Topic - Bonding
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are ions?
Charged particles - they can be single atoms or groups of atoms
What happens when metals form ions?
They lose electrons from their outer shell to form positive ions
What happens when non-metals form ions?
They gain electrons into their outer shell to form negative ions
What type of bonding happens when non metal + metal happens?
Ionic bonding
Why are non metals and metals particular attracted together?
Strong electrostatic forces between the oppositely charged ions. This attraction is called an ionic bond.
Which groups are the most likely to form ions?
Group 1 +2 and Group 6 +7
Advantages of dot and cross diagrams?
Show which atom the electrons in an ion originally came from
Show the arrangements in an atom or ion
Don’t show the structure of the compound
Don’t show the size of the ions or how they’re arranged
MAKE SURE TO UNDERSTAND DOT AND CROSS DIAGRAMS
YES OR NO?
What is the structure of ionic compounds?
Have a structure called a giant ionic lattice
Why do ionic compounds have ions closely packed together in a regular lattice arrangement?
As there are very strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, in all direction in the lattice.
How can a lattice be represented?
The ball and stick model
Properties of ionic compounds?
High melting/boiling points
When they’re solid - the ions are held in place so they can’t conduct electricity
When they melt the ions are delocalised so they can conduct electricity/heat
Some ionic compounds dissolve easily in water.
What type of bond form when non-metals react together?
Covalent bonds
What makes covalent bonds so strong?
The positively charged nuclei of the bonded atoms are attracted to the shared pair of electrons by electrostatic forces
MAKE SURE YOU KNOW HOW TO DO THE DOT AND CROSS DIAGRAMS FOR COVALENT BONDING
YES OR NO?
Explain why molecules using covalent bonds have a low boiling and melting point
Even tho the atoms within these molecules are held by strong covalent bonds - the forces of attraction between these molecules are very week. SO you need to break these feasible intermolecular forces take doesn’t require a lot of energy.
Properties of simple molecular substances that use covalent bonding?
Low melting and boiling point - gases or liquid at room temp
Don’t conduct electricity because they aren’t charged.
How are polymers held together?
Covalent bonds
How are polymers represented?
You can draw the shortest repeating section called the repeating unit
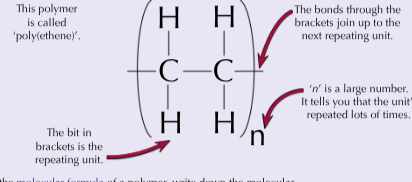
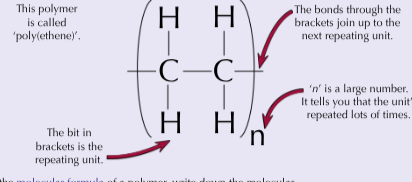
How to work out the molecular formula for polymers?
Write down the molecular formula of the repeating unit then put an “n” outside the brackets (CH)n
Are polymers solid at room temp and why?
Yes - intermolecular forces are larger
What a giant covalent structures?
A macromolecule - all the atoms are bonded to each other by strong covalent bonds
Properties of giant covalent structures?
Very high melting and boiling points
Don’t contain charged particles, so don’t conduct electricity
Examples of giant covalent structures?
Diamond and graphite
What are Allotropes?
Different structural forms of the same element in the same physical state
Properties of Diamond (allotrope of carbon)
Each carbon atom have 4 covalent bonds - making it really hard
Have a high melting and boiling points - requires a lot of energy to break strong covalent bonds
Doesn’t conduct electricity - there are no delocalised electrons/ions
Properties of Graphite?
Each carbon atom forms 3 covalent bonds, creating sheets of carbon atoms arranged in hexagons
Aren’t any covalent bonds between the layers -they’re free to move over each other - this makes graphite soft and slippery (good lubrication material)
Has a high melting and boiling point - needs lots of energy to break strong covalent bonds
Each carbon atom has one electron thats delocalised so can conduct electricity and thermal energy
What is Graphene?
One layer of graphite
Properties of Graphene?
One atom thick
Strong - network of covalent bonds make it strong and it’s incredibly light (can be added to composite materials to add strength without adding much weight)
Each carbon atom has 1 delocalised electron so can conduct electricity through the whole structure (can be used in electronics)
What are Fullerenes?
Molecules of carbon shaped like closed tubes or hollow balls
Uses of Fullerenes:
Can be used to deliver a drug into the body
Have a large surface area - make great industrial catalysts
Make great lubricants
Fullerenes can form nanotubes
What is metal + metal called?
Metallic bonding
How is metallic bonding completed?
The delocalised electron and the positive metal ion have strong forces of attraction that hold the atoms together in a regular structure
What are alloys?
A mixture of 2 or more metals or a metal and another element.
Difference between alloys and pure metals?
Alloys are harder than pure metals
What are the three categories of particles?
Course particles
Fine particles
Nanoparticles
What is the diameter of course particles?
Have a diameter between 2500nm and 10000nm
What is the diameter of fine particles?
Have a diameter between 100nm and 2500nm
What is the diameter of nanoparticles?
Have a diameter between 1nm and 100nm
How to workout SA to volume ratio?
SA to volume ratio - SA/volume
Do nanoparticles have a large and small SA to volume ratio?
Large
Uses of Nanoparticles?
Catalysts
Nanomedicine
Electric circuits
Antibacterial properties - medicine
Cosmetics
How/why are nanoparticles used as a catalyst?
Have a large Sa to volume ratio
How/why are nanoparticles used in nanomedicine?
Tiny particles like fullerenes can be easily absorbed by the body and can deliver drugs
How/why are nanoparticles used in electric circuits?
Some nanoparticles can conduct electricity
How/why are nanoparticles used in medicine?
Silver nanoparticles have antibacterial properties and can be added to polymer fibres that are used to make surgical masks and wound dressings
How/why are nanoparticles used in cosmetics?
Used to improve moisturisers without making them oily
Used in suncream as have a large SA to volume ratio - can cover more skin
Cons of nanoparticles?
Long-term effects on health aren’t fully understood:
They could damage cells
They might damage the environment