Amines and Amides
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What are the functional groups present in amines?
nitrogen atom with a lone pair bonded to one or more carbon groups
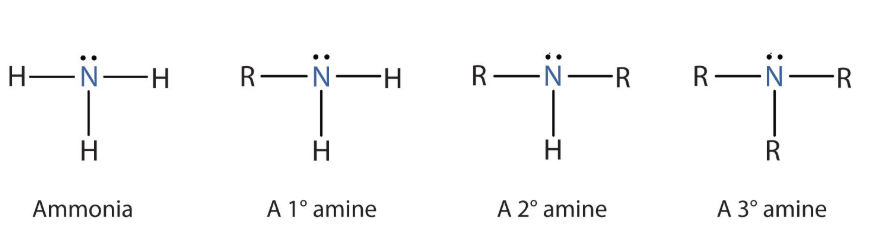
How can you classify an amine as either primary, secondary or tertiary?
By looking at how many hydrogens is attached to the nitrogen
A primary amine will have 2 hydrogens
A secondary amine will have 1 hydrogen
A tertiary amine will have 0 hydrogens
What are the IUPAC name rules for amines?
Identify the longest parent chain that has the nitrogen atom directly attached
Drop the -e from the alkane parent chain and the suffix -amine
Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain starting with the end closest to the nitrogen
Locate the position of the nitrogen atom and add the number to the beginning of the parent chain name
Locate and name any substituents
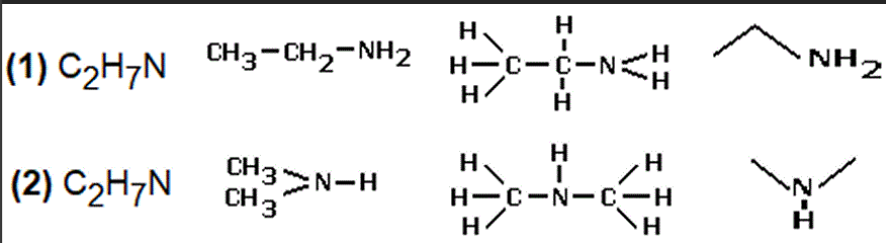
What is a skeletal isomer?
An isomer where the way the carbon is bonded to the atoms are different
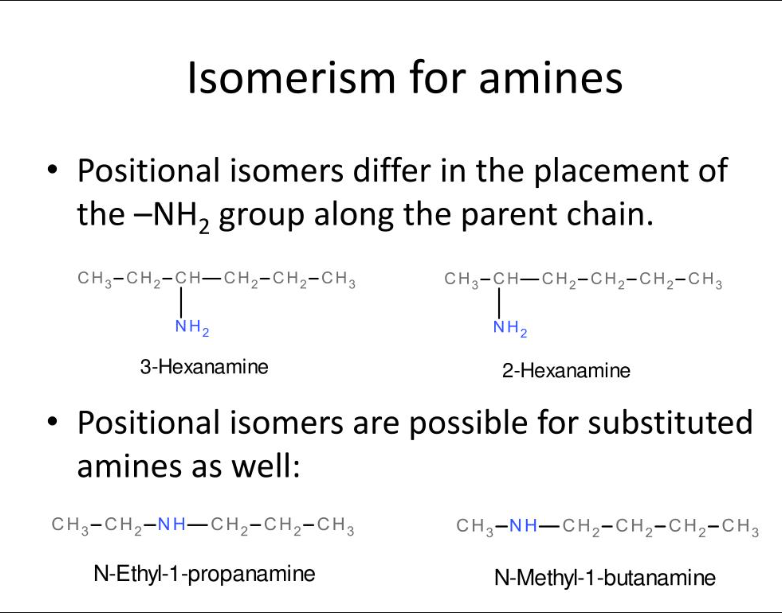
What are positional isomers?
An isomer where the position of the functional group is changed
How can nitrogen atoms bond?
By needing 3 additional electrons to form a full octet
will create 3 bonds
What is an amine?
An organic derivative of ammonia and which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced with an alkyl group
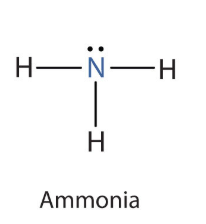
What compound is this?
Ammonia
What is an amino group?
A functional group present in a primary amine
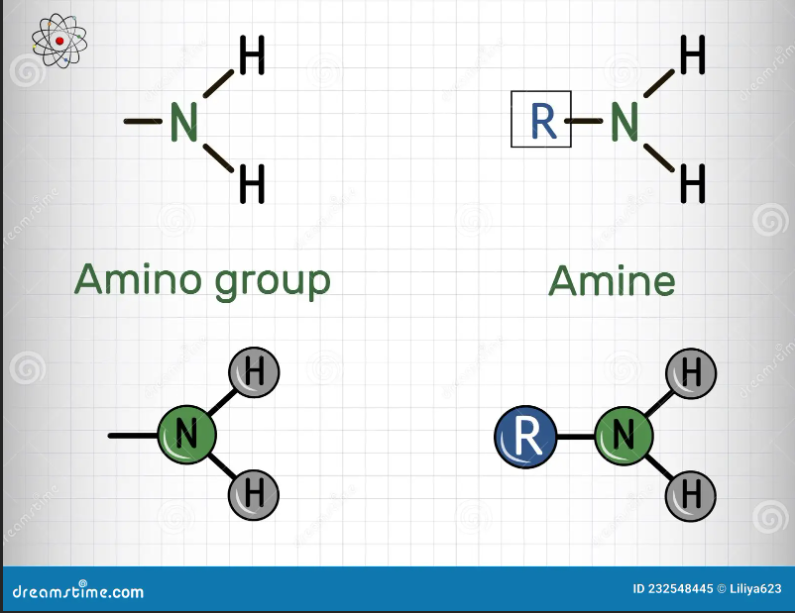
What are monosubstituted amino groups?
amino groups are functional groups present in a secondary amine
What is a distributed amino group?
amino groups are functional groups present in tertiary amines.
What are the IUPAC naming rules for diamines?
use the prefix di- with the suffix -amine.
add location number for both amine groups.
locate and name any substituents.
Are amines soluble in water?
Yes, it is soluble if the compound has fewer than 6 carbons
What is the relationship between the hydrogen bonding that occurs in between amines and water molecules?
The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen can interact with hydrogen in a water molecule that then makes them bond together
Why is the boiling point of amines lower than alcohol?
Nitrogen to hydrogen bonding is weaker than oxygen to hydrogen bonding
Which amine has the lowest boiling point? Why does it have the lowest BP?
Tertiary (3) amines will have the lowest BP
This is because of their lack of hydrogens present
Are amines able to act as a base or as an acid?
They act as a base
This is because of the lone pair of electrons that can accept hydrogens
Are amines strong or weak bases? What is their relationship of strength or weakness compared to alcohols and esters?
They are weak bases
Stronger than alcohols and esters
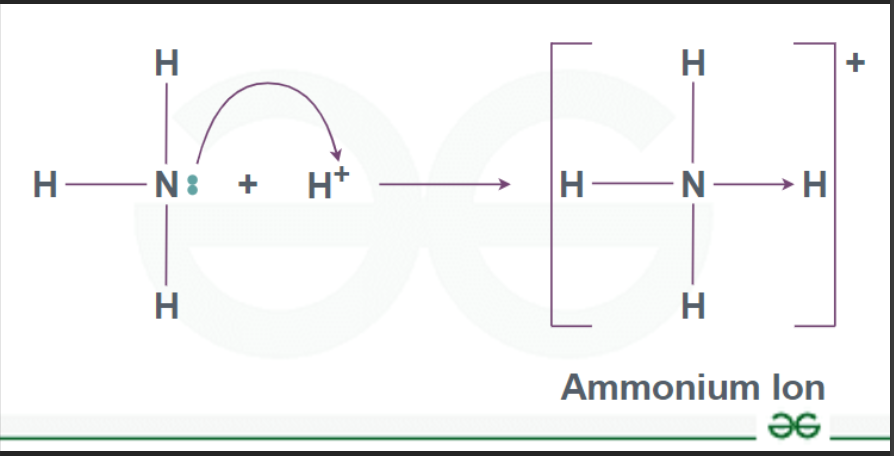
What is a substituted ammonium ion?
an ammonium ion that has one or more hydrogens replaced by an alkyl group
What is the general reaction for a neutralization reaction between amine and acid?
(methylamine ) CH3—NH2 + (Hydrochloric acid) H-Cl → (amine salt) CH3—NH3+Cl-
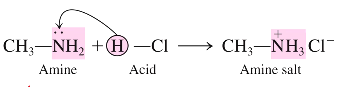
What are the products from an amine reacted with an acid?
A positively charged ammonium ion and a negatively charged chlorine ion that is attached to a methyl group
CH3-NH3+Cl-
amine salt
What is another term for the neutralization reaction of an amine and acid?
Protonation
What is the reverse of protonation?
Deprotonation
What is the general reaction for deprotonation?
methylamine (CH3-NH2) + Base (sodium hydroxide, (NaOH) → Amine (-NH2) + Sodium chloride (NaCl) + water (H2O)
What is a free amine?
A deprotonated form of amine salt
Aka a free amine = a (1,2,3) amine
What is an alkylation reaction?
The movement of an alkyl group from one molecule to another
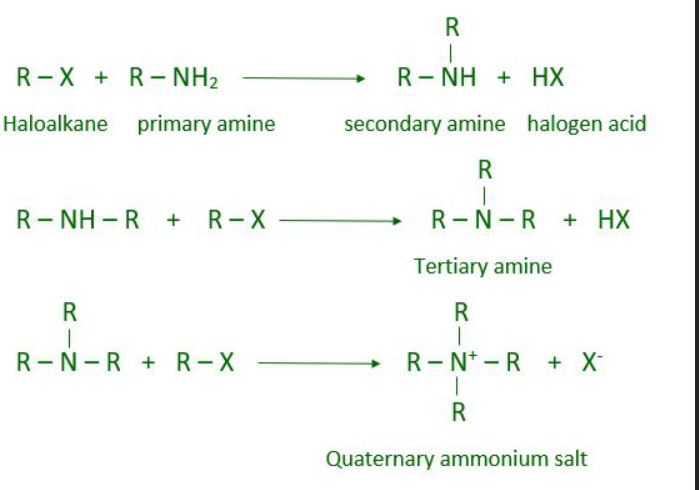
What is required in an alkylation reaction?
A strong base
How many steps are in an alkylation reaction? What are they?
Amine salt is produced
Amine salt reacts with base and is converted into a free amine
What are the different possible reactions of amines with alkyl halides? (Alkylation reactions)
Ammonia (-NH3) makes primary amine
Primary amine makes secondary amine
Secondary amine makes tertiary amine
Tertiary amine makes quaternary ammonium salt (photo attached)
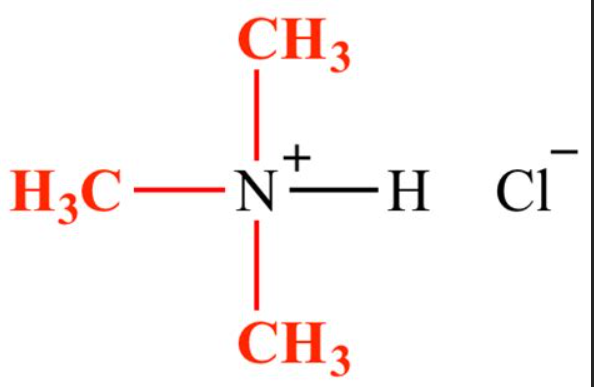
What are the biological uses of amine compounds for the human body?
They are what makes neurotransmitters
What is a heterocyclic amine?
A cyclic structure with nitrogen atoms apart of a ring system?
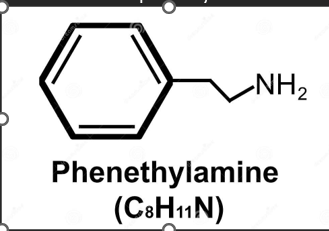
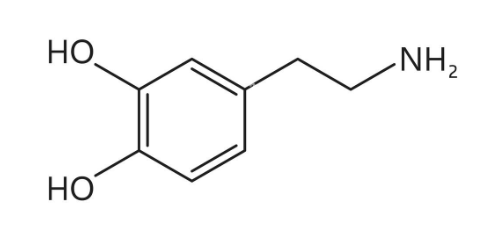
What compound is this? What is it used for?
Phenethylamine
Phenethyl amine creates three derivatives
Dopamine, Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
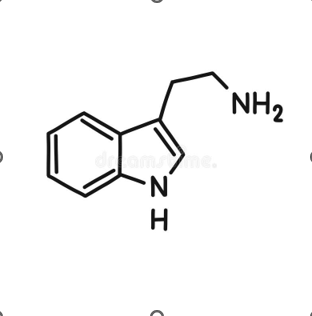
What compound is this? What is it used for?
Tryptamine
Tryptamine makes one derivative
Serotonin
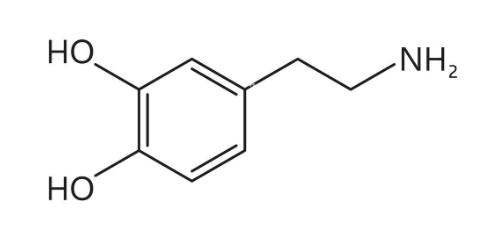
What is dopamine biologically synthesized by?
Where is it found?
What does the decrease of dopamine cause?
Tyrosine
The brain
Parkinson’s disease
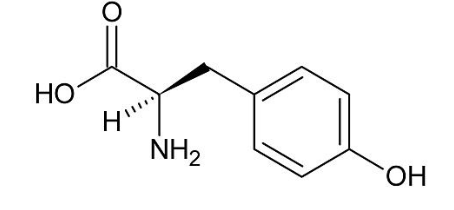

What is norepinephrine synthesized by?
Where is it found?
What does the increase of norepinephrine cause?
What is norepinephrine used to treat?
Tyrosine
The brain
Manic behavior
Low blood sugar or sepsis
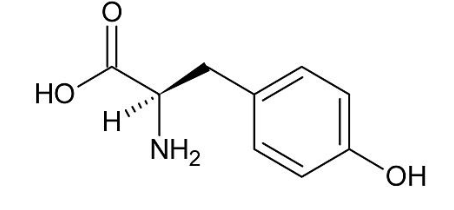
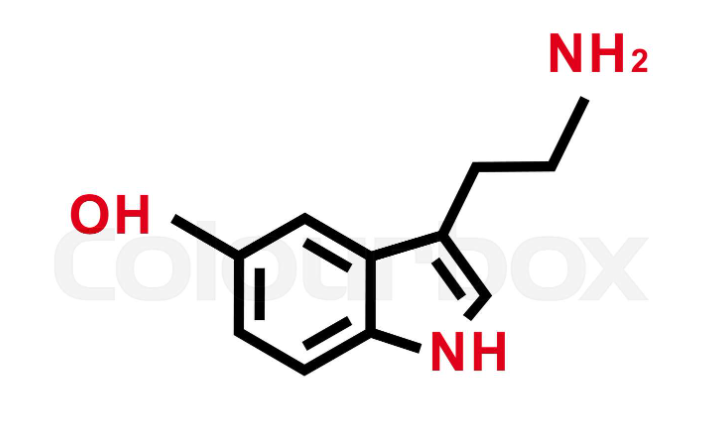
What is serotonin synthesized by?
Where is it found?
What does the decrease of serotonin cause?
What is serotonin also linked with?
Tryptophan
The brain
Mental illness
Lactation regulation
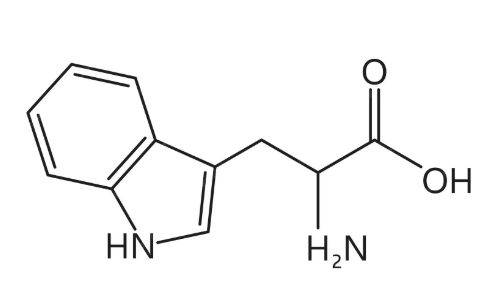
What compound is this?
Dopamine
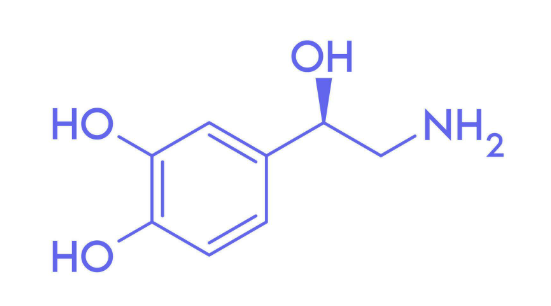
What compound is this?
Norepinephrine
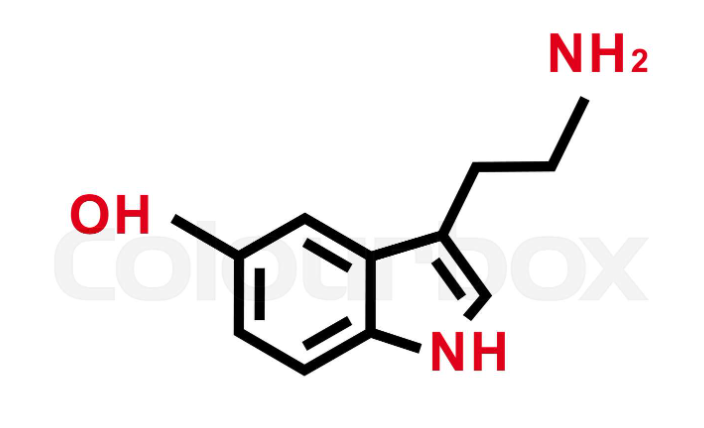
What compound is this?
Serotonin
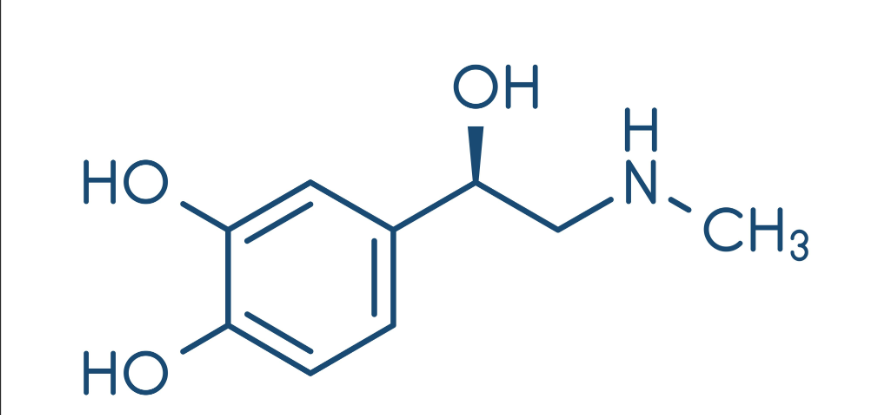
What is another name for epinephrine?
What is it produced by and in what gland?
What type of hormone is it?
What is epinephrine used to treat?
Adrenaline
Norepinephrine, adrenal glands
Sympathetic nervous system hormone
Anaphylactic shock
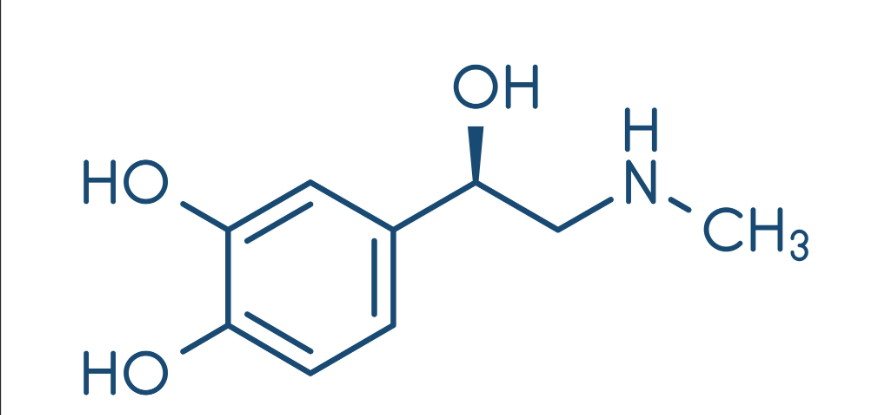
What compound is this?
epinephrine
What is an amide?
Carboxylic acid derivative in which the hydroxyl group has been replaced by an amino group
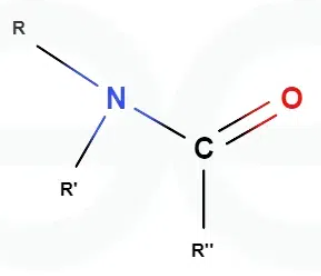
Do primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and amides share the same hydrogen counts?
Yes, for both amines and amides:
Primary = 2 hydrogens
Secondary = 1 hydrogen
Tertiary = 0 carbons
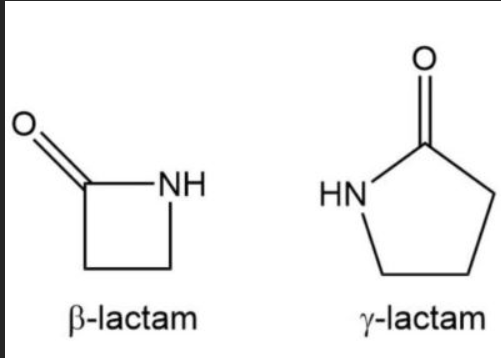
What are cyclic amides called?
Lactams
What are the uses for amides?
Urea → simplest and naturally occurring diamide → how the body rids itself of excess nitrogen
Melatonin → synthesized by the pineal gland → regulates internal alarm clock (circadian rhythm)
Acetaminophen → pain reliever
DEET → N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide → used in insect repellent
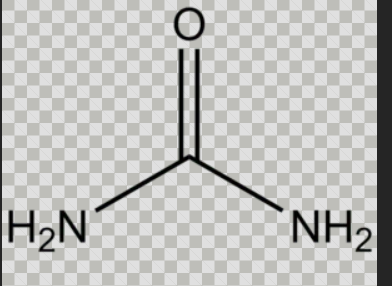
What compound is this?
Urea
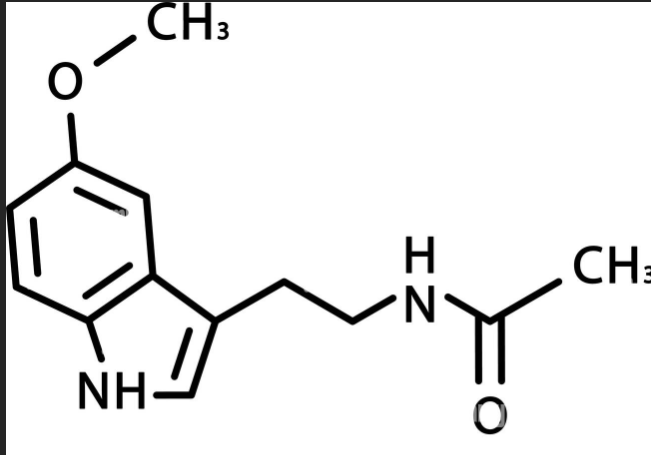
What compound is this?
Melatonin

What compound is this?
Acetaminophen
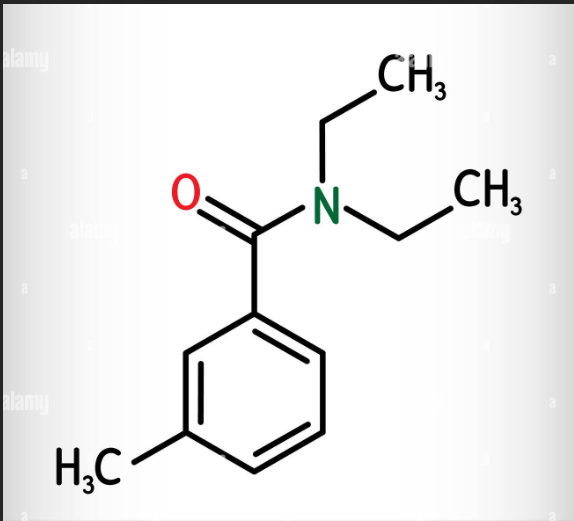
What compound is this?
DEET
How do you name amides?
identify the longest parent chain with the nitrogen attached
identify the alkyl or acyl groups attached to nitrogen
using N- to specify substituents on nitrogen, and for primary, secondary, or tertiary amides indicate the number of carbons attached to the nitrogen
replace parent chain suffix, -e, with -amide
Describe the solubility of amides
Soluble in water that has fewer than 6 carbons
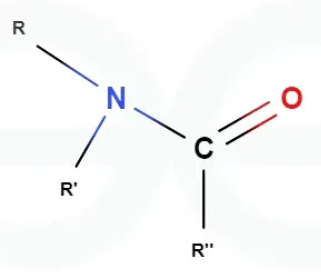
What are the different possible hydrogen bonding locations within an amide?
At the oxygen in the compound
The two other hydrogens attached to the nitrogen
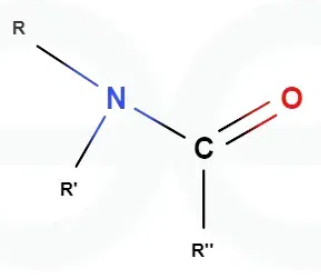
Can amides hydrogen bond to other molecules?
Yes, they can.
Why is the melting points of amides higher than other organic compounds?
Amides bond with hydrogen
this can form more hydrogen bonds than any other compounds because of the lone pair of electrons that nitrogen has
What happens to the melting point of an amide hydrogen bonds to another amide?
Melting point decreases
The number of R groups attached to the nitrogen increase
Are amides basic or acidic?
Weak acid
partial positive charge on the carbon inhibits nitrogen from accepting hydrogen
How are amides synthesized?
Condensation reactions
This is called amidification
What is the general reaction for an amidification reaction?
R-COOH (carboxylic acid) + R-N-R (amine) → O=C-N-R (1,2,3 amide)
Does amidifcation need to synthesize at a room temperature or high temperature?
What is produced if it is synthesized at room temperature?
High temperature
carboxylate salt (sodium ethanoate)
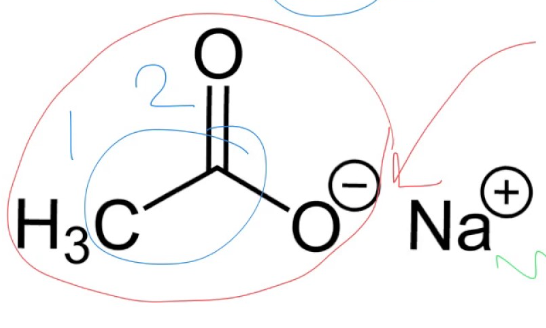
What are the different possible reactions to synthesize amides?
R-NH3 (ammonia) + R-COOH (carboxylic acid) @ (100 Celsius) → O=C-NH2 (1 amide)
O=C-NH2 (1 amide) @ (100 Celsius) → O=C-NH1 (2 amide)
O=C-NH1 (2 amide) @ (100 Celsius) → O=C-NH (3 amide)
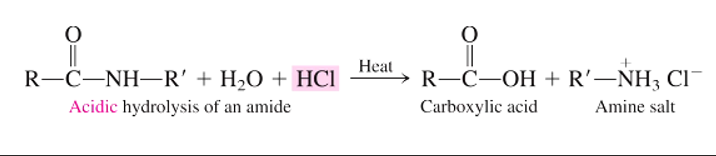
What is the general reaction for the acid hydrolysis of an amide?
Amide (O=C-N-R) + water + hydrochloric acid (HCl) W/ HEAT → carboxylic acid (R-C(-OH)=O) + amine salt (R-NH3+ Cl-)
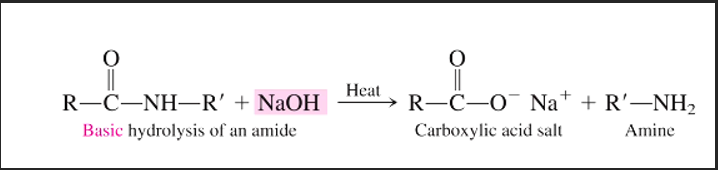
What is the general reaction of a base hydrolysis of amide?
Amide (O=C-N-R) + sodium hydroxyl (base, NaOH) W/ HEAT → carboxylic acid salt (C(-O-)=O Na+) + amine (R-NH)
What are the products of an acid hydrolysis of an amide?
amine salt
carboxylic acid
What are the products of a base hydrolysis of an amide?
carboxylic acid salt
amine
What is an alkaloid?
Nitrogen containing compound that is extracted from plant material that is used in both medicine and food
What is an example of alkaloids?
Caffeine
heroine
nicotine
morphine