inorganic chem
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
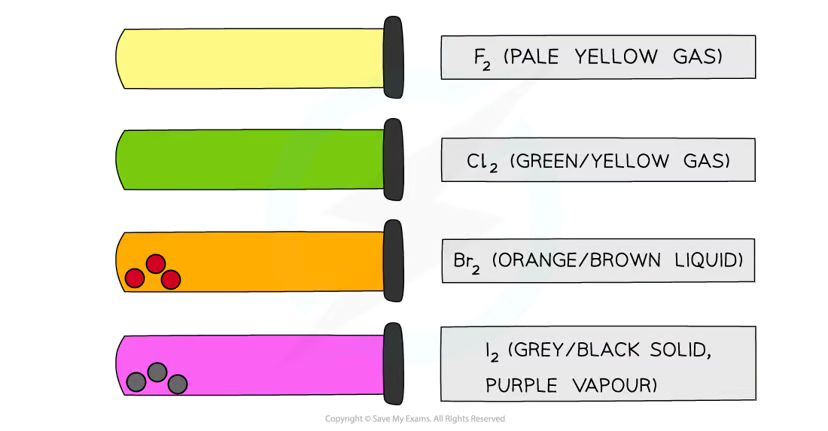
What are the colours and states of chlorine, bromine, and iodine, and what is the trend in colours down Group 17?
Trend:
The colours of halogens become darker as you move down the group due to increasing molecular size and electron density.
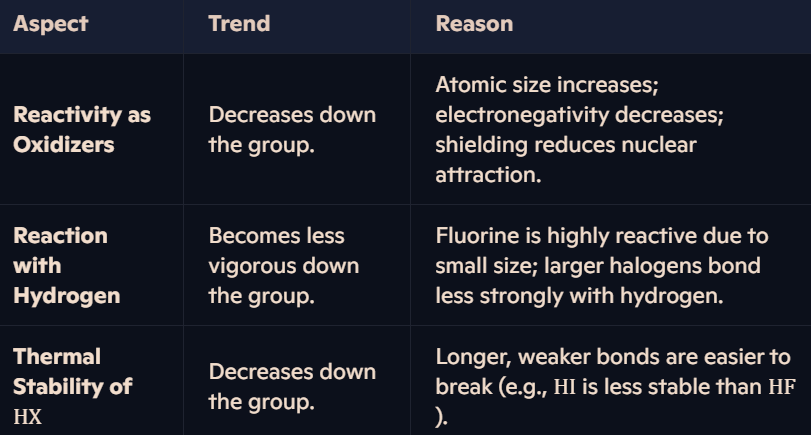
What are the reactions of halogens with hydrogen, and how does reactivity vary?

Halogen Reactivity, Reactions, and Thermal Stabilities
How do halide ions react with aqueous silver ions and ammonia?

What are the reactions of halide ions with concentrated sulfuric acid?

What is the reaction of chlorine with cold and hot alkali? Why is it a disproportionation reaction?

Halide Ions and Chlorine Reactions

The Group 2 elements react with oxygen, water and dilute acids
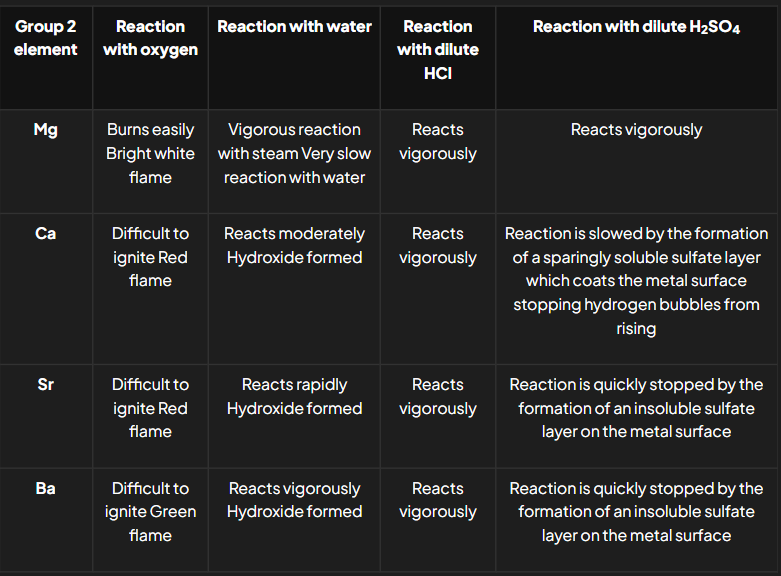
Group 2 reactions with oxygen & water chemical equations
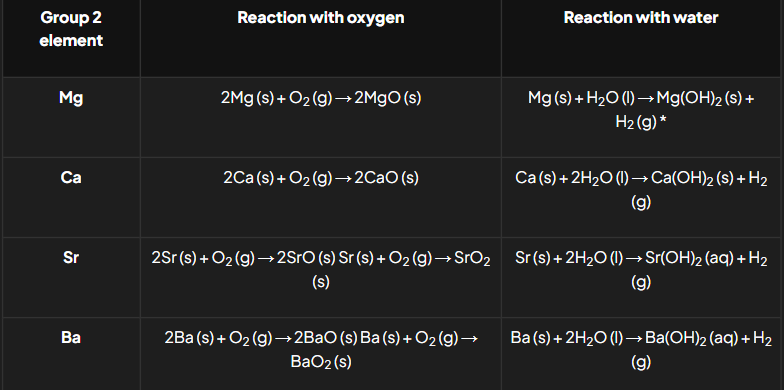
Group 2 reactions with dilute hydrochloric acid & dilute sulfuric acid chemical equations
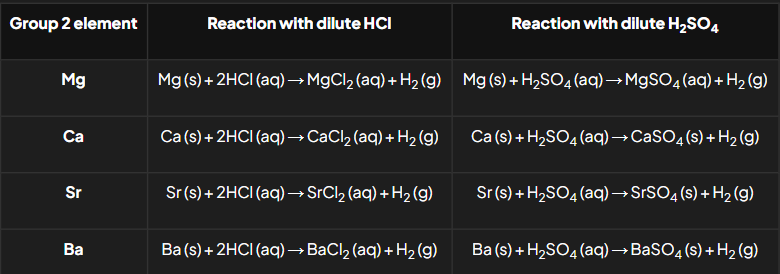
What are the general reactions of Group 2 elements with oxygen, water, dilute hydrochloric acid, and dilute sulfuric acid?

How do Group 2 oxides react with water and acids?
Reactions with Water:
General Equation: MO+H2O→ M(OH)_2.
Reactions with Acids:
General Equations:
MO+2HCl → MCl2 + H2O.
MO+H2SO4→ MSO4 + H2O.
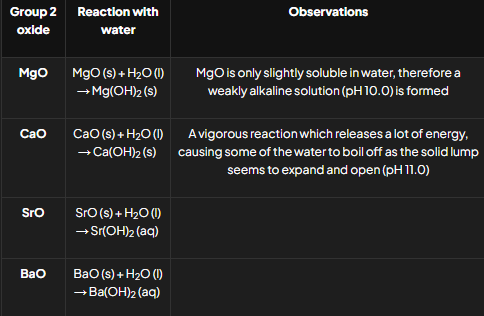
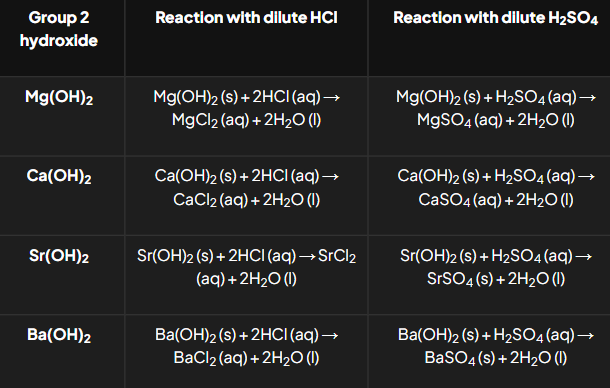
How do Group 2 hydroxides react with acids?
General Equations:
M(OH)2+2HCl → MCl2 + 2H2O.
M(OH)2+H2SO4→ MSO_4 + 2H_2O.
Trends:
Sulfates decrease in solubility down the group.
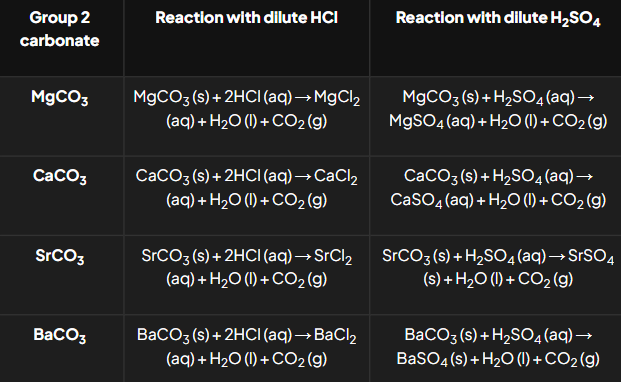
How do Group 2 carbonates react with acids?
General Reactions:
MCO3+2HCl→ MCl2 + H2O + CO2.
MCO3+H2SO4→ MSO4 + H2O + CO2.
Observations:
Effervescence (bubbling) from CO2CO_2 gas.
Insoluble sulfates (e.g., BaSO4) form surface layers that prevent further reactions.
What is the thermal decomposition of Group 2 carbonates?

What is the thermal decomposition of Group 2 nitrates?

What are the physical and chemical trends in Group 2 elements?

How do solubilities of Group 2 hydroxides and sulfates vary?

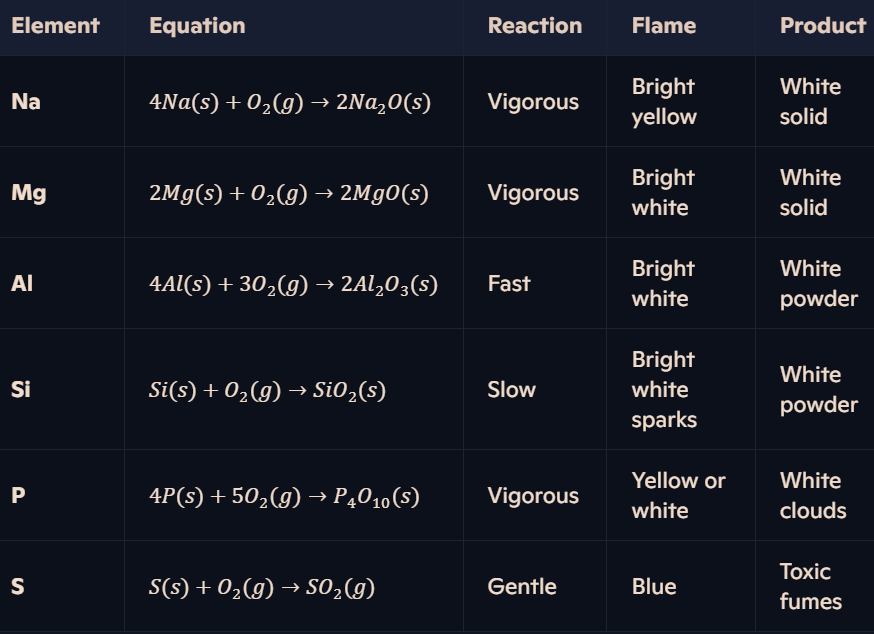
What are the reactions of Period 3 elements with oxygen?
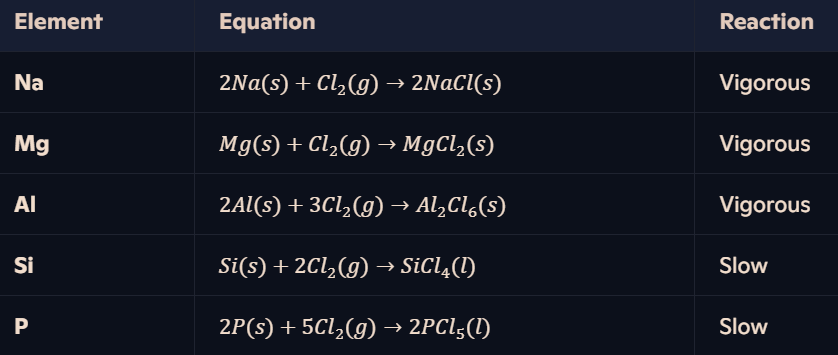
What are the reactions of Period 3 elements with chlorine?
What are the reactions of sodium and magnesium with water?
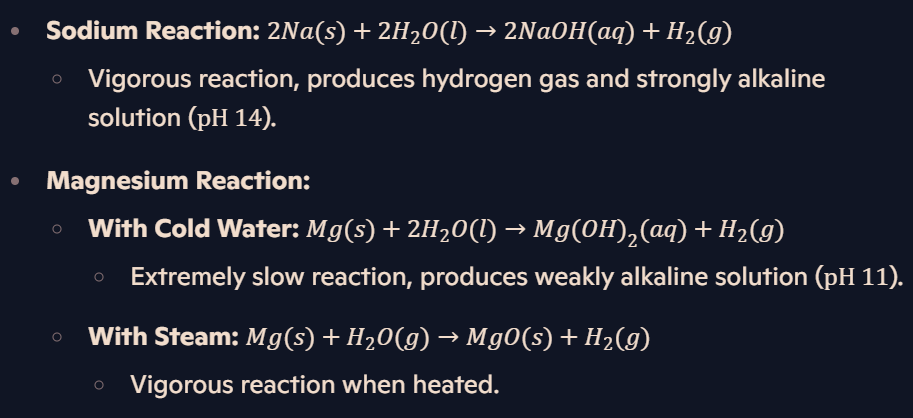
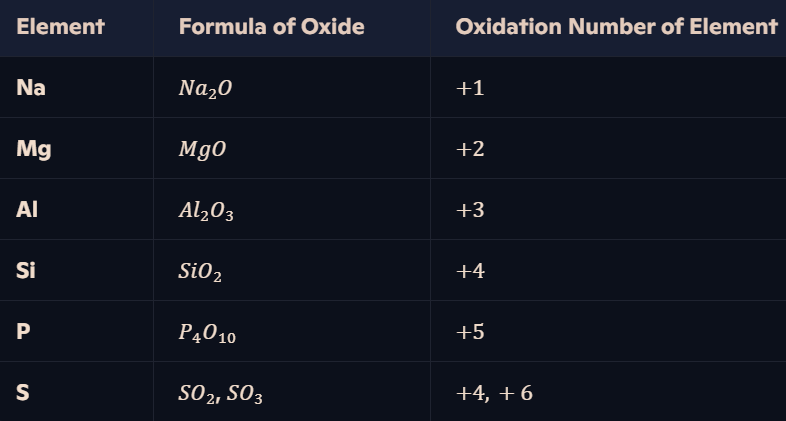
How do oxidation numbers vary in oxides of Period 3 elements?
Oxygen is the most electronegative element → Oxides have positive oxidation states for the Period 3 elements (−2 for oxygen).
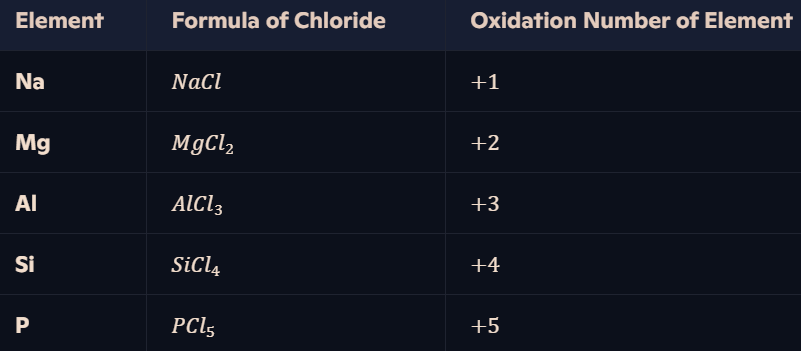
How do oxidation numbers vary in chlorides of Period 3 elements?
Chlorine (Cl\text{Cl}) is more electronegative than Period 3 elements → Chlorides have positive oxidation states for the Period 3 elements (-1 for chlorine).
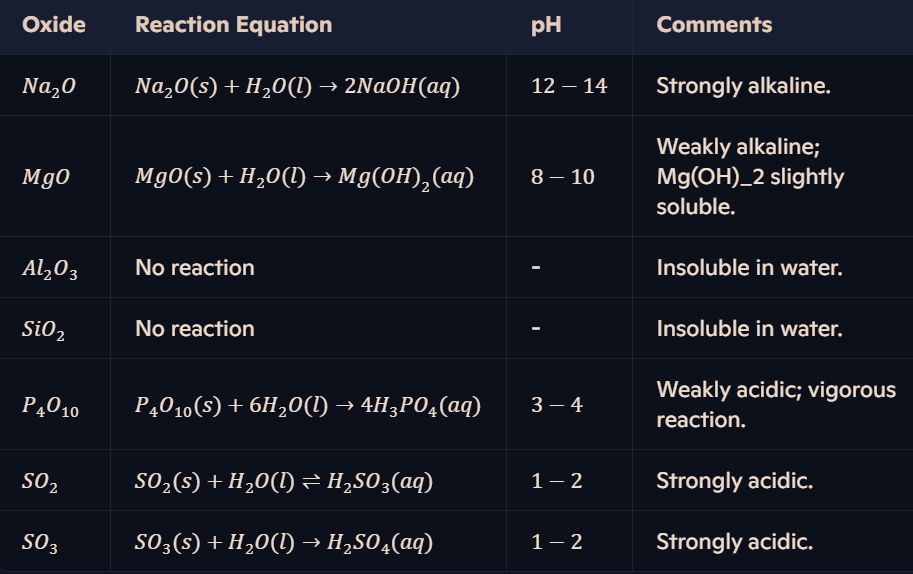
How do Period 3 oxides react with water, and what are the likely pH values?
What is the acid/base behavior of Period 3 oxides?

REACTIONS OF ACID/BASE BEHAVIOUR IN OXIDES
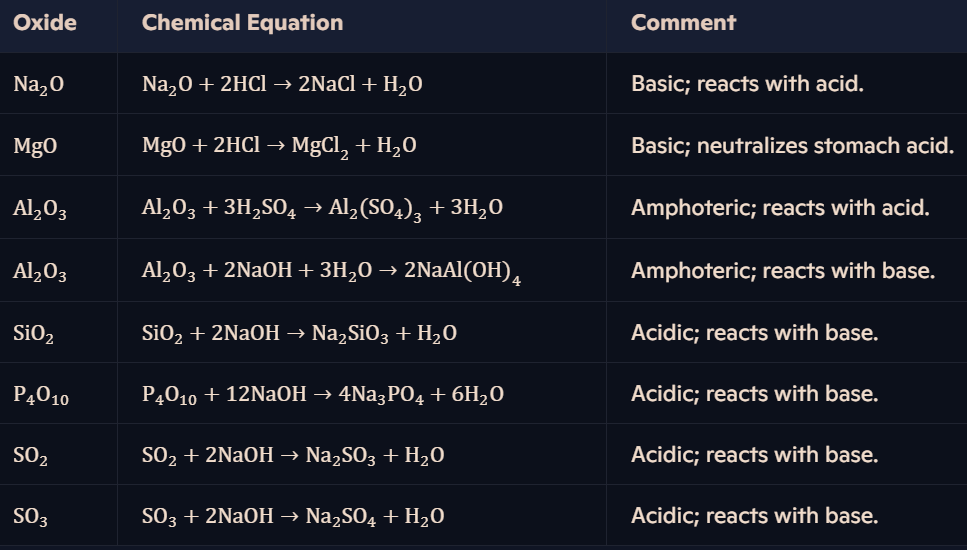
What is the acid/base behavior of Period 3 hydroxides?

How do Period 3 chlorides react with water, and what are the likely pH values of the solutions?

What are the bonding and structures of Period 3 elements?

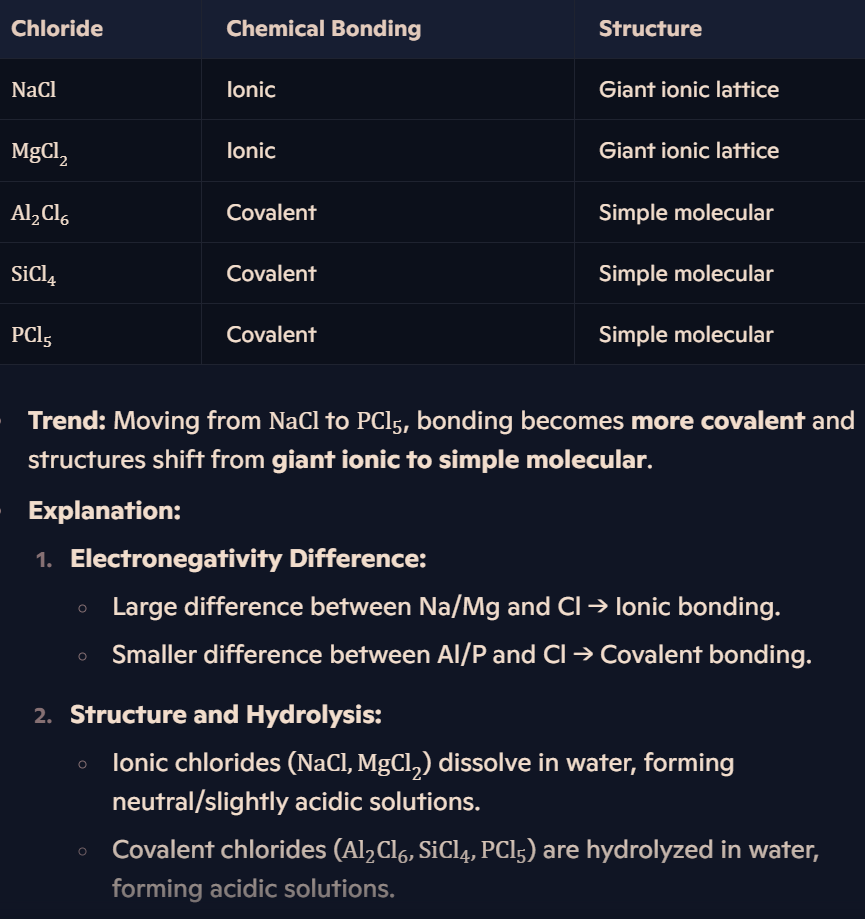
What are the trends in bonding and structure of Period 3 chlorides?
What are the trends in bonding and structure of Period 3 oxides?
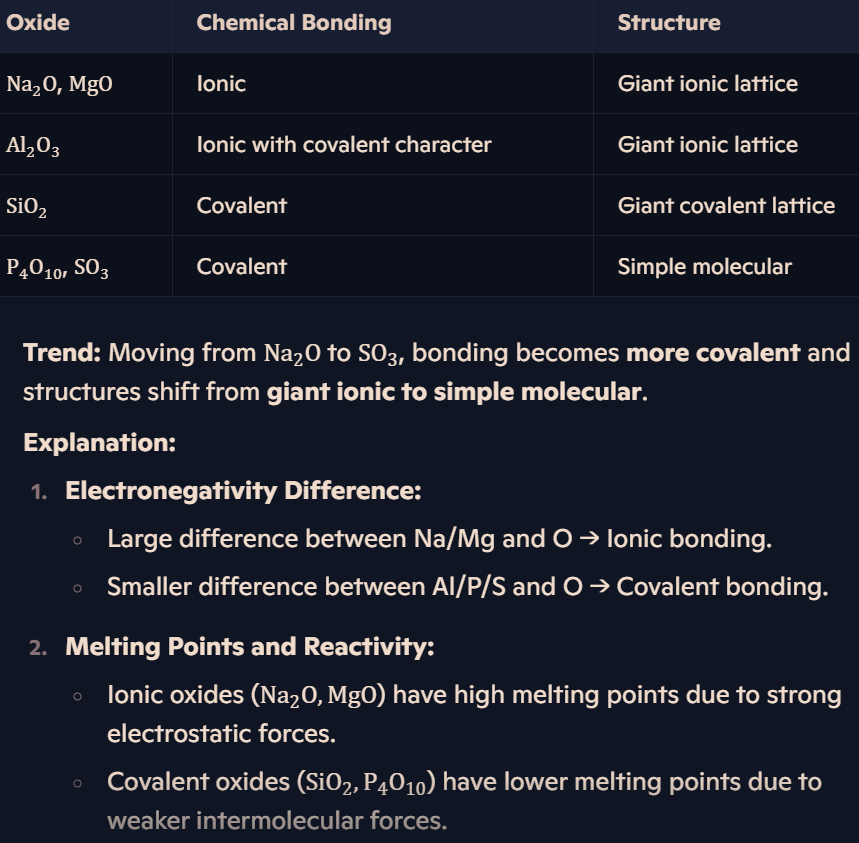
How do periodic trends link to bonding and structure?

What are the natural and man-made occurrences of nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2)?

How are nitrogen oxides removed from car exhaust fumes?
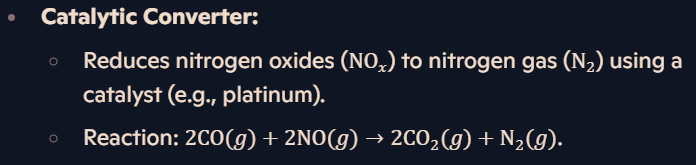
What is photochemical smog, and how is it related to nitrogen oxides?

How do nitrogen oxides contribute directly to acid rain formation?

How do nitrogen oxides catalyze the formation of sulfuric acid in acid rain?
