Test Review Enzymes and Photosynthesis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How can you tell that a molecule is an enzyme by just looking at the name? What is the common ending of most enzyme names?
-ASE
In an exergonic reaction, how does the free energy of the products compare to the free energy of the reactants? In an endergonic reaction, how does the free energy of the products compare to the free energy of the reactants?
In an exergonic reaction, the products have less free energy than the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. In an endergonic reaction, the products have more free energy than the reactants
Function of enzymes
Speed up reactions
Enzyme
biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions
Substrate
the molecule or surface upon which a reaction or process occurs
Enzyme substrate complex
a transient molecule that forms when an enzyme binds to its specific substrate
Active site
region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction
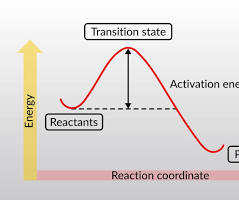
Activation energy
the minimum energy a chemical reaction needs to start, acting as an energy barrier
Induced fit
enzyme changes to fit substrate
Competitive inhibitor
molecules that compete with the substrate for binding to an enzyme's active site, blocking the substrate and preventing the reaction from occurring
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
reduce enzyme activity by binding to a different site on the enzyme, called the allosteric site
Feedback inhibition
regulatory process where the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme early in the same pathway, effectively shutting down the pathway once enough product has been made
When an noncompetitive inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of an enzyme, what happens to the active site?
alters the active site
If the active site of an enzyme was blocked or disrupted, what would happen to the ability of the enzyme to bind to its substrate?
decrease or cease entirely
Explain what happens when an enzyme driven reaction reaches the saturation point.
all available enzyme active sites are occupied by substrate, and the reaction rate reaches its maximum velocity
Explain why the curve levels of in the graph below that depicts the relationship between initial rate of product formation and reactant concentration in an enzyme catalyzed reaction.
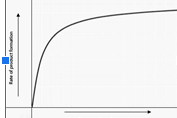
because the enzyme becomes saturated with the substrate
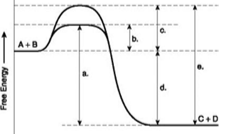
what are the letters

In a solution where the enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, what would be the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of product?
add more of the enzyme
What is the role of photosynthesis in an ecosystem?
To create O2
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?

How many types of chlorophyll are present in chloroplasts?
two main types of chlorophyll: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
What wavelengths of light does chlorophyll absorb best? Least?
Chlorophyll absorbs light most strongly in the blue and red parts of the visible light spectrum and absorbs green light the least
What are accessory pigments? What is their function?
photosynthetic pigments that absorb light energy at wavelengths not used by chlorophyll a and pass it to chlorophyll a to increase the efficiency of photosynthesis
What happens to the chlorophyll molecules when they are hit by light?
electron excitation
Where in the cell does photosynthesis occur?
Chloroplast
What is the source of 02 produced in photosynthesis?
The oxygen produced comes from the splitting of water molecules
Where in the chloroplast do the light reactions occur?
Thylakloid
From where does the chlorophyll in Photosystem I receive replacement electrons?
the electron transport chain
From where does the chlorophyll in Photosystem II receive replacement electrons?
the splitting of water molecules
Briefly describe what happens in each of the following:
Light Reactions
Calvin Cycle
Light Reactions, sunlight and water are used to produce energy-carrying molecules (ATP and NADPH) and release oxygen as a byproduct. The Calvin Cycle, or light-independent reactions, uses the ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar).
What is the role of water in the light reactions?
provide electrons, protons, and oxygen
What are the inputs and outputs of the light reactions?
light energy, water, ADP, and NADP+, while the outputs are ATP, NADPH, and oxygen
Describe what the impact would be if photosystem II was removed from the thylakoid membrane. What would happen if you removed the photosystem I?
halt the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH, preventing the production of reducing power and indirectly halting the creation of ATP via the full electron transport chain
Describe each of the following stages of the calvin cycle:
Carbon Fixation
Rearrangement
Regeneration
The Calvin cycle consists of three main stages: Carbon Fixation, Reduction, and Regeneration; where carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic molecules, these molecules are reduced using energy from ATP and NADPH, and finally, the cycle regenerates the starting molecule to continue the process.
What is Rubisco and what is its role in the calvin cycle?
Rubisco is the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle, which is the process of converting atmospheric carbon dioxide
What are the inputs and outputs of the calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle's inputs are carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH, which are used to create sugar. Its outputs are glucose
Where in the chloroplast does the calvin cycle occur?
the stroma
What is non cyclic electron flow? What are the products?
Non-cyclic electron flow is a process in photosynthesis where electrons move in a linear path from water through two photosystems (I and II) to produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen