Forensic Toxicology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What type of toxicology is the backbone of Forensic Toxicology
analytical toxicology
Applying chemistry to identify presence and amount of chemicals —> used to predict pass events on a living organism
What is the order of most important chemicals you should be identifying
Gases
Volatile substances
Corrosive agents
Metals
Anions and non-metals
Non-volatile organic substances
Miscellaneous
How are chemicals extracted from biological matrices
Chemicals are isolated by fractionations
If iterative (if a mix), increases solvent polarity with each extraction (start with low polar and go higher)
What does post-mortem investigations look at
include qualitative/quantitative analysis of chemicals in biological specimens collected at autopsy + interpretations of these findings on behavioural and physiological effects at the time of injury/death
What is the difference between manner and cause of death
Manner = may have lead to someone death but wasn’t the direct reason
May be on a drug and they jump off the building. The drug didn’t kill them the fall did effected the manner in how they died
Causes = directly causing death
Drug causing someone liver to shut down = direct cause of death
What is really important with samples (2)
Chain-of-custody tracks who was in charge of the specimen at all times → allows a court to hear the evidence
Good lab practices (e.g. standards, purity, calibration, record keeping) ensure high quality data
What are the 3 general step of investigating a poisoning death
1) Obtain case history and specimens,
2) Toxicological analyses, and
3) Interpretation of toxicological findings
What does a case history may look like
Age, sex, weight, medical history, occupation, treatments before death, gross autopsy findings, drugs available to deceased, interval between onset of symptoms and death, possible toxin identification at the death scene
Pathologist at autopsy collects specimens for toxicological analysis
What does specimen collection look like
Samples are collected before embalming (preserving) happens as the chemicals used in embalming may dilute poisons or render them indetectable
Limited amount of sample are collected so have to think about how these sample are going to before hand by predicting what is going on
Typical sample are blood, urine, liver, stomach contents
Extended sampels include bone marrow, hair, nails, even insects from putrefying corpses can provide chemicals for analysis of death
What type of chemicals can be found in the
Vitreous humour of eye good for finding drugs, anions, volatile poisons like alcohols, ketones, glycols'
What type of chemical can be found in the hair
Hair heavy metals arsenic mercury lead, drugs of abuse, pharmaceuticals, pesticides and plastics
What can a maggot analysis tell you
yield positive screens for barbiturates, benzos, phenothiazines, morphine, malathion or their metabolites
How does the administration of the poison tell you were it is most likely to be
Look at the organs which it targets because that is where it will build up
If a poison is ingestion (want to look at the GI tract for unabsorbed poison)
If the poison is exerted in the kidney, there should be metabolites in the pee
If the poison is inject must undergo first pass metabolism so may build up in the liver
Immunoassays can detect metabolites if you suspect a drug
What would you look for if you suspect someone drink and took cocaine
Would look for cocaethylene
What does decomposition produce and how does it do that
Decomposition produces cadaveric alkaloids like putrescine and cadaverine via bacterial decarboxylation of amino acids ornithine and lysine
Phenylalanine is converted to phenylethylamine
Macromolecules also decompose vi a hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction that can obscures isolation, identification and quantitation of target chemicals
What levels can go up and down with putrefaction
Cyanide, ethanol and CO
What poisons are stable and can remain the body for years
arsenic, barbiturates and strychnine
What are kinda the primary screens done (2)
Urine screen for ferric chloride, perchloric, nitric acid, FPN color test for phenothiazine drugs,
immunoassays for amphetamines, benzos, opiate derivatives
What is standard additions and how do they work
involve adding known amounts of a suspected chemical to a preserved specimen (e.g. embalmed organ) and the results are compared to normal tissue
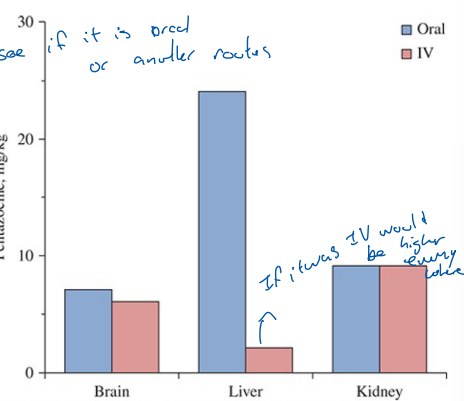
How can you tell what routes someone was administered the poison
In general, highest concentrations = site administered; GI tract, liver = oral ingestion; Lungs = inhalation
Ratio of relative distribution can determine it was oral or else
What happens when you smoke crack
Smoking introduces pyrolytic products of parent compound like smoking crack produces anhydroecgonine methyl ester
What is a con of urinalysis
is good for qualitative presence/absence, not cause of death
As some people react to different amount of poisons.
What physiological effects correlate with what
correlate with blood concentrations generally, which is the basis for therapeutic drug monitoring. Rather than urine levels
Why don’t people die imitate after given a poison
It takes time for a chemical to death and administration can allow redistribution, biotransformation and or exretion
How long does it tkae for for fatal acetaminophen to take place
Fatal acetaminophen OD takes 3-4 days so post-mortem blood acetaminophen is within therapeutic ranges
What is important to take into analysis of post-mortem analysis
If the individual went to the hospital they may have been treater with a drug so they may come up in the readigs
interpretations of toxicological findings
Drugs are not evenly distributed in cadavers, nor do they maintain the same distribution patterns after death
Site of the blood sample matter
What happens with drugs with high apparent volumes
They tend to have elevated blood concentrations over longer post-mortem intervals
Where are bloods normal taken
heart blood plus peripheral blood sample is taken