apes land and water use
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
externality
cost/benefit of a good/service not included in the purchase price
relevant negative externality examples
air pollution
pollution from fertilizers (runoff)
industrial waste
noise pollution
collapsing fish stocks
methane emissions from landfills
Tragedy of the Commons
when a common resource is shared without limits → eventual destruction through overuse
eg. overfishing
Solutions to Tragedy of the Commons
provide incentive so people think about long term consequences
regulate resource — restricting access, requiring permits, harvesting benefits, or in rare cases sell to private owners
Maximum Sustainable Yield
maximum amount a renewable resource can be harvested without compromising future availability
Rangeland — what is it and what is it used for?
a dry open grassland used for grazing
public; any rancher can use
environmental impacts: overgrazing
BoLM
Bureau of Land Management
manages grazing, mining, timber harvesting, and recreation
resource use and recreation
USFS
United States Forest Service
timber harvesting, grazing, and recreation
resource use and recreation
NPS
National Park Service
recreation and conservation
FWS
Fish and Wildlife Service
wildlife conservation, hunting, and recreation
Forests
land areas dominated by trees and woody vegetation
man used for commercial logging
National Parks
public lands protected from resource extraction and development
Yellowstone
wild spaces for public
Wildlife Reserves
focus on conservation + research
positive vs negative feedback loop
positive = further and further from equilibrium; negative = return to equilibrium
clear cutting
cutting down an area of trees + harvesting everything
pros and cons of clear cutting
pros: easy and efficient, cost effective, and direct sunlight for sun-loving species
cons: increased erosion, changes local climate to drier and warmer, slash left behind, loss of habitat
slash
undergrowth that serves as fuel for forest fires
selective cutting
removal of only some trees and leaving others
pros and cons of selective cutting
pros: still have old growth trees and less erosion
cons: habitat fragmentation, soil compaction (machines compact soil → less water infiltration)
Resource Conservation Ethic
dictates that the use of land should be ethical and minimally disturb the ecosystem
Taylor Grazing Act of 1934
creation of grazing districts — goal is to protect grazing lands by preventing overgrazing
tree plantations
large plantations typically planted with a single fast-growing tree species
reforestation
the replacement of deforested trees with tree plantations
National Forest
forest dedicated to resource use and responsible logging — managed by USFS
Tropical Deforestation
overuse of slash and burn agriculture due to poverty — short term solution; cut down trees and burn to farm b/c most nutrients are in plants so soil is poor
microclimate and area will NEVER be a tropical rainforest
fire maintained
ecosystems that have adapted to regular fires
places where fire has been suppressed have more undergrowth → worse fires than places where fire has been allowed to burn
pros and cons of fire management
pro: ecosystems adapted to burning
pro: provides many ecological benefits: seed germination, removal of unwanted species, renewal of nutrients
con: climate change
con: humans live in fire prone areas → property damage (eg. California)
prescribed burn
a fire intentionally set to reduce fuel for a future fire and control spread of pests/invasive species/disease
also:
exposes mineral soil for seed beds
improvement of natural ecosystems
Suburb
area surrounding a metropolitan center — comparatively low population density
Exurb
area much further out from a city center but not quite rural → expanding b/c we need more space + cheaper land
urban sprawl
urbanized areas that spread into rural areas → removes clear boundaries b/w urban and rural
sources of urban sprawl
automobiles + highway construction !!!!(MOST IMPORTANT)
living costs - cheaper land farther out
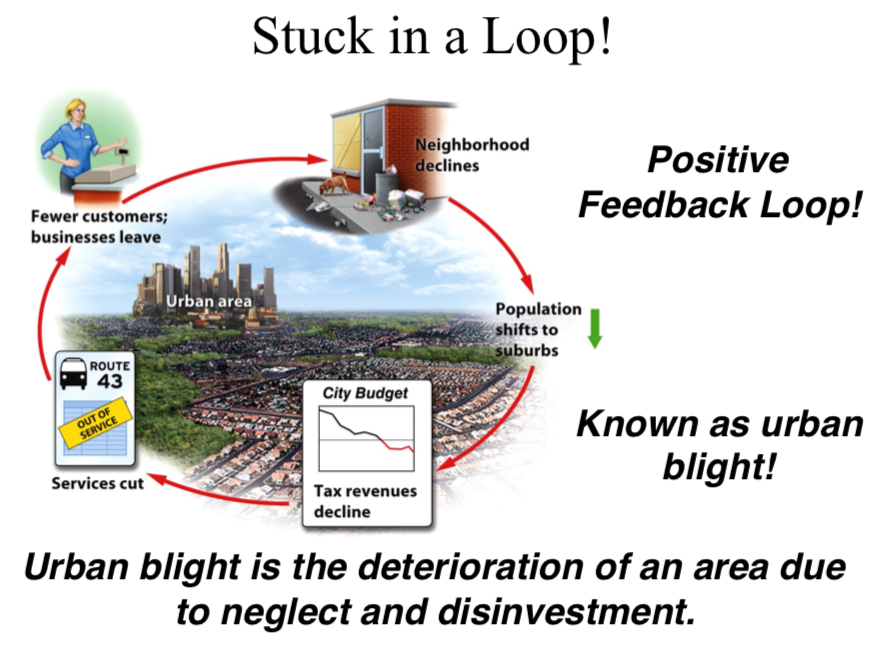
urban blight
zoning policies
zoning
tool for urban planning
leads to non-walkability because it creates distance between residential and business arias
separation of areas considered incompatible (businesses and residence)
urban blight
degradation of areas of the city — accompanies + accelerates migration to suburbs
consequences of urban sprawl
light and noise pollution → disrupts natural behaviors of animals eg. puffins
impacts to water cycle
heat island effect
Urban Heat Island Effect
urban areas noticeably warmer than surrounding areas
caused by:
more man-made surfaces with low albedo = heat absorption
less trees + vegetation → less evapotranspiration + shade
big impact @night → surfaces absorb and retain heat
all leads to heat-related death and disease
solutions to Urban Heat Island Effect
cool roofing - lighter colored roof → higher albedo + reduces insulation costs
green roofing - plants on roof → transfer heat energy into water vapor
pavement effects on the water cycle
impervious surface - doesn’t absorb water → less infiltration + more runoff → reduces groundwater recharge and increases flooding
less vegetation = less evapotranspiration
hazardous waste
liquid, solid, gaseous, or sludge waste material that is harmful to humans/ecosystems
RCRA - Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
makes sure companies dispose of waste correctly
designed to reduce/eliminate hazardous waste
“cradle-to-grave” tracking
CERCLA/Superfund Act
puts a tax on chemical + petroleum industries
revenue then used to clean up abandoned and non-operating hazardous waste sites where a responsible party cannot be found
requires federal government to respond
Superfund sites
1340 as of 2024 (not important)
usually involves chemical spills
considered too hazardous for human presence
eg. Love Canal
Brownfields
most hazardous waste sites
contaminated industrial/commercial sites that require cleanup before redevelopment
may involve asbestos/lead removal
eg. old dry cleaners, landfills, gas stations
waste
any output that is not useful/consumed
municipal solid waste (MSW)
refuse collected by municipalities from households, small businesses, and institutions such as schools, prisons, municipal buildings, and hospitals
e-waste
electronic waste; telephones, computers, cell phones — that contain toxic metals → generally shipped overseas to recycle
3 Rs
reduce: waste minimization/prevention
most environmentally beneficial
reuse: reuse of items instead of buying disposables
eg. buying a reusable metal water bottle
recycle:
materials are collected and converted into raw materials → used to produce new objects
closed-loop recycling
when an item is cut down/melted into raw materials then made into something recyclable
metal glass and paper
open-loop recycling
PLASTIC
when a recycled item is broken down and made into non-recyclable products; majority of plastic is NOT RECYCLABLE
composting
organic material that has decomposed under controlled conditions
pros and cons of composting
pros:
free and healthy fertilizer
waste reduction
cons:
smell
pests
landfills
MSW packed into cells and covered with dirt — capped w/ soil, clay, or plastic to prevent leakage
why should we not throw away food?
food undergoes anaerobic decomposition, which then produces methane and leakage of leachate
leachate
water that leaks to the bottom of solid waste that contains various chemical compounds from waste
leachate collection zone
clay liner
prevents water from leaking/entering
requirements of a landfill zone
remote but not too remote - why? b/c if too close, then pests bother humans and it smells bad, but if too far, then fuel costs and pollution
away from bodies of water and drinking supplies as to not contaminate
landfills vs. dumps — what’s the difference?
landfills focus on preventing pollution while dumps are short-term solutions
landfills
MSW packed into cells and covered with dirt
what do landfills try to prevent?
water leakage → leachate collection system
anaerobic decomposition → transformation of methane into energy
incineration
process of burning waste materials to reduce its volume and mass → sometimes generate electricity and heat
pros and cons of incineration
pros:
reduction in volume
less land use
energy transferred into heat
cons:
air pollution - CO2 + CO
more expensive
toxic ash — higher concentration of toxic materials in trash than would be in landfill
incineration ash
non-organic material that does not burn
safe ash can be used in road construction and cement
toxic ash goes to special ash landfills
percentages of salt v. freshwater
97% saltwater 3% freshwater
percentages of freshwater locations
68.7% icecaps and glaciers
30.1% groundwater
.3% surface water
.9% other (animals and plants)
groundwater
water found underground
RELIED ON IN RURAL AREAS
aquifer
underground lake/river
confined aquifer
impermeable boundaries with limited recharge space
unconfined aquifer
permeable boundaries → larger recharge space
**more likely to become contaminated
cone of depression
when someone overpumps ground water → shifts water to be pulled by one pump
changes water levels and creates a depression
saltwater intrusion
when water is pumped close to the ocean → results in movement of saltwater inward → creates brackish water unsuitable for drinking and irrigation
solution → inject freshwater and force flow back
aquifer subsidence
the sinking of land that happens when too much groundwater is pumped from an aquifer, causing the aquifer's sediment to compact and lose pressure → fissures and cracks form
eg. mexico city
aqueduct
pipes/canals/ditches used to transport water to people who need it → useful for people without clean water/no water source nearby
desalination
removal of salts from ocean water
distillation and reverse osmosis
no strain on water resources but EXPENSIVE
common in Middle East
salt leftover (brine water) is very salty and dense → can be put back but must meet salinity requirements and can impact benthic organisms
dam
barrier that runs across a river or stream to control flow of water
reservoir
water body created by damming a river/stream
fish ladder
stair-like structure that allows fish to get through dam