Scientific Revolution Scientists
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
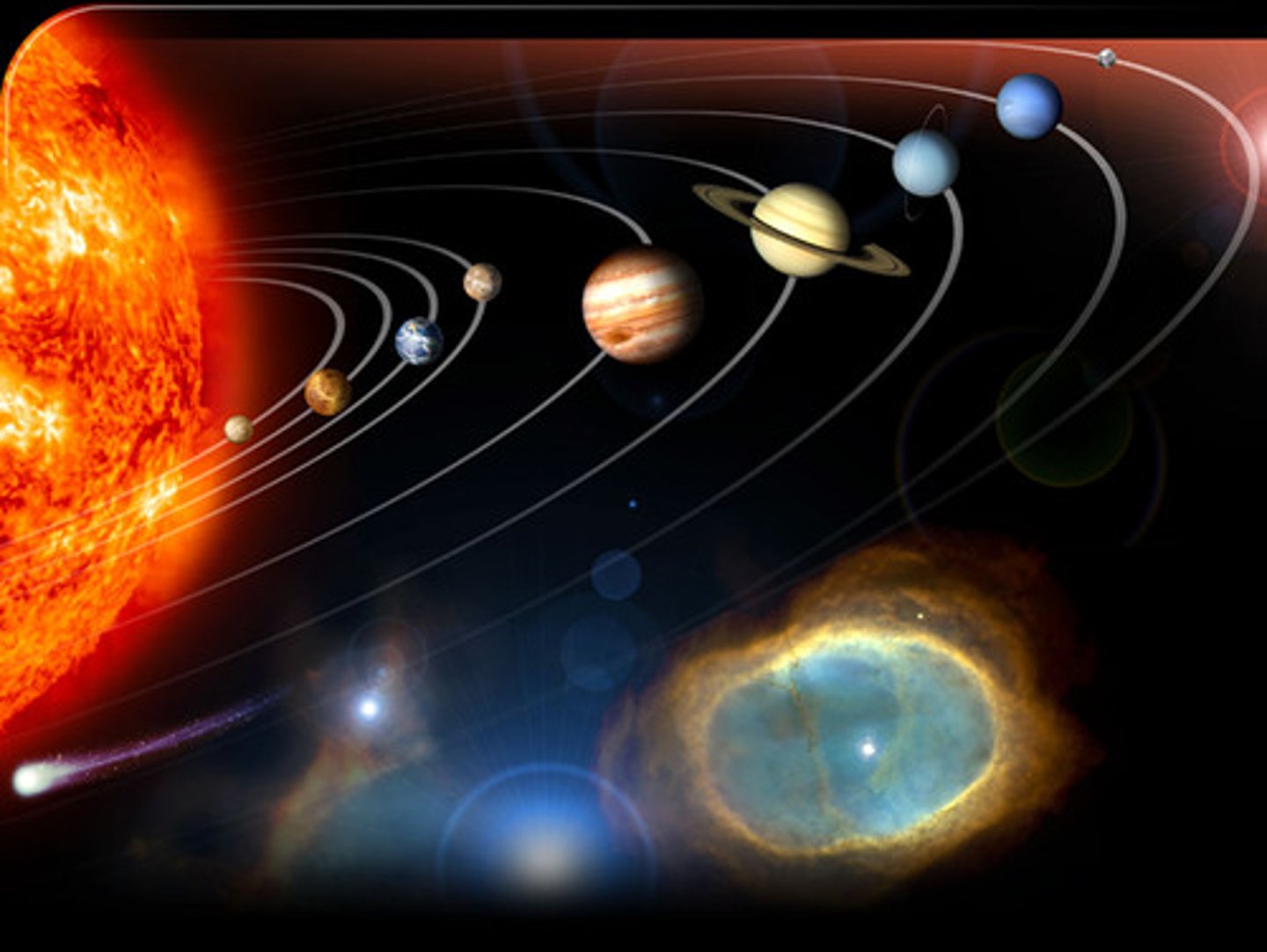
heliocentric
The theory that concluded that the sun is in the middle of the universe and the earth every other planet revolves around it
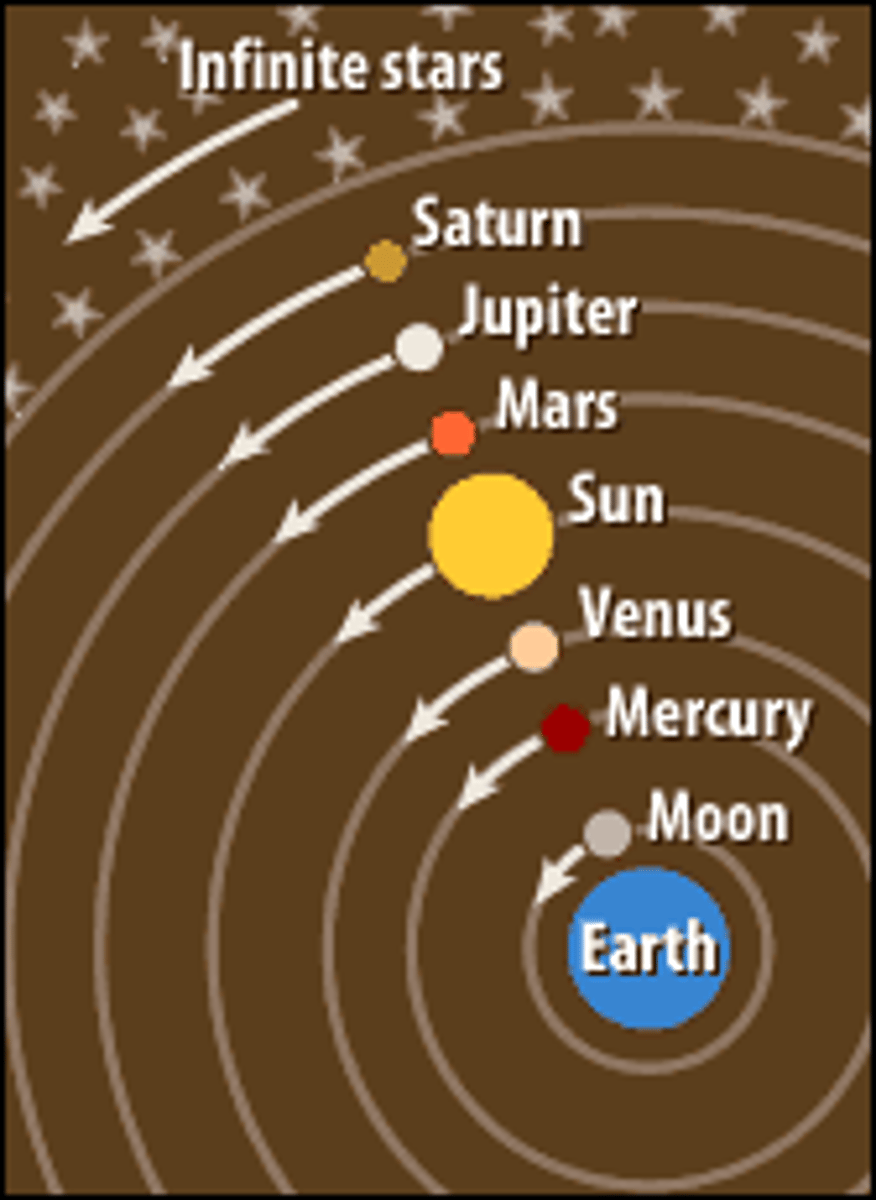
geocentric
The theory that concluded that the earth is in the middle of the universe and the sun and every other planet revolves around it
Scientific Revolution
is a concept used to explain the emergence of modern science during the early modern period when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transformed the views of society about nature

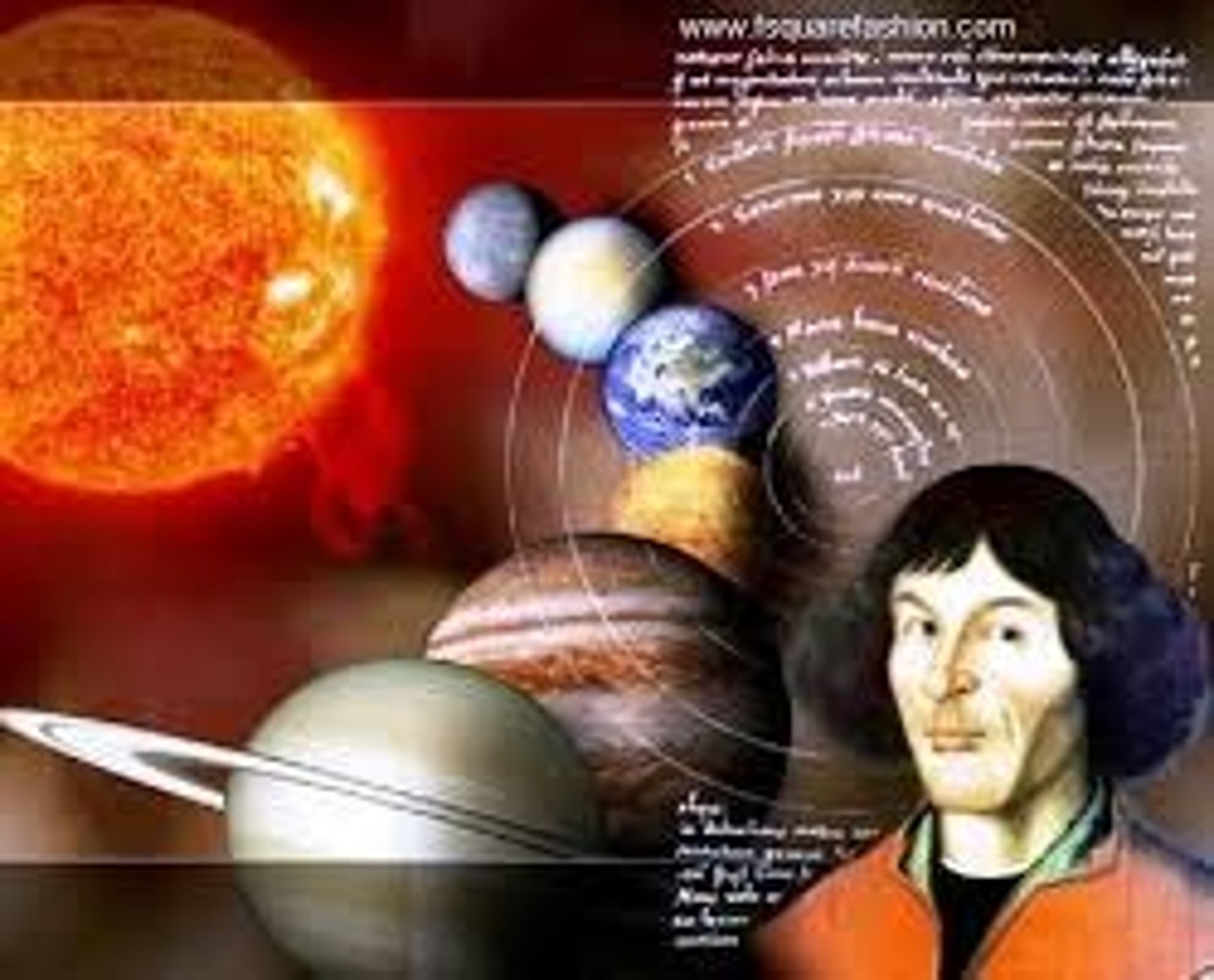
Nicholas Copernicus
A Polish scientist that studied astronomy and concluded the heliocentric theory known as the Copernican hypothesis
Tycho Brahe
A Dutch scientist that built observatories and created 20 years of tables of astronomical observations

Johannes Kepler
A German scientist that discovered laws of planetary motion

Galileo Galiei
A Florentine scientist that formulated the law of inertia with the use of a telescope

Issac Newton
An English scientist who is notorious for the law of gravitation and the prism

Copernicus
earth revolves around the sun
Brahe
20 years of tabless of astronomical observations
Kepler
planets move in elliptical orbits
Galileo
the moon is not a perfect sphere; jupiter has moons just like earth
Newton
objects in motion stay in motion; white light consists of several colors; calculus
Bacon
make observations before drawing conclusions
Descartes
"I think thereofere I am"; Begin with first principles, then make observation; skepticim; dualism
Machiavelli
rulers will do whatever to preserve their power, therefore preserving the state
believed it was better to be feared
insisted that if an end justified the means, then it was ok to do whatever was necessary to achieve those goals
ruthlessness was a neccessity, honor an option
wrote “The Prince”
was a famous Italian Renaissance political philosopher and statesman, secretary of the Florentine Republic
Voltaire
believed monarchy to be the key to progress and change
gov needed structure
thought only an enlightened monarch, advised by philosophers llike himself, could bring about change as it was in the kings’s rational interest to imptove the power and wealth of France in that world
favored an understanding of God beyond institutional religion
favored individualism
distrusted democracy
fought for civil rights, the right to a fair trial, freedom of religion, and denounced the hypocrises and injustices of the ancient regime
Blackstone
impeachment
rights
believed God has bult into the universe fundamental laws that are fixed, unchangeable, and must be obeyed
expressed human law is not to violate God’s law, but to decide what are right and wrong in regard to “things in themselves indifferent”
his commentaries influenced American law in many ways
theories influenced the writers of the US Constitution
Montesquieu
Checks and balances
concerned about relationship between religion and violence
argued not for atheism, but rather a secular (worldly) morality that is tolerant of many different religions
despite his belief in religious tolerance, he did not believe people were equal
approved of slavery
thought women weaker than men
according to him there are 3 forms of gov
monarchy
aristocracy
republicanism
Rousseau
believed people are born good, independent, and compassionate, unlike other philosophers of his time
people can both be ruled and free if they rule themselves
direct democracy was the ideal way for people to make decisions and ONLY through direct democracy can people’s freedom be preserved
even representative democracy is corrupt
Beccaria
believed laws should be enlightened, ratinal, logical, and shouls be the greatest good for the greatest number
individuals have free will and make choices on that free will
with the right punichment, the criminal justics system can control the free willed and rational human being
when one chooses to live in a society, then one chooses to give up some personal liberties in exchange for the safety and comfort of a society
inlfuence the US constitution and Bill of Rights
Mary Wollstonecraft
said that wimen had an inferior role in society bc of the environment in which they grew up
all people were equal and that every person possesses that natural right to determine his-her own destiny
called an end to monarchy
actively called for rights of women
Hobbes
argued people were naturally wicked and cannot be trusted to govern
believed people should voluntarily give power to a king who would guide the country
a ruler’s power comes not from God, but from, people rationally deciding that this is in their best interests
democracy wouldn’t work because selfish people would always put their own interests ahead of the nation’s
Locke
valued individual freedom of religion
people have the gift of reason/ability to think
people have the natural ability to govern themselves and look after the well being of society
did not believe in “divine right”
if any gov. abuses the rights of the people intead of protecting them, the people have the right to rebel and form a new gov.
gov. are formed to protect the right of life, the right to freedom, and the right to property
gov. should be divided into 3 branches