Marketing Strategies and Differentiation
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is the goal of strategic planning in marketing?
To align goals, capabilities, and market opportunities
What is benchmarking?
Comparing with best practices to improve
Which Ansoff strategy uses existing products and existing markets?
Market Penetration
In the BCG Matrix, what is a “Star”?
High growth, high market share
Process of Strategic Planning
Organization + KPI’s + Goals/Objectives
Where to compete in the strategic planning?
Arena (Knowing the industry, the competitors…)
A process that maintains strategic fit between:
firm’s goals, its capabilities, and changing market opportunities
Why is strategic planning important?
🙂 : Every time you buy something, you have an experience with the Product/Service, the client needs to be happy with the brand
How does marketing come into the picture?
If they don’t have customers, the brand doesn’t exist. Market = customers
Product vs Market - oriented business definitions
Benchmarking
Comparing the firm’s products and processes to those of competitors or leading firms in other industries to identify best practices and find ways to improve quality and performance.
What do you benchmark?
The competition of the firm, they sell similar product. The comparison is not only with the direct competition but also with the best in the market
Determine the objectives and relative importance of:
Current profitability
Market share growth
Cash flow
Technological leadership
Service leadership
Assessing Competitors
Determine objectives and relative importance of:
Current profitability
Market share growth
Cash flow
Technological leadership
Service leadership
Among others
Competitor’s Strategy
Pay attention to what the competitors are doing
Firm’s resemblance (is it similar to me and how?), then differentiate
Strategic group
A firm must identify:
Value delivered
P/S quality, features, and mix
Customer service
Pricing policy
Distribution coverage
Sales force strategy
Adveritising
Sales promotion
Online and social media programs
R&D
Manufacturing
Purchasing
Financial
Assessing competitor’s strenghts + weaknesses
What can competitors do?
Gather information on past: strategies, performance,and goals
Secondary data (INEGI…)
Personal experience
Word of mouth
Primary research: suppliers, customers, dealers
Check competitors’ online sites
Benchmarking
Estimating competitor’s reactions
What will our competitors do?
Develop a “competitor mentality” to anticipate moves
Selecting competitors to attack and avoid
With whom is better to compete?
Weak competitors
Strong competitors
Selecting competitors to attack and avoid/assess their strengths + weaknesses
Customer value analysis
Customer Value Analysis
Determine the benefits and attributes of target customer (what they really value?)
What is the importance of such benefits & attributes (rating grade/level). (How much you rate the product based on the benefits)
Assess the firm’s performance versus competing offers in those benefits & attributes (Knowing where you are standing)
Eventually everything competes against everything
Competing Partiners
Good or bad competitors?
Companies benefit from competitors
Share product development
Legitimize new technologies (like the USB-C cable)
Increase total demand
Good = Play by the industry rules
Bad = the opposite; play by their own rules
Finding an uncontested market
Create different P/S with no direct competition = blue ocean
Competitiveness Matrices
Strategic planning is defined as the administrative process to create and maintain a fit betweenthe objectives and resources of the organization and the changing opportunities of the market.
Strategic planning is the foundation of all marketing strategies and decisions. These decisions affect your resource allocation and, ultimately, your long-term financial success.
There are several tools that allow companies to manage the strategic direction of their business.
Ansoff Strategic Opportunity Matrix
It is a way of formulating alternatives by matching products to markets. Companies can explore 4 options
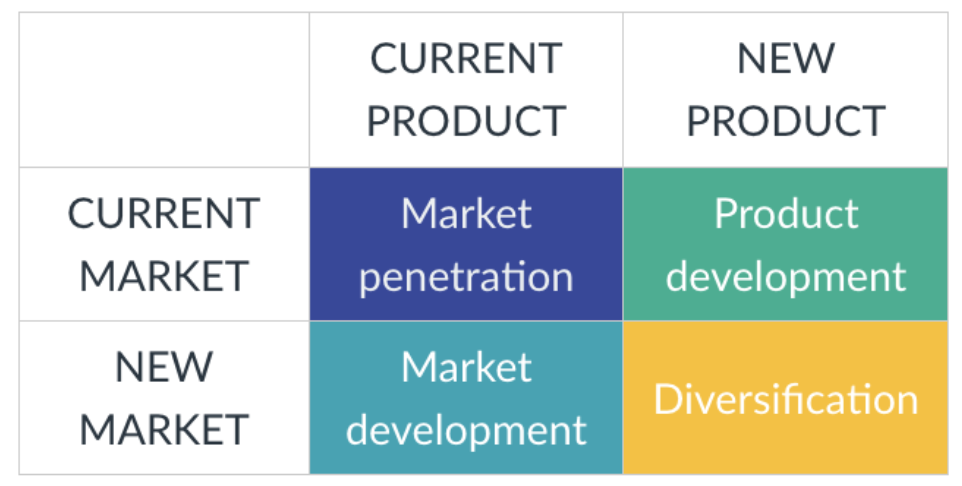
Market Penetration
When both the Market and the Product are current, that is, they already exist, the company applies the Market Penetration alternative, seeking to increase market share with existing customers.
That the same customers buy more of the same product
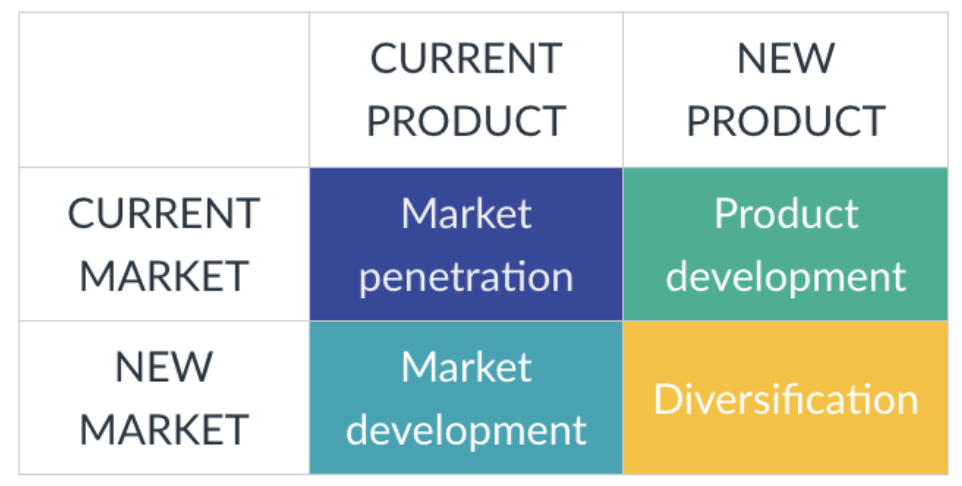
Market Development
When the Product is current, it already exists, but the Market is new, the company seeks to attract new customers for that product.
That other customers buy the same product
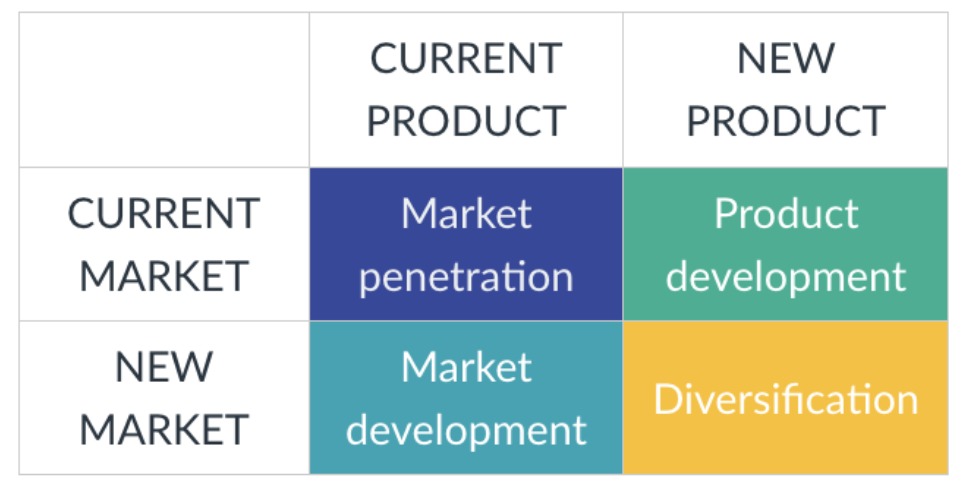
Product Development
When the Market is current, it already exists, but the Product is new
That the same customers buy the new product
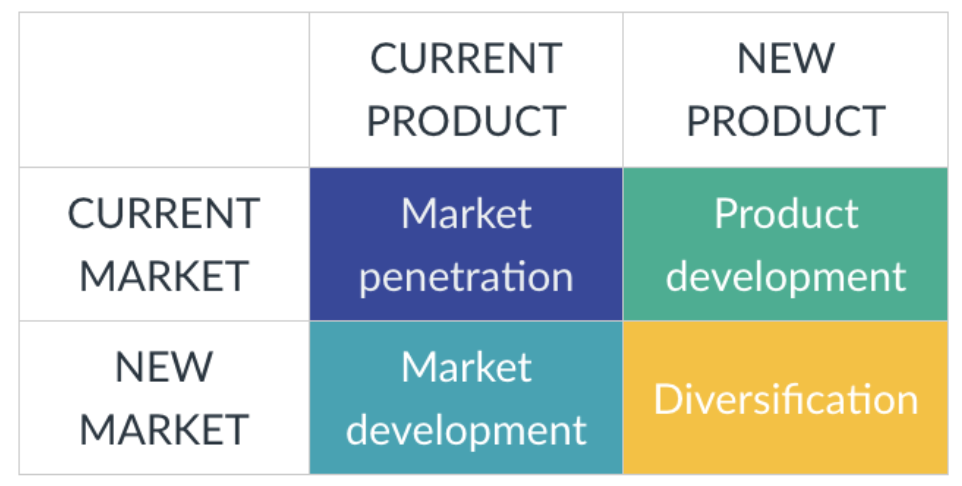
Diversification
When both the market and the product are new
Let new customers buy the new product
Portfolio Matrix or BGC (Boston Consulting Group)
Companies must find a balance between their products that allows them to generate the desired global growth and profits, but with an acceptable level of risk.
Some products generate huge amounts of money and others need it to fuel their growth.
The challenge is to find the balance for the best possible long-term performance.
Each product is classified in this matrix based on its growth and market share, present or forecast.


In the BCG Matrix, what is a “Star”?
It is a rapidly growing market leader. It generally produces large profits, although it takes a lot of money to finance its rapid growth.
The best practice is to protect existing market share, reinvest income to perfect the product, improve distribution, and increase promotion and production efficiency.
In the BCG Matrix, what is a “Money Cow”?
You make more money than you need to maintain your market share.
It is advisable to maintain market dominance as a leader and apply technological improvements to the product.
In the BCG Matrix, what is “Unknown”?
It has fast growth, but with low profit margins. It has a low market share in a high growth industry. The unknowns need a lot of money, if they are not supported, over time they can become a dog.
The option is to invest a lot to obtain a greater market share, if it is not achieved, you have to get rid of the product.
In the BCG Matrix, what is “Dog”?
It has little growth potential and a small market share. Over time, most of them leave the market.
The option is to harvest or discard.
Once the products are classified in the matrix, future resources are assigned to each one according to the most appropriate strategy:
Build: If the product has the potential to become a star.
Keep: If the product is a very successful cash cow, the goal would be to maintain market share so that the company can profit from the money it generates.
Harvest: This strategy is for all products except the stars. The goal is to increase short-term profits without worrying too much about their long-term effect.
Discard: It is often recommended to ditch low-share products in slow-growing markets. Unknowns and dogs are ideal for this strategy.
McKinsey Matrix, Market Appeal or GE (General Electric)
This model uses the dimensions of Market Appeal and Company Strength. It allows identifying how well the company is positioned to take advantage of market opportunities.
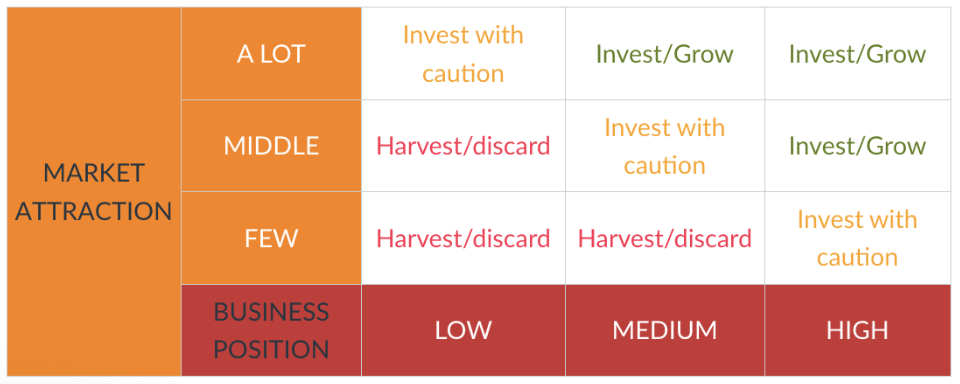
Secondary Information
Information that has been collected for any other purpose, that is, it already exists.
"Data previously collected by others" can be found if we browse the Internet, taking special care that the sources are reliable.
A good example is the databases that the Monterrey TEC has: Passport (Euromomitor), EBSCO
(Business Source Ultimate), Gartner Intraweb, EIU and Springer among others.
Primary Information
Is that once the secondary information has been obtained, the researcher specifically defines what he or she needs to know and collects this type of information through the following four techniques
Original information that is collected for a specific purpose or for a specific research project. "Data generated for the first time by the researcher"
Observation
Research method based on four kinds of observation:
People watching people
People who observe an activity
People-watching machines
Machines that observe an activity
Process for carrying out Observations | |
|
Focus Groups
From 7 to 10 people who meet the desired characteristics participate in a group discussion led by a moderator.
Process for carrying out Observations | |
|
Experiments
Method by which the researcher modifies one or more variables while observing the effects that these modifications produce in another variable
Surveys
Most popular technique for gathering data. In a survey, the researcher interacts with people to find out facts, opinions, and attitudes.
All the information collected, both secondary and primary, can be classified as quantitative or qualitative.
Qualitative information | Quantitative information |
It is objective, descriptive, provides figures, and measures variables. | It is subjective, delves into the problem, provides data, describes motivations, thoughts, and attitudes |
What it means to segment a market?
Common characteristics, needs, etc.
Individual?
Massive?
… and what is in between?
Meaningful
Identifiable
Brand manager. Marketing mix that is useful to the customers in that segment
Important?
Segmentation Criteria
Substantive: size
Measurable: how many?
Reachable: communication between brand + customers
Criteria to Segment the customer market
Characteristics pertaining to customers
Bad segmentation? =
1 variable can be used (age, gender, education, etc.)
1 variable = simple to use and understand
A lot of variables = the opposite
Trends: more variables = more precision
Secondary information?
Geography: region, size, density, weather
Demographic: age, gender, income, ethnicity, life cycle
Psychographic: personality (habits and attitudes), motives (emotions), lifestyles (time spent, important things around me, beliefs, education), geodemography (geography + demography + lifestyle)
Benefits: Which benefits are sought?
Usage: buy or consume (potential customers, past customers, first-time consumers, irregulars, etc.)
Segmentation: 80/20
Choose the product/service/market
Determine the segmentation bases. Managerial insights, creativity, market knowledge; variables?
Choose segmentation descriptors. For instance: demographic (age, gender, income)
Profile and analysis of the segment. Market size, expected growth, buying frequency, brand usage and loyalty, expected sales, and profit potential
(choose) Segment of the market. Natural step in the segmentation process. Impact for the company
Design, implementation, maintenance of the marketing mix
Objective to segment a market
Non-differentiated objective
Massive
1 marketing mix
Similar customers/clients
Focused Objective
Niche selection
Efforts towards the niche
Maybe more profitable
Multi-objective
2 or more segments
Same number of marketing mixes
Objective = target
Promotion and Communication Strategies
The promotional strategy is closely related to the communication process. As human beings we attribute meaning to feelings, ideas, facts, attitudes, and emotions. Communication is the process we use to exchange or share meanings.
The communication process consists of several steps. When a company wants to transmit a message to a target audience, it encodes that message using language and symbols that can be recognized by the recipient to whom that message is addressed, and then they send it through a communication channel. Noise in the transmission channel can distort the message that the source intends to transmit.
Reception occurs when the message fits within the receiver's frame of reference. It decodes the message and usually provides feedback to the source.
Normally the feedback is direct in the case of interpersonal communication and indirect in the case of mass communication.
Social media has increased the amount of feedback that businesses receive.
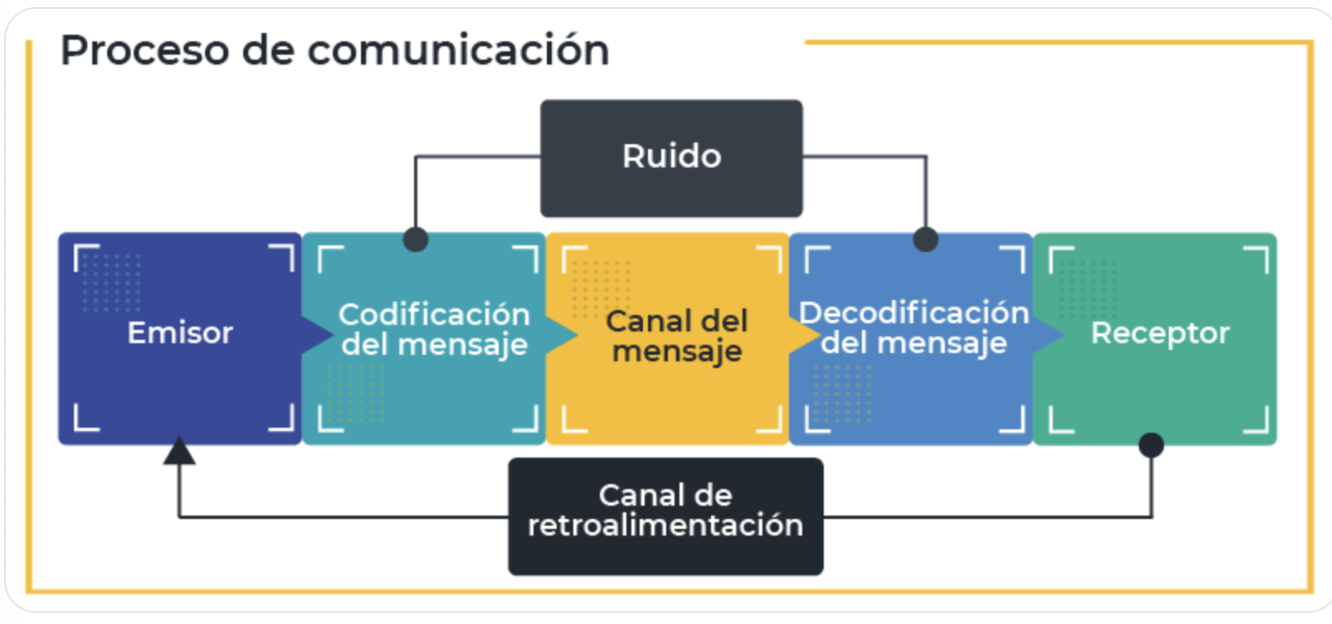
Communication process
The promotion strategy of each company is a plan to optimally use the promotional elements to achieve the marketing goals that are always linked to the overall goals of the company.
Marketing always starts from the global goals to combine the elements of the promotion strategy and make the ideal mix to reach the target market in the most efficient way.
The main function of the promotion strategy is to convince the target customers that the goods and services that the company offers represent a competitive advantage over those of the competition.
Step 1 in developing effective marketing communications
Identify the target audience:
Affect the communicator’s decision on:
What will be said
How it will be said
When it will be said
Where it will be said
Who will say it
Determine the communication objectives:
The buyer might be in any of these steps:
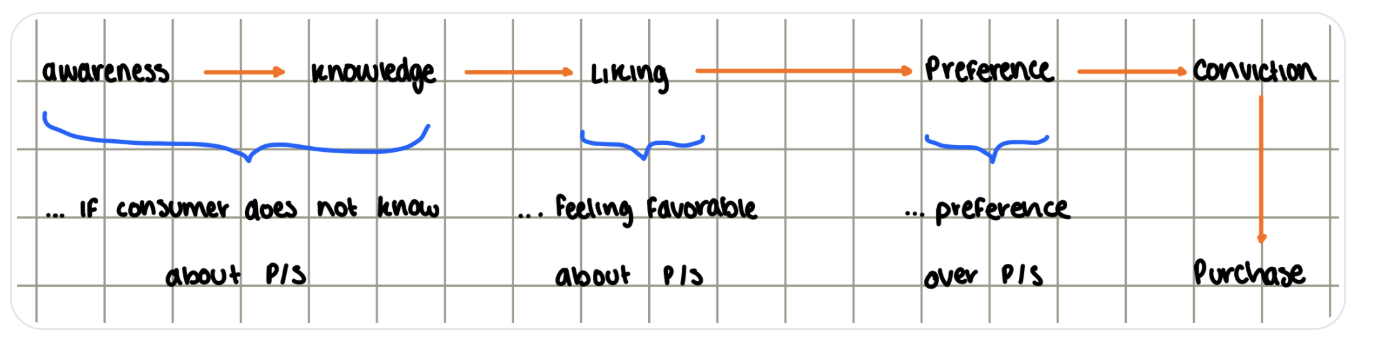
Design a message:
Message content
Message structure
Draw conclusions or leave it to the audience
Present strong arguments first or last
Present a one-sided argument (positive), or two-sided (pros+cons)
Message format
Print, TV, radio, etc
Choosing communication channels and media
Personal communication channels:
Word of mouth (personal or digital)
Independent experts, consumer advocates, bloggers
Buzz marketing: opinion leaders
Non-personal communication
Newspapers, magazines, direct mail
Selecting the message source
Message delivered by a highly credible spokesperson
Producto
Todo lo positivo y negativo que obtiene cuando una persona realiza un intercambio
Plaza (distribución)
Poner los products a disposición de los clientes en el lugar y el momento que deseen
Precio
Aquello que se sacrifica en un intercambio para adquirir un bien o servicio
Promoción
Comunicación que informa, persuade y recuerda un product a los compradores, con el propósito de influir en la opinión o generar una respuesta
Mezcla promocional
La combinación de herramientas de promoción utilizadas para llegar al mercado metas y cumplir las metas globales de la organización:
Publicidad
Relaciones públicas
Ventas personas
Promoción de ventas
Medios Sociales
Non-differentiated objective
Massive
1 Marketing mix
Similar customers / clients
Focused objectives
Niche-selection
Efforts towards the niche
Maybe more profitable
Multi-objective
2 or more segments
same number of marketing mixes
objective=target
AIDA
Attention
Interest
Desire
Action = Buy
Advertising
Massive impersonal and one-way communication about a product or organization that is borne (paid for) by the company
Public Relations
Marketing function that assesses public attitudes, identifies areas in the organization that might interest them, and executes a program of action to gain their understanding and acceptance
Personal Selling
A Purchase situation involving paid personal communication between two people trying to influence each other
Sales Promotion
Marketing activities, other than personal sales, advertising, or public relations, that encourage consumers to buy and increase the effectiveness of distributors
Social Media
Promotional (or not) tools used to facilitate online conversations between people
Paid Media: A kind of promotional tactic that is based on the traditional model of advertising, in which a brand buys space in the media
Earned Media: A kind of promotional tactic that is based on the model of public relations or free advertising, which causes customers to talk about products or services
Own Media: A New kind of promotional tactic that relies on brands publishing their own content in order to maximize brand equity for customers
Publicity
It is a way of getting the media to disseminate our brand for free
Omnichannel Marketing
Omnichannel Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that consists of harmonizing sales channels, organizing information from all channels to facilitate data management and optimize the purchase strategy.
Customer-focused
Puts the customer at the center of all channels for a seamless experience
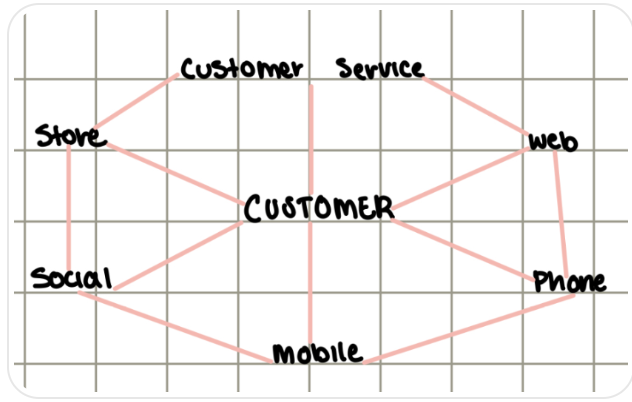
Multichannel Marketing
Company-focused
Starts with your business and trickles down to customers
What is the main purpose of customer value analysis?
Determine what customers truly value
What is a “good competitor”?
Plays by industry rules
Which Ansoff strategy is used when the product is new but the market alredy exists?
Product development
What are the two dimensions of the GE/McKinsey Matrix?
Market Appeal and Company Strength
Which research method involves modifying variables to see their effects?
Experiments
What type of data is collected for the first time by reseacher?
Primary Information
What is the key difference between multichannel and onmichannel?
Company-focused vs Customer-focused