Histology - Blood Formed Elements
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
what are the 2 components of blood?
ECM (plasma) containing albumin, globulin, fibrinogen
cell/cell gradments
red blood cells (erythrocytes)
white blood cells (leukocytes)
platelets (cell fragments)
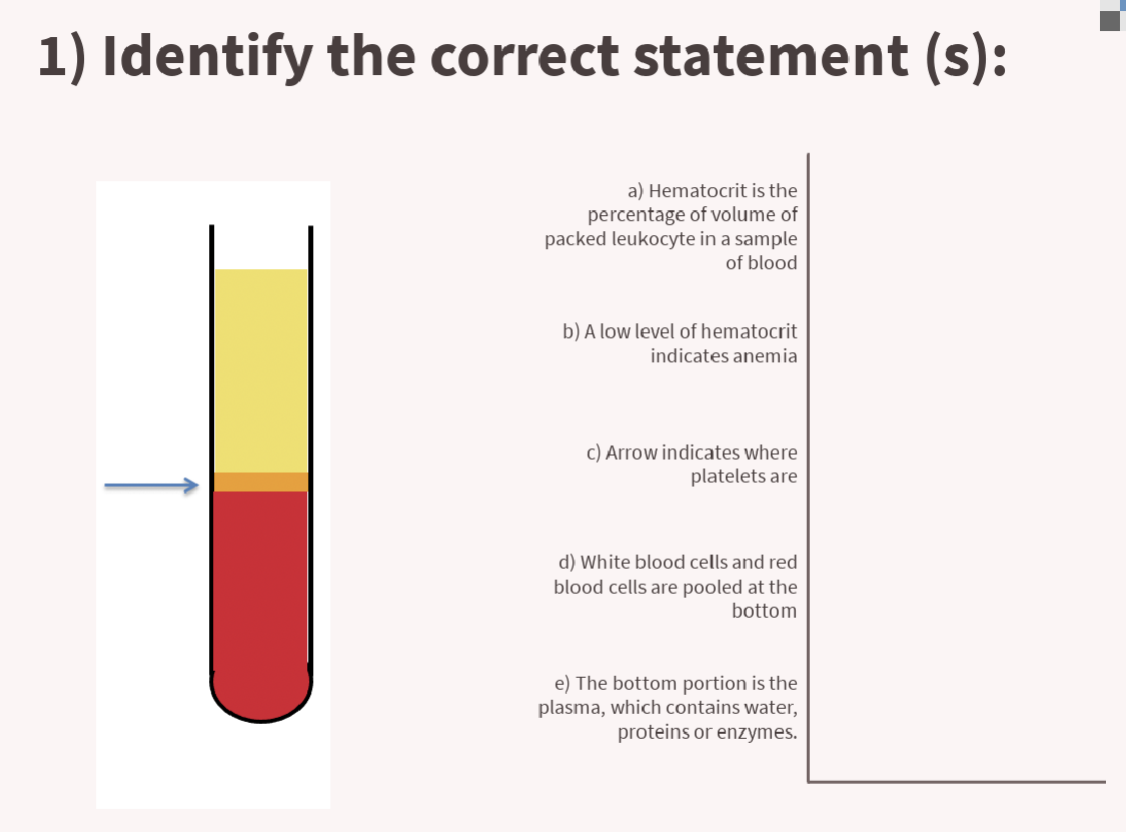
b) a low level of hematocrit indicates anemia
c) arrow indicates where platelets are
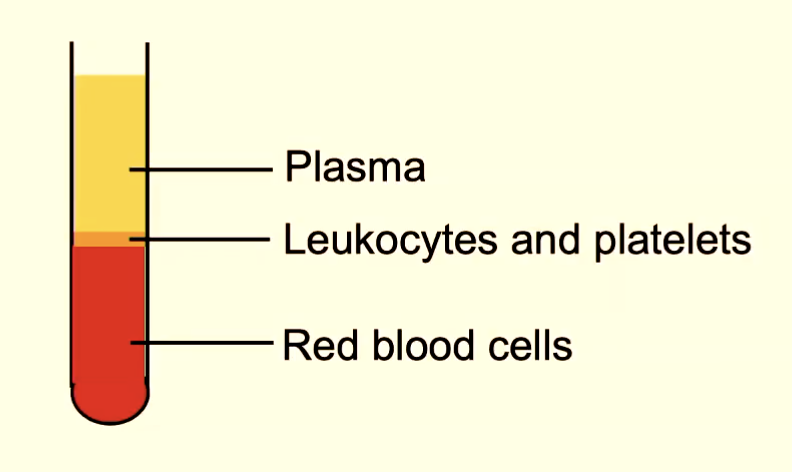
what is the volume of packed erythrocytes in a sample of blood called?
hematocrit
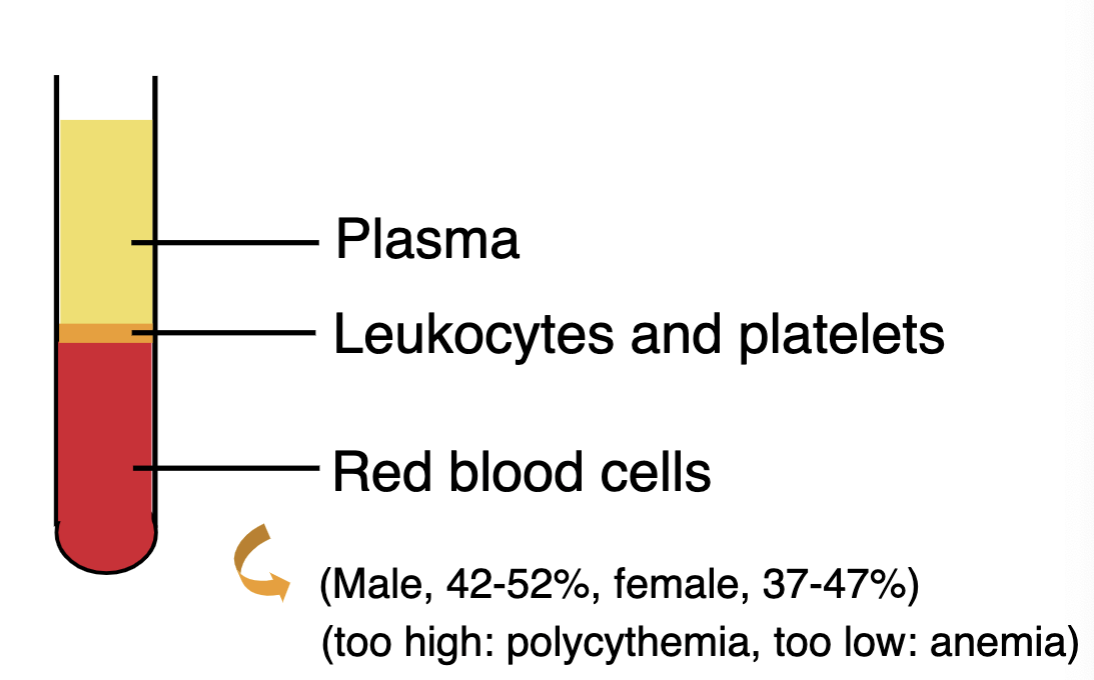
t/f: males generally have higher levels of red blood cells compared to females
true (Male, 42-52%, female, 37-47%)
what is it called when red blood cell levels are too high? too low?
too high: polycythemia, too low: anemia
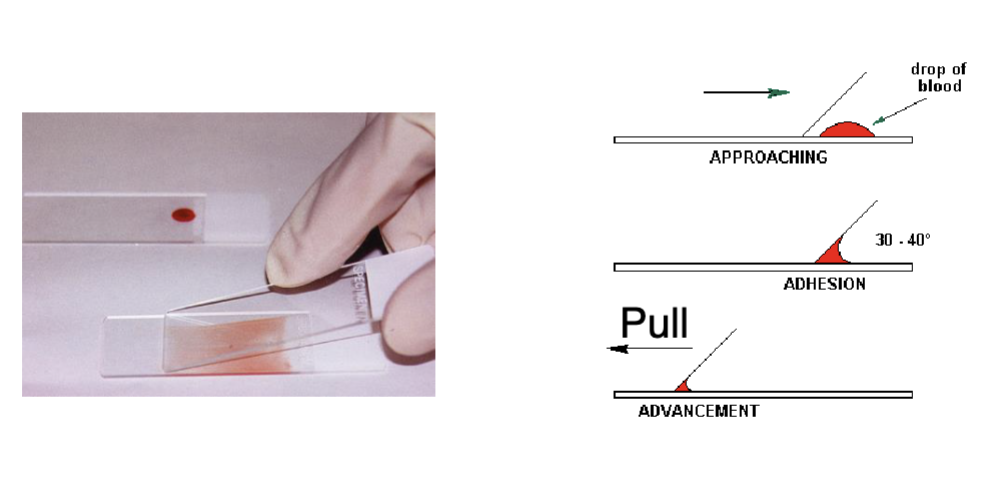
how to view blood cells? (why not just place a glass plate directly on top of a drop of blood?)
blood smear
avoid breaking red blood cells
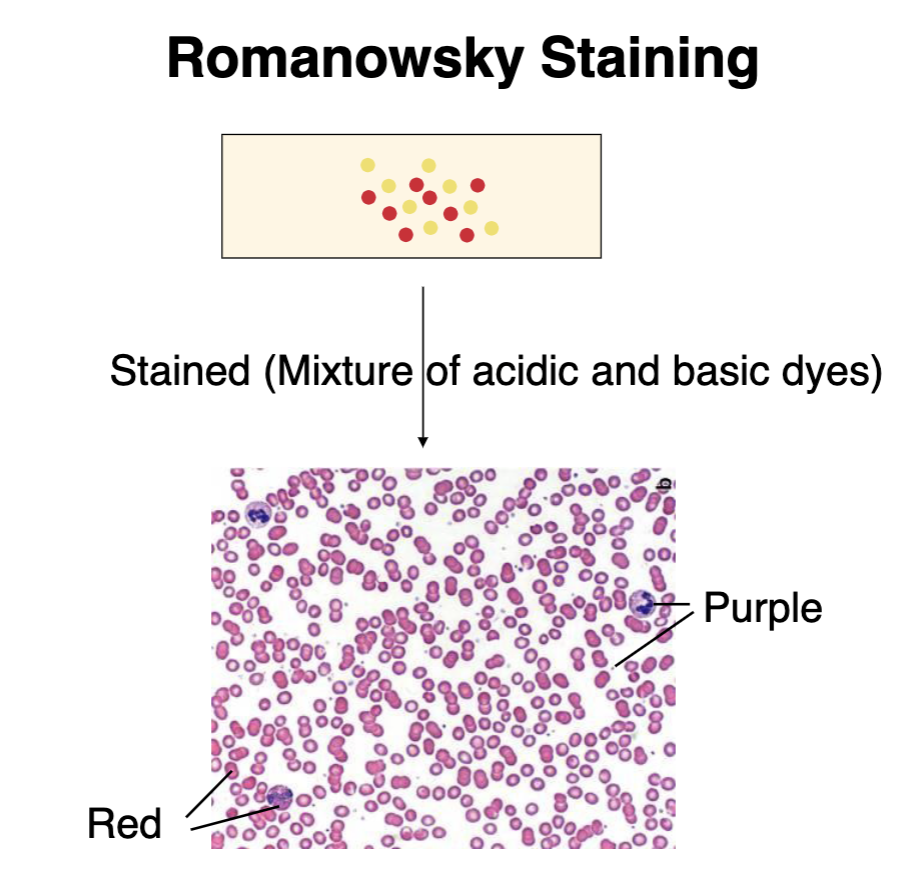
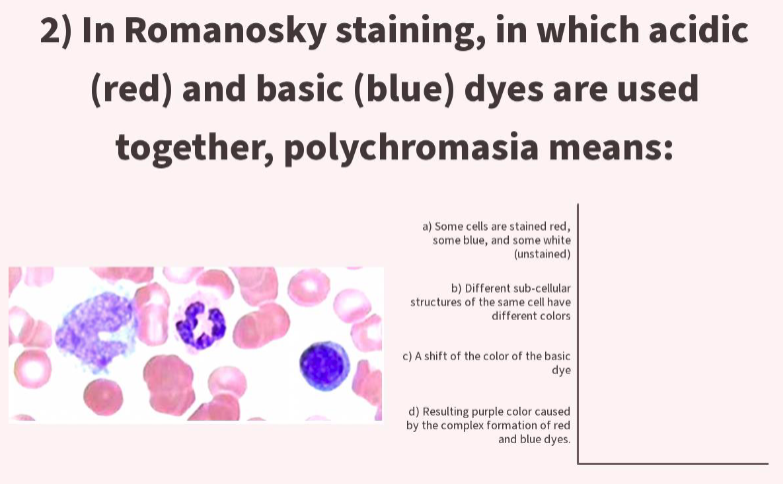
what type of staining can be done to differentiate different cells in a blood smear?
Romanowsky staining (mixture of acidic and basic dyes)
what components of blood demonstrate orthocrhomasia - red?
Erythrocytes, eosinophil granules
(stained only with acidic dye)
what components of blood demonstrate orthochromasia - gray blue or blue?
cytoplasm of monocyte
(stained only with basic dye)
what components of blood demonstrate metachromasia - violet purple?
Basophil granules
(color shift from certain basic dye from blue to violet purple)
what components of blood demonstrate polychromasia - purple?
Azurophilic granules
Neutrophil granules
Chromatin (nucleus)
Platelets
(layered with both basic and acidic dyes)
Metachromasia can happen with only certain basic dyes such as…?
toluidine blue, methylene blue
Metachromasia can happen any cell or tissues with abundant positive/negative charges: such as …?
negative
cartilage, mast cells
how does metachromasia happen in Romanowsky staining?
Polyion presence: when stained with a concentrated basic dye, the dye molecules are sufficiently close to form dimeric and polymeric aggregates---causing a shift in absorption properties
how does polychromasia happen in Romanowsky staining?
basic dye binds to cellular structures first
the acidic dye then binds to form a purple staining
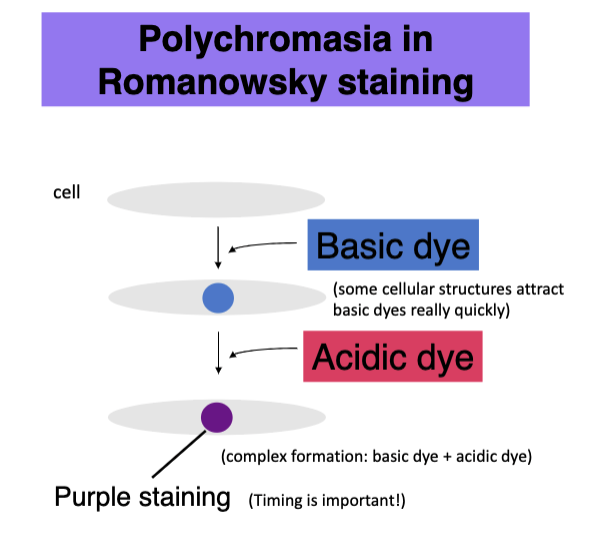
______ is important in polychromasia in Romanowsky staining
timing
how many dyes are involved in ortho and meta-chromasia? polychromasia?
Ortho- and meta-chromasia involve only 1 dye; polychromasia involves 2 dyes
D

A
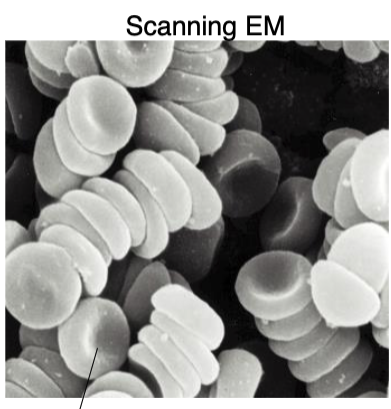
erythrocytes
what is the function of the biconcave disc shape of erythrocytes?
increasing surface area
what is the lifespan of erythrocytes?
120 days
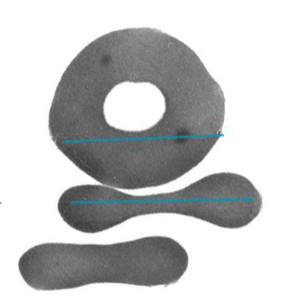
diameter of RBC?
7.5 micrometers
what are the predecessors of red blood cells? (immature RBCs?)
reticulocytes (contains remaining cell organelles so will stain basophilic → polychromasia)
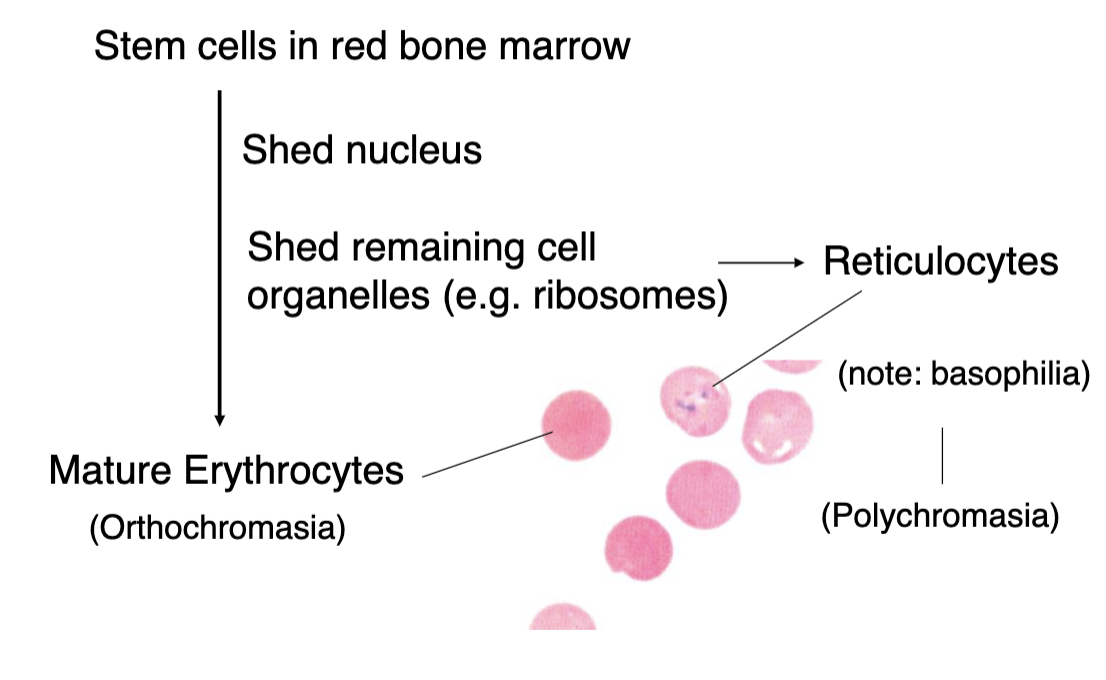
mature erythrocytes demonstrate what kind of staining?
orthochromasia
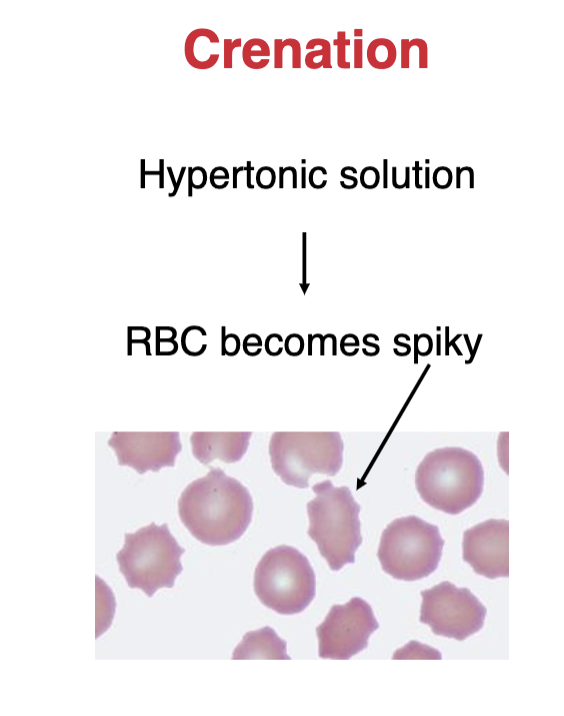
what is crenation?
RBC in hypertonic solution → spiky membrane
what is sickle cell anemia?
mutation in hemoglobin (Glu → Val)
distorts normal appearance to form sickle-like shape
cannot get through blood vessels easily
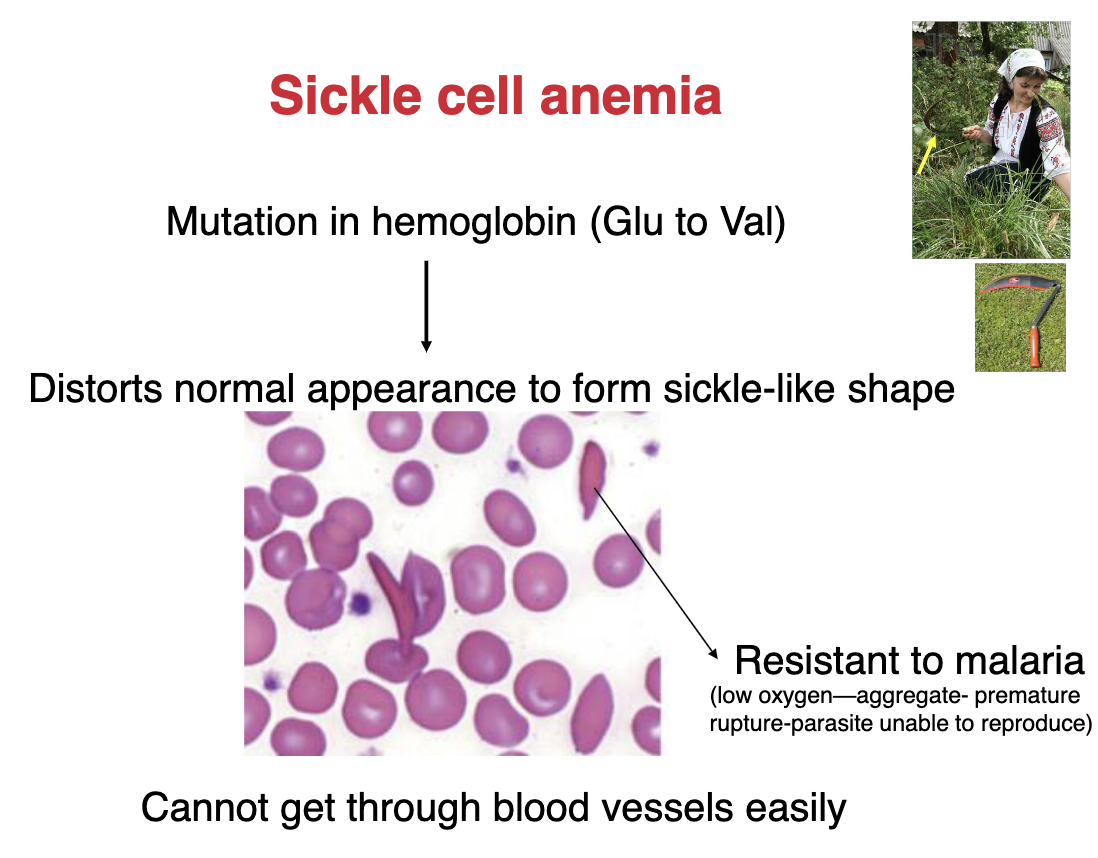
sicle cell anemia is resistant to…?
malaria
(low oxygen → aggregate → premature rupture → parasite unable to reproduce)
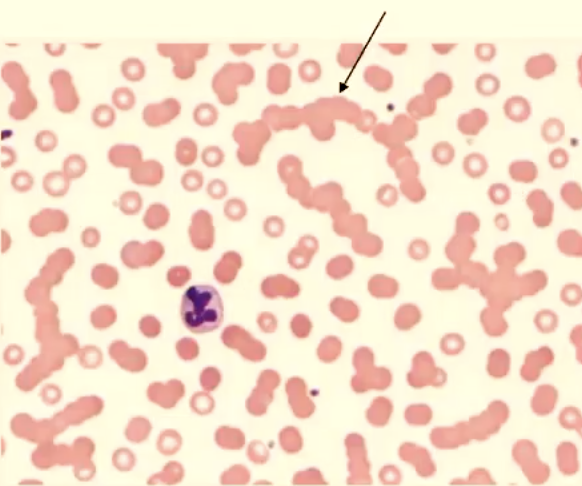
Rouleaux formation (stacks of RBCs)
old and diseased RBCs are usually cleared in the _____?
spleen
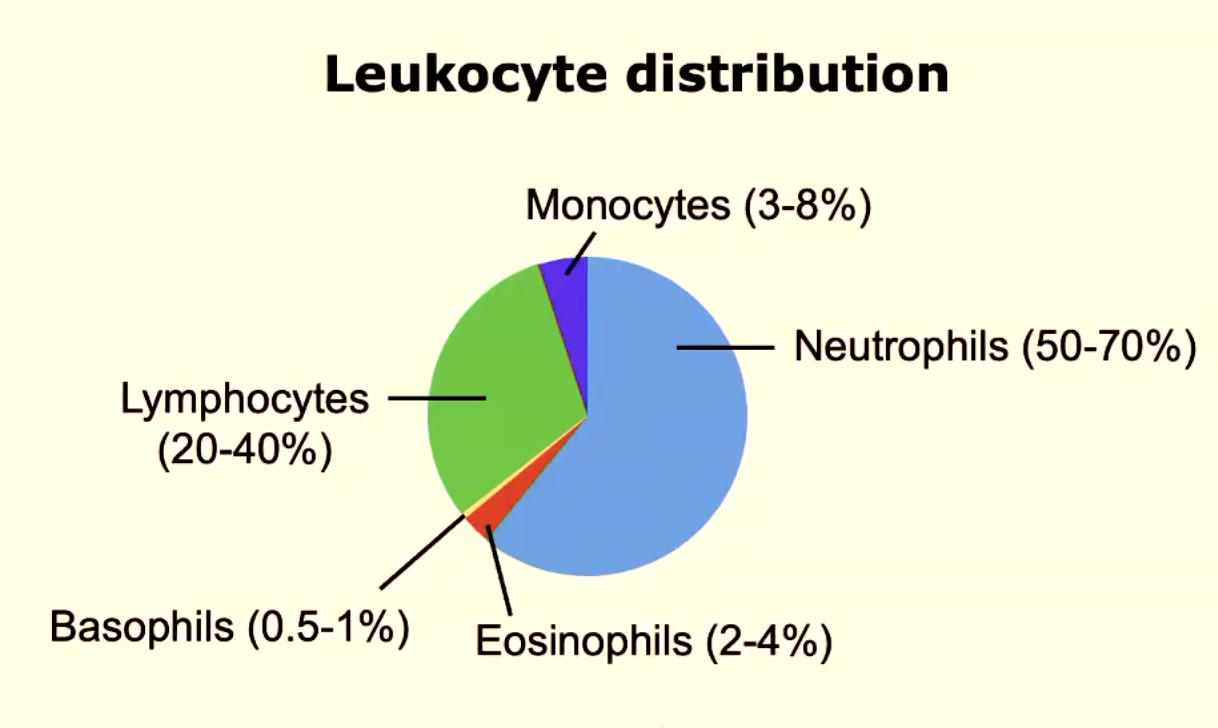
what is the distribution of leukocytes?
neutrophils (50-70%) → most abundant
lymphocytes (20-40%)
monocytes (3-8%)
eosinophils (2-4%)
basophils (0.5-1%) → least abundant
what are the 2 major types of white blood cells?
granulocytes (Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils)
Agranulocytes (Lymphocytes, Monocytes)
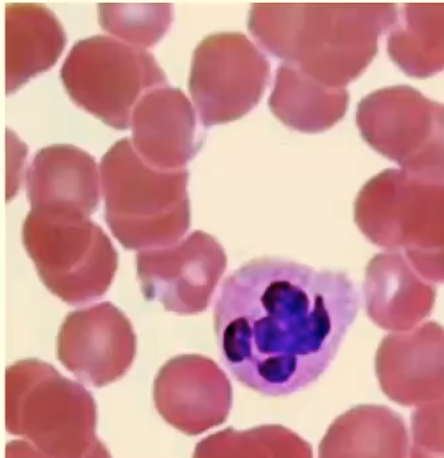
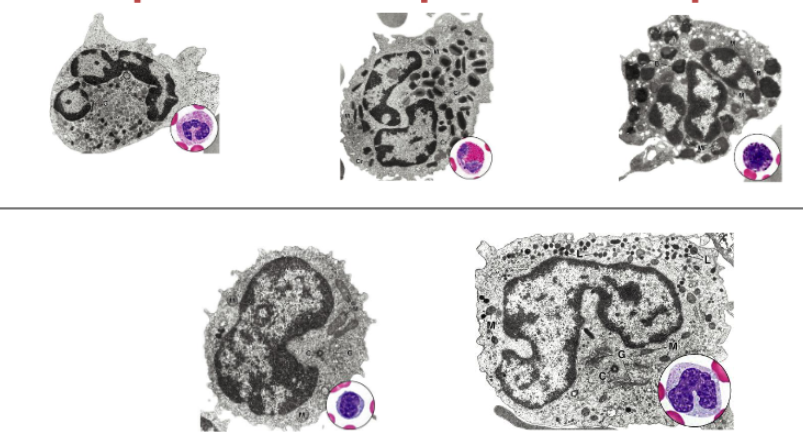
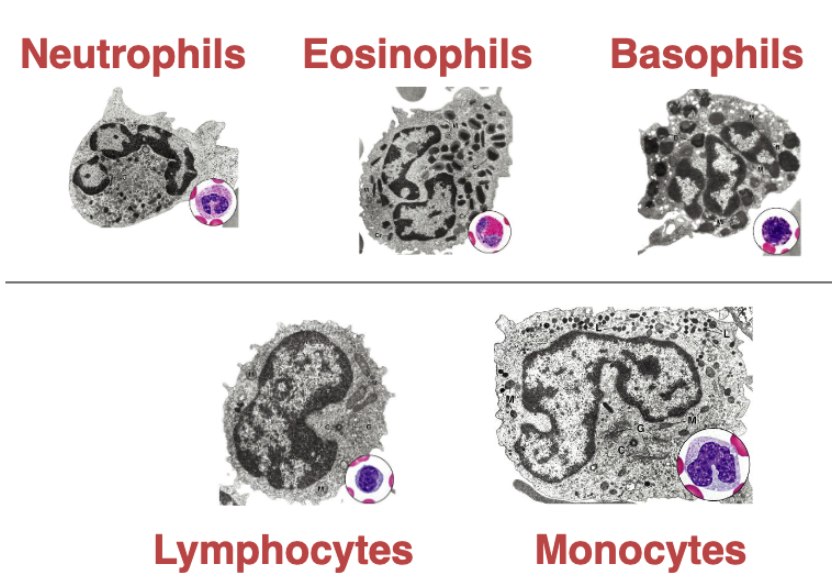
neutrophils (granulocytes)
what is the function of neutrophils?
phagocytic and bactericidal (attracted to chemokines)
characteristics of neutrophil structure
Nucleus: 2-5 lobes (polychromatic)
Granules: 3 types (polychromatic)
barr-body (condensed inactivated X-chromosome)
10-12 micrometers
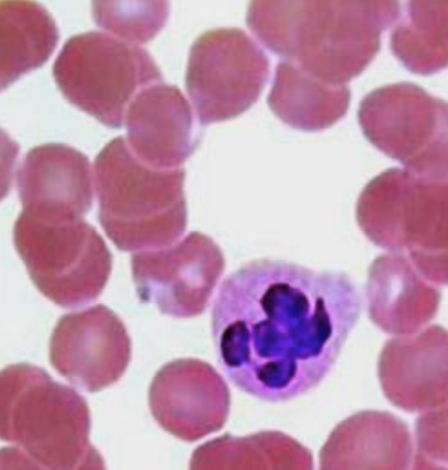
what are the 3 types of granules in neutrophils?
1. Azurophilic (lysosomes)
2. Specific (Bactericidal enzymes)
3. Anti-Bacteria factors, including those the prevent bacteria migration
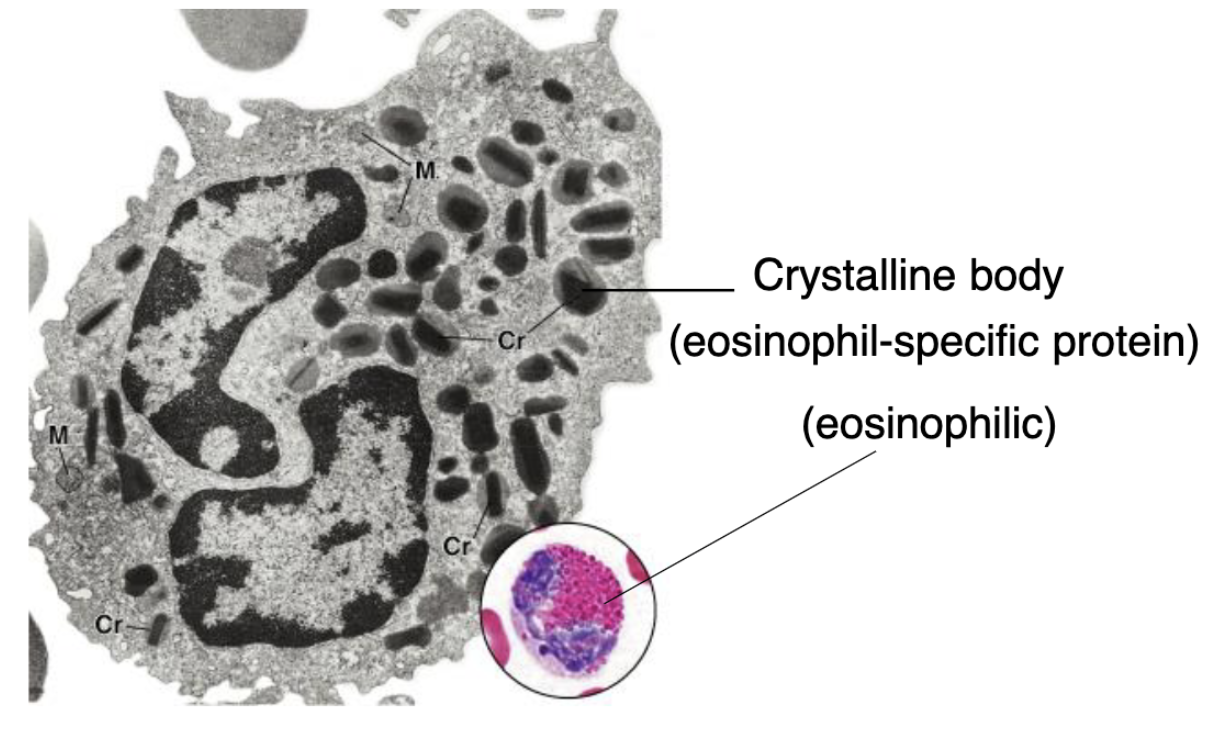
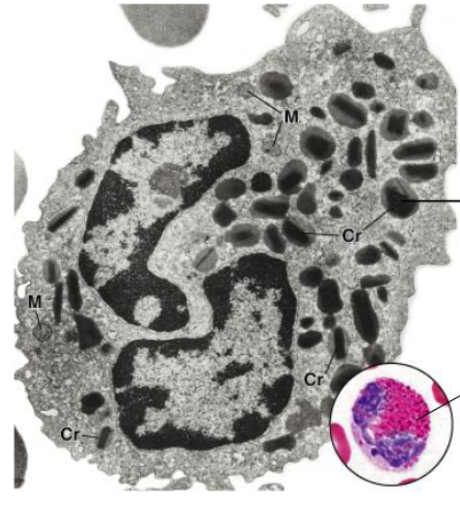
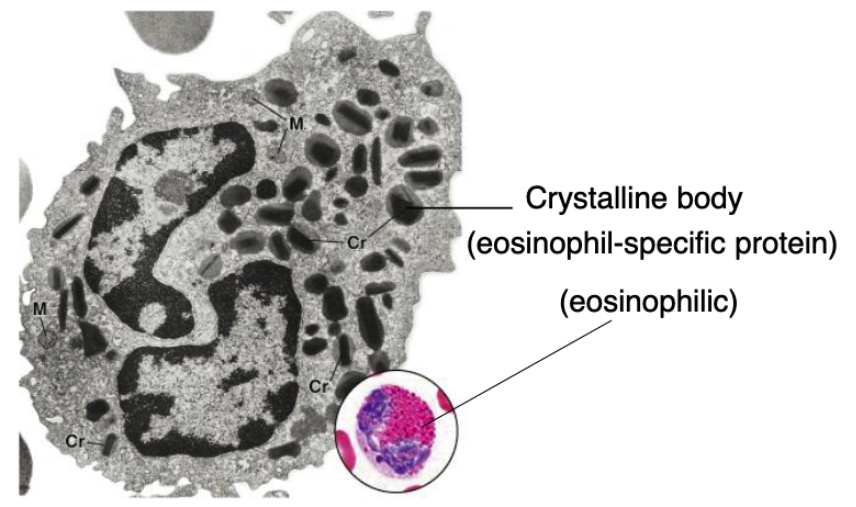
characteristics of eosinophils structure
nucleus?
granules?
other characteristics?
nucleus: 2 lobes
granules; orthochromatic
crystalline body (eosinophil-specific protein that gives red color)
function of eosinophils
anti-parasitic, allergy
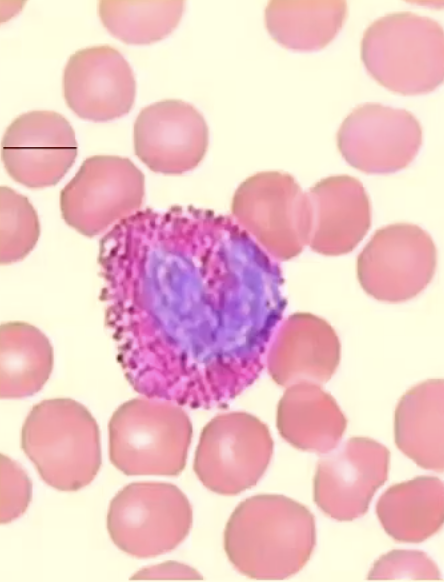
eosinophils
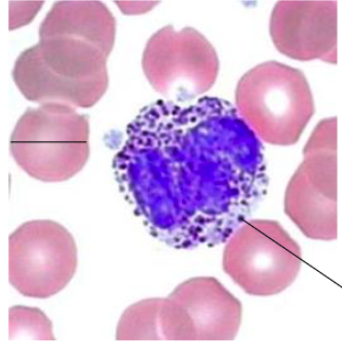
characteristics of basophils;
nucleus?
granules?
Nucleus:
often 2 lobes (polychromatic)
often masked by large and abundant granules
Granules:
Specific: contain histamine, and are very rich in glycosaminoglycan, which gives intense stainings (Metachromasia)
Azurophilic (lysosomes)
function of basophils?
Participate in allergic and parasitic reactions
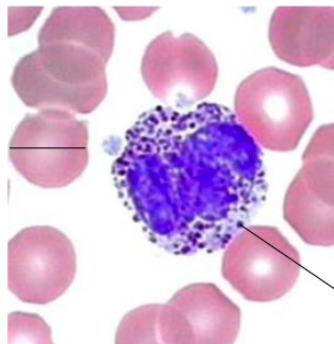
basophils

basophils
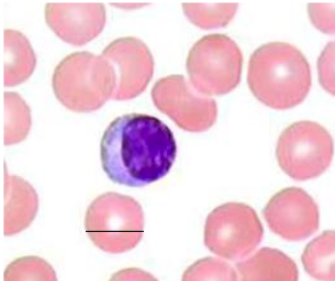
characteristics of lymphocytes
nucleus?
cytoplasm?
Nucleus: Spherical or oval (often occupying majority of cell)
Cytoplasm: thin (orthochromatic)
what are the 2 types of lymphocytes?
Small: B-cells, T-cells
Large: granular cells (natural killer cells)
lymphocytes
function of lymphocytes
Acquired immunity (cell-mediated defense; antibody production)
what are the types of granulocytes?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
what are the types of agranulocytes?
lymphocytes, monocytes
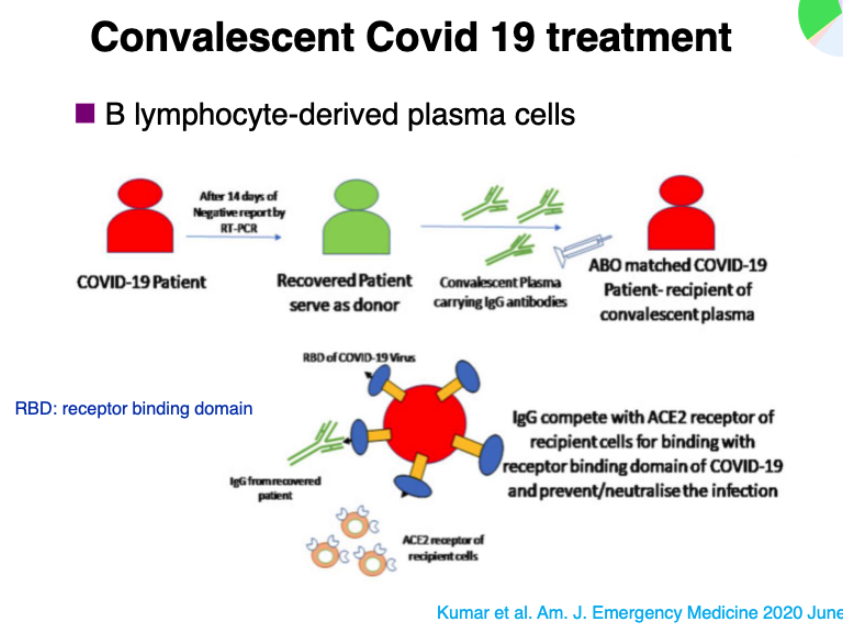
what is convalescent Covid 19 treatment?
using B lymphocyte derived plasma cells (antibodies from someone who already had covid) to help treat infected person
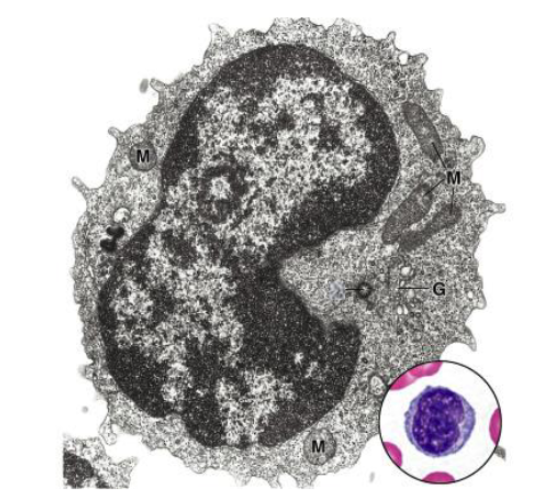
lymphocytes
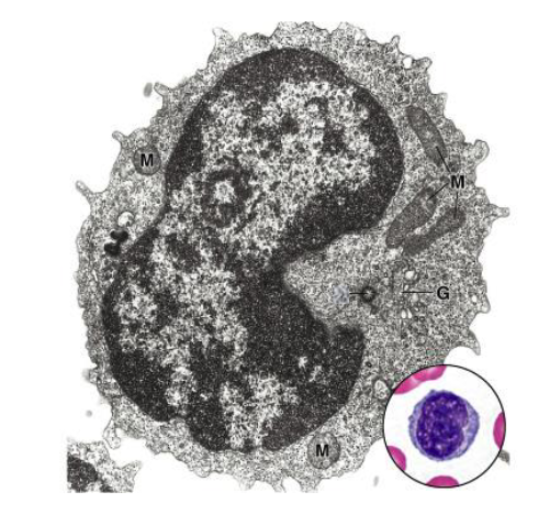
characteristics of monocytes:
nucleus?
cytoplasm?
Nucleus: Folded, U-shaped (kidney-bean shape)
Cytoplasm: mostly orthochromatic, with fine azurophilic granules
overall large in cell type
function of monocytes?
Precursors for mononuclear phagocyte system
monocytes
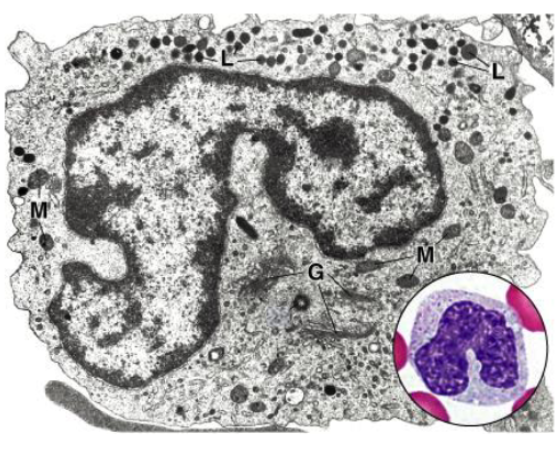
monocytes
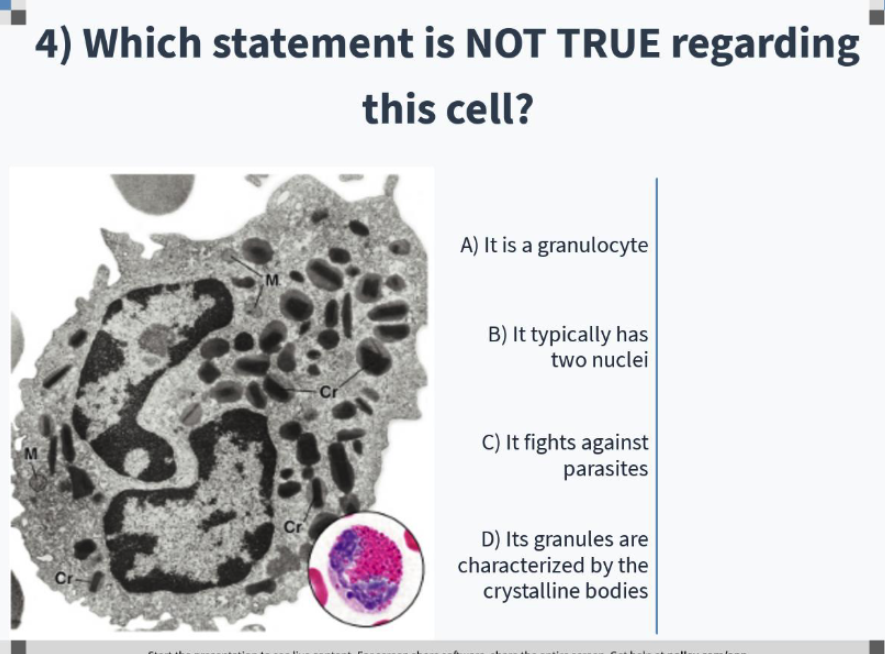
B
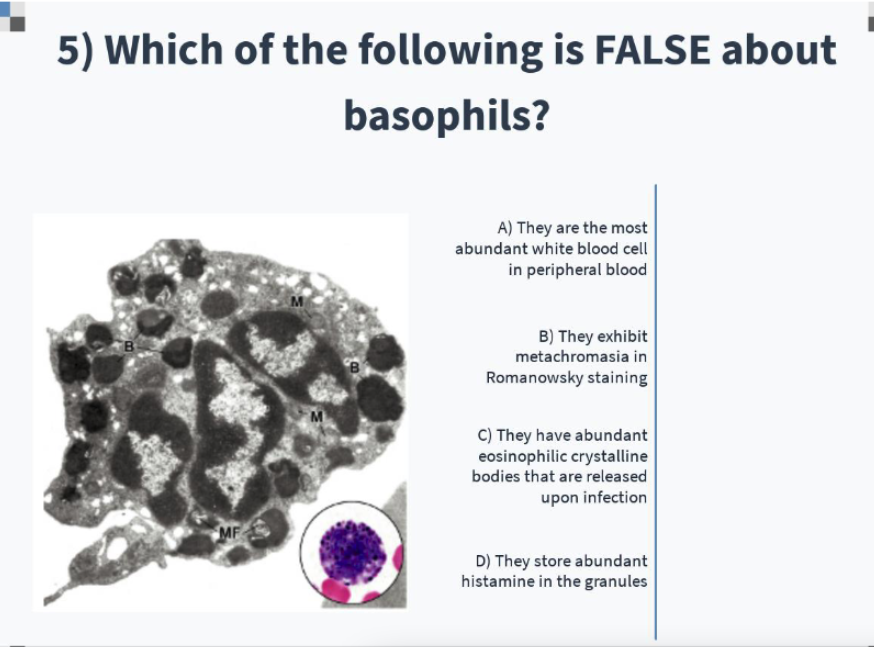
A
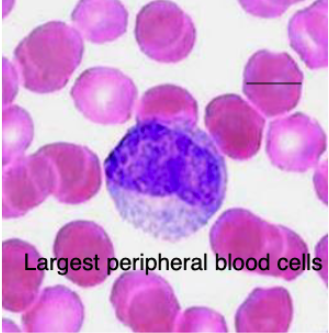
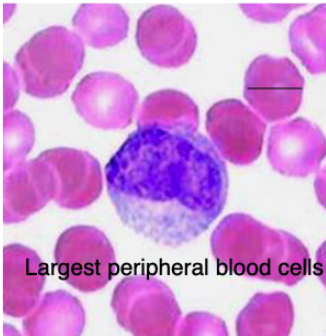
what are the largest peripheral blood cells?
monocytes
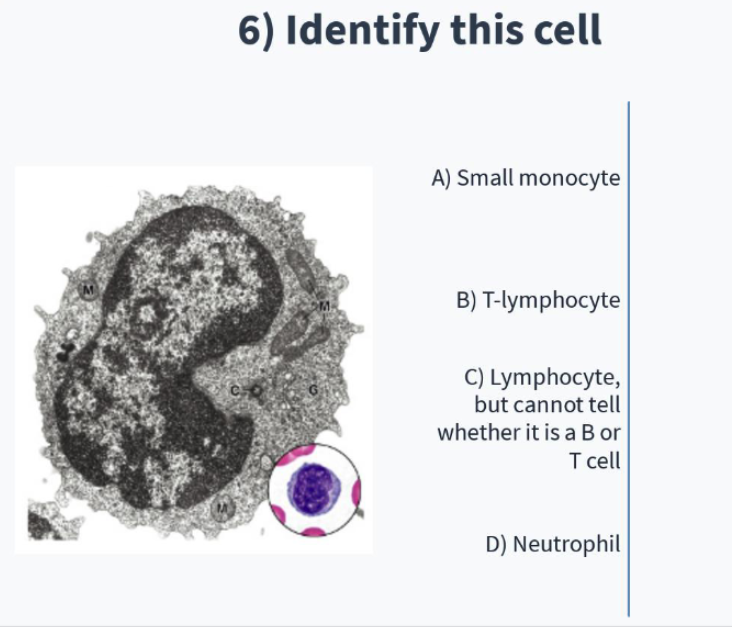
C

D
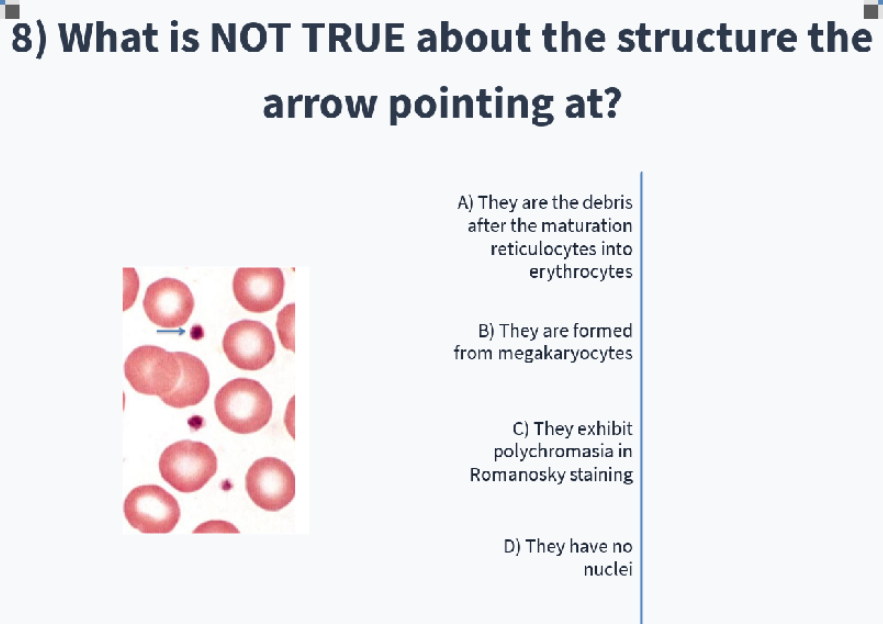
A
platelets contain 2 regions. what are they?
1. Central region: granulomere (darker staining), contains mitochondria, vacuoles, a-granules and glycogen
2. Peripheral region: pale staining, sends out fine cytoplasmic processes
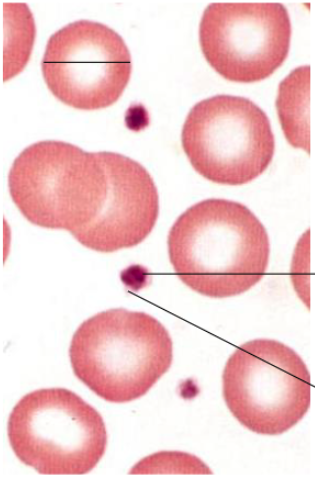
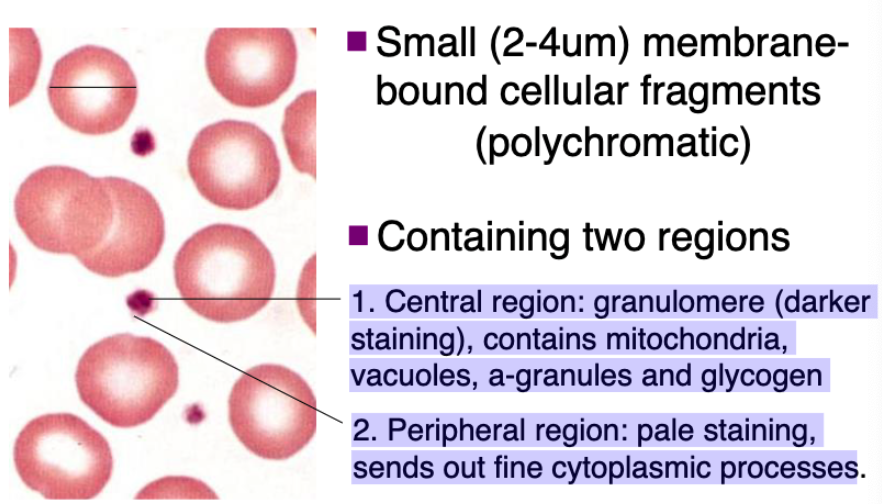
what are the small (2-4um) membrane-bound cellular fragments (polychromatic)?
platelets (cell fragments)
function of cell fragments (platelets)?
Aggregation and agglutination; clotting
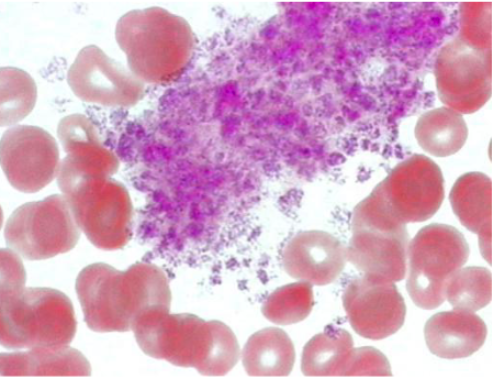
platelets
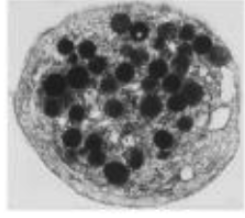
platelets
what is the formation of blood cells called?
hematopoesis
Cancer of early forming blood cells (usually white blood cells) is called?
leukemia
leukemia
D
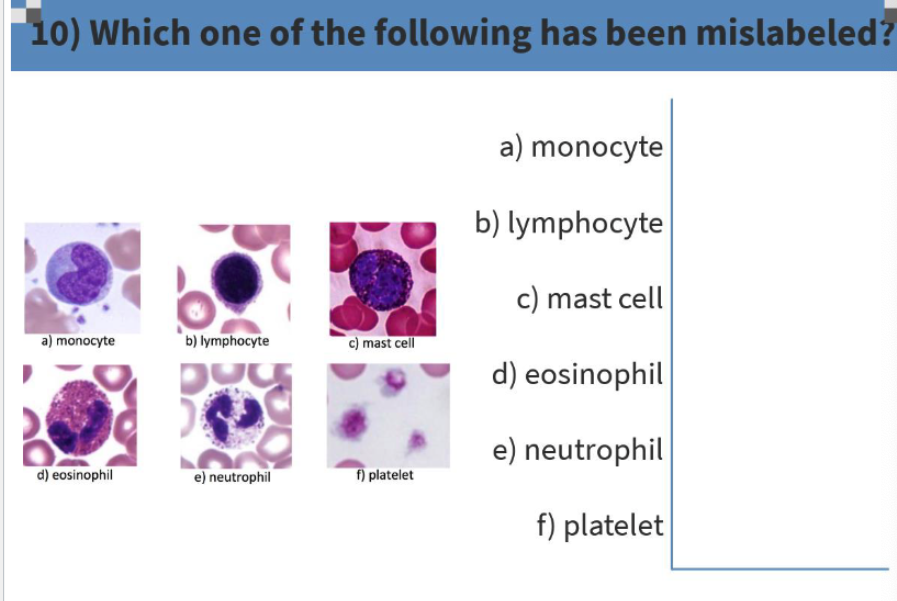
C (mast cells not present in peripheral blood)
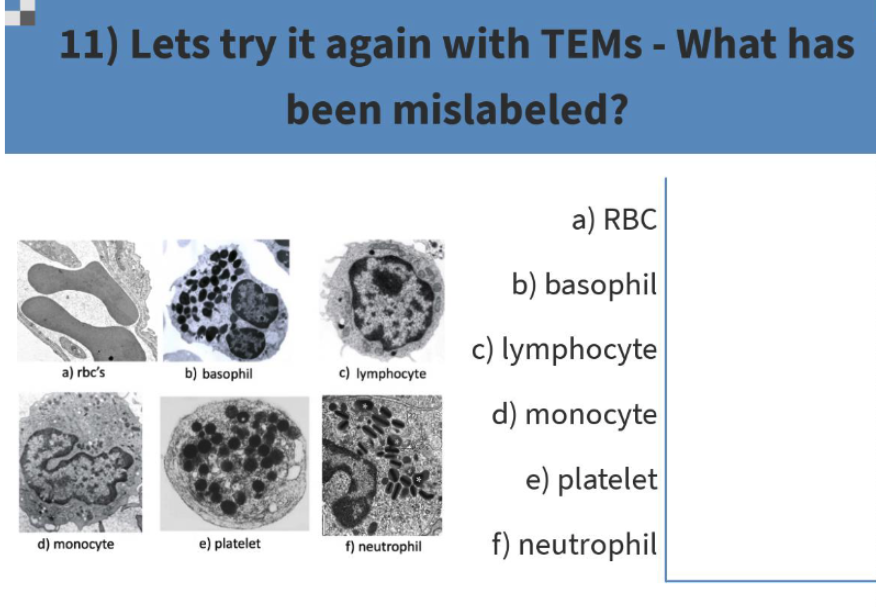
f