chemical coordination
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
The endocrine system includes:
Endocrine glands (well-organised, ductless)
Diffuse hormone-producing tissues/cells (present in various organs)
💡 These glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate body functions.
Gland | Location | Key Hormones Produced |
|---|
Gland | Location | Key Hormones Produced |
|---|---|---|
Pituitary | Base of brain (below hypothalamus) | GH, TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, Prolactin, ADH, Oxytocin |
Pineal | Center of brain (epithalamus) | Melatonin (biological clock) |
Thyroid | Neck (around trachea) | Thyroxine (T₄), Triiodothyronine (T₃), Calcitonin |
Parathyroid | Behind thyroid (4 lobes) | Parathyroid hormone (PTH) |
Adrenal | Top of each kidney (2 glands) | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline, Cortisol, Aldosterone |
Pancreas | Below stomach | Insulin, Glucagon, Somatostatin |
Thymus | Chest, behind sternum (temporary) | Thymosin (immunity in children) |
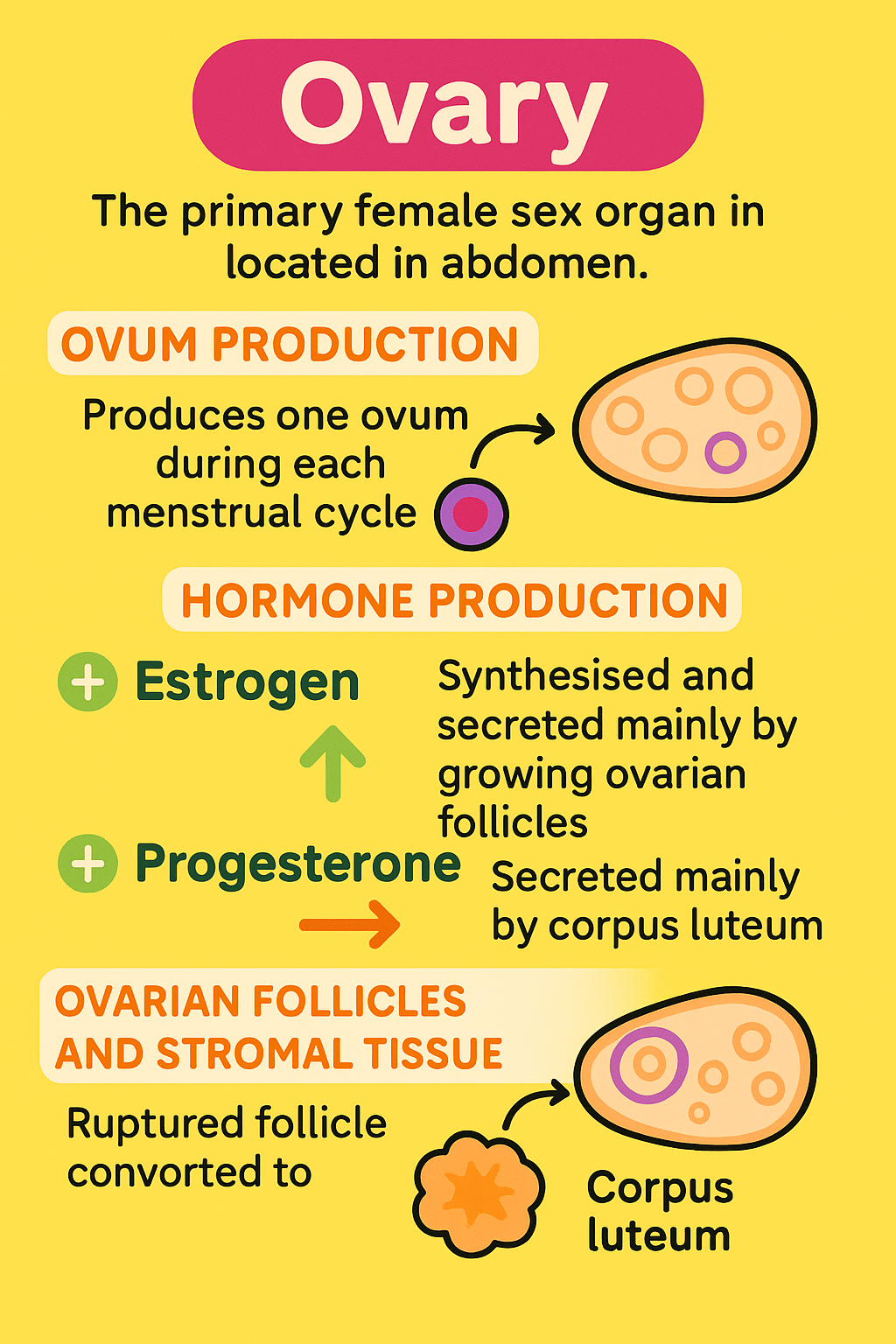
Gonads | Testes (males), Ovaries (females) | Testosterone, Estrogen, Progesterone |
⚙ Functions
Controls a wide range of body functions like:
Hunger, thirst
Sleep, body temperature
Emotional behaviour
Endocrine activities
🧪 Neurosecretory Cells
Hypothalamus contains groups of neurosecretory cells called nuclei.
These cells secrete hormones – NOT into blood directly, but into the pituitary portal circulation.
🔄 Types of Hormones from Hypothalamus
Hormone Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
Releasing Hormones (RH) | Stimulate anterior pituitary to release its hormones | GnRH – stimulates FSH & LH release |
Inhibiting Hormones (IH) | Inhibit anterior pituitary hormone secretion | Somatostatin – inhibits GH release |
🔁 How Hormones Work
Hormones are made in hypothalamic neurons
Travel down axons to nerve endings
Released into pituitary portal circulation
Act on anterior pituitary to regulate its hormone secretion
📌 Anterior Pituitary = Controlled via chemical hormones (RH/IH)
📌 Posterior Pituitary = Controlled via direct neural signals from hypothalamus
🧠 Key Examples
🧬 Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Stimulates release of FSH & LH from anterior pituitary.
🛑 Somatostatin
Inhibits growth hormone (GH) release.
NEET Highlights
Hypothalamus controls both anterior and posterior pituitary, but in different ways:
Anterior Pituitary = RH/IH via blood
Posterior Pituitary = Direct neural stimulation
This system ensures precise hormonal control over the body.
c) Somatostatin ✅
🧪 NEET Practice MCQ
Q: Which hormone from the hypothalamus inhibits GH secretion?
a) GnRH
b) CRH
c) Somatostatin
d) TRH
🧠 Pituitary Gland – The Master Gland 📍 Location & Structure
Located in a bony cavity called sella turcica of the skull.
Attached to the hypothalamus by a stalk.
Divided into:
Adenohypophysis (anterior part)
Neurohypophysis (posterior part)
🔷 Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary) Subdivisions:
Pars distalis → Major hormone-producing region.
Pars intermedia → Secretes MSH, almost merged with pars distalis in humans.
✨ Hormones from Pars Distalis
Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
GH (Growth Hormone) | Growth of body. Excess → Gigantism / Acromegaly; Less → Dwarfism |
PRL (Prolactin) | Milk production & growth of mammary glands |
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) | Stimulates thyroid to release T₃ and T₄ |
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) | Stimulates adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids |
LH (Luteinizing Hormone) | Males: Stimulates androgen (testosterone) secretion from testes |
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) | Males: Stimulates spermatogenesis |
✨ Hormone from Pars Intermedia
MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone)
→ Regulates skin pigmentation by acting on melanocytes.
🔷 Neurohypophysis (Posterior Pituitary)
Also called Pars Nervosa
Stores & releases hormones made by hypothalamus:
Hormone | Function |
|---|
Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
Oxytocin | Contracts uterus during childbirth & ejects milk from breasts |
Vasopressin / ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) | Acts on kidneys → Reabsorbs water → Prevents water loss via urine |
🔥 Deficiency of ADH → Diabetes Insipidus
💧 Symptoms: Excessive urination, dehydration
Quick NEET Pointers
🧪Gigantism → GH excess in childhood
Acromegaly → GH excess in adulthood
Diabetes Insipidus ≠ Diabetes Mellitus (No sugar in urine here)
🧠 NEET Memory Tricks:
FLAT PEG = Hormones of Anterior Pituitary:
FSH
LH
ACTH
TSH
Prolactin
Endorphins (not mentioned here)
GH
🌙 Pineal Gland – The Body's Biological Clock
📍 Location:
Situated on the dorsal side of the forebrain.
✨ Hormone Secreted:
Melatonin
🧠 Functions of Melatonin:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
⏰ Circadian Rhythm | Regulates the 24-hour (diurnal) rhythm – sleep-wake cycle |
🌡 Body Temperature | Helps maintain the body’s temperature cycle |
♀ Menstrual Cycle | Influences timing & rhythm of the menstrual cycle |
🛡 Immunity | Enhances defense capability |
🎨 Pigmentation | Affects skin pigmentation |
🔄 Metabolism | Influences metabolic processes |
🧪 NEET Quick Points:
Darkness increases melatonin secretion → Induces sleep
Light suppresses melatonin → Promotes wakefulness
Regulates biological clock in humans
Secreted more during night
💡 NEET Tip:
Think "Melatonin = Moon hormone" 🌓
It helps you "melo-down" for sleep 🛏💤
🦋 Thyroid Gland – The Metabolism Master
📍 Location & Structure:
Two lobes on either side of trachea
Connected by a thin flap of connective tissue → Isthmus
Made of follicles (with follicular cells) & stromal tissue
✨ Hormones Secreted:
Hormone | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
T₃ (Triiodothyronine) | Iodine-containing | More active form |
T₄ (Thyroxine / Tetraiodothyronine) | Iodine-containing | Major hormone secreted |
TCT (Thyrocalcitonin) | Protein hormone | Regulates blood calcium levels ↓ |
🧂 Iodine is essential for T₃ and T₄ production!
🧬 Functions of Thyroid Hormones (T₃ & T₄):
🚀 Increase BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate)
🔴 Stimulate RBC formation
🍞 Control metabolism of carbs, fats, proteins
💧 Help maintain water & electrolyte balance
🧠 Crucial for growth & nervous system development
🚨 Disorders:
Condition | Cause | Features |
|---|---|---|
Hypothyroidism | Iodine deficiency | Goitre, weight gain, tiredness |
Cretinism (in infants) | During pregnancy | Stunted growth, mental retardation |
Hyperthyroidism | Cancer/nodules | Exophthalmic goitre, weight loss, high BMR |
Graves’ Disease | Autoimmune hyperthyroidism | Eye bulging, anxiety, heat intolerance |
💡 NEET Tip:
Low Iodine → Goitre
T₃ is 3-5x more active than T₄
TCT = Calcium Tone = Lowers Ca²⁺ in blood
🧬 Parathyroid Gland – The Calcium Balancer
📍 Location:
4 small glands on the posterior surface of thyroid gland
1 pair per lobe of the thyroid
✨ Hormone Secreted:
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
🔹 Type: Peptide hormone
🔹 Secreted in response to low blood Ca²⁺ levels
🔁 Functions of PTH (Hypercalcemic Hormone):
Target | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
Bones | Stimulates bone resorption (breakdown) | Releases Ca²⁺ into blood |
Kidneys | Promotes Ca²⁺ reabsorption in tubules | Less Ca²⁺ lost in urine |
Intestine | Enhances Ca²⁺ absorption from digested food | ↑ Blood Ca²⁺ levels |
👆 Hypercalcemic hormone = Raises blood calcium
Works With:
⚖ Works With:
Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) from thyroid:
Opposite action (lowers blood Ca²⁺)
Together, they maintain calcium homeostasis
💡 NEET Tip:
PTH = "Pulls The calcium High"
Deficiency → Hypocalcemia
Excess → De-mineralization of bones (fragile bones)
Thymus – The Immunity Giver
📍 Location:
Between the lungs, behind the sternum, in front of the aorta
🧠 Structure:
Lobular gland
More active in children & adolescents
Begins to degenerate with age
✨ Hormone Secreted:
Thymosins (Peptide hormones)
💪 Functions of Thymosins:
Role | Action |
|---|---|
🧬 Cell-mediated Immunity | Helps in differentiation of T-lymphocytes |
🧫 Humoral Immunity | Promotes antibody production by B-cells |
⏳ Age-Related Changes:
Thymus degenerates in old age
↓ Thymosin → Weaker immune response in elderly
NEET Focus Point:
T-cells mature in Thymus (T for Thymus!)
Degeneration leads to immunosenescence
🌟 Adrenal Gland: The Emergency Worker
Location: One pair of adrenal glands located on top of each kidney.
Structure:
Adrenal Medulla (inner region)
Adrenal Cortex (outer region)
🧠 Adrenal Medulla: Hormones of "Fight or Flight"
Main Hormones:
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Functions:
🏃♂ Rapid response to stress and emergency (fight or flight)
✅ Increase heart rate, strengthen heart contractions, increase respiration rate
👀 Dilate pupils, raise hairs (piloerection), increase sweating
💥 Breakdown of glycogen → Raises blood glucose levels
🏋♂️ Stimulates breakdown of lipids and proteins
Adrenal Cortex
🌍: The Three Layers and Their Functions
The adrenal cortex has 3 layers:
Zona Glomerulosa (Outer)
Zona Fasciculata (Middle)
Zona Reticularis (Inner)
Main Hormones:
Glucocorticoids (Cortisol):
Regulate carbohydrate metabolism
✅ Stimulate gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and proteolysis
🔥 Anti-inflammatory, immune-suppressive
🩸 Stimulate RBC production
🫀 Maintain cardiovascular and kidney function
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone):
⚖ Regulate water and electrolyte balance
✅ Stimulate Na+ and water reabsorption in kidneys
✅ Excrete K+ and phosphate ions
Maintain blood pressure and osmotic pressure
Androgenic Steroids:
🎯 Influence the growth of axial hair, pubic hair, and facial hair during puberty
🚨 Disorders:
Addison's Disease: Caused by underproduction of adrenal cortex hormones → Fatigue, weakness
Hypersecretion of Adrenaline → Increased stress response (e.g., during emergencies)
Pancreas: Dual Role Gland
🩺
➡ It functions as both:
Exocrine Gland: Secretes digestive enzymes.
Endocrine Gland: Secretes hormones from Islets of Langerhans.
🧬 Islets of Langerhans – Tiny but Mighty!
🧪 Makes up only 1–2% of pancreas but controls sugar levels like a boss 😎
Has two main cell types:
Cell Type | Hormone Secreted | Function |
|---|---|---|
α-cells | Glucagon | Raises blood sugar (hyperglycemia) |
β-cells | Insulin | Lowers blood sugar (hypoglycemia) |
💉 Insulin (Secreted by β-cells)
Target Cells: Hepatocytes (liver) + Adipocytes (fat cells)
✅ Increases glucose uptake by cells
✅ Promotes glycogenesis (glucose → glycogen)
✅ Reduces blood sugar → Prevents hyperglycemia
💥 Deficiency leads to Diabetes Mellitus:
Glucose in urine
Formation of harmful ketone bodies
Treated with insulin therapy
🍬 Glucagon (Secreted by α-cells)
Target Organ: Liver
✅ Stimulates glycogenolysis (glycogen → glucose)
✅ Stimulates gluconeogenesis (non-carbs → glucose)
⬆ Increases blood sugar = Hyperglycemic hormone
⚖ Balance Between Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin 🧊 cools down sugar levels
Glucagon 🔥 fires them up
➡ Together, they maintain glucose homeostasis in blood
🌟 Testis: The Male Reproductive and Endocrine Organ
Location: A pair of testes located in the scrotal sac (outside the abdomen).
Functions:
Primary sex organ: Responsible for sperm production.
Endocrine gland: Produces hormones, especially androgens like testosterone.
🧬 Structure:
Seminiferous Tubules: Site of spermatogenesis (sperm formation).
Leydig Cells (Interstitial Cells): Located between the seminiferous tubules, they produce androgens (mainly testosterone).
🧪 Role of Androgens (Testosterone):
Male Sexual Development:
Regulate growth and function of male accessory sex organs: epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethra.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics:
Stimulate muscle growth, facial & axillary hair growth, and a low-pitched voice.
Spermatogenesis:
Stimulate sperm production in the seminiferous tubules.
Sexual Behavior:
Influence libido (sexual drive).
Metabolism:
Have anabolic effects: Increase protein and carbohydrate metabolism.