Skeletal System - Anatomy Midterm
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
mature bone
osteocytes
responsible for bone remodeling
osteoclasts and osteoblasts
osteocytes
regulate existing bone, completely surrounded by matrix
osteoclasts
erode and recycle bone matrix during remodeling, calcium
osteoblasts
deposit new bone matrix
the ends of long bones
epiphysis
long bone shaft
diaphysis
membrane that covers the outer surface of bones
periosteum
fingers and toes
phalanges
breastbone
sternum
kneecap
patella
shoulder blade
scapula
thigh bone
femur
long bones of hand
metacarpals
upper jaw
mandible
collar bone
clavicle
thumb side forearm
radius
shin bone
tibia
wrist bones
carpals
upper arm bone
humorous
little finger/pinky forearm
ulna
long bones
humorous
tibia
femur
short bones
tarsals
carpals
flat bones
sternum
parietal
irregular — usually cant fall under any other bone type
sacrum
vertebrae
formed from fused vertebrae
sacrum and coccyx
how many bones in the cranium
8
frontal, parietal (2), occipital, temporal (2), sphenoid, ethmoid
how many facial bones
14
number of metatarsal bones
10
number of tarsal bones
10
number of phalange bones
56
number of carpal bones
16
number of cervical vertebrae
7
number of thoracic vertebrae
12
number of lumbar vertebrae
5
number of pairs of true ribs
7
number of pairs of false ribs
5
number of clavicle bones
2
scoliosis symptoms
Sideways curvature of the spine “c” or “s”
Common in children
Uneven shoulders or hips
scoliosis treatments
Exercise
PT - if curvature is small
Wear brace
Surgery
osteoporosis symptoms
Loss of height
Stooped posture
Back pain from spinal fixtures
osteoporosis treatments
Calcium and Vitamin D intake
Weight bearing exercises
Medications
paget’s disease symptoms
Bone pain
Numbness or tingling
Headaches
Hearing loss
No symptoms but find out through x-ray
paget’s disease treatments
Pain relievers
Surgery
Change in lifestyle exercise
Slow bone erosion using biophosphates
osteomalacia symptoms
Aching bone pain, hips and legs
Muscle weakness
Cramps and fatigue
Waddling gait
osteomalacia treatments
Taking vitamin D and calcium supplements
Exposure to sunlight
Dietary changes
word that means dried up body
skeleton
hard, dense bone
compact bone

fracture that breaks bone into many fragments
comminuted

fracture that crushes bone
compression

fracture in which broken bone is pressed inward
depressed

fracture in which broken bone ends are forced into each other
impacted

fracture in which broken bones are twisted, spiral shape
spiral

fracture in which bone is broken incompletely
greenstick
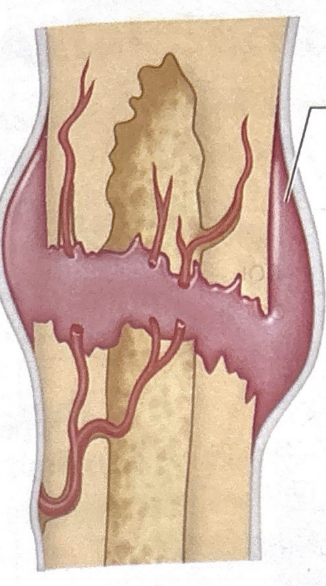
first stage of bone fracture healing
hematoma formation
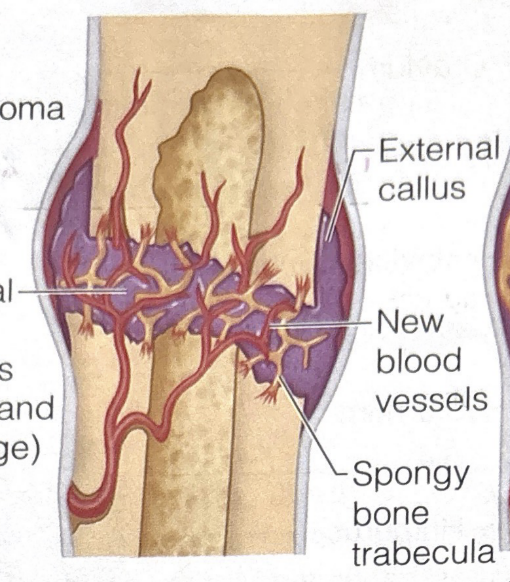
second stage of bone fracture healing
fibrocartilage callus formation
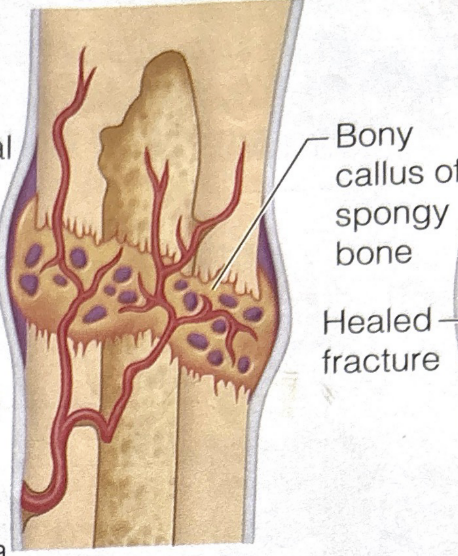
third stage of bone fracture healing
bony callus formation
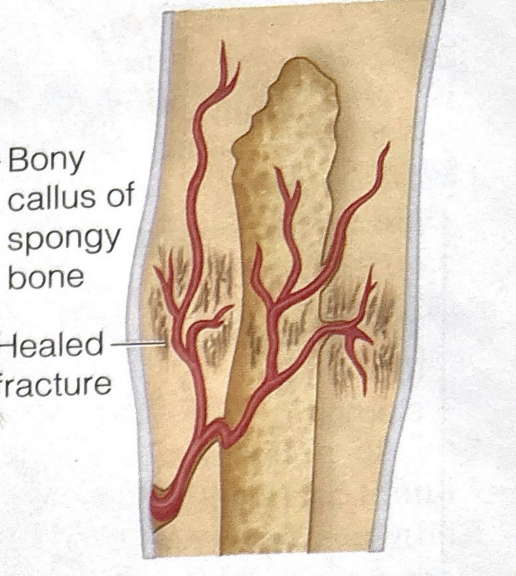
fourth stage of bone fracture healing
bone remodeling
axial skeleton
longitudinal axis of the body —
skull
thoracic cage (ribs & sternum)
vertebral column
sacrum & coccyx
appendicular skeleton
composed of 126 bones of the limbs (appendages)
pectoral and pelvic girdles — attach limbs to axial skeleton
arms, legs
upper and lower limbs
longest and strongest bone of the body
femur
attach bone to bone
ligaments (BBL - Bone Bone Ligament)
dislocation
takes longer to heal than a fracture
bone dislocates at joint
types of arthritis
osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis
osteoarthritis
chronic degenerative condition causing cartilage to wear down and bones to rub
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder
gouty arthritis
uric acid accumulates in blood
number of bones in human body
206
functions of the skeletal system
support/framework *
protect soft tissue
levers for movement w/ muscle
stores minerals & fats
blood cell formation
what is responsible for blood cell formation
bone marrow
skeletal components
bone, joint, cartilage, tendon, ligament
what connects bone to muscle
tendon
is bone living tissue
yes
type of bone responsible for making red blood cells
flat bones
types of bone tissue
spongy and compact
spongy bones contain
red bone marrow
consist of mostly compact bone
long bone
consist of mostly spongy bone
short bones
arteries…
nourish bone cells
embryo skeleton
hyaline cartilage
what happens with growth at the epiphysial plates
old cartilage ossifies → new cartilage forms
hematoma
bruise
compound (open) fracture
broken bone that penetrates skin
simple (closed) fracture
broken bone that does not penetrate skin