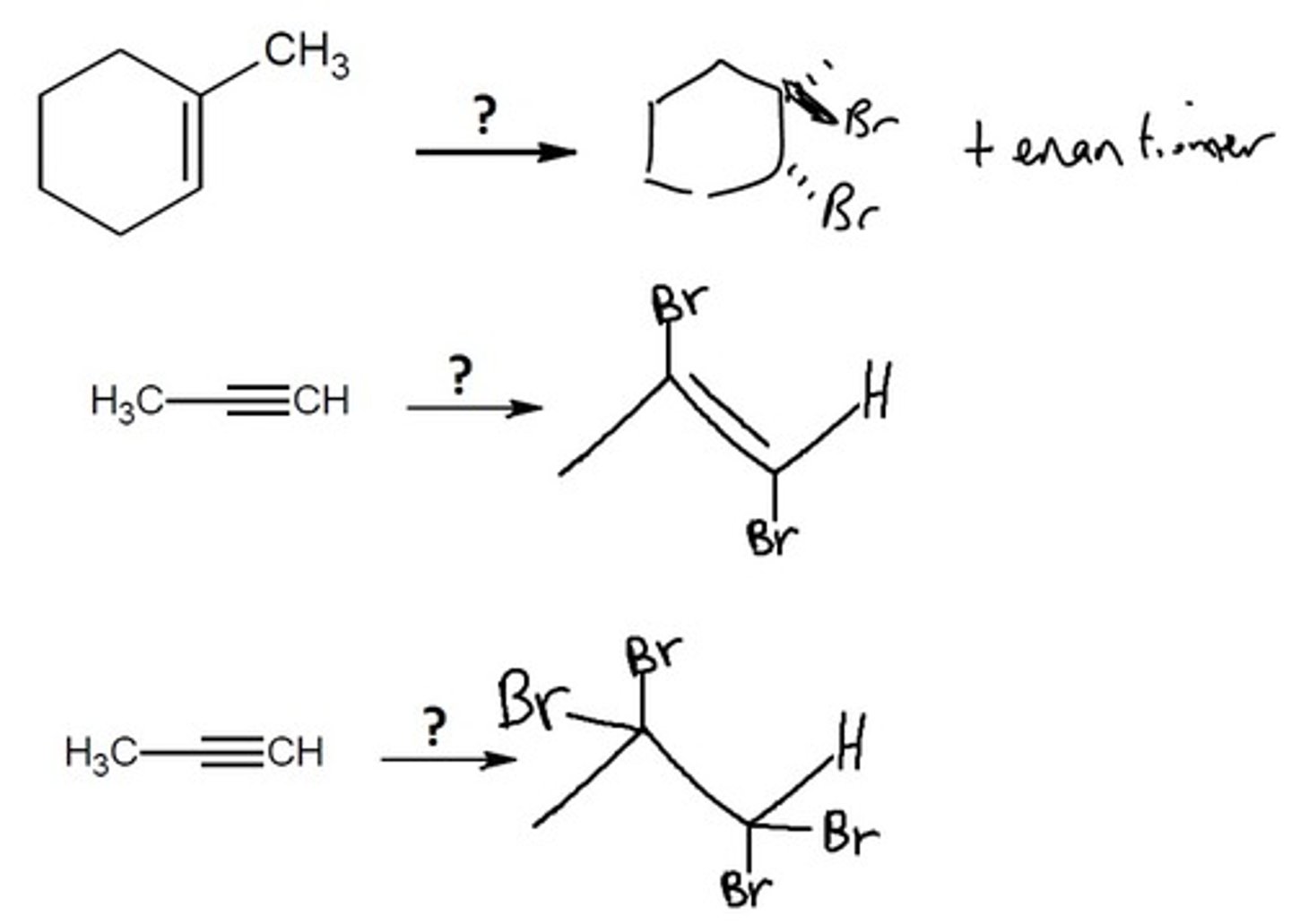
Halogenation
Alkyne Chemistry
Br2 or 2 eq Br2
Creates a TRANS product OR a double TRANS product
Final Product: reduces an Alkyne to an Alkene with 2 halogens added trans of the molecule and reduces an Alkene to an Alkane with 2 mol halogen with 4 halogens added trans of the molecule
(Br attack on opposite sides of the molecule)
Complete Reduction (H2, Pd/C)
Alkyne Chemistry
H2, Pd/C
Completely Reduces to only sigma bonding
Final Product: Reduces an Alkyne to an Alkane with 2 added hydrogens across the double pi bond twice (both carbons on both sides of the triple bond get an added H2)
NOTE: under these conditions, you cannot stop after the first reduction.
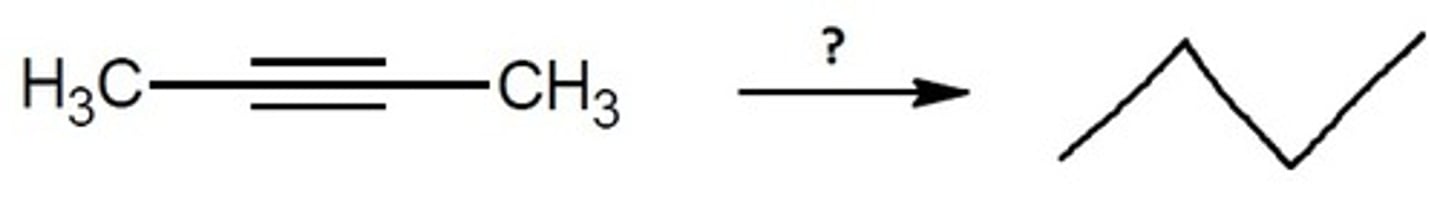
Cis- Reduction (H2, Lindlar)
Alkyne Chemistry
H2, Lindlar's Catalyst
SYN addition of H2 across a double pi bond
Final Product: Reduces an Alkyne to an Alkene with 1 added hydrogen across the double pi bond on the same side
(both carbons on both sides of the triple bond get one added H)
NOTE: poisons the catalyst

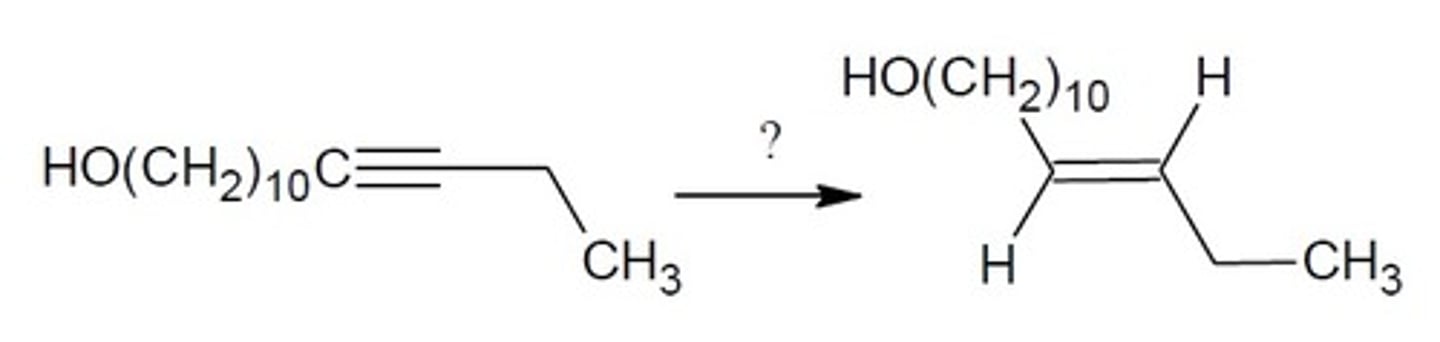
Trans- Reduction (Na, NH3)
Alkyne Chemistry
Na, NH3 (This is sodium metal, ammonia)
ANTI addition of H2 across a double pi bond
Final Product: Reduces an Alkyne to an Alkene with 1 added hydrogen across the double pi bond on the opposite side (both carbons on both sides of the triple bond get one added H).
Radical Halogenation of alkanes
Radical Chemistry
1. Br2 2. light (hv), or heat (Δ), or ROOR
HIGHLY selective radical reagent
1.) A hydrogen atom is pulled off, leaving a radical in its place
2.) A halogen then adds at the radical position
Final Product: One halogen is added at the radical position
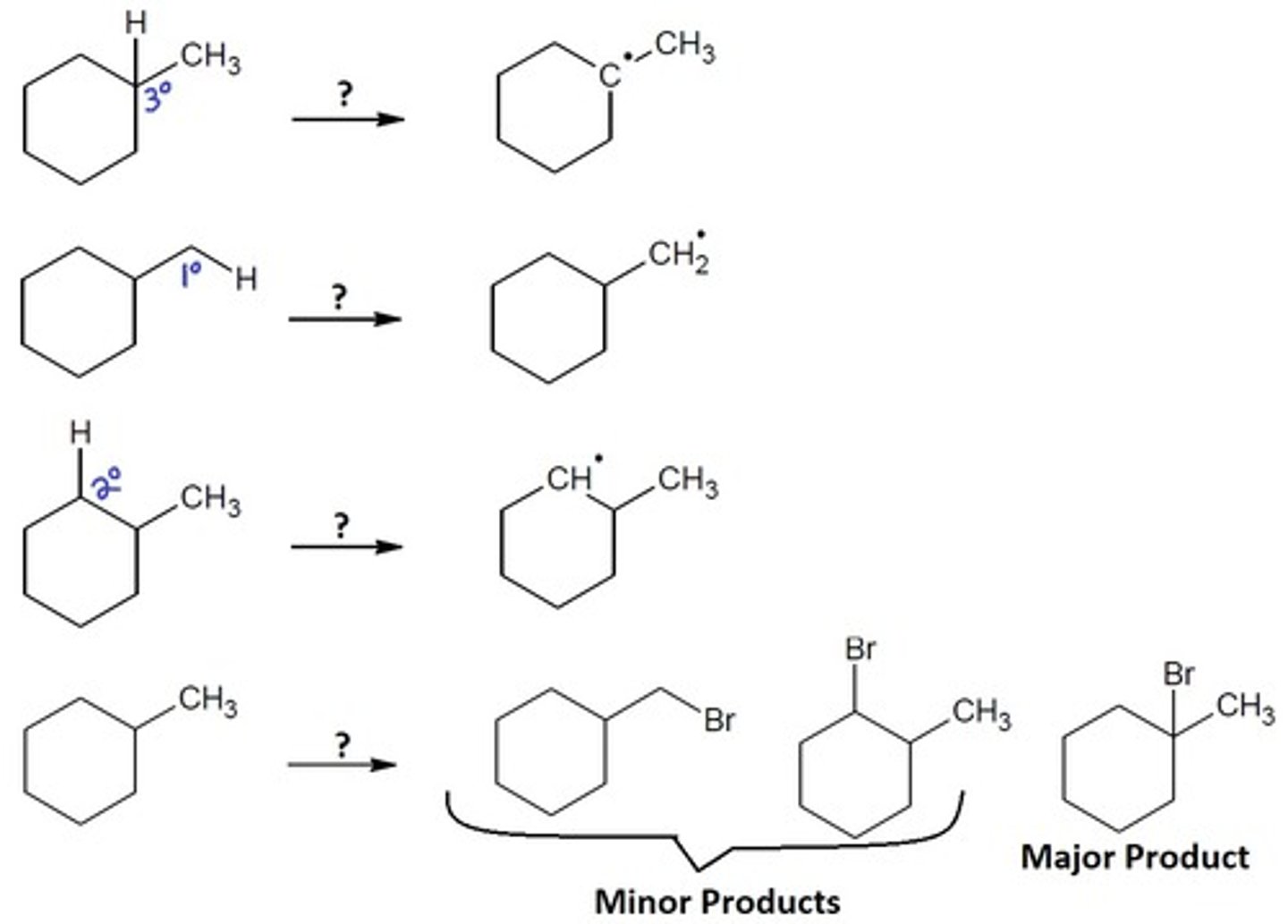
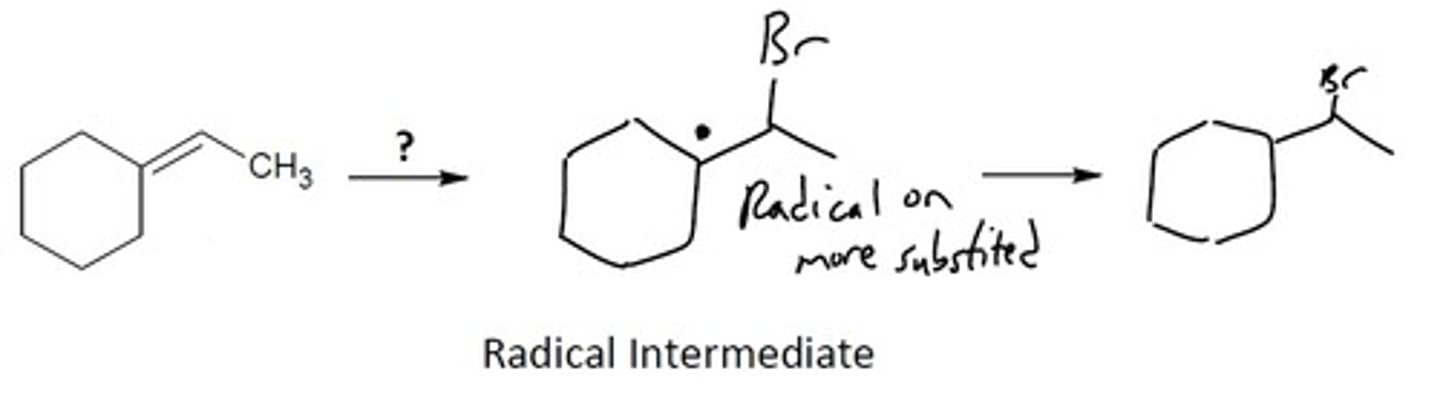
Radical Anti-markovnikov addition of HX
Radical Chemistry
1. HBr 2. light (hv), or heat (Δ), or ROOR
Creates an Anti-Markovnikov product
Final Product: Puts the halogen on the LEAST substituted carbon and puts a radical on the MORE substituted carbon.
SN1
Alkyl Halides
Step by step reaction
Rate = k [RX]
Alkyl Halides: Prefers the more substituted carbon because there is more carbocation stability. The halides must be either a: 2° or 3°
Nucleophile must be: weak
Stereochemistry: Racemic mixture of enantiomers
Final Product:

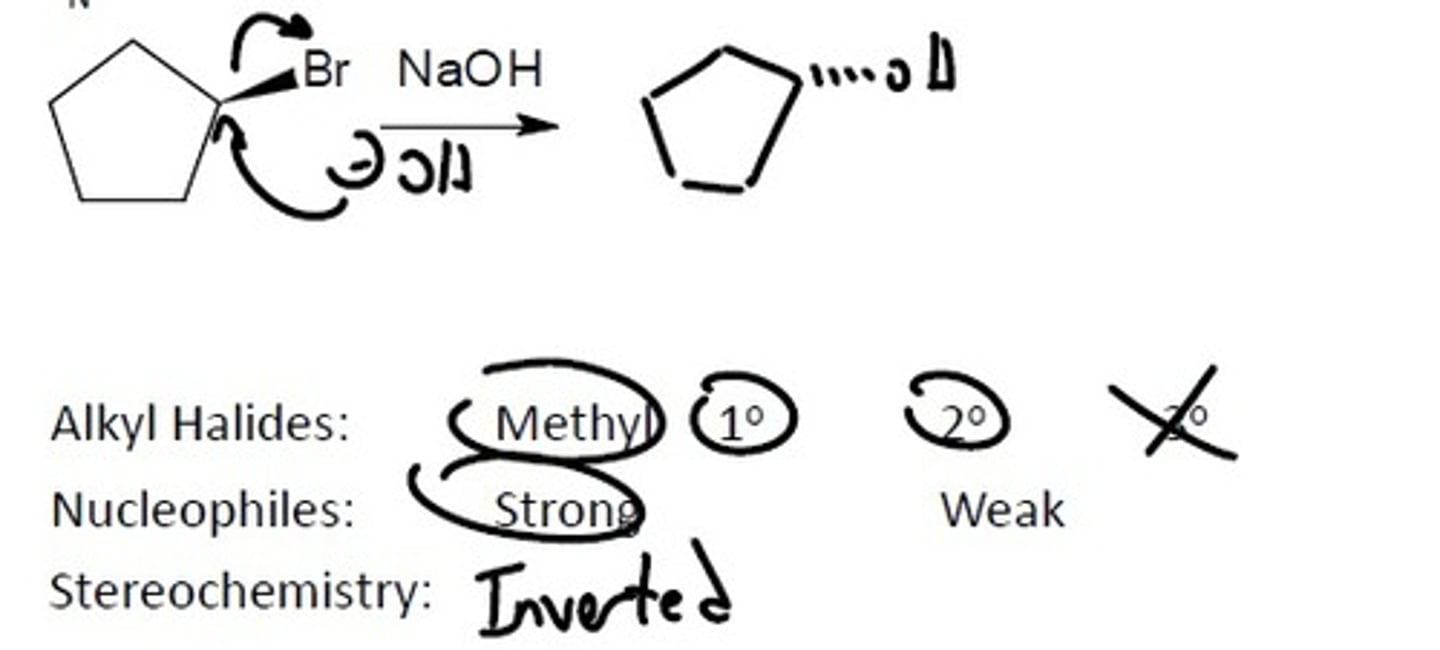
SN2
Alkyl Halides
Happens all at once
Rate = k [RX] [Nuc]
Alkyl Halides: Prefers the least substituted carbon because there is the least steric strain. The halides must be either a: Methyl, 1°, or 2°
Nucleophile must be: Strong
Stereochemistry: Inverted
Final Product:
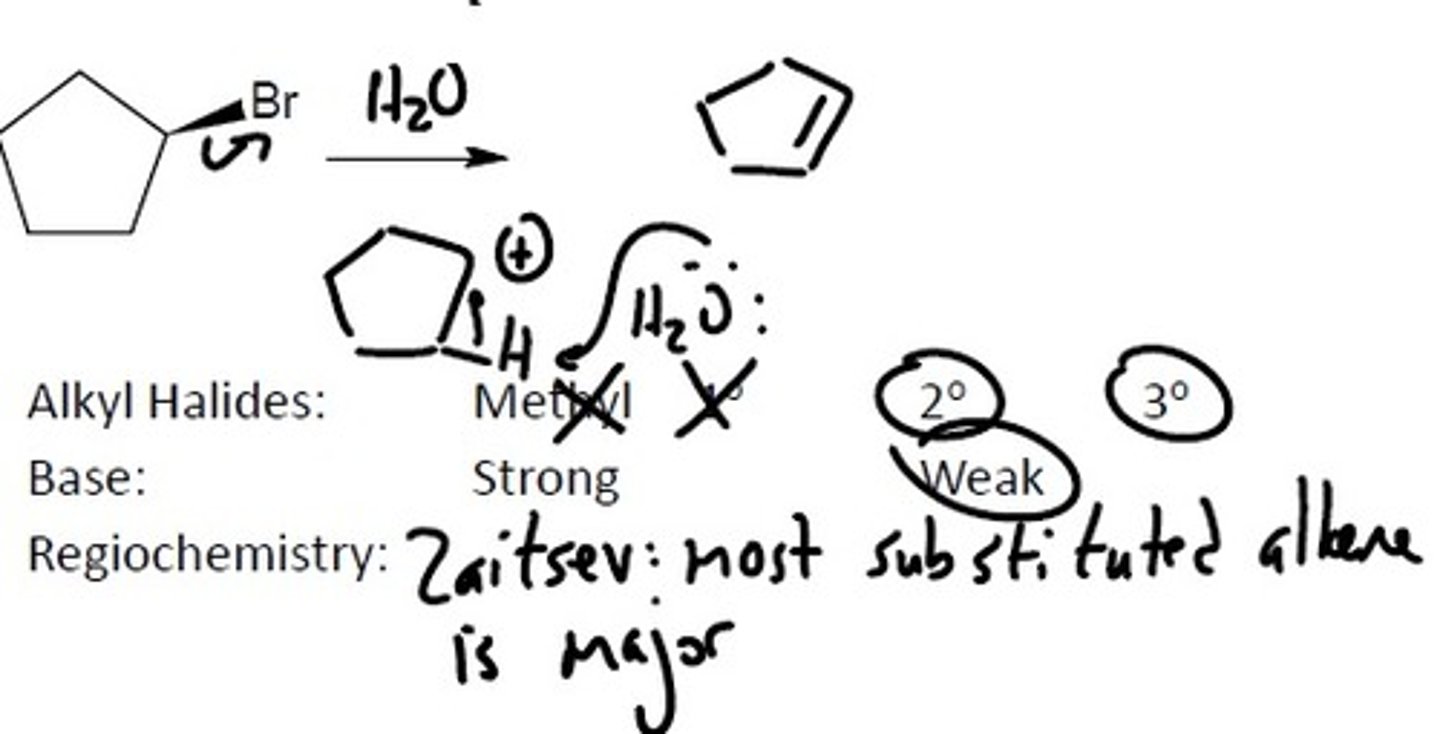
E1
Alkyl Halides
Alkyl Halides: Prefers the more substituted carbon because there is more carbocation stability. The halides must be either a: 2° or 3°
Base must be: Weak, Stable
A weak, stable base means that it is not charged and is stabilized by ARIO
Regiochemistry: Zaitsev's Rule- Most substituted alkene is the major product
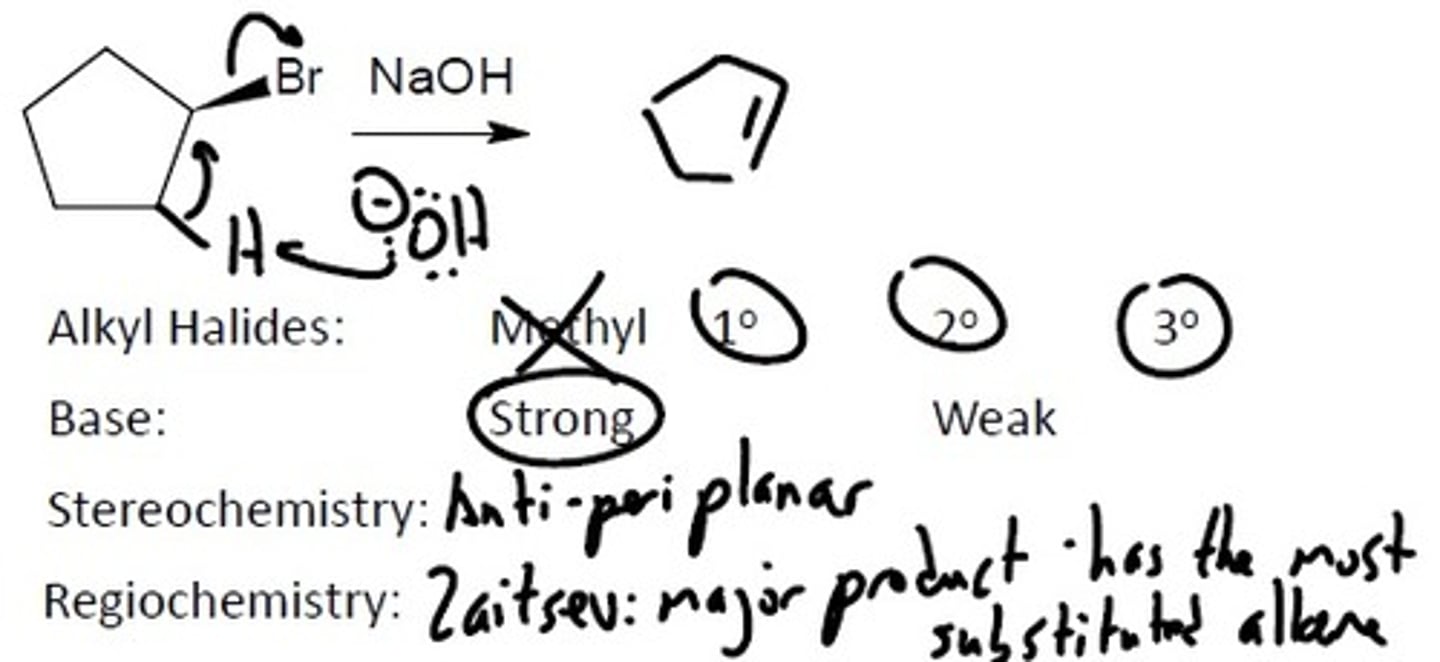
E2
Alkyl Halides
Alkyl Halides: Prefers the more substituted carbon because there is more carbocation stability. The halides must be either a: 1°, 2°, or 3°
Base must be: Strong, Unstable
A strong, unstable base means that it is charged and is not stabilized in any way by ARIO
Stereochemistry- Anti-periplanar
Regiochemistry: Zaitsev's Rule- Most substituted alkene is the major product
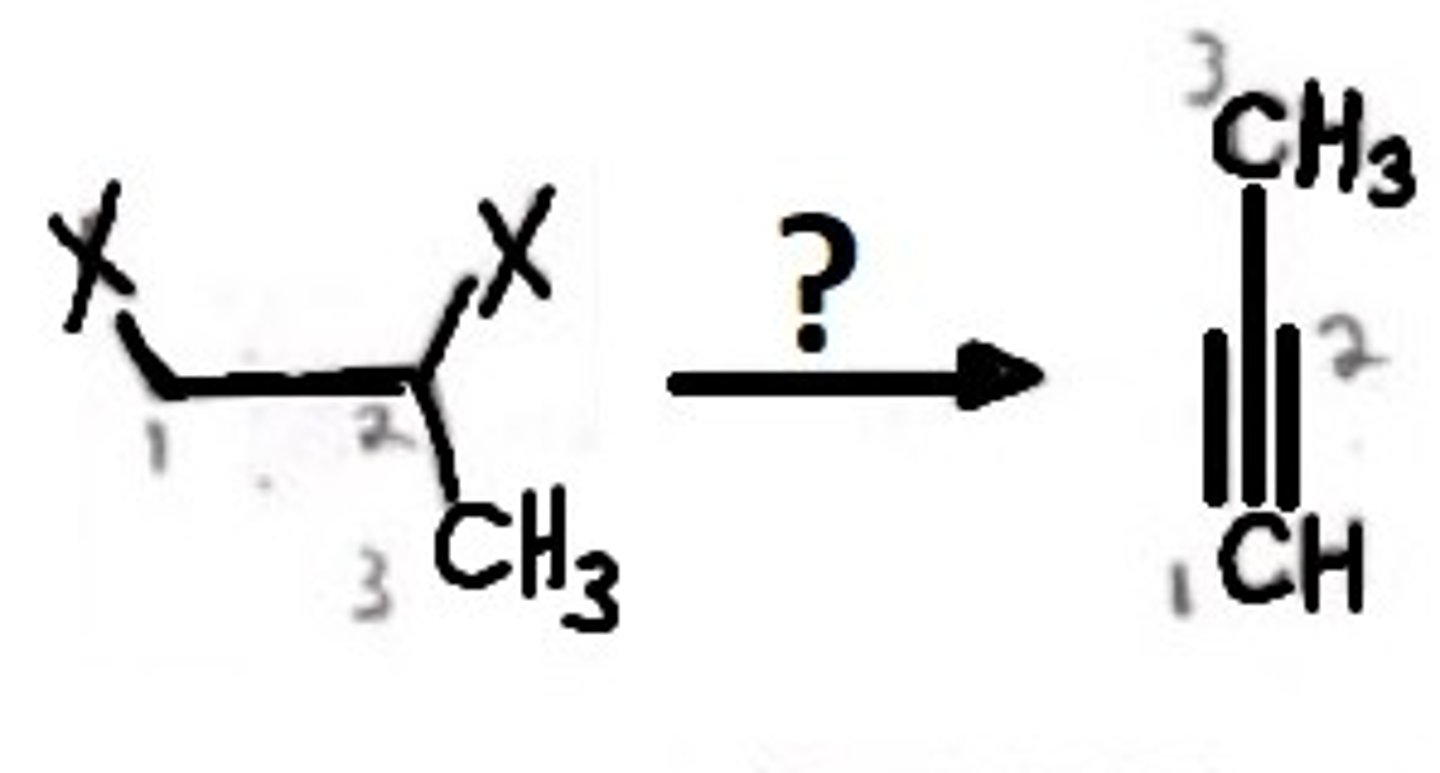
Formation of Alkynes from dihalides
Alkyl Halides
NaNH2
Alkane to an Alkyne
Final Product: an alkyne is formed by removing the halogen groups and adding bonds in their place
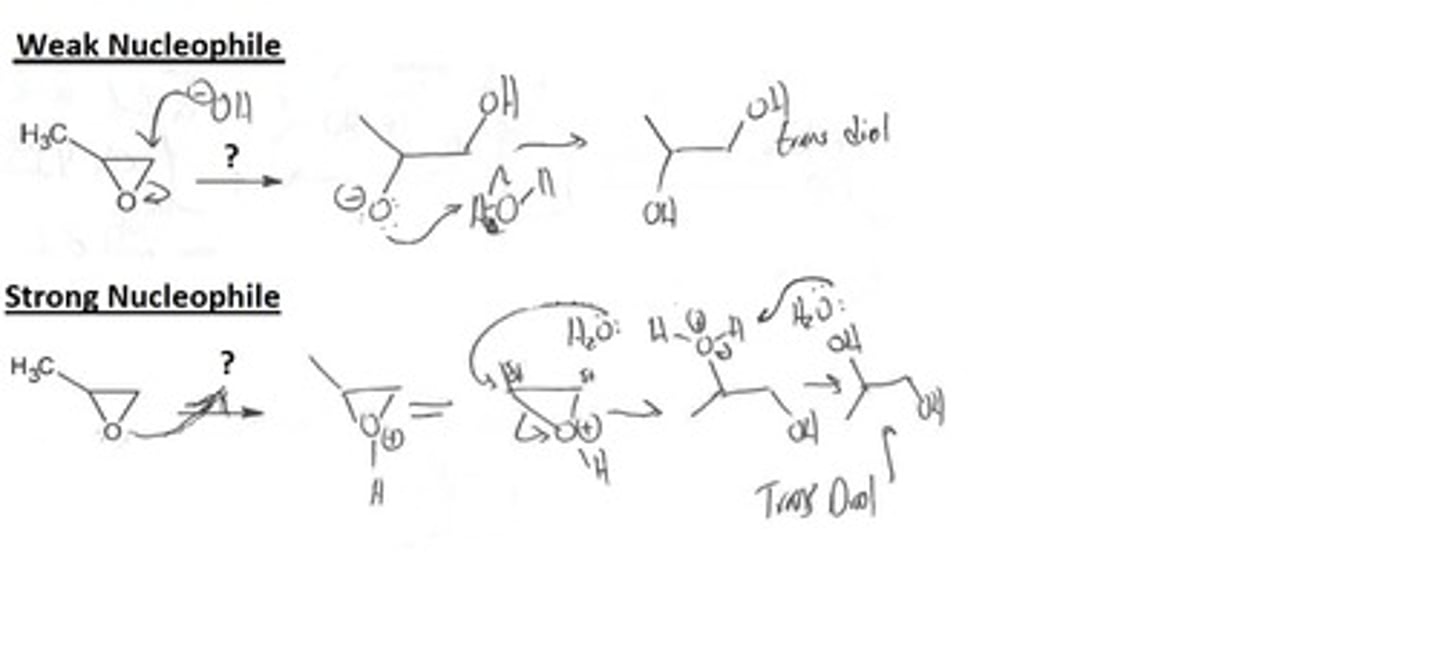
Epoxide Opening: weak nucleophile, acidic conditions
Epoxides
Weak Nucleophile and H+
1.) protonation
2.) nucleophilic attack on less substituted carbon
3. Deprotonate
ANTI- forms a trans-diol
Think SN1: bond lengthens so that the substitution happens at the more substituted carbon

Epoxide Opening: strong nucleophile
Epoxides
Strong nucleophile and H2O
1.) protonation
2.) nucleophilic attack on less substituted carbon
ANTI- forms a trans-diol
Think SN2: reduce sterics and attack the less substituted carbon

Trans diol formation from epoxides
Epoxides
1.) protonation
2.) nucleophilic attack on more/less substituted carbon depending on whether it is a strong (less substituted)or weak (more substitued) nucleophile
3. Deprotonate (if necessary- weak nucleophile and H+)
Final Product: Adds two OH groups trans