ATC Quiz Questions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
If a pilot informs ATC that they are performing a wind shear escape maneuver, what should the controller do?
Do not issue control instructions
Issue safety alerts and traffic advisories as needed
A pilot calls the associated approach control to enter Class C airspace. The controller responds with "[Callsign], standby." Is the pilot allowed to enter the Class C airspace?
Yes
What does a steady green light pointed at an aircraft indicate?
An arriving aircraft is cleared to land, or a departing aircraft is cleared for takeoff
Rank the braking action values in order from best braking quality to worst braking quality.
Good
Good to Medium
Medium
Medium to Poor
Poor
Nil
All jet-powered aircraft
Category III
All helicopters
Category I
Single-engine propeller driven weighing 12,500 pounds or less
Category I
Twin-engine propeller driven weighing 12,500 pounds or less
Category II
Small weight class
41,000 pounds or less
Large weight class
More than 41,000 pounds but less than 300,000 pounds
Heavy weight class
300,000 pounds or more
If a Category III aircraft is holding in position on the runway and another Category III has just departed the same runway, what is the minimum separation required before the holding aircraft can begin its takeoff roll (assuming the preceding aircraft is not a Super or a Heavy)?
6,000 feet and airborne
If a heavy aircraft just departed and a large aircraft will depart the same runway, how much time must pass before the large aircraft can begin its takeoff roll?
2 minutes
What is the cutoff for an arrival for the purpose of determining runway separation?
Once it crosses the runway/landing threshold
What is the minimum altitude allowed for an aircraft instructed to perform an altitude-restricted low approach?
500 AGL
When VFR aircraft operating below the minimum altitude for IFR operations requests an IFR clearance and the pilot informs ATC that they are unable to climb in VFR conditions to the minimum IFR altitude (MIA), what should the controller do?
Ask if the pilot is able to maintain terrain and obstruction clearance during a climb to the MIAand provide instructions accordingly.
What is the minimum vertical separation between two IFR aircraft below FL290?
1,000 feet
A westbound VFR aircraft is level at 6,500 feet. Is this the proper altitude for direction of flight?
True
Radar facilities may clear an aircraft to any fix at least 3nm outside the final approach fix (FAF) along the final approach course at an intercept angle of 30 degrees or less.
True
Circling instructions can be given to aircraft landing at uncontrolled airports.
False
An aircraft on an IFR flight plan is cleared for a practice instrument approach and has been assigned alternate climb-out instructions. What should the pilot do after completion of the approach?
Follow the alternate climb-out instructions
An aircraft on an IFR flight is requesting practice approaches that may disrupt the flow of other arriving and departing aircraft. What should the controller do?
Make a decision to approve or deny based on traffic conditions
VFR aircraft cleared for a practice instrument approach are not required to comply with VFR flight rules.
False
When are VFR aircraft authorized to execute the published missed approach procedure for a practice instrument approach?
Only if the pilot requests and the controller approves
When should a controller issue appropriate climb-out instructions to an aircraft planning a low approach or touch-and-go?
Before it begins its final descent
What methods of radar identification can be used for aircraft without a transponder?
Observing a departing aircraft target within 1 mile of the runway end at a controlled airport
Position correlation
Identifying turns
What methods of radar identification can be used for aircraft with a transponder?
Observing a departing aircraft target within 1 mile of the runway end at a controlled airport
Instructing the pilot to "IDENT"
Position correlation
Identifying turns
Assign a beacon code and observe the code change
Instruct a pilot to turn the transponder to "standby" then back to "normal"
(all of the above)
An action taken to transfer the radar ID of an aircraft to another controller when the aircraft will enter the receiving controller’s airspace and radio communications are transferred
handoff
An action taken to transfer the radar ID of an aircraft to another controller when the aircraft will enter the receiving controller’s airspace and radio communications are not transferred
Point-out
A term used to transfer the radar ID to another controller when the aircraft will be in close proximity to another controller’s airspace or affecting their traffic
traffic
Target resolution is a process used by controllers to ensure that radar targets do not touch.
True
Two small IFR aircraft at the same altitude within 40 miles of the radar antenna are required to be separated by a minimum of:
3 miles
A large aircraft operating directly behind a heavy aircraft at the same altitude must be a minimum of behind the heavy aircraft.
5 miles
Diverging courses separation (divergence) can be applied when aircraft are on the same or crossing courses and one of the aircraft has crossed the projected path of the other, and the angular difference between their courses is at least 15 degrees.
True
If the reported weather at the landing airport is showing a cloud ceiling of less than 1000 feet, how far from the final approach fix (FAF) must an aircraft be vectored to intercept the final approach course?
At least 3 miles outside the FAF
(The aircraft needs to be vectored to join the final approach course at least 2 miles outside the approach gate. The approach gate is 1 mile from the FAF. Therefore, the aircraft needs to join final at least 3 miles outside the FAF.)
If a pilot being vectored for an ILS approach requests that you vector them to intercept final within 2 miles of the approach gate, what is the maximum intercept angle allowed?
20 degrees
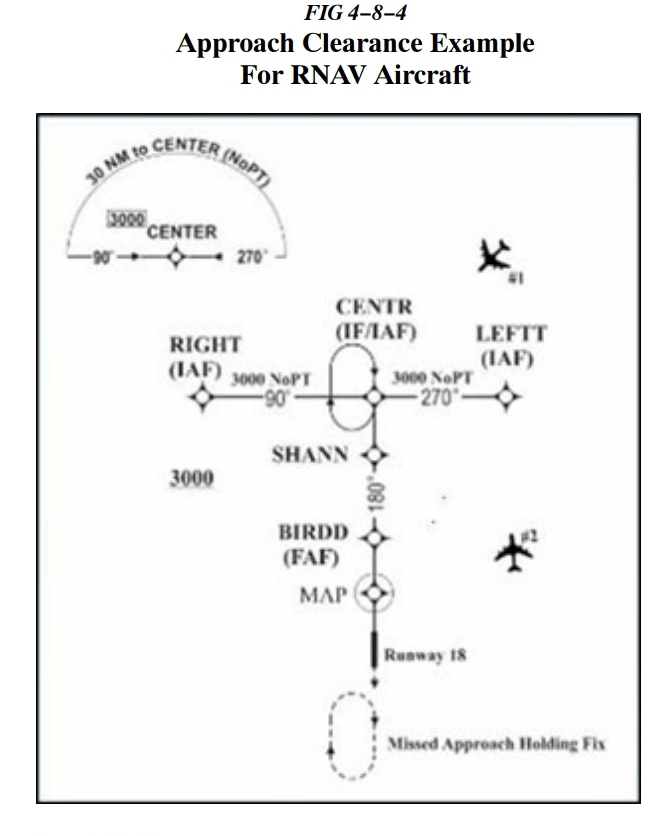
What is the maximum angle that Aircraft #2 can join the approach at LEFTT?
90 degrees
Pilot-applied visual separation may be used in lieu of any other form of standard separation below FL180.
True
Tower-applied visual separation may always be used when wake turbulence is involved.
False
(Tower-applied visual separation can only be used when the preceding aircraft is the same or smaller weight class and not a heavy or super.)
In order to use pilot-applied visual separation, the controller must do which of the following?
Tell the pilot about the other aircraft including position, direction, and type
Obtain acknowledgement from the pilot (with their callsign) that the other aircraft is in sight
Instruct the pilot to maintain visual separation from the aircraft
(All of the above)
An aircraft on a VFR-on-top clearance is still allowed to fly through clouds and is provided IFR separation services.
False
If an aircraft being vectored for an instrument approach to a controlled airport reports the airport in sight, and the official weather at the airport reports a ceiling of 900 feet, can a visual approach clearance be issued?
No
(Even if the pilot reports otherwise, a visual approach clearance can only be issued if the official reported weather is at least 3 miles of visibility and a ceiling of at least 1,000 feet. This does not apply to aircraft landing at uncontrolled airports.)
If a preceding aircraft has been cleared for a visual approach to runway 32R, and a succeeding aircraft landing Runway 32L reports the airport and the preceding aircraft in sight, what is the proper phraseology to clear the succeeding aircraft for the visual approach to Runway 32L while also applying visual separation?
"[Number 2 callsign] maintain visual separation with [number 1 traffic], cleared visual approach Runway 32L."
An aircraft may be cleared for a Contact Approach only when:
The pilot requests a contact approach
If an aircraft requests to land at a Class C airport that is reporting visibility of 2 miles, and the pilot is unable to maintain basic VFR conditions, what should the pilot do?
Request a Special VFR clearance
Basic radar services to aircraft operating in Class C airspace and outer area include:
Traffic advisories and safety alerts
Sequencing to the primary airport
What are the separation minima between a VFR aircraft and a jet-powered aircraft operating in Class B airspace?
1.5 miles or 500 feet