OA: Medical Records Management
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Medical Records
Permanent account of client interactions and services.
Legibility
Records must be readable by all team members.
Computerized Records
Digital records accessible from any computer.
Legal Document
Medical records must be inked, not pencil.
Ink Requirements
Use blue or black ink only for records.
Record Correction
Cross out mistakes, correct, and initial error.
Filing Systems
Organize paper records alphabetically or numerically.
Color-Coding
Use colors to identify misfiled charts.
Warning Stickers
Indicate special conditions like 'Will Bite!'.

Records Release
Confidential; requires owner's consent for sharing.
Privacy Act of 1974
Protects client records from unauthorized disclosure.
Client Copy Rights
Clients can request copies; originals stay with practice.
SOAP Format
Structure for organizing patient medical records.
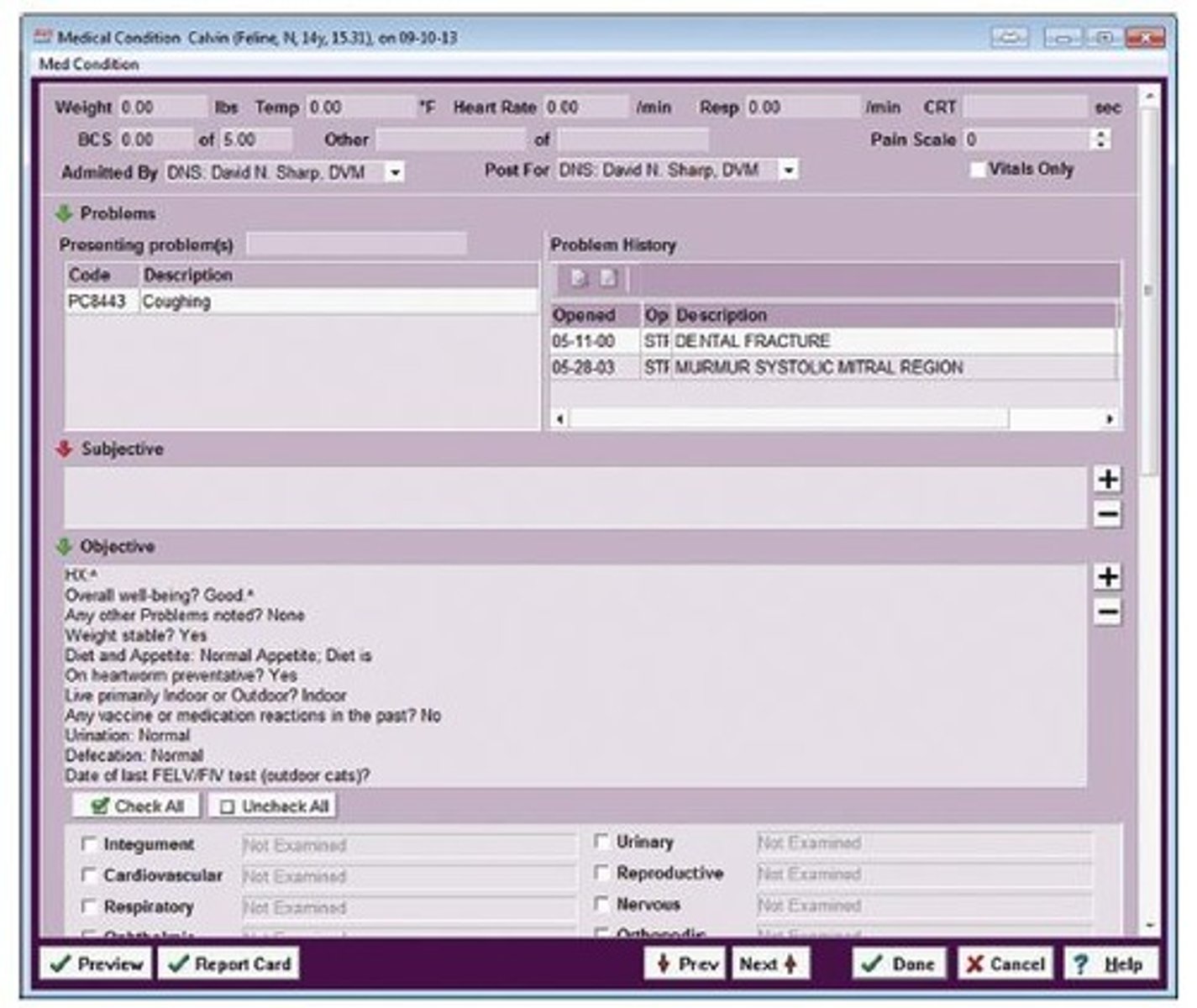
Medical Record Components
Includes history, exam, diagnosis, and treatments.
History Taking
Summarizes client information for accurate diagnosis.
Problem-Oriented Records
Organized by problems, using SOAP method.
Drug Documentation
Must specify dosage and administration route clearly.
Fluid Administration
Document type and rate of fluids given.
Record Retention
Maintain records for at least three years.
Inactive Records
Records of clients not seen in one year.
Discharge Instructions
Clients receive written and verbal care instructions.
Medication Information
Includes type, dosage, frequency, and side effects.
Common Abbreviations
Includes PO, IM, IV, SID, BID, etc.
Radiographs
Must include client and patient identification details.
Radiograph Checkout Log
Tracks loaned radiographs to prevent loss.
Backup System
Daily backups using multiple methods for data safety.
Master Problem List
Comprehensive list of patient issues for reference.
Laboratory Flow Sheet
Tracks diagnostic tests and results systematically.