biology exam revision (battleships cards)
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
feel free to add anything!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Which bases are purines?
adenine and guanine
which bases are pyrimidines?
cytosine, guanine and uracil
how many histone in a nucleus?
9 (8 on the DNA and histone one)
what is euchromatin?
regions of DNA where the nucleosome which are loosely bound
what is heterochromatin?
regions of DNA with nucleosomes which are tighty bound
where does transcription take place?
euchromatin
what is transcription?
the process in which DNA is used as a template to produce RNA (first stage of protein synthesis)
when did Chargaff falsify the tetra-nucelotide hypothesis?
early 1950’s
explain 5’ to 3’ direction on nucleic acid strands
designates the end of the DNA or RNA strand that has the fifth carbon in the sugar-ring of the deoxyribose or ribose at its terminus
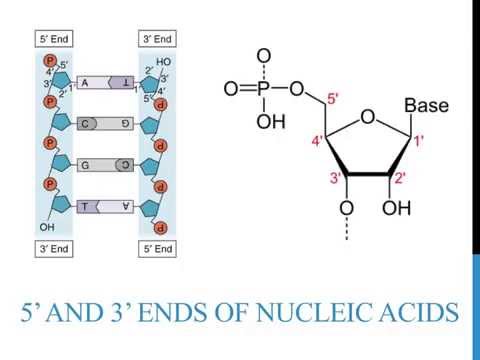
what types of bonds are present in the backbone of DNA?
phosphodiester bonds and covalent bonds
what is a nucleotide made of?
phosphate group, pentose sugar (deoxyribose) and nitrogenous base
what is name and type of reaction that joins monomers?
polymerisation - condensation reaction
who was the scientist who discovered and extracted DNA?
Friedrich Miescher
difference between allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation
allopatric - different geographical locations - unable to reproduce with one another. sympatric - same geographical location but cannot reproduce with each other due to isolating mechanisms like behaviour and temporal isolation
what does density dependent mean?
impacted by size/density of the population - e.g. natural disasters
give an example of sympatric speciation
Hawthorn maggot in North America - when apples were domesticated, some maggots started to use them as food sources. Therefore due to nature and the behaviours of maggots became too different for them to reproduce with one another and became their own speciations of maggots
what is an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphisms)
term used to describe the difference between single DNA nucleotides.
3 types of horizontal gene transfer
conjugation, transformation, transaction
uses of SNPs are:
DNA testing for genealogical companies, forensic DNA testing, paternity testing
what is the biological species concept?
States that a group of organisms can be defined as a species IF they are able to produce fertile offspring.
exceptions to the biological species concept are
bacteria (due to horizontal transfer) and hybrid animals
what is a species?
a group of organisms that can produce fertile offspring with one another
what is the role of complementary base pairing?
stabilises the structure and enables DNA replication to be accurate
where on a sugar carbon does the DNA polymerase attatch to?
3’ OH
what is the difference in the sugars of DNA and RNA
RNA has ribose sugar - DNA has deoxyribose sugar. This indicates that RNA has an extra oxygen on the second carbon.
How many bonds are between Adenine and Thymine
2 hydrogen bonds
Which molecules contain ribose sugars?
RNA
reasons to why organisms are NOT considered living organisms
do NOT metabolise, do NOT use homeostasis, do NOT grow, need another organism to reproduce (host), do NOT excrete waste, do NOT need nutrition
2 methods of cell replication for eukaryotes
mitosis and meiosis
what is one quality that the mitochondria and chloroplast BOTH possess
double membrane, their own DNA
name an organelle ONLY found in plant cells
chloroplasts
describe the structure of a phospholipid
amphipathic molecule - hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
outline the differences between prokaryote and eukaryote cells?
prokaryotes - naked DNA, plasmid, 70s ribosomes, DNA nucleoid
eukaryotes - DNA wrapped around in nucleus, 80s, ribosomes
what is binary fission?
asexual reproduction which an organism divides into two, each part carrying one cope of genetic material.
what is the size of ribosome in prokaryotes
70s
the 3 principles of cell theory
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
cells are the most basic unit of structure of organisms
all cells come from pre-existing cells
define the ‘Goldilocks’ zone
the habitable zone where it is ‘not too hot or too cold’ refers to the orbital distance from a star hat will resets in the presence of liquid water.
why is water polar?
due to the unequal sharing of electrons (the electronegativity of O is more than H so the electrons will be more attracted to the O)
how does water’s polarity influence its solvent properties
it will allow other polar substance dissolve as it is a polar solute
why does water have a high specific heat capacity?
hydrogen bonds will need to be broken to raise the temperature
what is cohesion a result of?
it occurs as a result of water being a polar molecule
complete the substance: all substances that dissolve water are…
hydrophilic
what is the order of the hierarchy of taxonomy?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
what is a clade?
a group of organisms that descend from a common ancestor
what are 3 parts of a cladogram
root - represents most ancient common ancestor
node - represents a hypothetical common ancestor
terminal brunch - represents an existing species
what are cladistics
they are a way to work out the evolutionary relationships between species based on shared traits and genetic evidence
findings of Miller-Urey
a primordial soup which contained basic organic monomers (amino acids, lipids and carbohydrates)
8 requirements for life
Metabolism, Response, Homeostasis, Movement, Growth, Excretion, Reproduction, Nutrition
4 hypotheses for the origin of cells NOT including the ‘RNA first’ hypothesis
miller-urey
metabolism ‘first’
‘sulfur world’
‘lipid world’
outline the main features of EARLY earth’s atmosphere
lacked free oxygen, NO ozone layer present, majority of the atmosphere consisted of Methane and Ammonia gases
state the gases used in Miller-Urey experiments
methane, ammonia, water vapour, hydrogen gas
state the purpose of catalysts
LOWERS the activation energy to speed up the rate of reaction
describe what the Miller-Urey experiment helped to prove
non-living synthesis organic molecule was possible in the conditions existing on early Earth
state the biological catalyst found in our bodies and cells
enzymes
outline the 5 details for the spontaneous origin for cells
synthesis of simple organic molecules
catalysis - acceleration of chemical reactions
self -assembly: Larger organic molecules including RNA and phospholipids were assembled from smaller molecules
self replication: Some of these molecules, including RNA were able to self-replicate.
compartmentalisation: Formation of a membrane-bound compartment (the cell surface membrane) allowed the internal chemistry of the cell to become different from that outside the compartment.
components of miller-urey experiment
closed system set up containing water (simulates the ocean)
gas inlet to add to reducing the gases
electrical sparks to simulate electrical storms
describe the aim of Hershey and Chase
to determine whether DNA or protein make up the genetic material
what is allopatric speciaton
is essentially geographical isolation - when a species is split into 2 due to geographical barriers preventing them to exchange genetic material
what are atypical cells
cells that do not fit into our classification of cells or living things
what are the two main ways of classifyinfg species and which is more accurate?
physical traits and molecular sequences. molecular sequencing is more accurate as scientists can see the DNA differences
how do black throated loons utilise thermal conductivity
oiled exterior feathers exude water, insulated by air trapped down by feathers
the characteristic of LUCA
existed between 2.5-3.5 billion year ago
existed in alkaline hydrothermal vents, which were rich in hydrogen and dissolved minerals like sulfur, methane and iron
was anaerobic - oxygen was absent
antotrophic
what does LUCA stand for
Last Universal Common Ancestor
define specific heat capacity
Amount of energy needed to RAISE the temperature of one unit of mass of a substance by one unity of temperature.
what is molecular phylogeny
way to proving the common origin of life via comparative analysis of DNA bases sequences, RNA, amino acids and proteins
why is the classification of organisms needed?
grouping similar ideas helps to organise them
common language for better communication
to easily find and categorise things (efficiency)
further research by identifying patterns
explain the electronegativity of water
electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a bond
oxygen have a stronger electronegativity than hydrogen and thus the electrons will spend more time around the oxygen atom than the hydrogen atom
oxygen has a partial negative charge whereas hydrogen has a partial positive change