Intro to Medical Radiography - Exam 1
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Radio waves, light, and x-rays are all examples of _________ energy.
thermal
electromagnetic
electrical
nuclear
electromagnetic
What is the removal of an electron from an atom called?
Pair production
Ionization
Electricity
Irradiation
Ionization
The biggest source of man-made ionizing radiation exposure to the public is ______________.
nuclear power plants
atomic fallout
smoke detectors
diagnostic x-rays
diagnostic X-rays
Ionizing radiation is capable of removing ____________ from atoms as it passes through the matter.
neutrons
ions
electrons
protons
electrons
Today, radiology is considered to be a(n) ___________ occupation.
high-risk
safe
dangerous
unsafe
safe
What does ALARA mean?
All Level Alert Radiation Accident
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
As Low As Regulations Allow
Always Leave A Restricted Area
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Filtration is used to ____________________.
absorb low-energy x-rays
remove high-energy x-rays
fabricate gonadal shields
restrict the useful beam to the body part imaged
absorb low-energy x-rays
___________ is a special quantity of radiologic science.
Mass
Velocity
Radioactivity
Momentum
Radioactivity
A moving object has ____________ energy
nuclear
potential
kinetic
electromagnetic
kinetic
In a neutral atom, the atomic number does NOT indicate the number of:
protons.
electrons.
neutrons.
neutrons.
The L shell can hold _______ electrons.
8
4
2
1
8
The simplest form of the substances that form matter is the:
compound.
atomic mass number.
atomic number.
element.
element.
The number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus is the:
atomic mass number.
element.
atomic number.
compound.
atomic mass number
The electron shell closest to the nucleus is lettered
“M”.
“K”.
“H”.
“E”.
“K”
Two or more atoms that bond together form a(n)
atomic mass number.
atomic number.
compound.
element.
compound
Except for the K shell, the maximum number of electrons that can be in the outermost shell of an atom is
32.
8.
4.
16.
8
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is reflected in its
atomic number.
element.
atomic mass number.
compound.
atomic number
If an atom has 15 electrons, which will be the outermost shell?
“M”
“L”
“N”
“O”
M
The N shell can hold _______ electrons.
64
8
4
32
32
The force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus is the
proton/neutron energy.
electron binding energy.
atomic energy.
nuclear binding energy.
nuclear binding energy.
If an atom has the same number of electrons and protons it will
have a negative charge.
be electrically neutral.
none of these.
have a positive charge.
be electrically neutral
A negative ion is
an atom with more electrons than protons.
an electron.
an atom with more neutrons that electrons.
an atom with more protons than electrons.
an atom with more electrons than protons
When an atom becomes negatively or positively charged it is usually due to a change in the number of
protons.
all of these.
neutrons.
electrons.
electrons
The electron binding energy is stronger when:
there are more protons and the electron is farther from the nucleus.
there are more protons and the electron is closer to the nucleus.
there are fewer protons and the electron is farther from the nucleus.
there are fewer protons and the electron is closer to the nucleus.
there are more protons and the electron is closer to the nucleus.
The electrons stay in orbit around the nucleus because of:
their attraction to the neutrons.
their attraction to the protons.
their attraction to the other electrons.
all of these.
their attraction to the protons.
A positive ion is:
an atom with more protons than electrons.
an atom with more neutrons that electrons.
an atom with more electrons than protons.
a proton.
an atom with more protons than electrons.
If an atom has more electrons than protons, it will:
have neither a positive nor negative charge.
be electrically neutral.
have a positive charge.
have a negative charge.
have a negative charge.
The electron binding energy does NOT depend on:
how close it is to the nucleus.
how many protons there are in the nucleus.
how many neutrons there are in the nucleus.
how many neutrons there are in the nucleus.
If a particle strikes a nucleus with the same amount of energy as the atom’s nuclear binding energy:
the atom will become a positive ion.
it can fuse the atom.
the atom will become a negative ion.
it can split the atom.
it can split the atom.
The fundamental component of the atom that has the smallest mass is the
none of these.
neutron.
proton.
electron.
electron
If an atom has more protons than electrons, it will
have neither a positive nor negative charge.
have a negative charge.
be electrically neutral.
have a positive charge.
have a positive charge
The most commonly known modern atomic theory was developed by
Thomson.
Bohr.
Rutherford.
Dalton.
Bohr
The atomic nucleus contains:
electrons and neutrons.
all of these.
protons and electrons.
protons and neutrons.
protons and neutrons
The earliest atomic theory based on an arrangement similar to the solar system is attributed to:
Dalton.
Rutherford.
Bohr.
Thomson.
Rutherford
The mass of an atom is primarily due to the mass of the:
nucleus.
electrons.
neutrons.
protons.
nucleus
The component of the nucleus that has mass but no electrical charge is the:
proton.
none of these.
electron.
neutron.
neutron
The component of the nucleus that has a positive charge and mass is the:
none of these.
proton.
electron.
neutron.
proton
The three fundamental particles of the atom are the:
electron, nucleus, and proton.
neutron, electron, and proton.
element, nucleus, and electron.
nucleus, proton, and neutron.
neutron, electron, and proton.
The “plum pudding model” is associated with:
Rutherford.
Thomson.
Bohr.
Dalton.
Thomson
Define the following terms and provide with examples to support your discussion.
Isotopes
Isobars
Isomers
Isotones
Isotones are elements with the same number of neutrons.
Isotopes are elements with the same number of protons.
Isomers are elements with the same mass, atomic number, and everything except for their metastate is the same.
Isobars are elements with the same Atomic Mass Number.
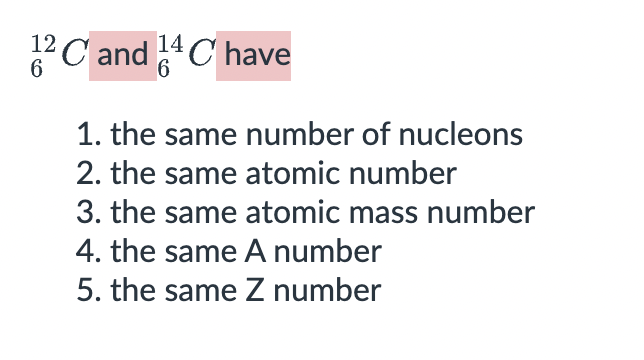
2 and 3
The word atom is derived from the Greek word atomos, meaning:
nuclear.
indivisible.
invisible.
small.
indivisible
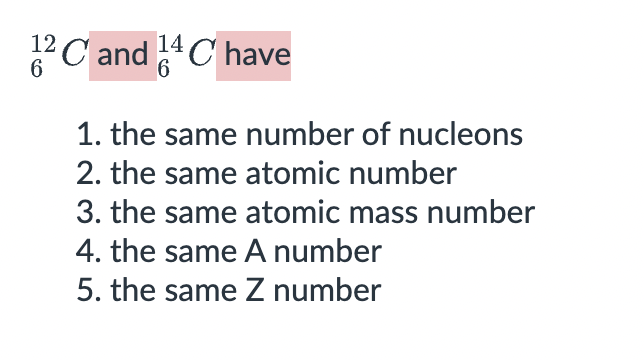
2 and 5
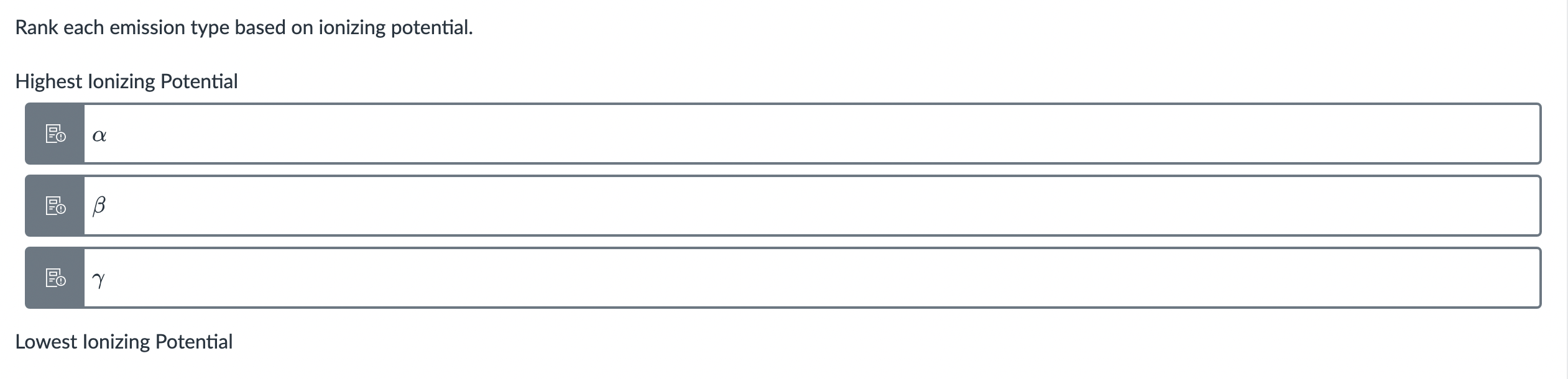

Of the following fundamental particles, which two have approximately the same mass?
neutron and electron
electron and proton
proton and photon
neutron and proton
neutron and proton
In the early 1800s English chemist John Dalton theorized that:
atoms are unique to each element in size and mass.
elements form compounds.
a chemical reaction results from atoms being rearranged.
all of these.
all of these

129
Discovery of the electron is attributed to:
Bohr.
Rutherford.
Thomson.
Dalton.
Thomson.
Of the following radiations, the most penetrating should be a:
2.5 MeV beta particle
5.0 MeV alpha particle
12.0 MeV electron beam
100 KeV gamma ray
100 KeV gamma ray
An ionic bond results in an electrically charged molecule or compound.
False
True
False
Elements can only occur naturally.
False
True
False
The electrons rotate around the nucleus at a single energy level.
False
True
False
All compounds are molecules and all molecules are compounds.
False
True
false
Electron shells are the hard coating around the electron.
False
True
False
The outermost shell of an atom can hold fewer than 8 electrons.
False
True
True
In the middle of the periodic table of elements there are elements that don’t fit exactly into one of the eight groups.
False
True
True
Each element has an unchanging number of protons.
False
True
True
Each electron shell has a specific limit to the amounts of electrons it can hold.
False
True
True
The atoms of the elements at the top of the periodic table of elements are the most complex.
False
True
False
Atoms with the same atomic number and atomic mass number but have different energy within their nuclei are
isotones.
isomers.
isotopes.
isobars.
isomers
The periodic table of elements classifies by period and group. The group is the:
period.
row.
type of element.
column.
column
Atoms in each period have the same number of
electron shells.
electrons in the outermost shell.
electrons.
atomic mass number.
electron shells.
A compound consists of
all of these.
at least two different materials.
at least two elements.
at least two molecules.
at least two elements
The periodic table of elements classifies by period and group. The period is the
row.
group.
column.
type of element.
row
2311Na is an _______________ of 2211Na.
isobars
isotopes
isotones
isomers
isotopes
When the bond between two atoms is due to one atom giving up an electron and the other atom gaining an electron, it is called a
ionic bond.
compounding bond.
molecular bond.
covalent bond.
ionic bond
73Li and 74Be are
isomers.
isotopes.
isobars.
isotones.
isobars
13153I and 13254Xe are
isotones.
isobars.
isomers.
isotopes.
isotones
Atoms in each group have the same number of
electron shells.
atomic mass number.
electrons.
electrons in the outermost shell.
electrons in the outermost shell.