Comsci Paper 2 - flashcards | Quizlet
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Internet
- Interconnected set of networks and computers
- Permits transfer of data
- Permits delivery of services
- Data transfer governed by protocols (TCP/IP)
- Protocols and guidelines developed by W3C
World Wide Web (WWW)
- Set of hypertext-linked resources
- Resources identified by URIs (unique resource identifier)
- Transfers data between client and server via internet
- Resources can be read using a browser
Web 1.0
Consisted of read-only webpages made for information sharing; one-way content
Web 2.0
Consisted of read and write webpages in which people could interact, often used for social media; two-way content
Web 3.0
Consists of webpages that can read, write, and execute, designed for immersion; interconnected content
Hypertext
Text displayed with references (hyperlinks) to other text/files that the reader can immediately access, i.e. wikipedia.org links to Wikipedia's files
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol, governs transfer or exchange of hypertext. Protocol exists on the application layer
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Encrypts data wiht SSL or TLS to create a more secure form of HTTP
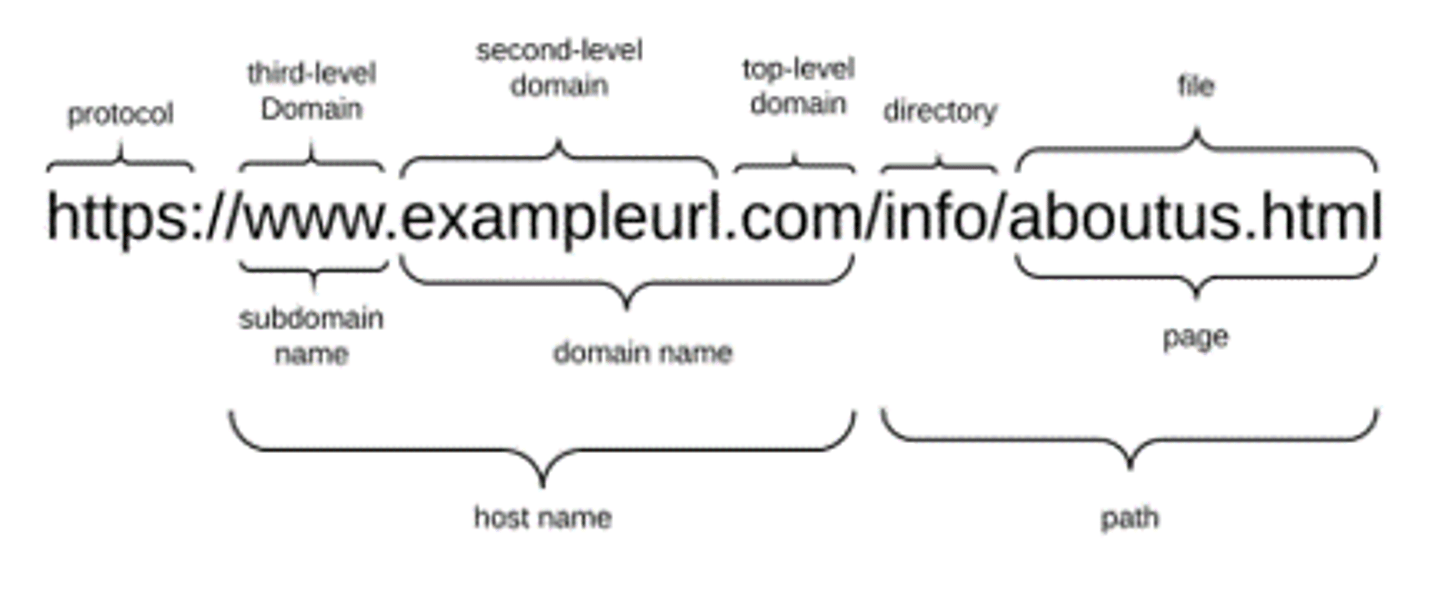
URL
Universal Resource Locator. Defines a pathway to a resource, i.e. web addresses. Consists of a protocol, domain name, directory, and file
Markup Language
Language that uses tags to annotate the information in a document for structuring, organization, and formatting
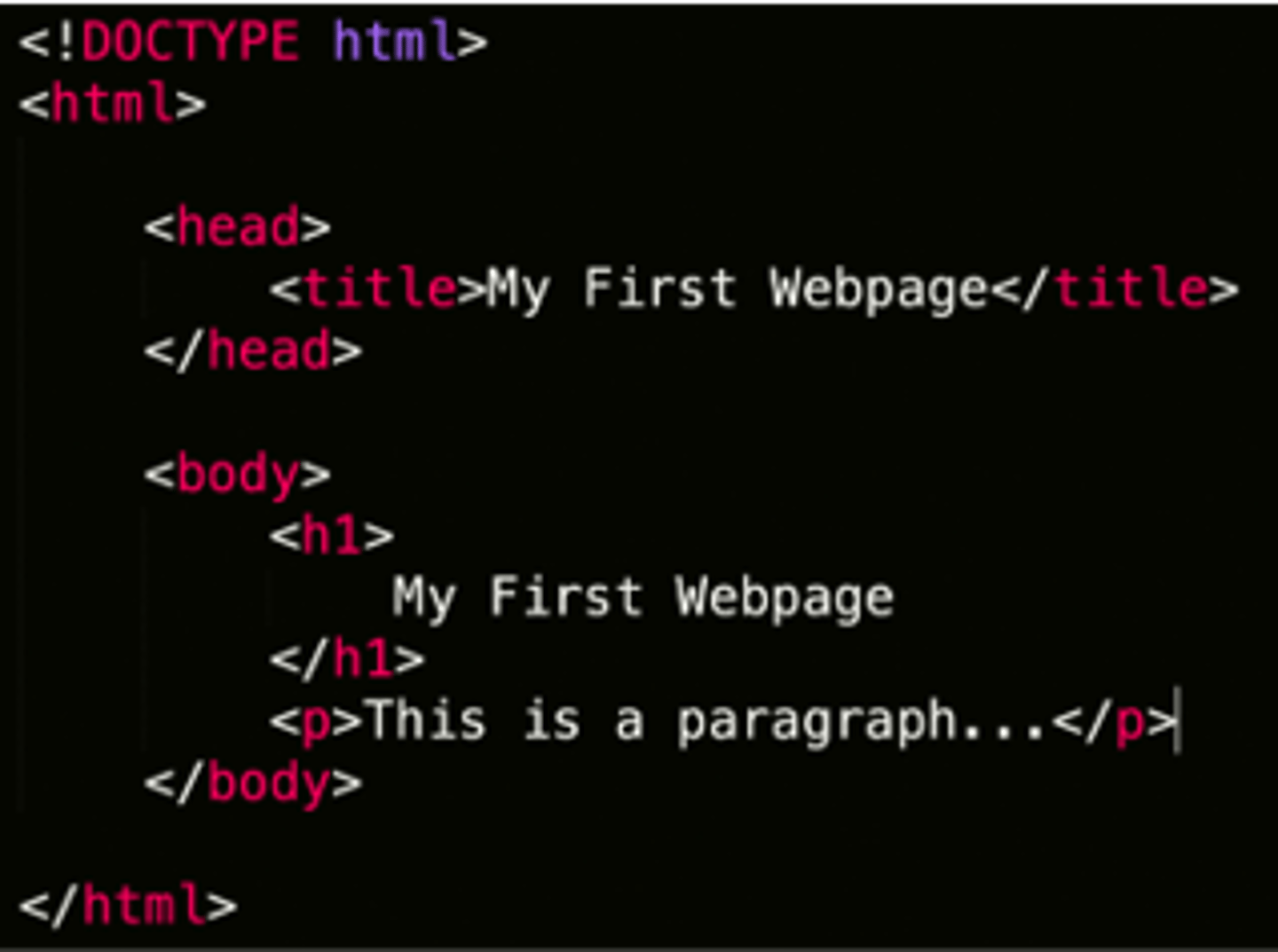
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language. Markup language for describing structure of a web page. May retrieve content with hyperlinks, and displays content sent over the internet
XML
Extensible Markup Language. A language for storing and transporting data. Extensible = easy addition of new information. Provides a common platform for sharing document information across applications.

XSLT
Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations. Transforms XML into an output document, and contains template rules/instructions
JavaScript (JS)
Scripting language to add functionality to webpages. It is embedded into HTML along with CSS. Code is executed when page is download or an "event" (such as button press) is triggered, and allows dynamic web pages (changeable content without reload).
CSS
Cascading Style Sheets. Describes the visual presentation of a webpage, and is independent from HTML
DNS
Domain Name System. Part of the TCP/IP protocol, and translates text-based web addresses to numerical IP addresses, and vice versa.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol. Receives packets of data from an application and divides it into segments, ready for IP. Establishes an initial connection.
IP
Internet Protocol. Delivers packets of data to the correct addresses. Defines the format of a packet, and includes routing information as a header in front of the TCP to tell where the packets should go.
TCP/IP
The set of protocols that governs the transfer of data over the Internet; TCP controls the retrieval, while IP controls the delivery.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. Protocol for transferring files over a TCP based network.
Components of a Web Page
Header, Body, Footer, Navigation Bar, Banner, Hyperlinks, Sidebar
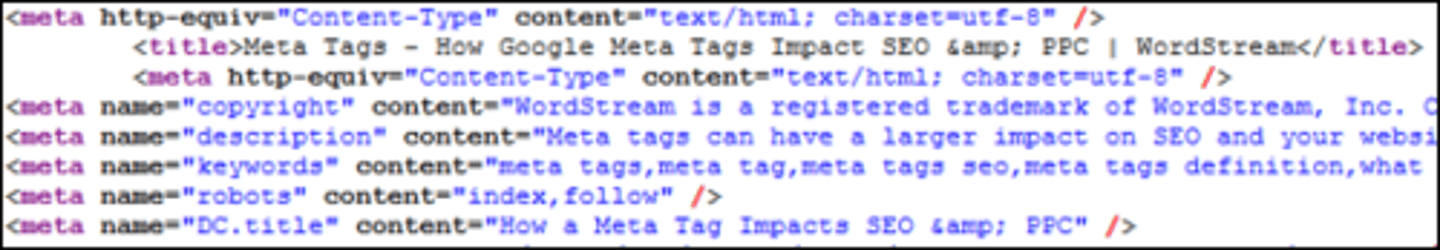
Meta tags
Information within the header that contains information about the webpage for search engines
Protocol
A set of rules to successfully carry out some process, i.e. TCP/IP for data transfer
Standards
Set of technical specifications that should be adhered to, to allow for functionality/safety/quality. Allows for interoperability (ability to exchange data) and accessibility (usable by as many people possible)
Search Engine
A program that searches for and identifies items in a database that correspond to keywords or characters specified by the user, used especially for finding particular sites on the World Wide Web
Web Crawler
AKA Web Spider/Web Robot. Browses the WWW and creates a copy of every web page it visits. It follows all the links of all the websites it visits (recursively), and indexes them, processing all their data and storing it in the search engine's database. It initially looks for robots.txt to know which links/pages to ignore.
Used by search engines to maintain real-time information by looking at metatags
SEO
Search Engine Optimization. Helps website to be better "crawled", or searched, by search engines
News Page
A website that provides relevant articles, audio and video on current news
Business Page
A website that is used to officially represent a brand on the Internet, and which is often used as the landing page for advertising content
Personal Page
A website created by an individual, or small group like a band, to contain content of a personal nature rather than content pertaining to a company, organization or institution
Blogs
Web log. A regularly updated website typically run by an individual or small group, that is written in an informal or conversational style on a particular topic
Forum
An online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages
Ecommerce Pages
Online portals that facilitate online transactions of goods and services through means of the transfer of information and funds over the Internet
Wiki
A website that allows collaborative editing of its content and structure by its users
Social Media
Forms of electronic communication (such as websites for social networking and microblogging) through which users create online communities to share information, ideas, personal messages, and other content (such as videos)
Static Webpage
Fixed webpage that does not change unless re-designed on the serverside. Allows no interaction nor any input
Dynamic webpage
Content may be changed by user or a program. Client-side scripting allows changes to be made in response to the user, and server-side scripting allows the page to produce different content depending on the user's profile/requests
PHP
Server-side scripting language, used to make dynamic and interactive web pages, mainly for data inputs.
MySQL
Database system used on the web to store data
Web Browser
Software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web
Browser Plugin
External program that runs within a web browser, usually to manage content that a browser is not designed to process
Client-Side Scripting
Scripts that run on the client device which allow changes in the webpage to be made in response to the user's actions, i.e. JS
Server-Side Scripting
Scripts that run on the server to produce different content depending on the user's profile/requests. Generally used to customize the content of a webpage for the user, i.e. personal customization, paywalls, etc.
Cookie
A piece of data from a website that is stored within a web browser that the website can retrieve at a later time
Server-Side Database
An organized collection of data stored on the server, often used to store user data
Server-Side XML
XML on the server-side, rather than storing user data, stores data for the features of the server and webpages
CGI
Common Gateway Interface. An interface which tells the webserver how to pass data to and from the database. It describes how the data in requests are transferred (inputted and outputted to and from databases/web browser)
CGI Scripts
Used to process a query (request) from the user and function as the glue between the query and the database
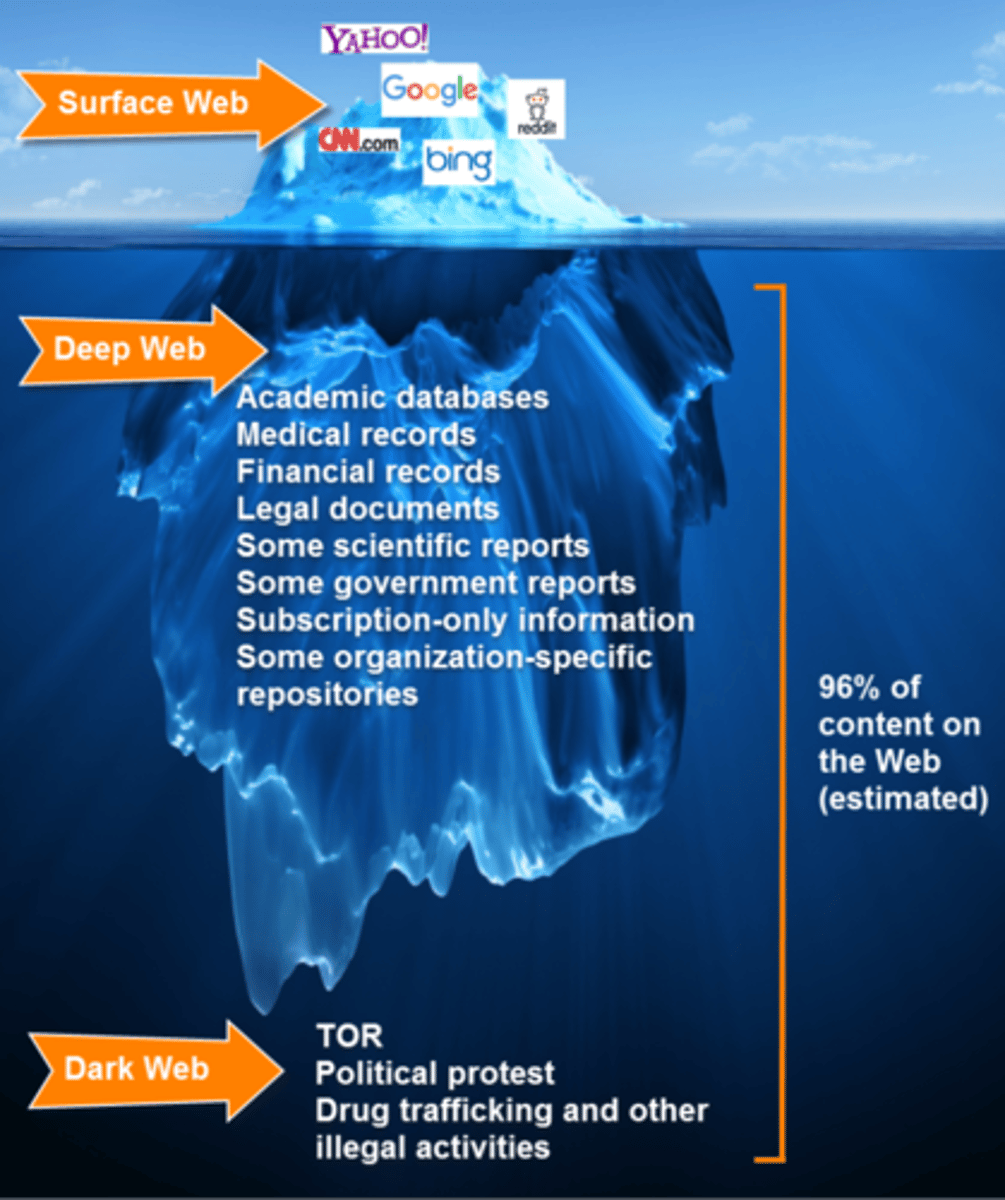
Surface Web
Pages that can be reached by search engine or links from other sites
Deep Web
Pages that can NOT be reached by search engine, considerably larger than surface web
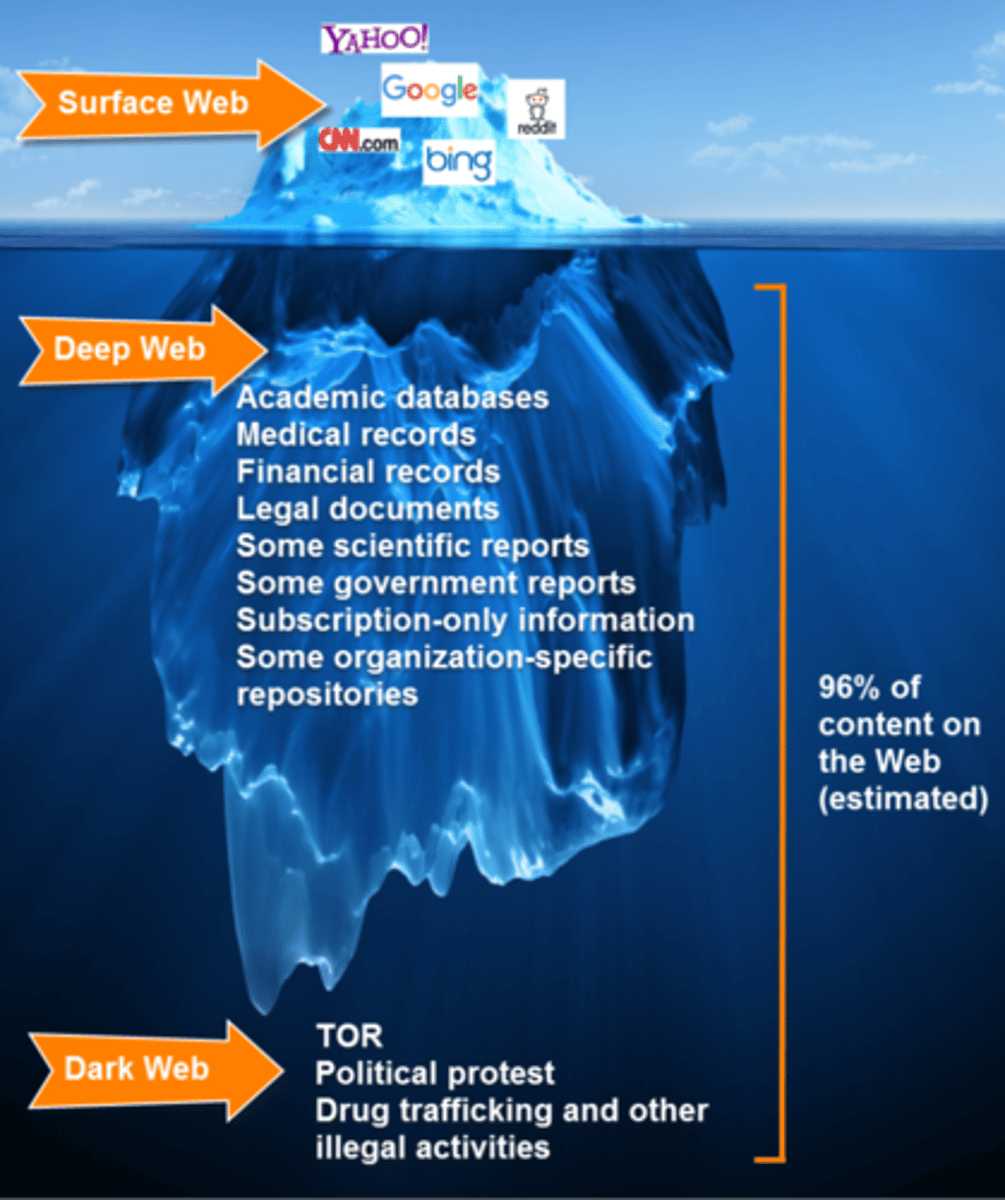
Deep Web Content
Deep Web may include dynamically generated pages, password protected pages, or pages without inlinks such as academic databases or legal documents
Inlinks
Links from other pages/sites which link INTO a page
Outlinks
Links from a page which links OUT to another page
Algorithm
A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer
Google PageRank Algorithm
Importance of a webpage is determined by how many inlinks it has (other webpages linking/pointing to it). Other factors alongside this algorithm such as time the page has existed and frequency of search keywords determine what Google shows
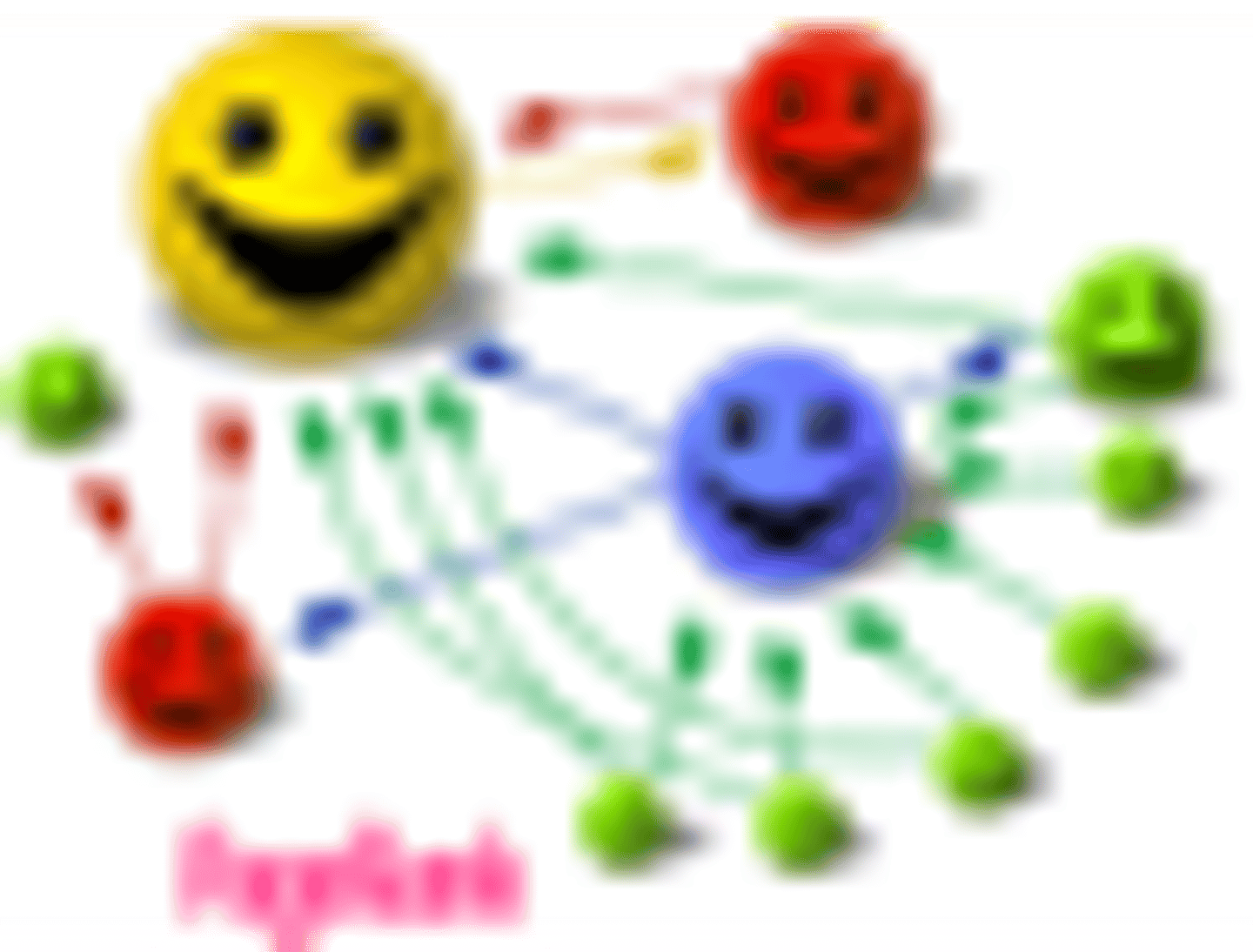
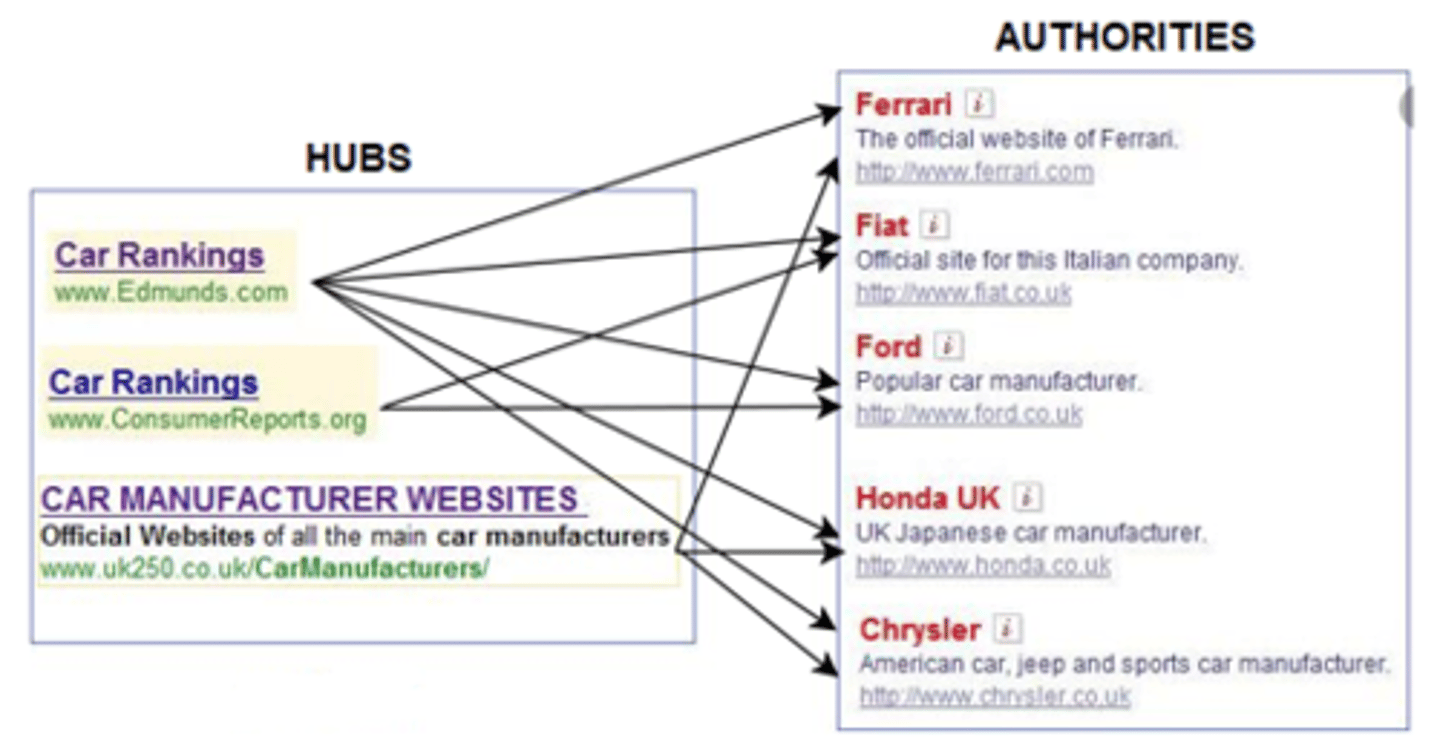
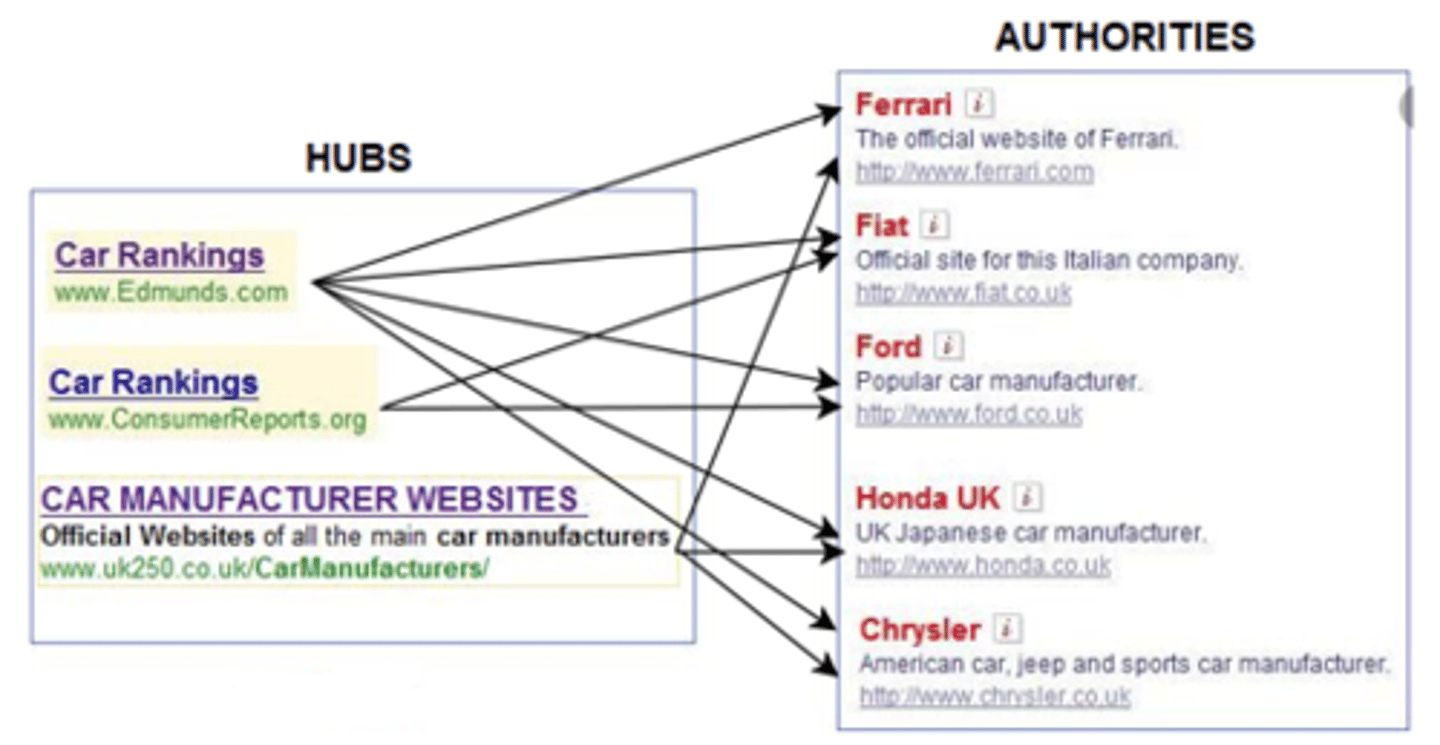
Hubs
Page that contains large directories or compilations of links to authorities. The more high-authority pages it links to, the better the hub page/hub score
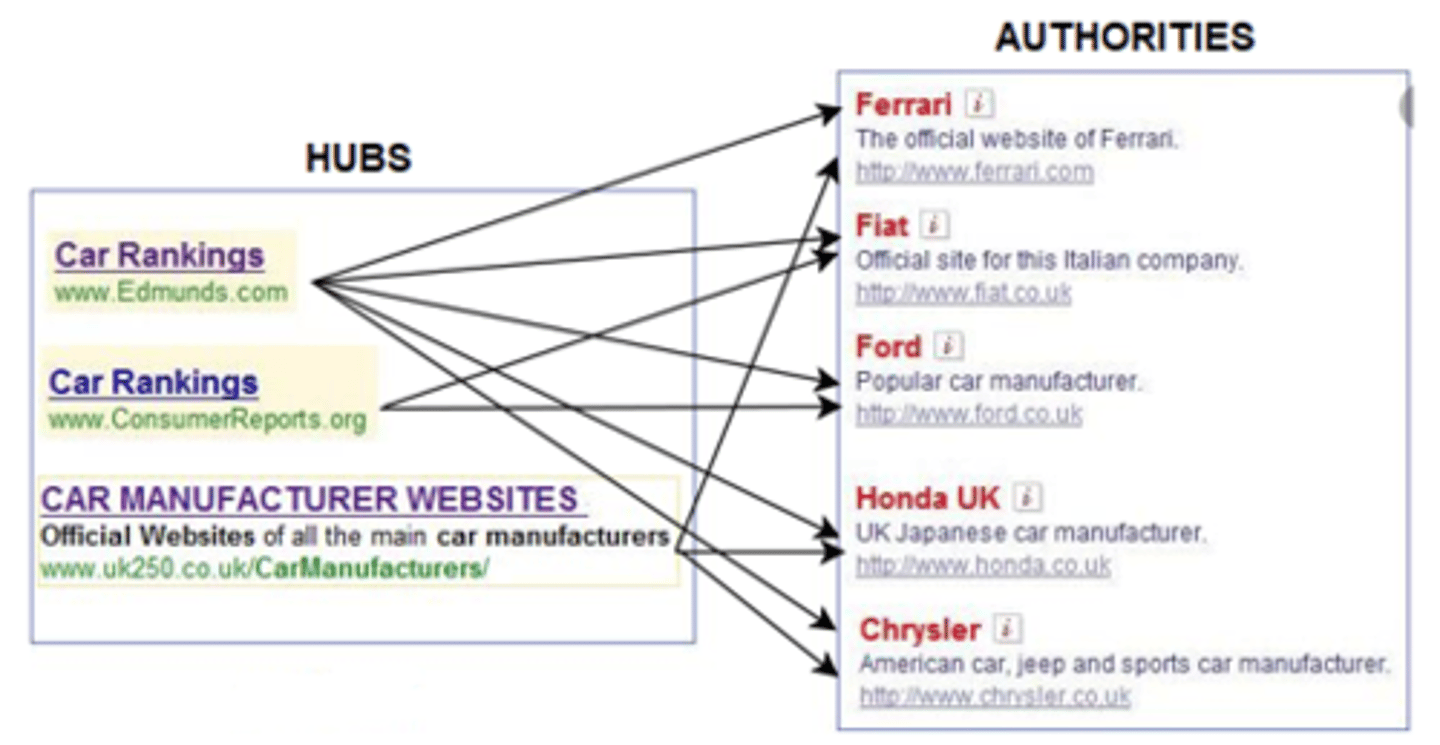
Authority
Page that contains information on specific topics. The more hubs linked to it, the better the authority page/authority score
HITS Algorithm
Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search. Search algorithm that ranks pages by the sum of their hub and authority score. Good hubs link to good authorities, and vice versa. Iterative/repetetive process, and thus relatively slow, and more susceptible to spamming
Web Scraper
Copies content from other sites to be used in other places. Allows the user to format said data to fit their needs
Meta Tags
Words inserted by the web designer which contains keywords/concepts for the web crawler to quickly understand what the page is about, and the description/title can be shown in search results
Web Crawler Types
Some web crawlers only focus on the metadata, while others will also include titles and subtitles, or sometimes even every single word on the page
Local/On Premises Hosting
Hosting a system onsite/at the business. Can be better for larger/more complex systems, more consistent, faster, and better security. However, higher costs as the business itself needs to maintain it
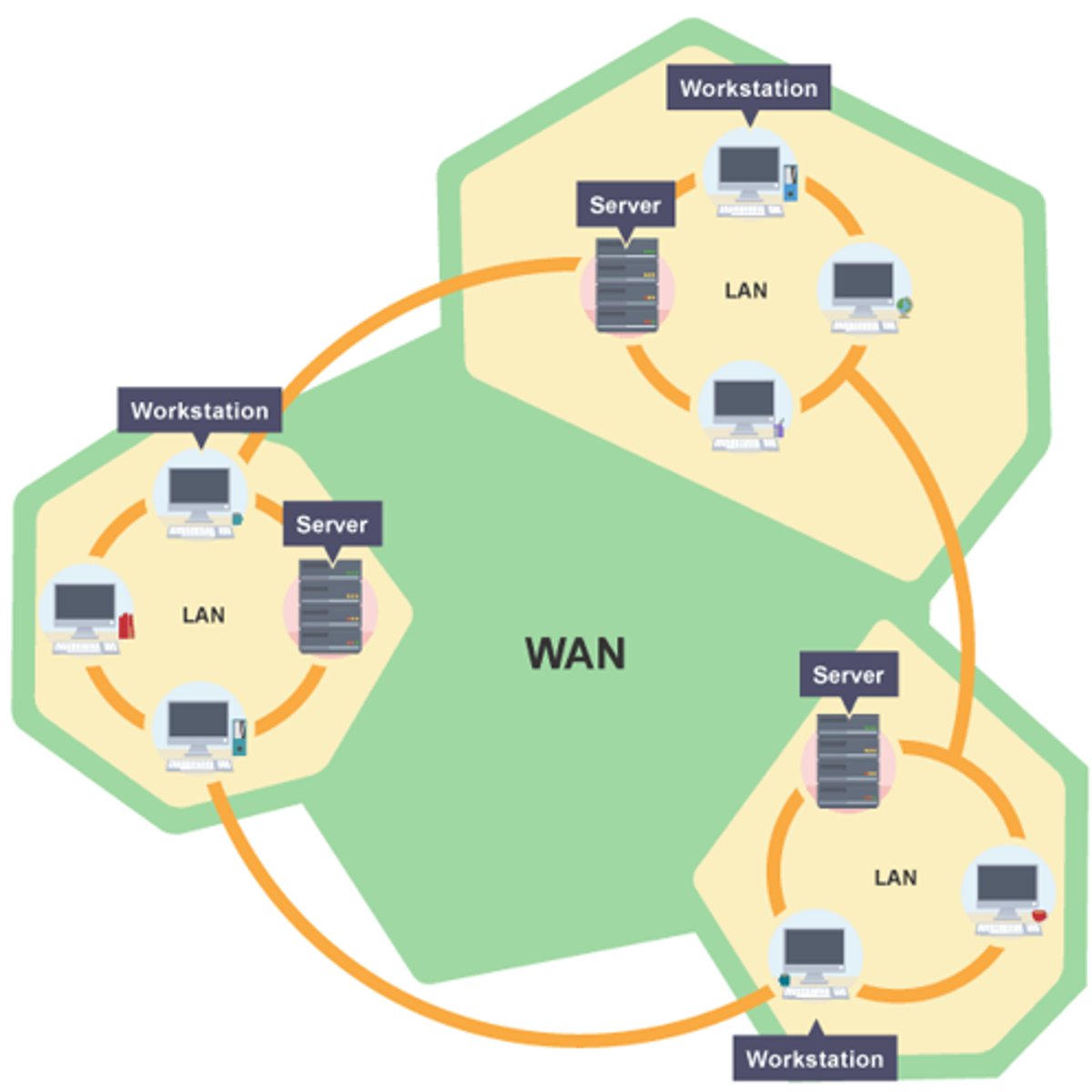
Remote/Cloud Hosting
Hosting a system offsite. Allows for better scalability and better outsourcing, and may be used anywhere, but likely to be less efficient than local hosting
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service. Only thing being remotely hosted is the infrastructure required, such as servers and storage, while platform (OS+middleware) and software is hosted locally
PaaS
Platform as a Service. Remotely hosting the infrastructure and platform (OS+middleware), while software is hosted locally
SaaS
Software as a Service. Remotely hosting everything, from infrastructure to the platform and software, e.g. google docs
Distributed Systems
Type of network spread over multiple networks
Distributed Systems Function
Can distribute systems management, communication, and data processing, and network management software helps oversee systems/allow access. Allows for higher fault tolerance, stability, scalability, privacy, and data portability, but harder to maintain/manage
Mobile Computing
Also called nomadic computing. Use of portable computing devices and mobile communications technology, e.g. phones, laptops, tablets
Mobile Computing Features
Reduced size
- Light
- Portable
- Has batter power
- Lower power CPUs/processors
- SSDs
Ubiquitous Computing
Also called pervasive computing. Incorporation of scalable computing devices into daily life, e.g. IoT devices (fridges, speakers, etc.). Middleware is used to help connect systems
Ubiquitous Computing Features
- CPUs/processors embedded into everyday objects
- Uses wireless technology for connection
- Unobtrusive
- Devices can "talk" to each other
P2P Networks
Peer-to-Peer Networks. Network without distinctive clients and servers where individual nodes, or peers, both deliver and receive data, e.g. piracy
P2P Network Features
- Each computer may function as both server and client
- Used primarily for file sharing
- Often used to maintain user privacy
- May use a central server for coordination, but largely decentralized
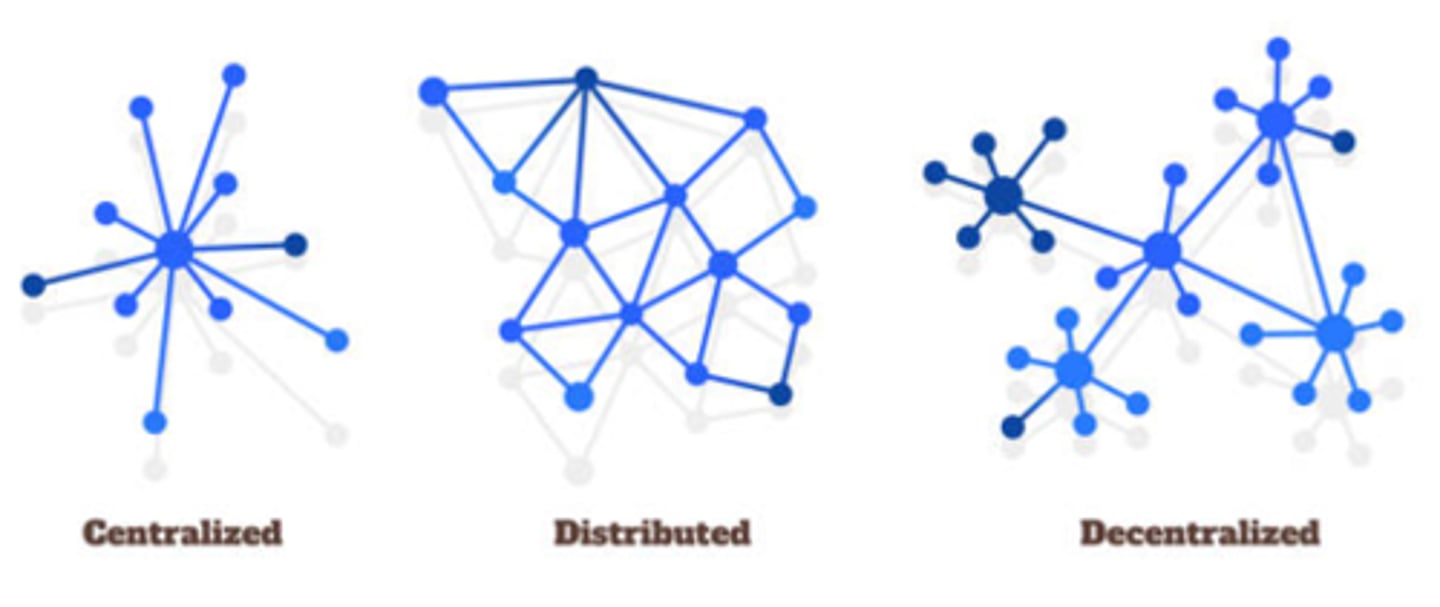
Decentralized vs Centralized Network
Decentralized networks have no "main hub" for control, being distributed across nodes, while centralized networks have a single entity which controls the network
Grid Computing
Use of remote computers to act as a larger virtual unit, often used for data intensive problems
Grid Computing Features
- Distributed system with central control
- Geographically dispersed (computers in diff locations)
- Little/no communication between nodes
- "Virtual" supercomputer
- Highly scalable
- Uses standard computers
Node
Any device in a network that may act as a client, server, or both
Compression
Reducing a file's size by altering different properties of a file, encoding information using fewer bits than the original. Often done with images, audio, and video which typically take more storage. May be done with groups of files, e.g. ZIP
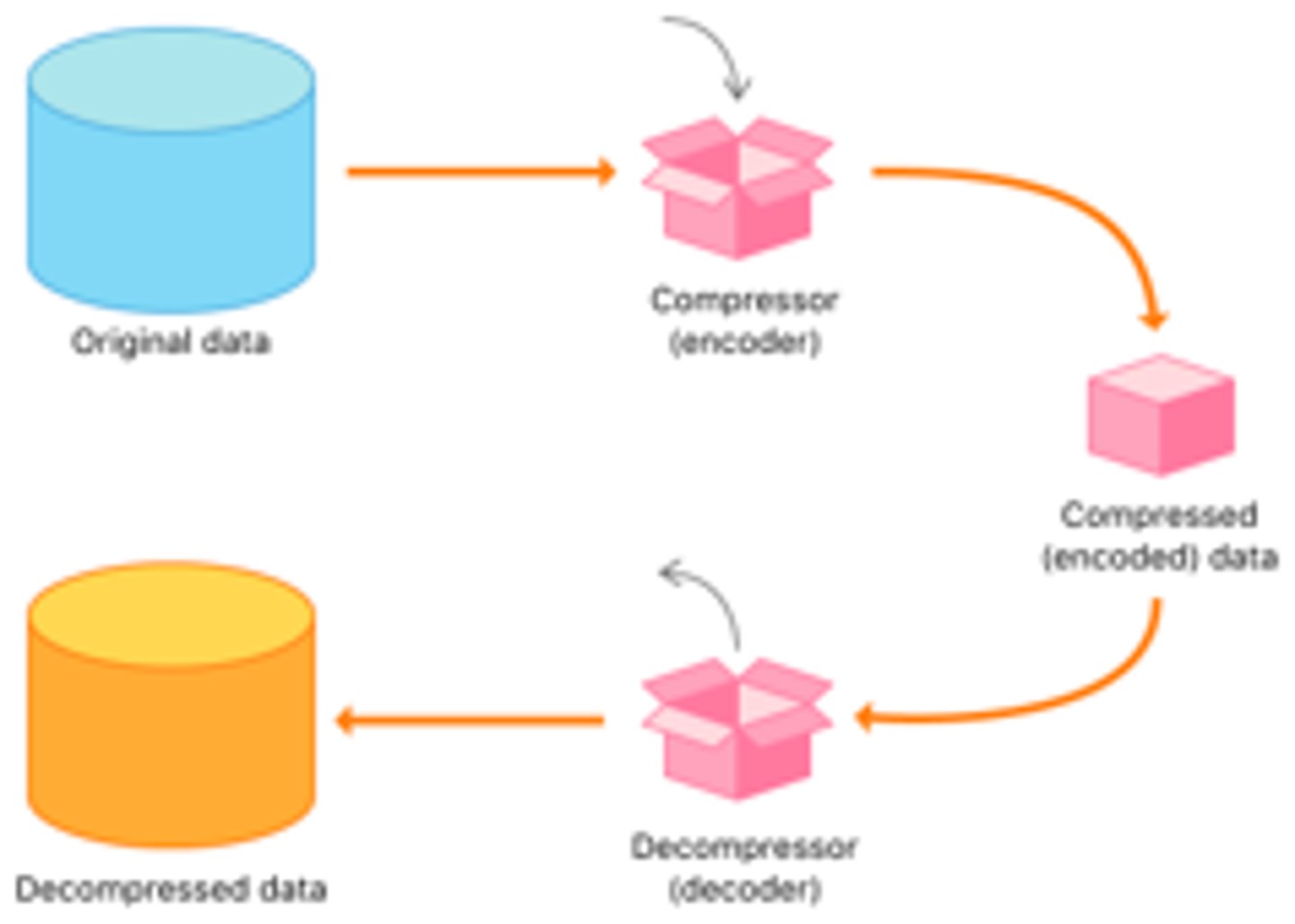
Compression Benefits
Reduces file size, saves network bandwidth, and higher performance when viewing/listening (since less data to load). However, may have reduced data quality (if lossy) and additional time is needed to compress+decompress
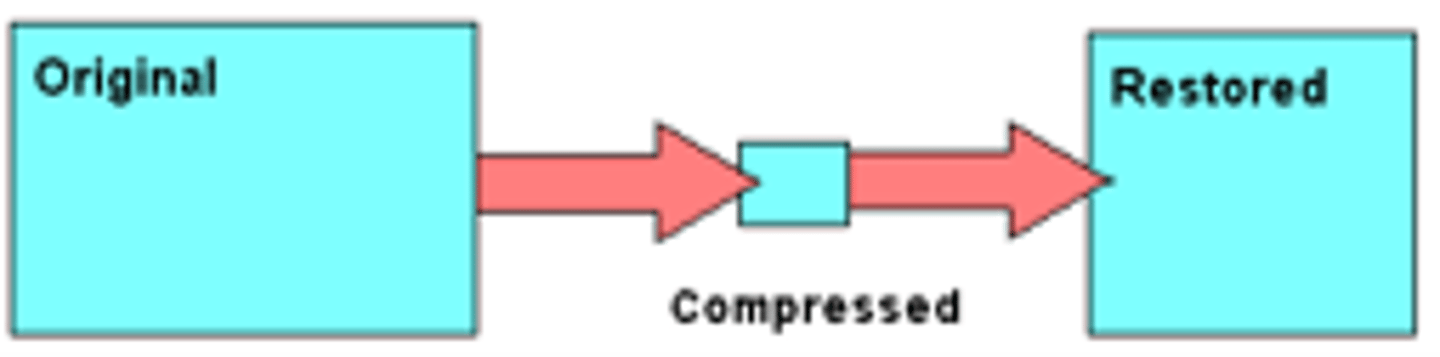
Lossy Compression
Some data removed to reduce size, higher compression ratio over lossless. Usually done when users won't notice, e.g. when resized down like a pfp
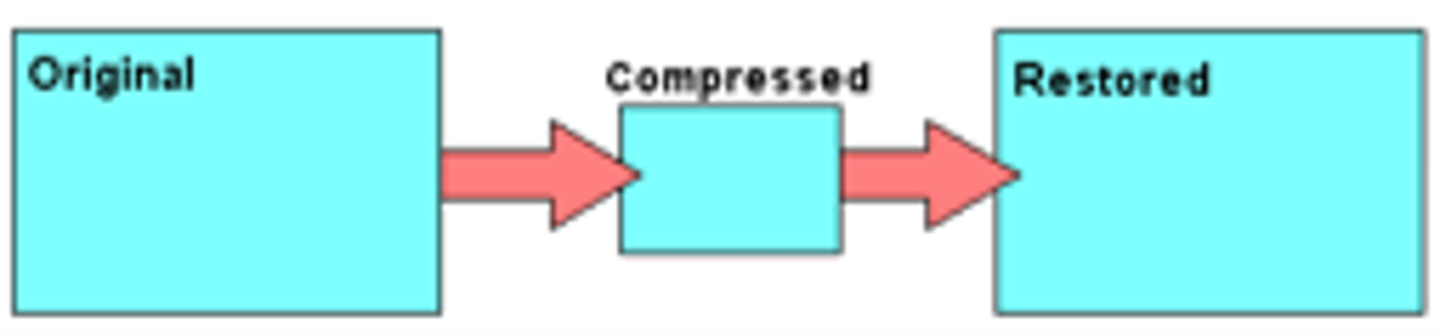
Lossless Compression
No loss of data, but lower compression ratio over lossy. Usually done when quality is needed, e.g. Marcell's ASA picture
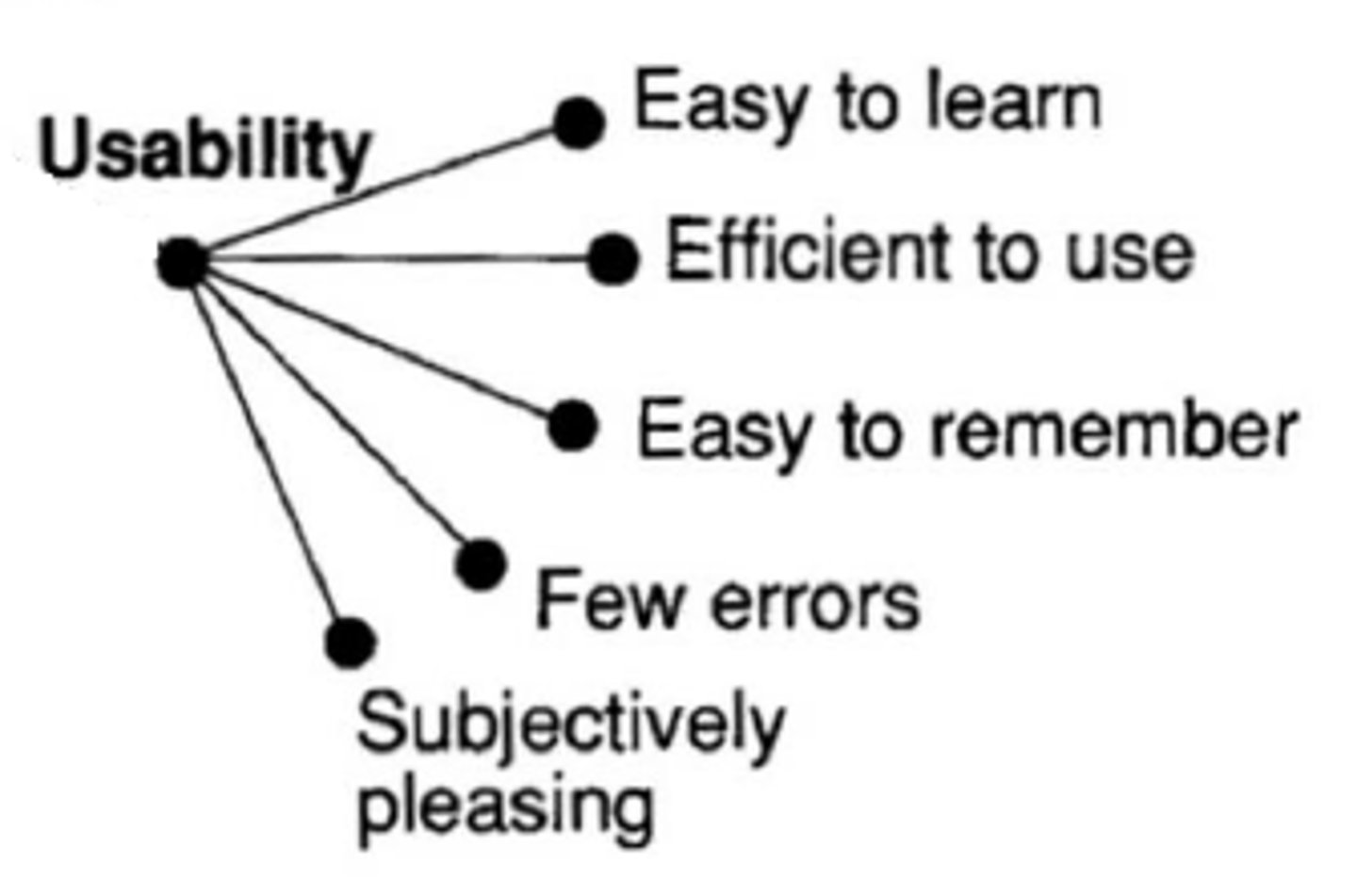
Usability
A measure of how well a specific user in a specific context (i.e. non-disabled people) can use a product/design to achieve a defined goal effectively, efficiently and satisfactorily
Intuitive Design
Software designed to be simple and obvious to use and understand even without conscious reasoning, high degree of usability
Ergonomics
The scientific discipline which studies how humans interact with a system and its elements, to optimize both wellbeing and performance
Accessibility
Design of products, devices, services, or environments for people with disabilities or specific needs, with a goal of being inclusive. Different from usability
Key Usability Issues
- Difficult to handle hardware
- Difficult to understand software
- Complex UI
- Need to have prior knowledge
- Specialist support needed to use device
- No standards for similar devices
Examples to Improve Accessibility
1. Touchscreen
2. Voice recognition, e.g. Siri
3. TTS (Text-To-Speech)
4. Braille Keyboard
Common Usability Issues
- Hard to navigate
- Unclear instructions
- Layout/design complexity
- Not user friendly
Usability Issue Examples
Voice recognition - trouble with accents
Ticketing system - Unclear instructions, design complexity
Online payroll - Too many steps, not user friendly
Parallel Web Crawling
Simultaneously visiting multiple web pages using multiple threads or processes. Crucial for efficiently collecting and processing large amounts of data
Parralel Web Crawling Uses
Used in search engines, data mining, market research, and social media analysis with the goals of:
- Maximizing performance
- Minimizing overheads
- Avoiding duplication
- Communicate with each other
- Work across different geographical areas
Web Indexing
Method used to prioritize and/or organize the contents of a website, or the whole internet. Typically uses keywords and metadata for more practical/useful terms in searching the web
Search Engine Metrics
A standard of measurement used by search engines to help classify the quality of websites, such as popularity
White Hat SEO
Follows the guidelines given by search engines to improve website rankings, such as quality content and image descriptions
Black Hat SEO
Goes against search engine guidelines to improve website rankings, and can be illegal
Black Hat SEO Methods
- Duplicate content
- Keyword stuffing
- Link farming
- Hidden text
- Doorway pages
- Comment spamming/botting
- Scraping (plagiarism)
Search Issues
- Information overload (sifting relevant info may be difficult)
- Content quality (difficult to classify "high quality")
- Natural language processing (NLP, AI generated content)
- Multilingualism (Lots of content in different languages)
- Personalization (Users often want more customizable or personalized options)
- Privacy (History should be private)
Copyright
The exclusive right to publish and sell a work, protecting it form unauthorized duplication/selling
Copyleft
An approach which allows for the modification and distribution of a work (with limits)